
The Medicinal Properties of Eleusine indica (Goosegrass) in Traditional and Modern Medicine
Known in Vietnam as cỏ mần trầu, this humble grass has long been valued in Traditional Eastern Medicine for its cooling, detoxifying, and blood-regulating effects. Despite being a common weed found throughout tropical Asia, Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. — also called Goosegrass, Cow Grass, or Wiregrass — is a powerful natural remedy with both ancient and scientifically proven benefits.
🌾 Botanical Description
Eleusine indica belongs to the Poaceae (grass) family. It is a small annual herb that grows abundantly in warm, humid climates — from the lowlands to high mountainous regions.
-
Height: 30–50 cm
-
Stems: Creeping at first, later erect and branching
-
Leaves: Flat, slender, alternately arranged with soft hairs at the sheath base
-
Flowers: Clustered in 5–7 slender spikes radiating from a single point, resembling a fan shape
-
Fruiting season: Typically May to July
Because of its shape, E. indica is sometimes confused with Dactyloctenium aegyptium (crowfoot grass), but the latter has shorter stems and tighter flower clusters.
According to the Vietnam Institute of Medicinal Plants (2023), E. indica is a hardy plant that thrives even in poor soil, which explains its widespread presence in rural and urban landscapes.
🌿 Medicinal Characteristics in Traditional Medicine
In Vietnamese and Chinese Traditional Medicine (TCM), cỏ mần trầu is described as having a sweet, slightly bitter taste and a cool (hàn) nature. It acts mainly on the liver, kidney, and urinary meridians, with the following effects:
-
Clears heat and detoxifies the liver
-
Promotes urination and reduces internal inflammation
-
Relieves fever and supports blood circulation
-
Eases swelling and reduces hypertension
-
Helps calm the fetus and alleviate pregnancy-related heat symptoms
It has traditionally been used to treat:
-
Headache, dizziness, and mild hypertension
-
Fever and sore throat
-
Urinary retention or yellow urine
-
Postpartum inflammation
-
Skin rashes, boils, and mouth ulcers
-
Heat-induced restlessness, anxiety, and insomnia
In Malaysian folk medicine, the juice of E. indica is given to postpartum women to help expel lochia (post-birth fluids).
In Chinese herbal records, it is used to treat hepatitis, nephritis, dysentery, and epidemic encephalitis.
🧪 Active Compounds and Modern Pharmacological Studies
Modern research has confirmed that Eleusine indica contains several bioactive compounds responsible for its medicinal effects.
Chemical analysis has identified:
-
Flavonoids (C-glycosylflavones)
-
β-sitosterol derivatives
-
Palmitoyl esters
-
Phenolic acids
-
Tannins and alkaloids
These compounds provide a range of anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant actions.
1️⃣ Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory Effects
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology (2021) found that extracts of E. indica at 600 mg/kg reduced fever in test animals as effectively as aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, 100 mg/kg).
Researchers observed that the extract inhibited cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and suppressed prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthesis — the same pathway targeted by many modern anti-inflammatory drugs.
2️⃣ Antihypertensive Action
In animal studies, E. indica extract demonstrated a blood pressure–lowering effect comparable to Losartan (12.5 mg/kg) in models of L-NAME-induced hypertension (Asian Journal of Traditional Medicine, 2020).
The mechanism appears to involve restoration of nitric oxide (NO) production, improving vascular relaxation and kidney filtration.
3️⃣ Antimicrobial Activity
Laboratory testing has shown that E. indica extracts inhibit bacterial growth against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella choleraesuis.
A 2019 NCBI study concluded that its moderate antibacterial properties make it a useful adjunct in treating skin infections and minor wounds.
4️⃣ Kidney Protection
In rodent studies, E. indica extract (200 mg/kg) significantly improved creatinine, urea, and electrolyte balance, protecting against L-NAME-induced renal damage. The results were comparable to Losartan-treated groups. (Phytomedicine Research, 2022).
5️⃣ Liver Protection and Cholesterol Regulation
Hexane extracts of E. indica reduced total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglycerides while increasing HDL-C in obese test animals.
Researchers at the University of Malaya (2022) concluded that the plant’s flavonoids enhance liver detoxification enzymes, supporting its use for fatty liver disease and dyslipidemia.
🌸 Traditional Herbal Formulas Using Eleusine indica
🌿 For High Blood Pressure
-
500 g fresh E. indica, crushed and mixed with 1 cup of cooled boiled water.
-
Filter, add a small amount of sugar, and drink twice daily (morning and afternoon).
🌿 For High Fever
-
120 g fresh E. indica boiled in 600 ml water until 400 ml remains.
-
Add a pinch of salt and divide into several doses over 12 hours.
🌿 For Jaundice and Liver Heat
-
60 g E. indica + 30 g Gardenia jasminoides (Zhi Zi).
-
Boil and drink 2–3 times daily.
🌿 For Urinary Infections or Red Rashes
-
16 g E. indica + 16 g Imperata cylindrica (cỏ tranh).
-
Decoction taken throughout the day.
🌿 To Cool the Body and Calm the Fetus
-
8 g each: E. indica, Centella asiatica, Eclipta prostrata, Artemisia vulgaris, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Bidens pilosa; plus 2 g ginger, 4 g lemongrass, 4 g dried tangerine peel.
-
Boil together and drink warm.
🌿 For Hair Graying and Fatigue
-
10 g E. indica, 15 g Eucommia ulmoides, 15 g Schefflera heptaphylla, 25 g Smilax glabra, 5 g Glycyrrhiza uralensis, and 5 g Adenosma caeruleum.
-
Simmer and drink before meals.
⚠️ Precautions and Usage Notes
Although E. indica is generally safe when used properly, practitioners recommend caution:
-
Clean thoroughly before use. The plant often grows in contaminated soil and can carry dust or pathogens.
-
Avoid long-term or excessive use. Continuous consumption may affect internal organ balance due to its cooling nature.
-
Consult a doctor. Especially for individuals with chronic illness, kidney disease, or pregnancy.
-
Avoid use in young children unless under professional supervision.
The World Health Organization (WHO, 2023) notes that even beneficial herbal medicines should be used under expert guidance to avoid drug-herb interactions or overuse toxicity.
🌱 Summary
From ancient folk remedies to modern pharmacological research, Eleusine indica — cỏ mần trầu — continues to prove its worth as a versatile medicinal herb.
Its traditional roles in detoxification, fever reduction, and blood regulation are now supported by scientific evidence showing anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and organ-protective properties.
Used with care and understanding, this humble weed from rice fields and roadsides embodies the harmony between traditional wisdom and modern science. 🌿
News in the same category


