
Crush Papaya Leaves Every Night – Your White Hair May Start Turning Dark and Growing Like Crazy by Morning

Papaya Leaves and Hair Health: Traditional Use, Biological Properties, and Scientific Perspective
Hair thinning and premature graying are common concerns among adults over the age of 50. These changes are often linked to aging-related reductions in melanin production, oxidative stress, inflammation of the scalp, and decreased follicular activity. While commercial hair-growth and color-restoring products dominate the market, many traditional medical systems have long relied on plant-based remedies. Among these, papaya leaves (Carica papaya) have been widely used in parts of Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean as a topical treatment for scalp and hair health.
Papaya leaves contain a unique combination of bioactive compounds, including the proteolytic enzyme papain, flavonoids, polyphenols, and vitamins A, C, and E. These substances are known to support skin renewal, reduce oxidative stress, and improve local circulation. A phytochemical analysis published in Journal of Medicinal Plants Research confirmed that papaya leaves possess strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity due to their high polyphenol and flavonoid content (Maisarah et al., 2013). Antioxidants are particularly relevant to hair pigmentation, as oxidative stress is a key contributor to melanocyte dysfunction and hair graying.
Papain, the primary enzyme in papaya leaves, exhibits gentle exfoliating properties that may help remove excess sebum, dead skin cells, and protein buildup on the scalp. A healthier scalp environment supports follicular function and may reduce hair shedding. Research in Pharmacognosy Reviews reports that papain enhances skin permeability and cellular turnover, potentially improving nutrient delivery to hair follicles (Aravind et al., 2013). This mechanism may explain anecdotal reports of improved hair thickness and reduced hair fall with regular topical use.
Vitamins present in papaya leaves also play supportive roles in hair biology. Vitamin C contributes to collagen synthesis and iron absorption, both essential for healthy hair growth. Vitamin E helps protect follicular cells from oxidative damage, while vitamin A supports sebum regulation. According to Dermatologic Therapy, deficiencies in these micronutrients are associated with hair fragility, thinning, and slowed growth (Almohanna et al., 2019). When applied topically, these nutrients may complement dietary intake by supporting scalp health locally.
Claims regarding the reversal of gray hair, however, should be interpreted cautiously. Hair graying primarily results from the gradual loss of melanocyte activity within hair follicles, a process strongly influenced by genetics and aging. While antioxidants may help preserve remaining melanocyte function, current clinical evidence does not support guaranteed reversal of gray hair through topical herbal treatments, as noted in reviews published in Experimental Dermatology. Improvements in hair color reported by users may reflect enhanced shine, reduced oxidative dullness, or the appearance of new pigmented hairs rather than full restoration of original color.
In conclusion, papaya leaves represent a nutrient-rich, traditionally valued botanical that may support scalp health, reduce hair shedding, and improve the overall appearance and vitality of hair when used consistently. Their antioxidant and enzymatic properties provide a plausible biological basis for these effects. However, while anecdotal reports are compelling, robust clinical trials are still needed to confirm claims related to hair regrowth rates and gray hair reversal. Papaya leaf treatments should therefore be viewed as a complementary, low-risk self-care practice rather than a guaranteed solution. Individuals with scalp sensitivity or underlying dermatological conditions should consult a healthcare professional before regular use.
News in the same category


If You Have a Kalanchoe Plant at Home, You Might Own a Hidden Treasure

Get Soft, Pink Lips Naturally: A Simple DIY Scrub for Smoother Lips

Over 60? Waking Up at 2 A.M. Every Night? This One Warm Drink May Help You Sleep Through Till Morning

