Never store your cooked rice without knowing this
Leftover rice might seem harmless — a quick, easy meal waiting in the fridge for the next day. But food safety experts warn that storing it the wrong way could turn a simple side dish into a serious health hazard. The culprit is a little-known but surprisingly common condition nicknamed “fried rice syndrome.”
Many families cook in large batches, then refrigerate what’s left for later. While this may seem efficient, rice is uniquely prone to bacterial contamination if not handled properly. The main threat comes from Bacillus cereus, a bacteria that thrives in cooked rice under certain conditions.

Why Cooked Rice Can Become Dangerous
When rice is cooked, any Bacillus cereus spores present in the raw grains can survive the cooking process. If the rice is left sitting at room temperature for more than an hour, these spores can multiply rapidly, producing toxins that are resistant to heat. This means even reheating might not destroy them.
Food poisoning from contaminated rice can appear quickly — sometimes within just an hour after eating. Symptoms include nausea, stomach cramps, fever, vomiting, and acute diarrhea. In severe cases, dehydration and electrolyte imbalance can occur, posing greater risks for children, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems.
What makes the problem worse is that most people never suspect rice as the source of their illness, often blaming other foods instead.
Even Refrigeration Has Risks
While refrigeration slows bacterial growth, it doesn’t stop it entirely. If rice is cooled and stored improperly, bacteria may still spread — just at a slower pace. This is why how you store leftover rice is just as important as where you store it.

The Safest Way to Store Cooked Rice
Food safety specialists recommend the following steps to reduce bacterial growth and keep your rice safe to eat:
- Cool It Quickly – Do not leave rice sitting in the pot after cooking. Instead, spread it out on a clean tray or shallow dish so it cools faster.
- Use Shallow, Airtight Containers – Transfer cooled rice into a shallow, sealed container to prevent moisture buildup and bacterial contamination.
- Refrigerate Within One Hour – Place the container in the fridge as soon as possible — ideally within 60 minutes of cooking.
- Eat Within 24–48 Hours – The sooner you consume leftover rice, the safer it is.
- Freeze for Longer Storage – When frozen, cooked rice can last up to six months without significant quality loss.
Reheating Rules You Shouldn’t Ignore
When reheating leftover rice, ensure it reaches an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) before serving. This helps destroy most bacteria that may have grown during storage. However, keep in mind that some bacterial toxins are heat-resistant, so safe storage is still the first line of defense.
Important: Never reheat rice more than once. Each reheating cycle increases the risk of bacterial contamination and toxin production.
Final Takeaway
Rice might be a simple staple, but improper storage can turn it into a surprising source of foodborne illness. By cooling it quickly, storing it in airtight containers, and following strict reheating guidelines, you can enjoy your leftovers safely — without worrying about fried rice syndrome.
Sometimes, the smallest kitchen habits make the biggest difference in keeping your family healthy.
News in the same category


Nurse reveals the 4 final phrases she hears people say before they die
A veteran hospice nurse has shared the deeply moving — and sometimes surprising — last phrases she’s heard from patients in their final moments. Her insights reveal that real-life goodbyes are far from the dramatic Hollywood scenes we’ve come to e

The Ultimate Guide to Cloves: Benefits, Uses, and How They Work
Cloves aren’t just a fragrant kitchen spice — they’re a centuries-old natural remedy packed with healing power. From boosting immunity to easing pain, these tiny buds hold surprising benefits you can easily tap into at home.

Many People Still Think That These 2 Buttons Are Just For Flushing

One Button, Big Savings: Cut Energy Costs with Every Wash

10 Types of Toxic Friends to Avoid

Index Finger Length: Personality and Fortune

Underwater City Near 'Noah's Ark' Discovery Might Change The Bible Story We Thought We Knew

Reason Mark Zuckerberg Just Spent $15,000,000,000 to Hire This 28-Year-Old ‘College Drop Out’ for Meta

Cut a lemon in four and keep it in your bedroom overnight – the reason is brilliant
This lemon trick is a small change that makes a big difference.

Italy just upgraded dogs to cabin class. No more cargo holds for dogs!

11 Heartbreaking Signs Your Dog Is Nearing the End—And How To Give Them The Love They Deserve

15 Things That Might Hint at Her Romantic Past

Depressing find at the bottom of the Mariana Trench is a warning to the world
The Mariana Trench, Earth’s deepest ocean abyss, was once thought to be untouched by human hands. But the discovery of a single plastic bag in its darkest depths has become a chilling symbol of how far our pollution has reached.

Unveiling Personality Secrets: What’s the First Color You See?