8 Plants Snakes Hate: Grow These Around Your Home to Keep Them Away Naturally

How to Tell If Your Rice Noodles Are Safe — The Simple Clue That Reveals Hidden Chemicals

The 3 Golden Times to Drink Green Tea — Boosting Both Health and Beauty

The Famous 42-Day “Breuss Juice” Diet from Austria: Origins, Recipe, and What Science Says

The World’s Healthiest Vegetable, Rated #1 by the U.S. CDC — and It’s Abundant in Vietnam

Why Your Neighbor’s Jar of Starfruit in Rock Sugar Might Be a Hidden Health Remedy

‘This Man Can’t Do Nothing Right’: Jonathan Owens’ Steamy On-Field Video with Simone Biles Has the Internet Divided as Fans Rush to Their Defense

Serena Williams Becomes Part Owner of Canada’s First WNBA Team, Toronto Tempo

Meet The Woman Who Single-Handedly Preserved Over 30 Years Of TV History

Ohio Couple Adopts Two Sets Of Twin Siblings Who Were Separated In The Foster Care System

Brooklyn Man Transforms Wasteland Into Community Garden, Distributing Over 10,000 Pounds Of Food

Meet The Founder Of The First Black-woman Owned Electric Vehicle Recharging Station

Meet The Owner Of The First Black Woman-Owned Winery And Tasting Room In Alameda County, California

Why Electric Kettles Are Rare in Western Homes — Despite Their Convenience

Should You Throw Toilet Paper in the Trash or Flush It?