7 Everyday Foods That Help Maintain Muscle Strength and Stay Active After Age 50
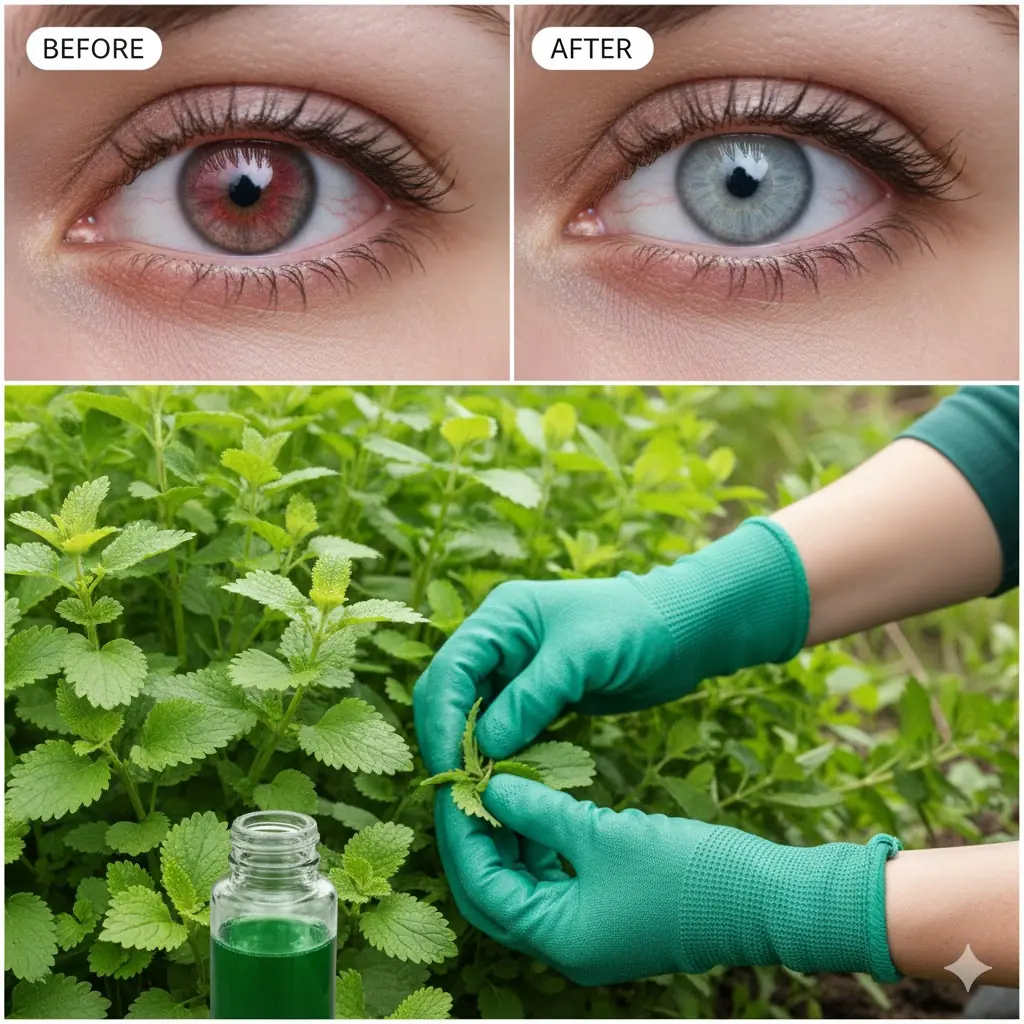

Oregano for Eyes: The Little Leaf That May Protect Your Vision After 40

Could a Simple Kitchen Herb Help Support Long-Term Eye Comfort and Clarity?