If you see square waves forming in the ocean, get out of the water immediately
The mesmerizing chessboard-like patterns on the ocean’s surface may seem harmless, but they’re hiding a dangerous secret. Scientists warn that these rare formations, known as square waves, can turn the sea into a deadly hazard in seconds.

The flowers you love the most uncover hidden aspects of your personality
Flowers don’t just brighten our surroundings — they can also serve as a fascinating mirror to our inner world. From the joyful daisy to the mysterious violet, your favorite bloom could reveal your emotional depth, values, and the way you connect with

Experts warn: Don’t swap your oven for an air fryer

The Truth About Eating the Black Vein in Shrimp Tails
News Post

Woman is diagnosed with cancer — believes a popular sandwich is to blame
When investigative journalist Lucie Morris-Marr was told she had stage-four bowel cancer, she was at the peak of her personal and professional life. Now, she’s speaking out about a hidden dietary danger she believes more people need to take seriously

8 Potential Health Benefits of Nuts

Study Links Fries, but Not Other Forms of Potato, With Diabetes

How to Lower High Blood Pressure Quickly Without Medications (Evidence Based)

Why You Should Start Using Coconut Oil as a Toothpaste

20 Early Cancer Signs You Should Never Ignore

7 Signs That Your Partner Isn’t In Love And Is Just Settling For You

5 Warning Signs That Could Indicate Colon Cancer

Nurse reveals the 4 final phrases she hears people say before they die
A veteran hospice nurse has shared the deeply moving — and sometimes surprising — last phrases she’s heard from patients in their final moments. Her insights reveal that real-life goodbyes are far from the dramatic Hollywood scenes we’ve come to e
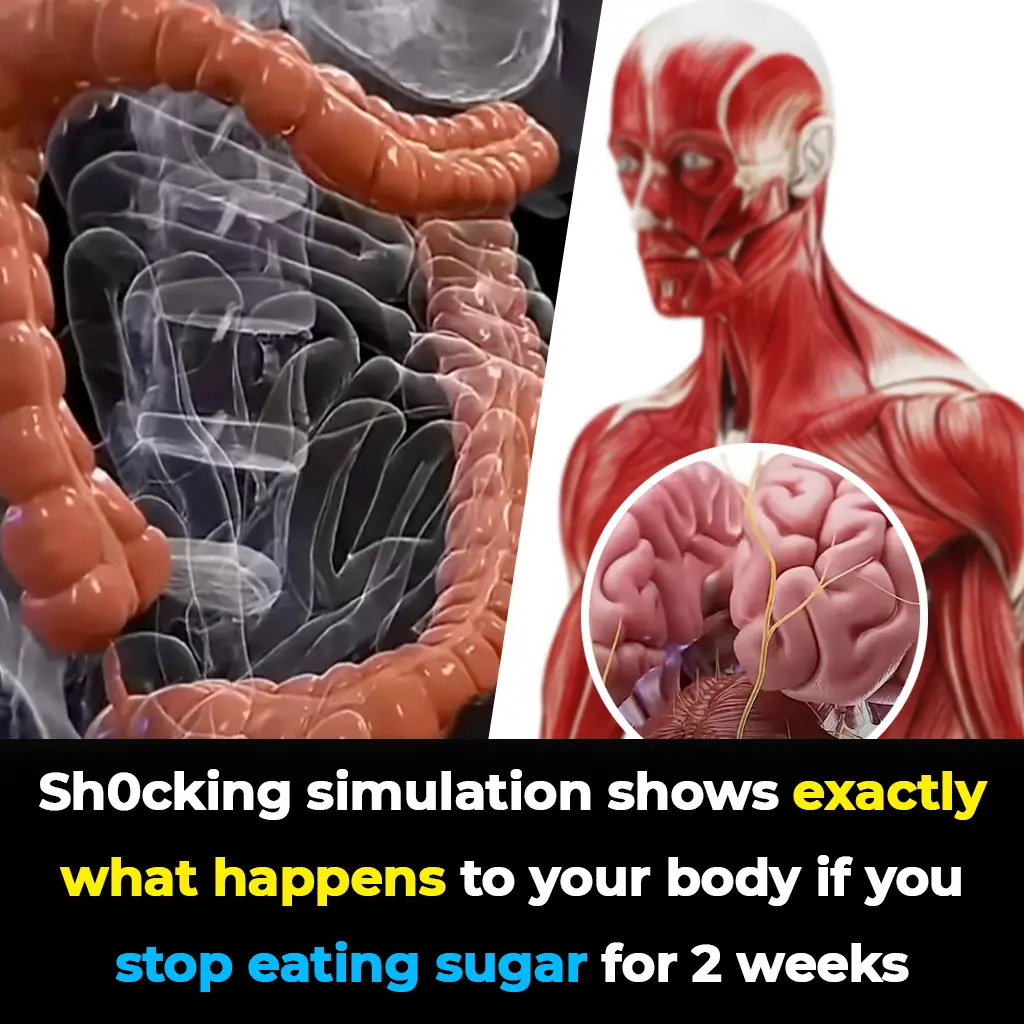
Shocking simulation shows exactly what happens to your body if you stop eating sugar for 2 weeks
Giving up sugar for two weeks may sound like a simple diet tweak, but a new simulation shows the change can trigger a chain reaction inside your body — from energy surges to mental clarity. The journey isn’t without its challenges, but the long-term r

