Allergic Rhinitis: What Triggers It and How to Manage It
Allergic Rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, is a chronic allergic condition that affects the nose and sinuses. Although it isn’t life-threatening, it can seriously disrupt sleep, concentration, work productivity, and overall quality of life—especially when left untreated.

What Is Allergic Rhinitis?
Allergic rhinitis occurs when your immune system overreacts to harmless airborne substances, triggering inflammation of the nasal lining. This reaction leads to persistent nasal and eye symptoms that can last weeks, months, or even year-round.
There are two main types:
-
Seasonal allergic rhinitis – linked to pollen (spring, summer, fall)
-
Perennial allergic rhinitis – triggered year-round by indoor allergens
Common Triggers You Should Know
Outdoor Allergens
-
Tree pollen
-
Grass pollen
-
Weed pollen
Indoor Allergens
-
Dust mite allergy
-
Pet dander
-
Mold spores
-
Cockroach debris
Irritants That Worsen Symptoms
-
Cigarette smoke
-
Air pollution
-
Strong perfumes or cleaning chemicals
-
Cold, dry air
Key Symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis
Unlike colds or flu, allergic rhinitis does not cause fever and often persists as long as exposure continues.
Nasal & Eye Symptoms
-
Sneezing (often in bursts)
-
Runny or congested nose
-
Itchy nose, throat, or ears
-
Watery, red, itchy eyes
Whole-Body Effects
-
Fatigue and brain fog
-
Poor sleep quality
-
Headaches or sinus pressure
-
Reduced sense of smell
Why Allergic Rhinitis Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Untreated allergic rhinitis can lead to:
-
Chronic sinusitis
-
Ear infections
-
Worsening asthma symptoms
-
Sleep apnea or chronic fatigue
-
Decreased academic or work performance
How Allergic Rhinitis Is Diagnosed
Doctors may use:
-
Symptom history and physical exam
-
Skin prick allergy testing
-
Blood tests (IgE levels)
-
Response to allergy medications
Accurate diagnosis helps identify specific triggers, making treatment more effective.
Effective Management & Treatment Options
1. Avoidance (First Line of Defense)
-
Keep windows closed during high-pollen seasons
-
Wash bedding weekly in hot water
-
Use HEPA air purifiers
-
Shower after outdoor exposure
2. Medications
-
Antihistamines – reduce sneezing and itching
-
Nasal corticosteroid sprays – most effective for congestion
-
Decongestants (short-term only)
-
Leukotriene inhibitors (especially for asthma sufferers)
3. Immunotherapy (Long-Term Solution)
-
Allergy shots or sublingual tablets
-
Gradually retrain the immune system
-
Can reduce symptoms for years
Natural & Lifestyle Support
-
Saline nasal rinses to clear allergens
-
Anti-inflammatory diet (omega-3s, fruits, vegetables)
-
Adequate sleep to regulate immune response
-
Stress reduction (stress worsens allergy reactions)
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if:
-
Symptoms last longer than 2–3 weeks
-
Over-the-counter meds stop working
-
Sleep or breathing is affected
-
Asthma symptoms worsen
Can Allergic Rhinitis Be Prevented?
While it can’t always be prevented, early management dramatically reduces severity and complications. Many people achieve near-complete symptom control with the right combination of strategies.
News in the same category


The #1 Food Proven to Support Kidney Cleansing and Protection

High Olive Oil Intake Linked to Significantly Lower Risk of HER2-Negative Breast Cancer

Tight Junction Proteins and Permeability Improved by Roasted Garlic in Mice with Induced Colitis
Randomized Controlled Trial Confirms NEM® Efficacy and Safety in Reducing Osteoarthritis Pain and Stiffness

Whole Fish Trumps Pills: Study Finds Whole-Food Factors, Not Isolated Omega-3s, Lower Autism Risk