Discover the Natural Power of Rosemary and Cloves for Healthier Hair, Glowing Skin, Better Digestion, and Natural Pain Relief
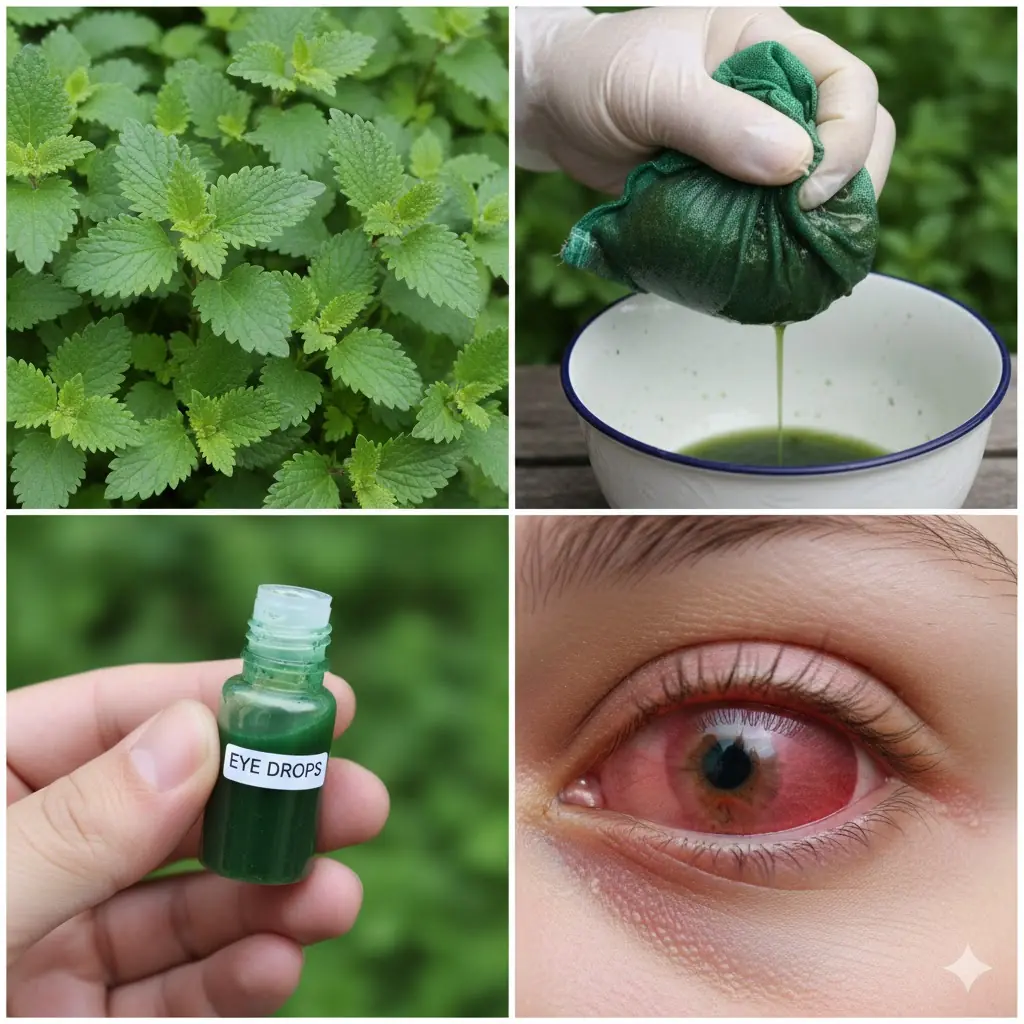

Discover How One Forgotten Leaf Is Quieting Puffy Eyes and Brightening Gazes Overnight

Three Nutrient-Rich Leaves That May Support Your Body’s Natural Defenses

Over 60? 10 Early Dementia Warning Signs You Must NEVER Ignore (Catch Them Before It’s Too Late)
The Cheapest Superfood Most Seniors Overlook That Could Transform Bone Health After 60

