Chinese Scientists Created a ‘Bone Glue’ That Repairs Fractures in Minutes With a Single Injection
Breaking a bone traditionally means months of slow healing and painful recovery. Standard orthopedic surgery requires cutting through layers of tissue, drilling into bone, and installing metal plates and screws. Patients face significant pain, the risk of infection, and the likelihood of undergoing a second surgery later to remove the hardware.
A research team in China may have rewritten this long-standing narrative. Scientists at Zhejiang University have developed an injectable adhesive capable of bonding shattered bone fragments in just three minutes. With one injection through a small incision, surgeons can avoid hours of reconstruction and dramatically shorten healing times—all without metal plates, screws, or follow-up operations.
Early trial results are astonishing: patients have walked out of treatment rooms with fully stabilized fractures after procedures shorter than a coffee break, and follow-up examinations three months later show complete healing without complications. If further trials confirm these results, fracture treatment could undergo the most dramatic transformation in decades.
A Breakthrough Called Bone-02
The new substance, named Bone-02, works in environments where traditional adhesives fail—wet, bloody, constantly shifting spaces deep inside the body. Engineers based its design on mechanisms found in marine life, which maintain powerful adhesion underwater despite strong currents and turbulence.
The research team is led by Dr. Lin Xianfeng, an associate chief orthopedic surgeon at Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital in Hangzhou. After witnessing countless complex fracture repairs with limited long-term success, Lin believed nature offered better answers than existing medical hardware could provide.
Bone-02 proved to be that answer. Delivered through a needle, the adhesive flows into fracture gaps and hardens within two to three minutes. According to Lin, “The adhesive can achieve precise fixation within minutes, even in a blood-rich environment.” Clinical trials have demonstrated effectiveness across a wide range of fractures, including those that typically require extensive plates and screws.
Laboratory assessments confirm that Bone-02 meets or exceeds mechanical strength requirements for load-bearing bones. Tests show high biocompatibility, low infection rates, and seamless integration with natural bone tissue.
To many clinicians, this represents not just an improvement, but a potential paradigm shift in fracture care.
Why Traditional Fracture Surgery Is So Difficult
Orthopedic repairs are among the most demanding procedures in medicine. Fixing something as common as a broken wrist requires opening the tissue layers, exposing the fracture site, drilling holes into bone fragments, and mounting metal plates to hold everything in place.
Recovery is long and painful. Between the surgical trauma and the body’s natural inflammatory response, patients often struggle for months before regaining function. Even then, many never recover full strength or range of motion.
Metal hardware introduces its own challenges:
-
Plates and screws can irritate tissues or cause discomfort during movement and cold weather.
-
Bacteria can colonize metal surfaces, forming hard-to-treat biofilms.
-
Athletes often require hardware removal to restore peak performance.
-
Children may need repeated surgeries because their bones grow.
Protection from stress can even weaken bones around the plates, a phenomenon known as stress shielding. All of this adds up to a process that is effective but far from ideal.
The Challenge No Ordinary Adhesive Could Overcome
Fracture sites are notoriously hostile to glues. Blood continuously coats exposed bone ends. Joints add lubrication. Muscles generate movement even during immobilization. Commercial adhesives dissolve, lose strength, or fail entirely under these shifting, fluid-rich conditions.
Furthermore, internal body conditions fluctuate constantly—temperature, pH, inflammation, pressure—requiring an adhesive that can adapt without breaking down.
Bone-02 succeeds where others fail because it was engineered to work with the body's natural environment rather than against it. Moisture activates the adhesive instead of interfering with it, and the resulting chemical bond is strong enough to withstand the mechanical loads of everyday movement.
An Oyster on a Bridge: The Spark Behind the Innovation
Dr. Lin’s breakthrough dates back to 2016. During a walk near the water, he noticed oysters clinging stubbornly to a bridge piling despite the pounding waves, dramatic tidal changes, and corrosive salt water. These mollusks remained fixed where metal bolts and synthetic glues would fail.
Oysters produce a protein-rich bio-cement that bonds powerfully in wet, dynamic environments. Scientists found that its proteins cross-link with minerals and organic compounds to create extremely durable adhesive structures.
Lin realized that the conditions oysters thrive in—constant moisture, movement, pressure—mirror those found at bone fracture sites. If oysters could stick to rocks underwater, a similar compound might allow bones to stick to themselves inside the body.
His team spent years designing synthetic molecules inspired by oyster cement but optimized for human physiology. They adjusted the hardening speed, bonding chemistry, and biomechanical strength until they achieved a glue suitable for surgical use.
How Bone-02 Works: From Broken to Bonded in Three Minutes
Bone-02 treatment begins with a small incision, typically around 3 centimeters long. Using imaging guidance, surgeons insert a needle directly into the fracture and inject the adhesive.
Once inside, Bone-02 flows into the fracture gap and reacts with the moisture and minerals present in bone. This triggers rapid hardening, creating a stable matrix that binds fragments together. Surgeons can still adjust alignment in the first couple of minutes before the adhesive fully sets.
When the glue stabilizes, the fracture becomes strong enough to support limited movement. Patients can begin gentle activity far earlier than with traditional surgery, reducing muscle atrophy and joint stiffness.
Imaging studies show that the adhesive fills microscopic spaces between fragments, providing a continuous load-bearing bridge that supports natural bone growth.
A Wrist Fracture Repaired Without Metal Hardware
One clinical case involved a patient with a complex wrist fracture. Instead of a long incision, plates, and screws, surgeons made a small 3-centimeter opening, injected Bone-02, and were finished in under three minutes.
A comparable traditional surgery would last an hour or more and require months of recovery, followed by a second operation to remove the hardware.
Three months after the Bone-02 procedure, X-rays revealed complete healing with new bone formation. The patient regained full range of motion and strength, reporting minimal pain throughout the recovery process.
The Numbers Behind the Bond: As Strong as Bone Itself
Laboratory testing confirmed Bone-02’s impressive performance:
-
Bonding force: over 400 pounds
-
Shear strength: roughly 0.5 MPa, comparable to biological tissues that withstand twisting
-
Compressive strength: around 10 MPa, suitable for weight-bearing regions of the skeleton
These measurements suggest the adhesive can replace metal hardware for many fractures while offering better biological compatibility and fewer complications.
Additionally, because Bone-02 gradually biodegrades, it allows bone tissue to strengthen naturally over time rather than becoming dependent on rigid plates.
Lower Infection Rates and Fewer Long-Term Complications
Early results indicate that Bone-02 significantly reduces infection risks compared to conventional surgery:
-
Smaller incisions minimize bacterial exposure
-
Shorter surgical times reduce tissue trauma
-
No permanent hardware exists for bacteria to colonize
Patients also avoid immune system reactions commonly triggered by surgical metals. As the adhesive gradually breaks down, bone remodels naturally, eliminating the long-term issues that metal plates often create.
When Will Patients Have Access to Bone-02?
For now, Bone-02 remains in clinical trials. Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital is expanding test groups to verify long-term outcomes, evaluate rare complications, and assess the adhesive’s effectiveness across a wider range of fractures.
Regulatory approval in China and internationally will require extensive documentation, manufacturing quality control, and independent validation studies. Scaling production is another challenge, as bio-adhesives demand extremely precise chemical consistency.
Even with these hurdles, enthusiasm in the medical community is strong. If trials continue to show promising results, Bone-02 could move from experimental innovation to worldwide clinical practice within a few years.
A future where broken bones heal in minutes instead of months—through a single injection inspired by an oyster—is no longer science fiction. It is quickly becoming a medical reality.
News in the same category