7 Subtle Health Problems That Could Be Early Warning Signs of Cancer

‘Learn How to Drive!’: Connecticut Karen Embarrasses Her Husband and Herself Over Parking Spot That Was Never Blocked

Meet Demi Johnson, the Teen Scientist Helping Restore Oyster Reefs in Mississippi
News Post
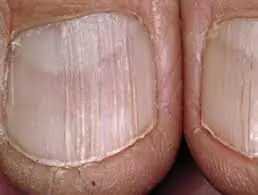
Vertical Nail Ridges? Here’s What Causes Them — and How to Fix It

The Unseen Heroes: A Rescue Dog's Loyalty That Saved My Life
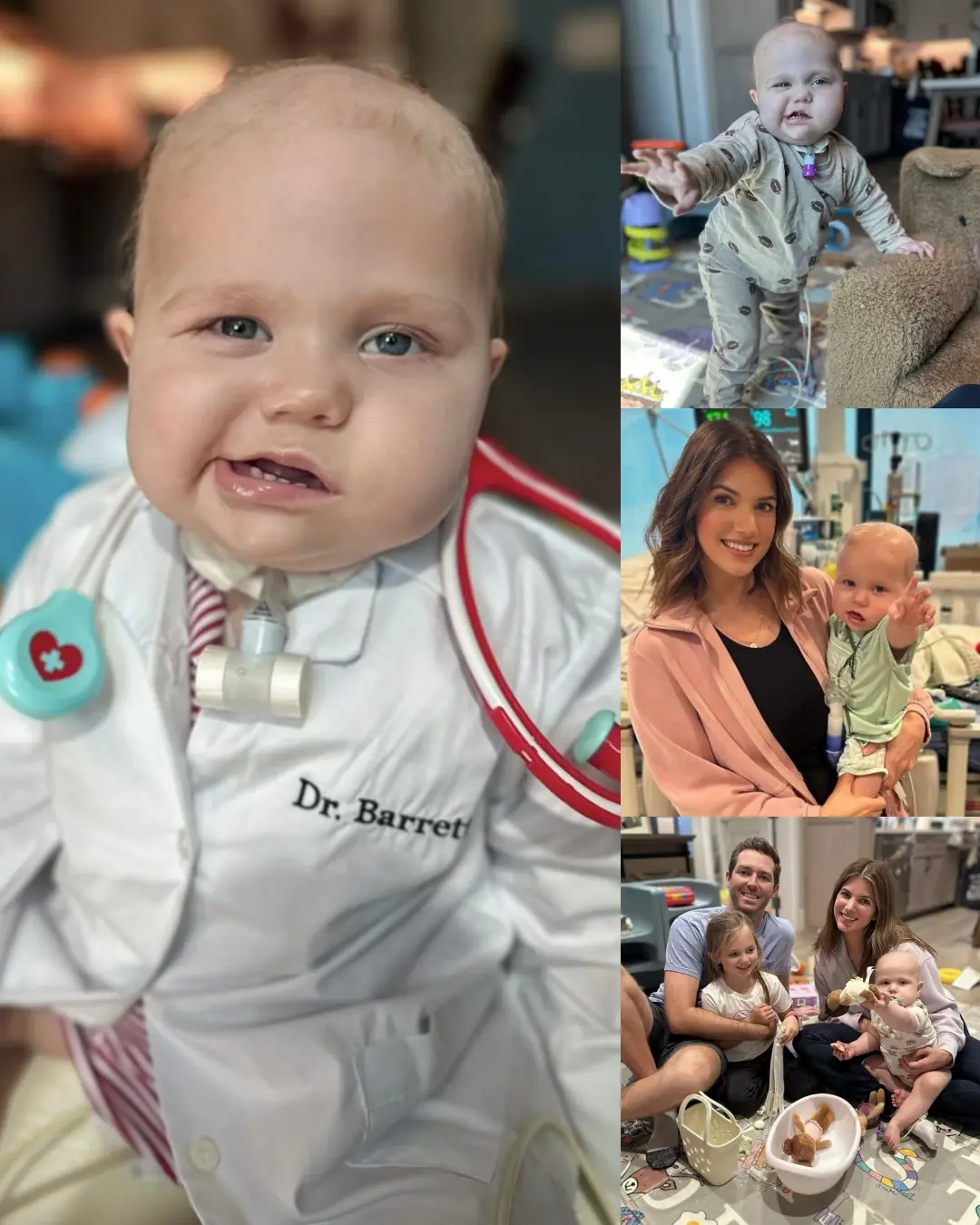