9 Hidden Garlic & Honey Benefits at Night (99% Don’t Know)
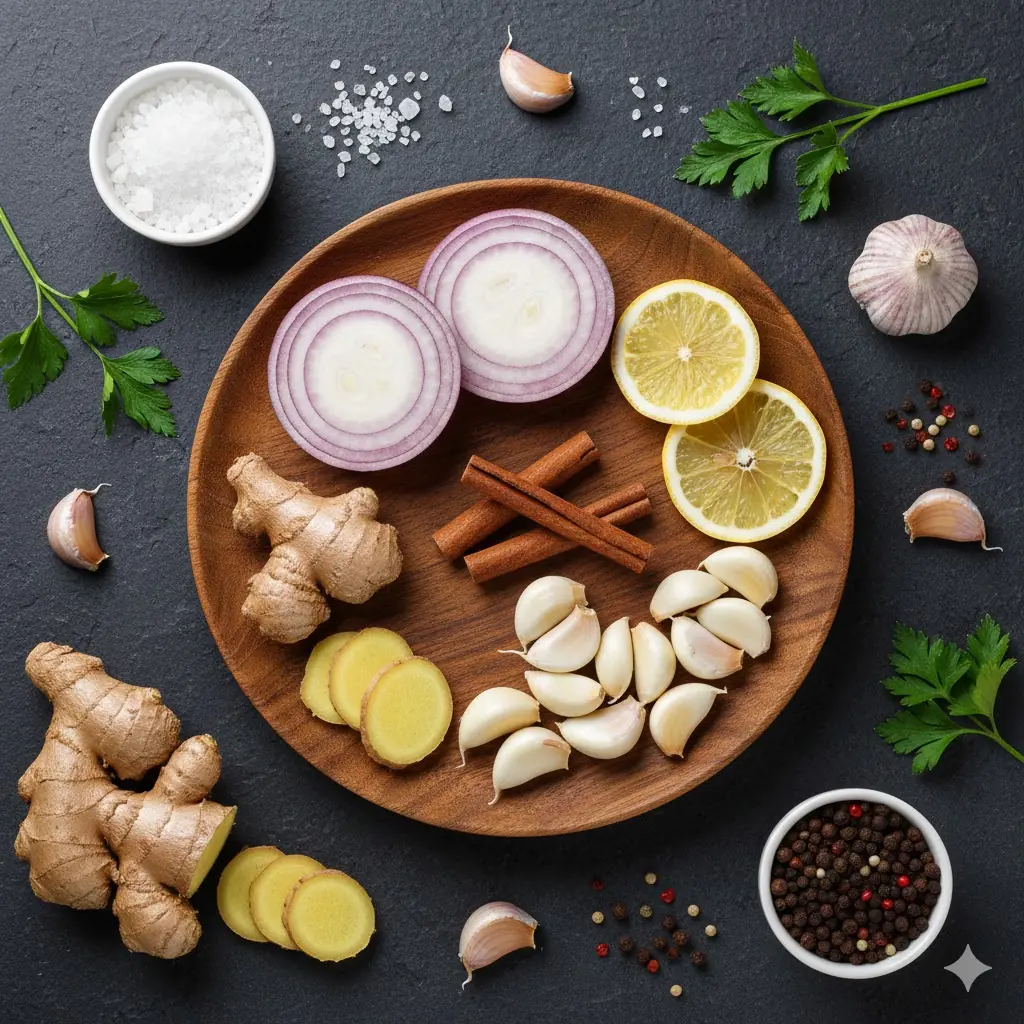

Boil Cinnamon, Cloves, Garlic, Ginger, Lemon & Onion for 15 Minutes – Your Body Will Feel the Difference by Day 3

Discover Oregano: The Golden Herb That May Gently Support Your Eye Health

How to Grow Your Nails Really Fast and Long in Just 10 Days

You don’t need complicated supplements to support digestion.
Garlic with Olive Oil Over 50: The Irreversible Body Reaction Everyone’s Talking About
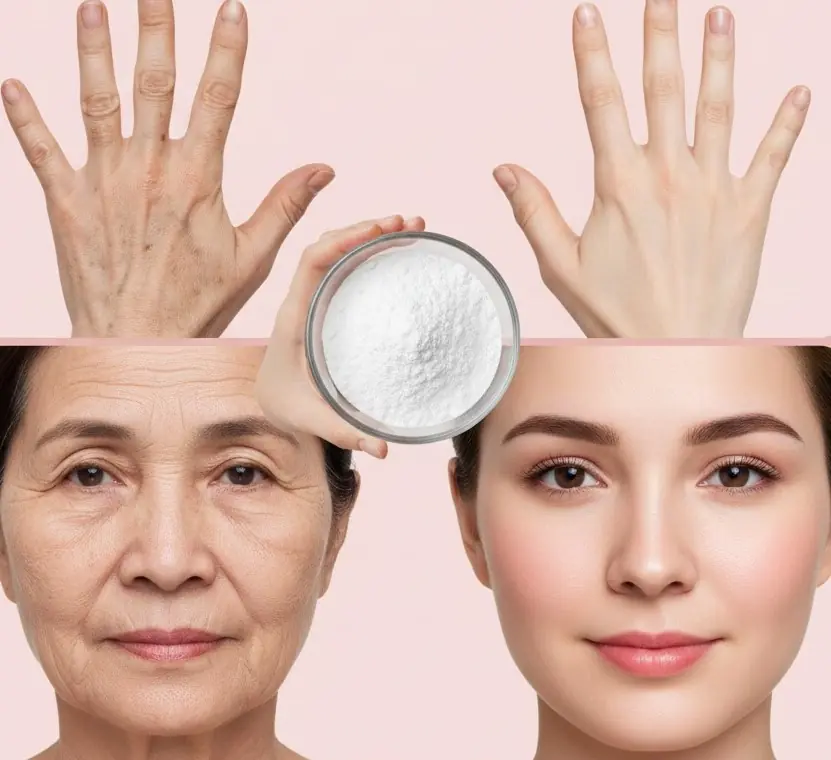