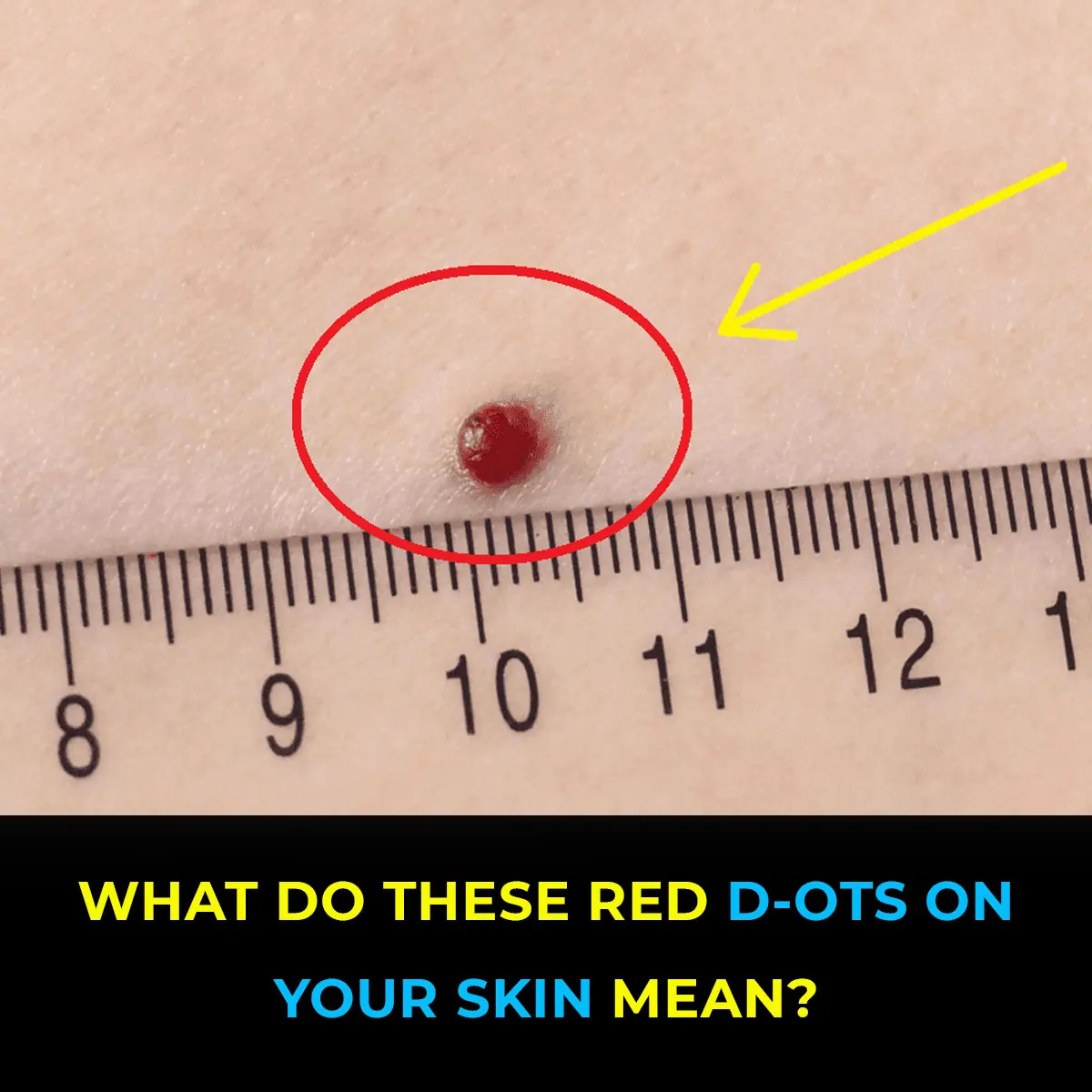
11 Sh0cking Causes of Red Dots on Your Skin and How to Treat Them
While some red dots on your skin may resolve on their own or with simple remedies, others can and should require medical attention.
Healing Power of Castor Leaves: Natural Benefits and Must-Know Safety Tips

Here’s Why You Shouldn’t Sleep With A Fan At Night
Sleeping with a fan might seem harmless — even comforting — but its hidden effects can chip away at your comfort and long-term sleep quality.