Barrett’s Miracle: A Journey of Faith, Strength, and Prayer
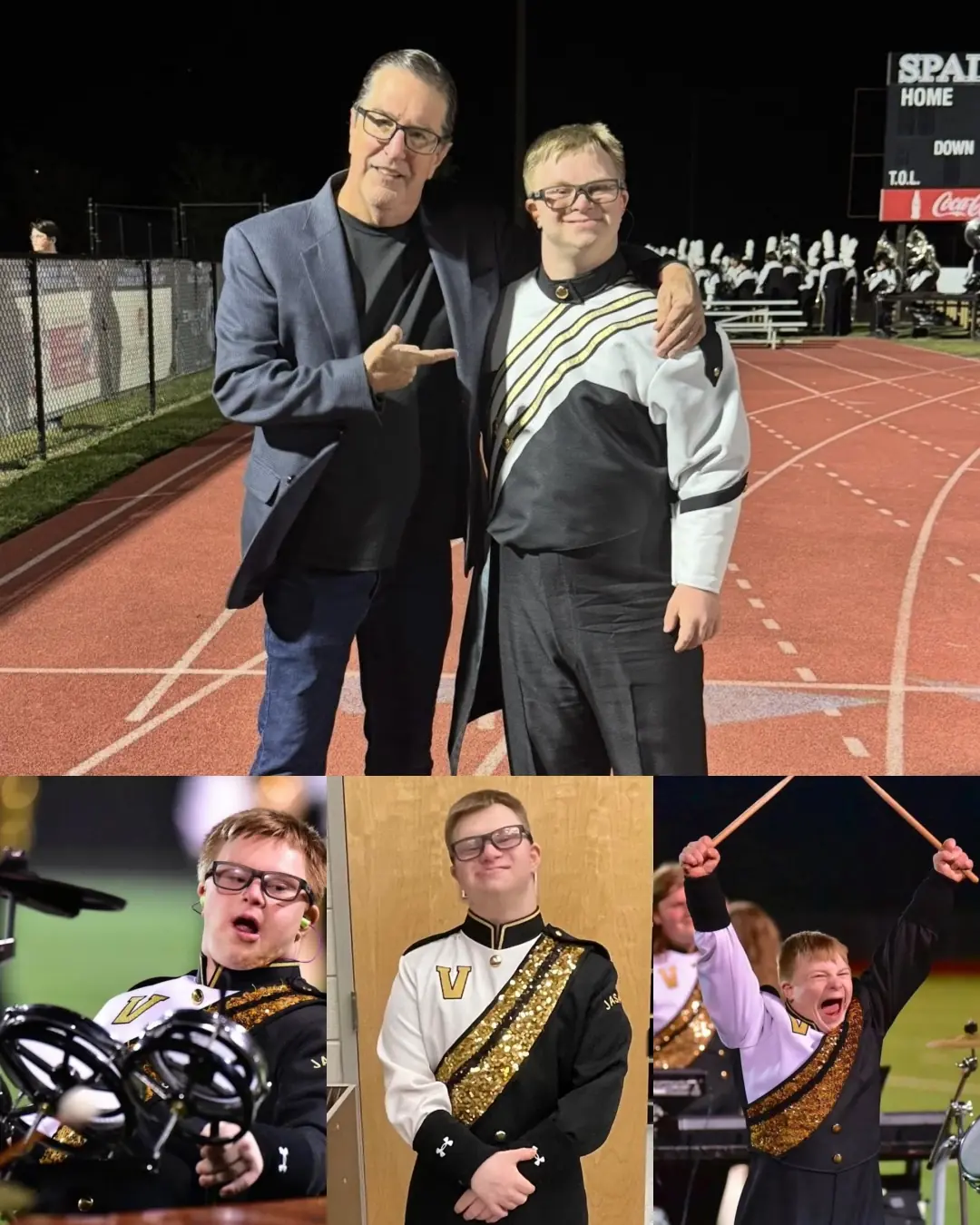

