Alarming Discovery: High Aluminum Levels Found in Brains with Alzheimer's, Autism, and MS
Alarming Discovery: High Aluminum Levels Found in Brains with Alzheimer's, Autism, and MS
A significant study recently published in the prestigious journal Nature has raised a red flag concerning the potential link between aluminum and several serious neurological conditions. Researchers meticulously compared the aluminum content in human brain tissue from individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease (including familial Alzheimer’s), autism spectrum disorder, and multiple sclerosis against healthy control subjects. The findings are prompting new questions about brain health.
Key Findings: Aluminum Significantly Elevated in Diseased Brains
According to the study's authors, their "detailed statistical analyses showed that aluminum was significantly increased in each of these disease groups compared to control tissues." This means that in every neurological condition examined, the amount of aluminum found in the brain was noticeably higher than in healthy brains.
The researchers further elaborated: "We have confirmed previous conclusions that the aluminum content of brain tissue in Alzheimer’s disease, autism spectrum disorder and multiple sclerosis is significantly elevated. Further research is required to understand the role played by high levels of aluminum in the aetiology of human neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disease."
For their comparison, the scientists used brain tissue from twenty healthy individuals as a control group. The consistent observation that all the disease groups (Alzheimer's, familial Alzheimer's, autism spectrum disorder, and multiple sclerosis) had significantly higher brain aluminum content than the healthy control group is certainly concerning and warrants serious attention.
What Does This Mean? Correlation vs. Causation
It's crucial to understand the implications of these findings carefully. While this study highlights a strong correlation between elevated brain aluminum levels and these neurological conditions, it does not definitively prove that aluminum directly causes these diseases. This is a vital distinction in scientific research.
Think of it this way: just because two things happen together doesn't mean one causes the other. For example, ice cream sales and shark attacks both increase in the summer, but ice cream doesn't cause shark attacks. Similarly, it's possible that the presence of Alzheimer's, autism, or MS might somehow lead to increased aluminum accumulation in the brain, rather than aluminum being the initial trigger.
However, the consistent pattern of elevated aluminum across such diverse and debilitating neurological disorders is too significant to ignore. It suggests a potential involvement that needs to be thoroughly investigated.
The Path Forward: More Research is Essential
The study's authors themselves emphasize that "further research is required" to fully understand the role of high aluminum levels. This research opens up critical avenues for future studies to explore:
-
Mechanisms of Action: How exactly might aluminum interact with brain cells? Could it contribute to inflammation, oxidative stress, or disrupt cellular processes?
-
Source of Accumulation: Where is this excess aluminum coming from? Is it from diet, environmental exposure, or other factors?
-
Causal Link: Can scientists establish a direct causal link, or is aluminum accumulation a consequence of these diseases?
Understanding this complex relationship could be a pivotal step toward developing new preventative strategies, diagnostic tools, or even treatments for these challenging neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental conditions. While immediate answers aren't available, this study undoubtedly adds an important piece to the puzzle of brain health.
What are your thoughts on this study's findings and the potential implications of environmental factors on brain health?
News in the same category

Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common
Doctor's "Deeply Concerning" Warning After Man Injects Sperm to 'Cure Back Pain'
Non-Smoker Diagnosed with Lung Cancer Shares His Only 'Silent' Symptom
First Human Trial Launched for Stem Cell Therapy to Reverse Spinal Cord Injuries
From Despair to Hope: Joe Tippens' Incredible Cancer Recovery Story with Fenbendazole

100-Year-Old Doctor Reveals: 7 Daily Habits to Help You Live a Healthy Life
Diagnosed with Terminal Cancer, Preparing for the End – A Man’s Miraculous Survival Thanks to 3 Major Life Changes
Warning signs of stroke 30 minutes before – remember them to save your life and your loved ones
Your Body's Silent Alarms: 9 Subtle Signals of a Heart Attack, Up to a Month Before It Strikes

31 Foods Experts Say You Should Avoid (Or Severely Limit)

Heart Surgeon Warns: 4 Foods and Drinks You Should "Always Avoid" to Protect Your Body

12-year-old girl dies of rare cancer—parents noticed worrying sign as she brushed teeth

Just Two Hours of Sitting in Silence May Spark Growth of New Brain Cells, Study Finds
Rising Kidney Failure in Young People: One Harmful Habit Many Are Unknowingly Practicing
5 Early Signs of Liver Failure: Seek Medical Help Early to Prolong Life – Number 2 Is Especially Common