Stop Counting Calories — The “100g Protein Rule” That Boosts Energy and Crushes Cravings

10 Supplement Combinations You Should Never Take Together
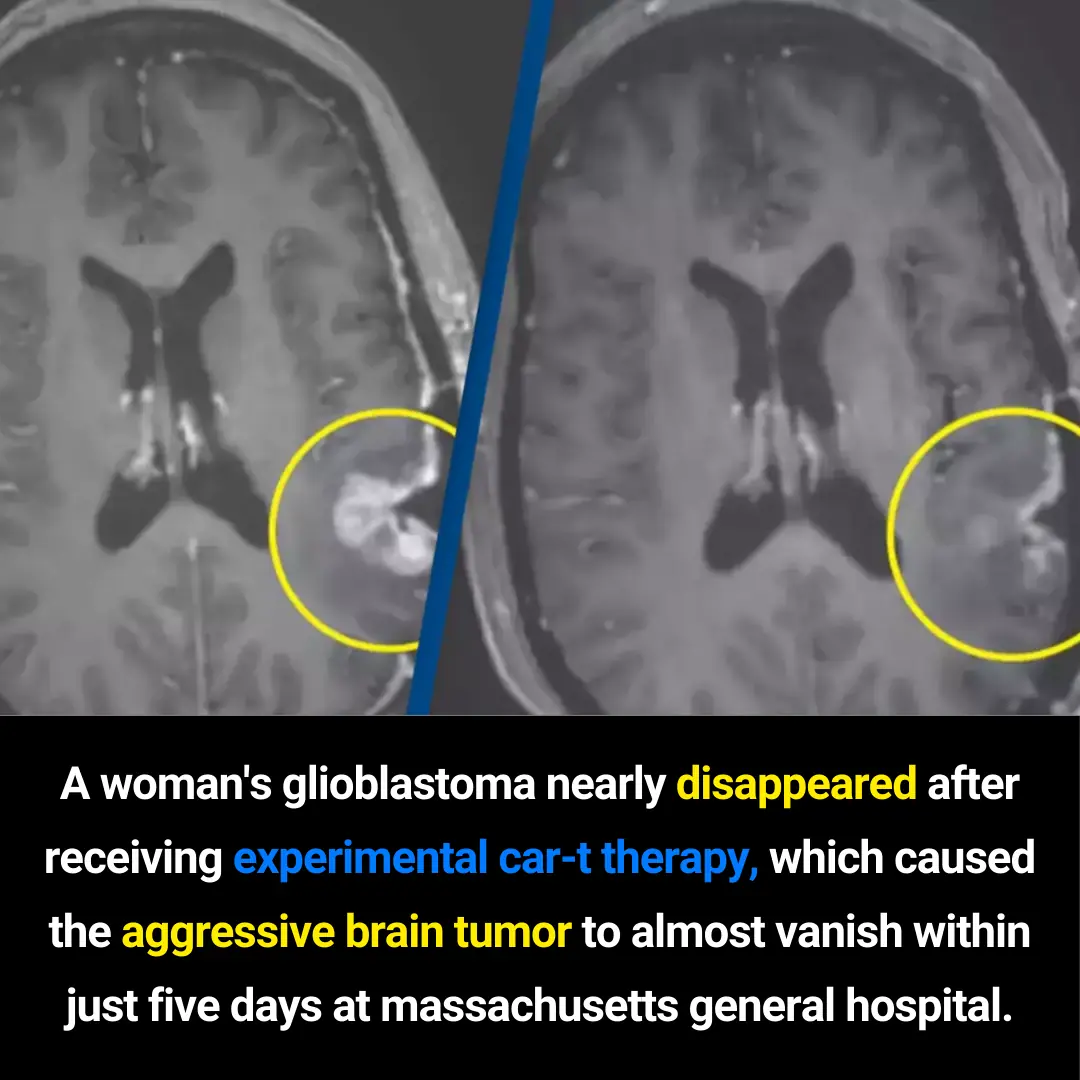
🦴 This Could Be the Vitamin Your Body Is Missing When Your Legs and Bones Hurt

Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) and Stomach Pain: Can It Help or Hurt? The Complete Guide
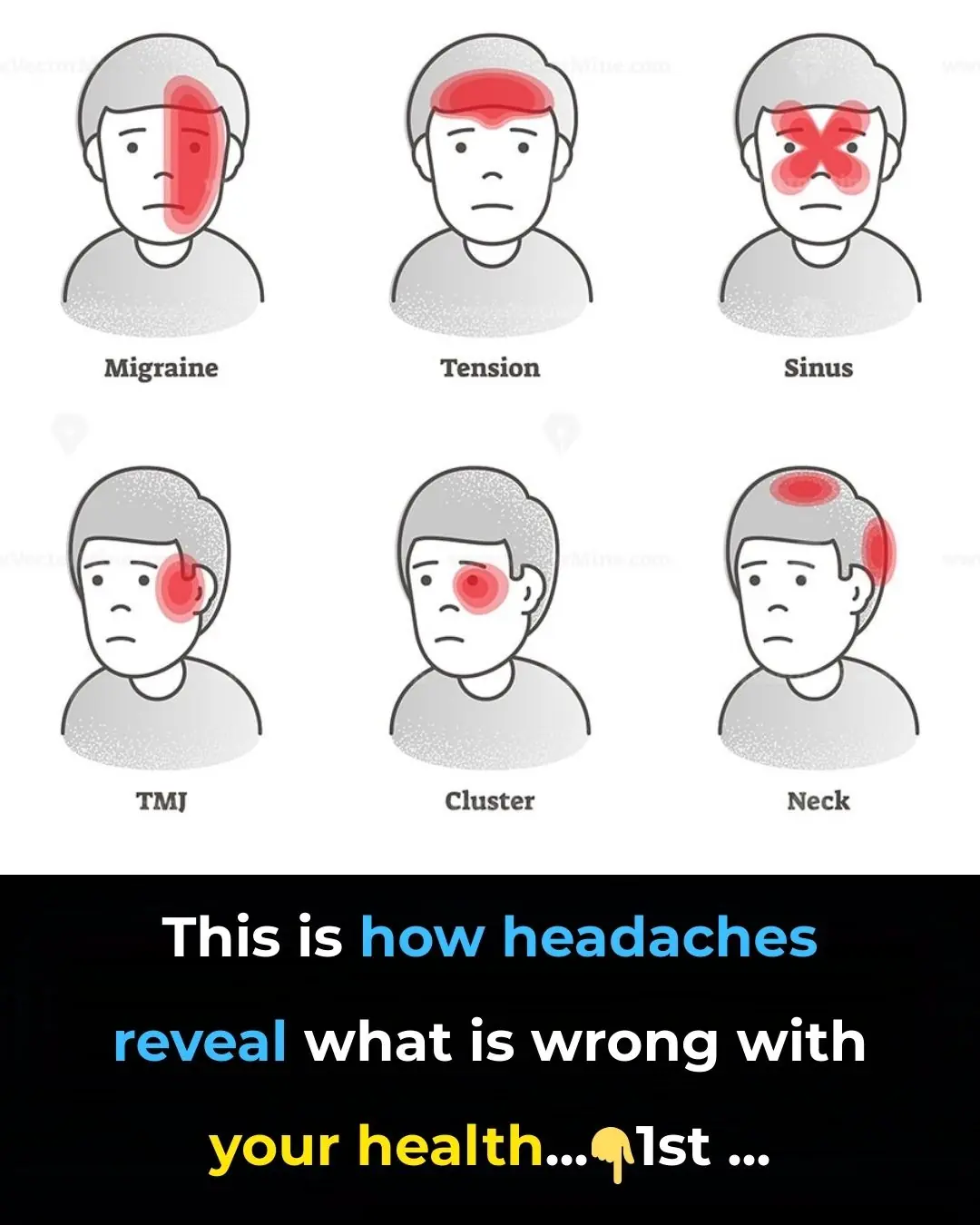
This is How Headaches Reveal What is Wrong With Your Health