Dark chocolate and tea found to significantly lower blood pressure
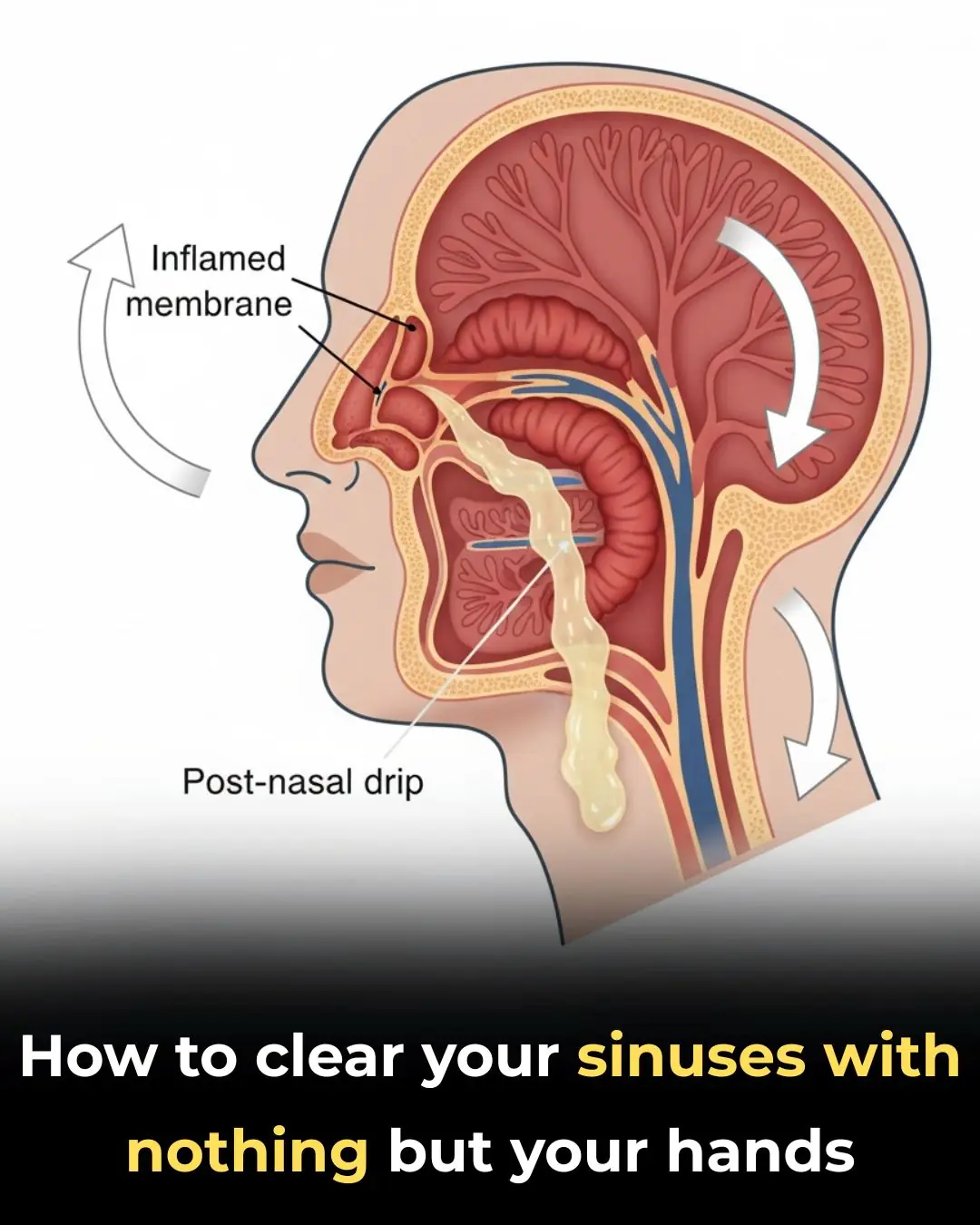
How To Clear Your Sinuses

How to lower blood sugar without giving up carbs

Doctor reveals 5 nutrient deficiencies linked to brain fog, dementia and Alzheimer’s

10 powerful plants to eliminate excess mucus and phlegm naturally

Why This Doctor Chooses Not to Prescribe Statins for High Cholesterol — and What He Recommends Instead

5 Foods You Must Avoid If You Have High Blood Pressure

21 Effective Home Remedies for Kidney Stones to Relieve Pain Fast

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart

12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know
8 warning signs of colon cancer you should never ignore
The daily drink that helps clear blocked arteries naturally

This old school home remedy will soothe your back, joints & knee pain in just 7 days!

Sleep Apnea: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment Solutions
News Post

Intensive Gum Disease Treatment Slows Artery Thickening, Benefiting Heart and Brain Health

The #1 Food Proven to Support Kidney Cleansing and Protection

High Olive Oil Intake Linked to Significantly Lower Risk of HER2-Negative Breast Cancer

Tight Junction Proteins and Permeability Improved by Roasted Garlic in Mice with Induced Colitis

Randomized Controlled Trial Confirms NEM® Efficacy and Safety in Reducing Osteoarthritis Pain and Stiffness

Whole Fish Trumps Pills: Study Finds Whole-Food Factors, Not Isolated Omega-3s, Lower Autism Risk

Dark chocolate and tea found to significantly lower blood pressure

Burglar Uncovers Shocking Crime During Robbery, Turns Himself In and Exposes Serious Offense

The Black Diamond Apple: A Rare Gem from the Mountains of Tibet

The Power of Pine Needles: 30 Benefits and Homemade Uses

Marvin Harvin Becomes One of the First Incarcerated Individuals to Graduate from Yale University, Highlighting the Power of Education in Prison Reform

The Hidden Power of Pistachio Shells: Benefits and Clever Homemade Uses

Warren Buffett’s Ice Cream Quote: A Simple Yet Powerful Lesson on Taxes

Papaya Seeds: A Powerful Remedy for Liver Health and How to Use Them as a Pepper Substitute

30 Amazing Benefits of Lactuca serriola (Wild Lettuce)

Why Do Button-Down Shirts Have Loops On the Back

World's Oldest Little Blue Penguin Reaches Remarkable 25 Years in Managed Care

How To Clear Your Sinuses

Mullein: The Wild Plant That Clears Your Lungs Naturally