Discover How Baking Soda Could Transform Your Skin’s Appearance in Minutes – Even After 70!
News Post
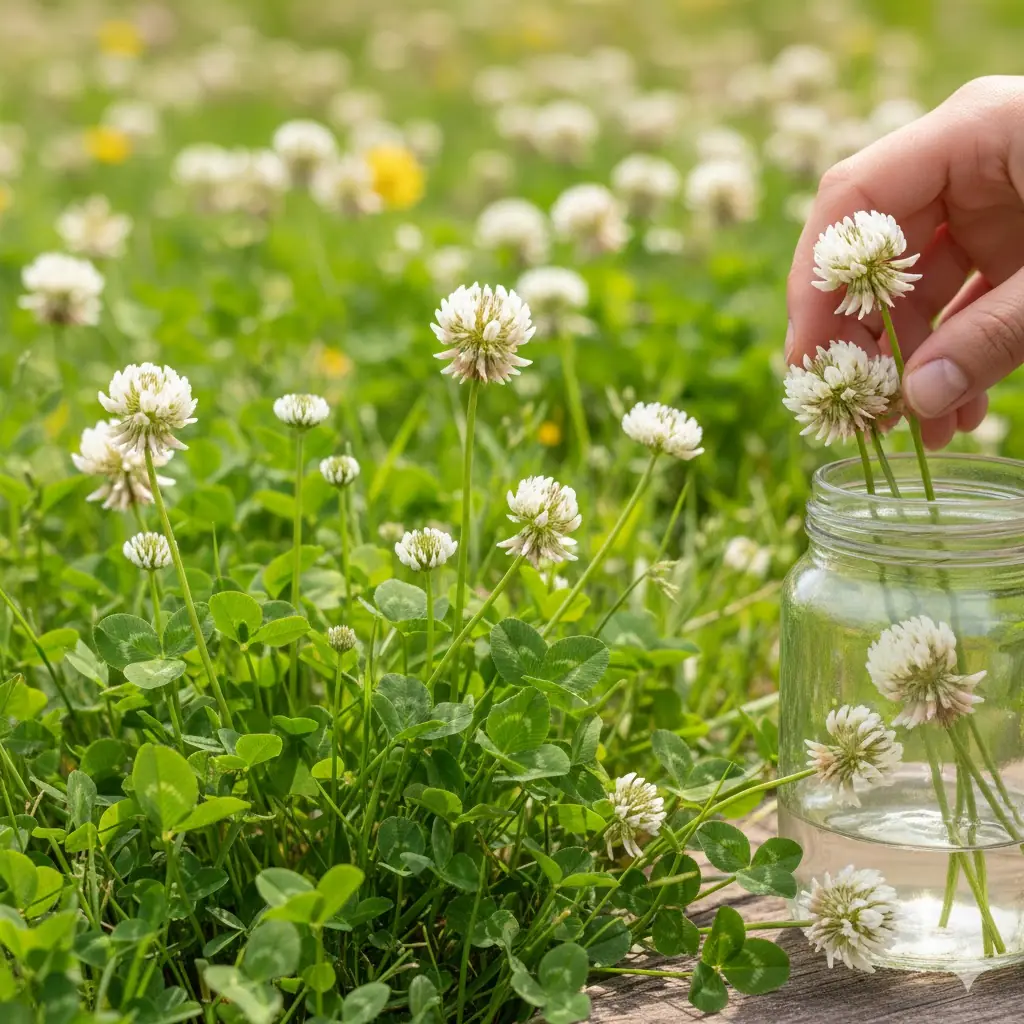

White Clover (Trifolium repens): Benefits and Uses

Peter Greene, Pulp Fiction and The Mask Actor, Dies at 60
Discover the Surprising Nutritional Powerhouse: 10 Benefits and Everyday Uses of Purslane

Euphorbia Hirta: 9 key health benefits of this versatile plant

If You Have a Kalanchoe Plant at Home, You Might Own a Hidden Treasure

Natural Home Remedies for Cough and Sore Throat

John Cena's last match: Results, grades and highlights as WWE legend retires on emotional farewell show
Medicine Breaks New Ground as Ultrasound Builds Tissue Without Surgery

A Heartbreaking Survival Trick: How a Stray Cat Learned to Hide His Pain

Bears Turn Honey Theft Into a Surprising Taste Test in Turkey

Scientists Say Your Butt Shape May Say More About Your Health Than You Think
The Rare Condition That Makes Human Bones Slowly Vanish

Mexico Ends Marine Animal Shows and Sparks a Health Centered Conservation Shift

California Turns Irrigation Canals Into Solar Power and Water-Saving Systems

Jesy Nelson's celebrity friends including ex Chris Hughes show support as Little Mix singer reveals twin girls' devastating diagnosis
People with weak kidneys often do these 4 things every day: If you don't stop soon, it can easily damage your kidneys

Get Soft, Pink Lips Naturally: A Simple DIY Scrub for Smoother Lips

Over 60? Waking Up at 2 A.M. Every Night? This One Warm Drink May Help You Sleep Through Till Morning

7 Everyday Foods That Help Maintain Muscle Strength and Stay Active After Age 50