7 Health Problems That Can Happen If You Don’t Drink Enough Water
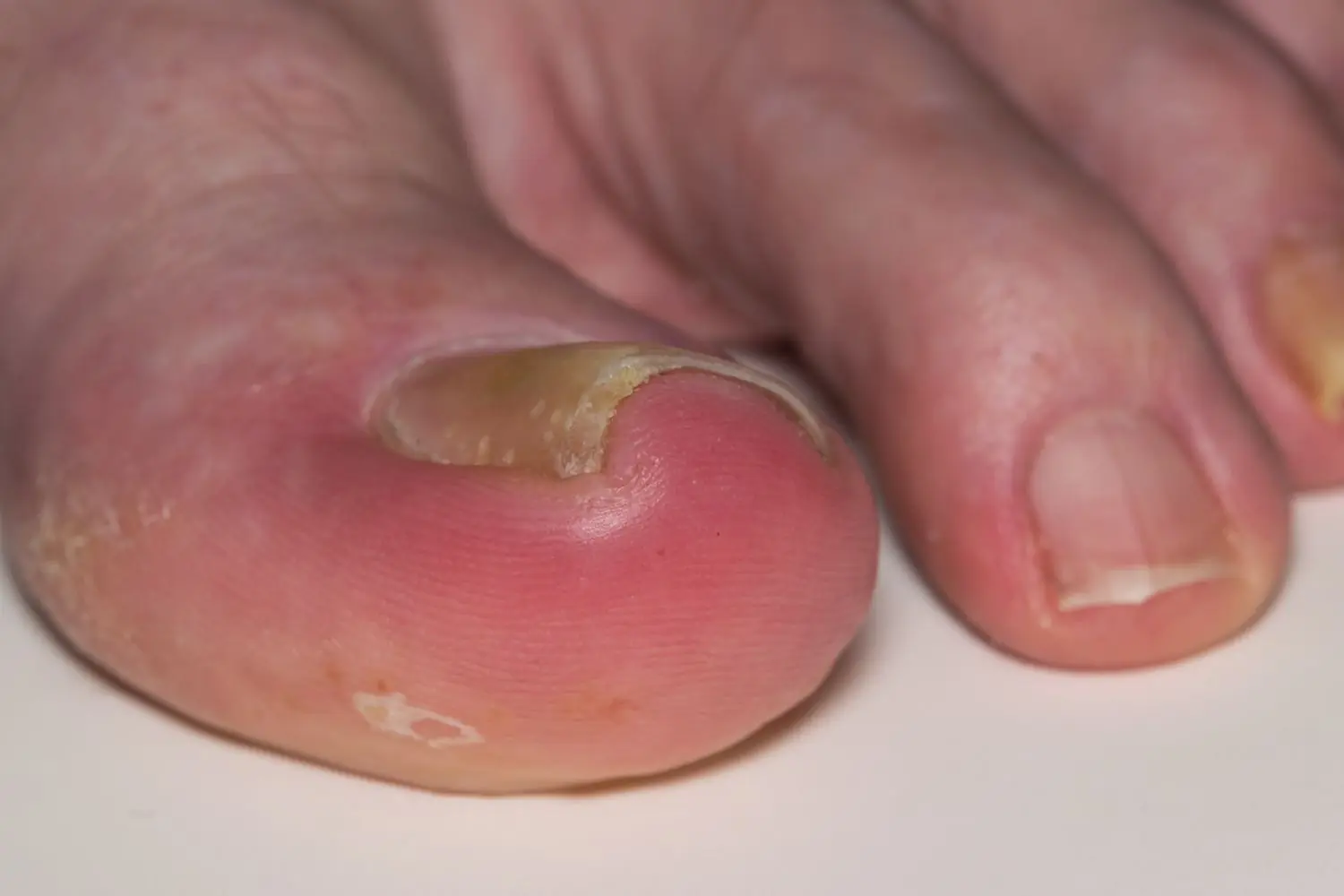
Home Remedies to Treat and Prevent Ingrown Toenails (Onychocryptosis)
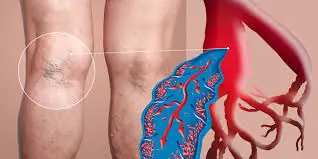
Blood Clot in Leg: Crucial Signs and Symptoms You Can't Afford to Ignore
News Post

Protect Your Home and Wallet: Unplug These 5 Appliances When You’re Done Using Them

Some People Still Think These Two Buttons Are Only For Flushing

Terrifying Study: Up to 30% of Americans Could Be Infected with Brain-Impacting Parasite

Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common

Doctor's "Deeply Concerning" Warning After Man Injects Sperm to 'Cure Back Pain'

Non-Smoker Diagnosed with Lung Cancer Shares His Only 'Silent' Symptom

The Dark Year: What Made 536 So Devastating For Civilization

First Human Trial Launched for Stem Cell Therapy to Reverse Spinal Cord Injuries

From Despair to Hope: Joe Tippens' Incredible Cancer Recovery Story with Fenbendazole