The natural kitchen mix people use to break down stubborn plaque buildup

10 Amazing Health Benefits of Dates (and Why You Need To Start Eating Them!)

The Surprising Truth: Wooden Boards Kill Bacteria Better Than Plastic
Cell Therapy Begins Human Trials to Reverse Spinal Cord Injury

Overripe Bananas Could Help Fight Cancer Naturally

Could a Nearly Universal Virus Be the Root Cause of Lupus

Castor Oil for Peripheral Neuropathy Relief: A Natural Remedy Worth Trying?

The New Science Behind Killing Cancer

Beware: U.S Salmon May be Crawling with Japanese Tapeworm, Say Scientists

How to Use Guava for Eye Comfort | Natural Remedies for Healthy Eyes
Top 10 foods that improve blood circulation in legs

Orthopedist’s Secret: How to Support Natural Cartilage Repair in Just 24 Hours
15 visible signs of low thyroid you can see – don’t ignore #7!
News Post

Meet the First Woman Graduate From Howard University Law School, Charlotte E. Ray

Beating Seasonal Depression: 8 Directories To Help You Find An Affordable Black Therapist

Hip-Hop Pioneer Rakim Launches New ‘Notes’ Fintech Platform to Empower Independent Artists

New ‘Eddie’ Documentary About Comedy Legend Eddie Murphy Is Coming to Netflix

Remembering Roberta Flack, Legendary Songstress, Educator, and Howard University Alumna

New CBS Show ‘The Gates’ Marks Return of Predominantly Black Cast to Daytime Soaps for First Time in Three Decades

4 Inspiring Things You Never Learned About W.E.B. Du Bois

6 Inspiring Achievements That Black Women Accomplished First

Afrobeats Star Tems Joins San Diego FC Major League Soccer Ownership Group

Khaby Lame Becomes The Most-Followed Person On TikTok

Hattie McDaniel: Everything You Need To Know About The First Black Oscar Winner

40 Years Ago, Michael Jackson’s ‘Thriller’ Album Made History at the Grammys

Raspberry Leaf Power: 30 Benefits and How to Use It

7 Powerful Bay Leaf Benefits for Heart Health and Smoother Blood Flow

Stop Counting Calories — The “100g Protein Rule” That Boosts Energy and Crushes Cravings

How Cats Use Smell and Earth’s Magnetic Field to Navigate Home Over Long Distances

10 Supplement Combinations You Should Never Take Together

Japan’s Visionary Floating City: A Sustainable Urban Model for 2030 and Beyond

🦴 This Could Be the Vitamin Your Body Is Missing When Your Legs and Bones Hurt