36-Year-Old Teacher D!es From Diabetes Caused by Common Foods, Experts Say
Diabetes is a serious health condition with long-term consequences if left unmanaged.
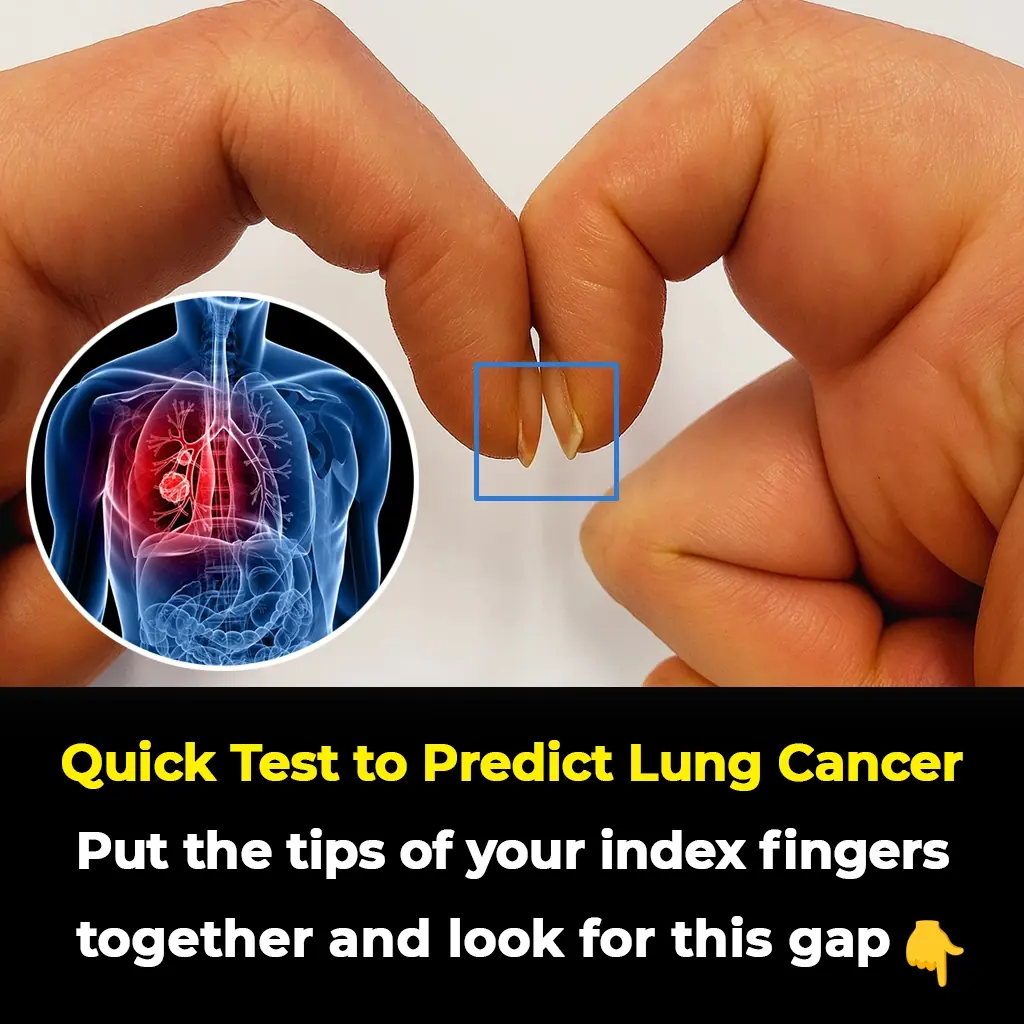
Finger Test For Lung Cancer Could Determine Cancer Risk
While finger clubbing itself is a symptom rather than a disease, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce the risk of underlying conditions that cause it.

The Ultimate Guide to Cloves: Benefits, Uses, and How They Work
Cloves aren’t just a fragrant kitchen spice — they’re a centuries-old natural remedy packed with healing power. From boosting immunity to easing pain, these tiny buds hold surprising benefits you can easily tap into at home.
What Are Eye Floaters? Here What To Do If you Start Seeing Them, According to an Eye Doctor

Many People Still Think That These 2 Buttons Are Just For Flushing