Elon Musk Claims He’s A 3,000-Year-Old Time-Traveling Alien

The Volume Buttons on Your iPhone Have Countless Hidden Features

10 Safest Countries To Be In If World War 3 Breaks Out

2050 Climate Crisis Death Toll Could Be Catastrophic, Researchers Warn

This Image Has People Perplexed. Can You Solve It?
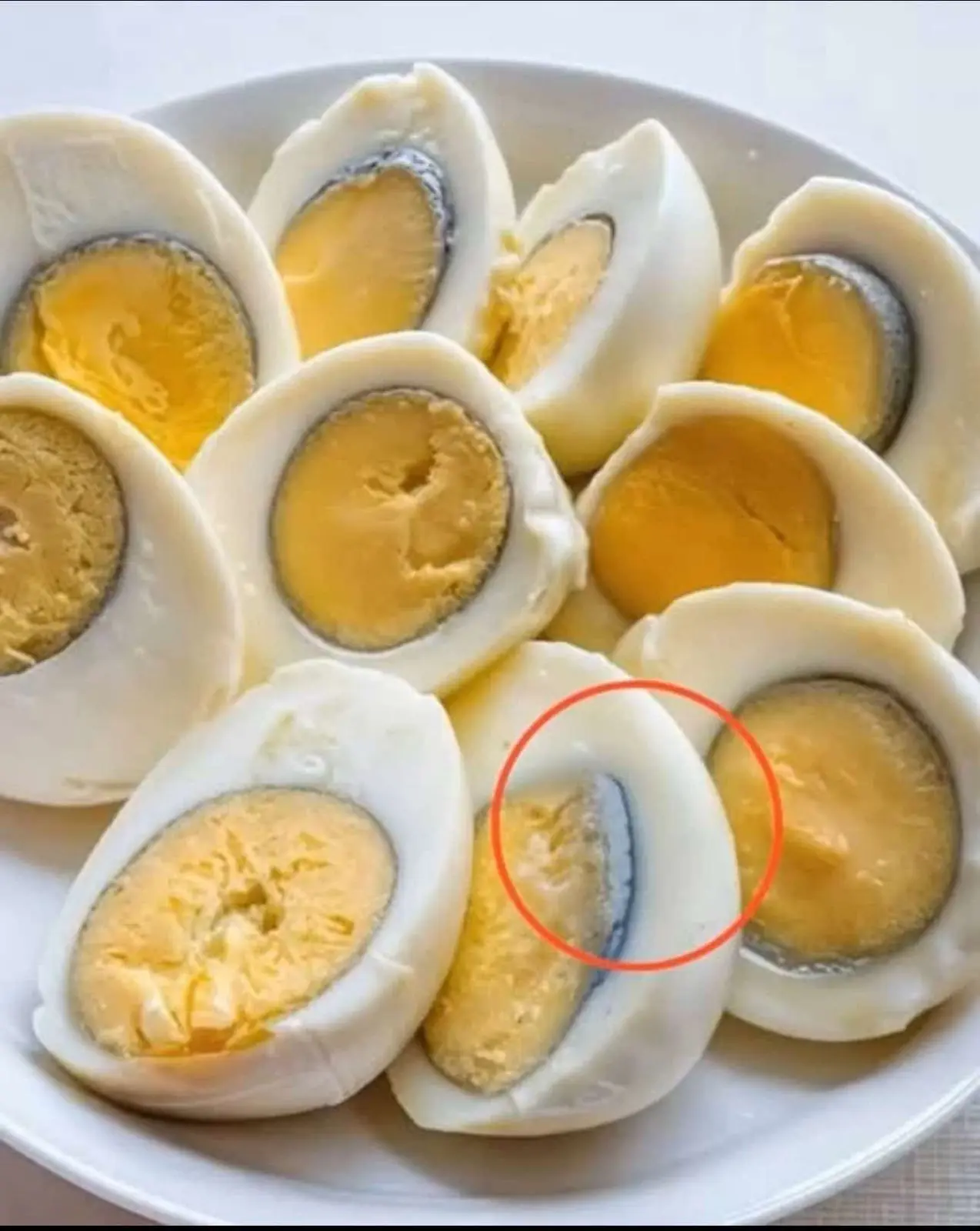

What causes the green ring around hard-boiled eggs?

Ditch Bad Vision for Good! Carrots Can Boost Your Eyesight, Hearing, Memory & Immunity

Watermelon Juice with Carrot, Beetroot, and Ginger: A Refreshing, Nutrient-Packed Drink

Shocking Secret Revealed: Erase Facial Hair Naturally with THIS Kitchen Staple!