A Farewell to a Friend and His Passion for Music

Top 5 Nutrients to Reduce Swelling in Feet and Legs
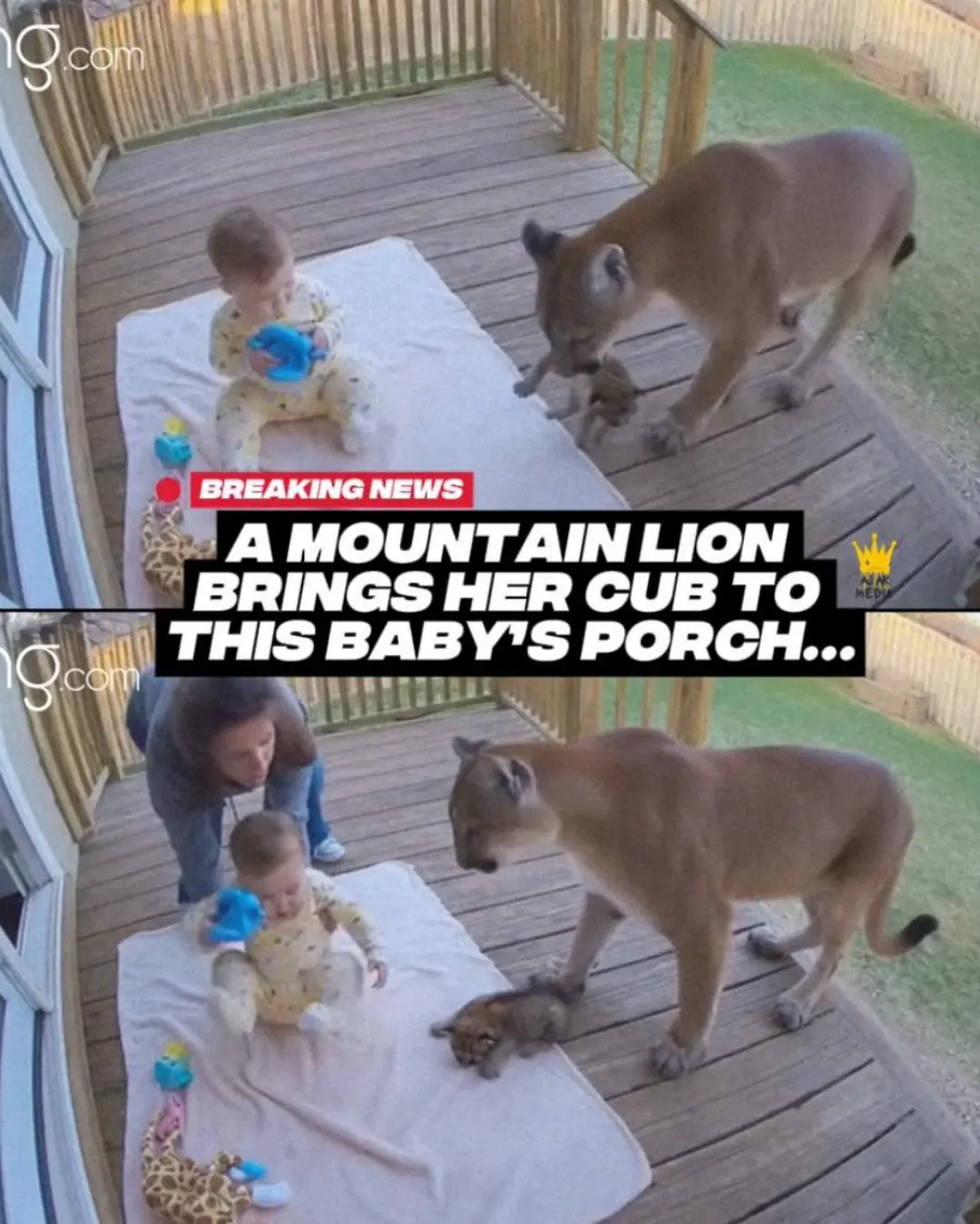

A Rare Encounter: The Moment a Mountain Lion Meets a Baby

Stray Cats Bring a Bitcoin Mine to a Standstill — And Melt Hearts in the Process

If you sleep with socks on, see what happens
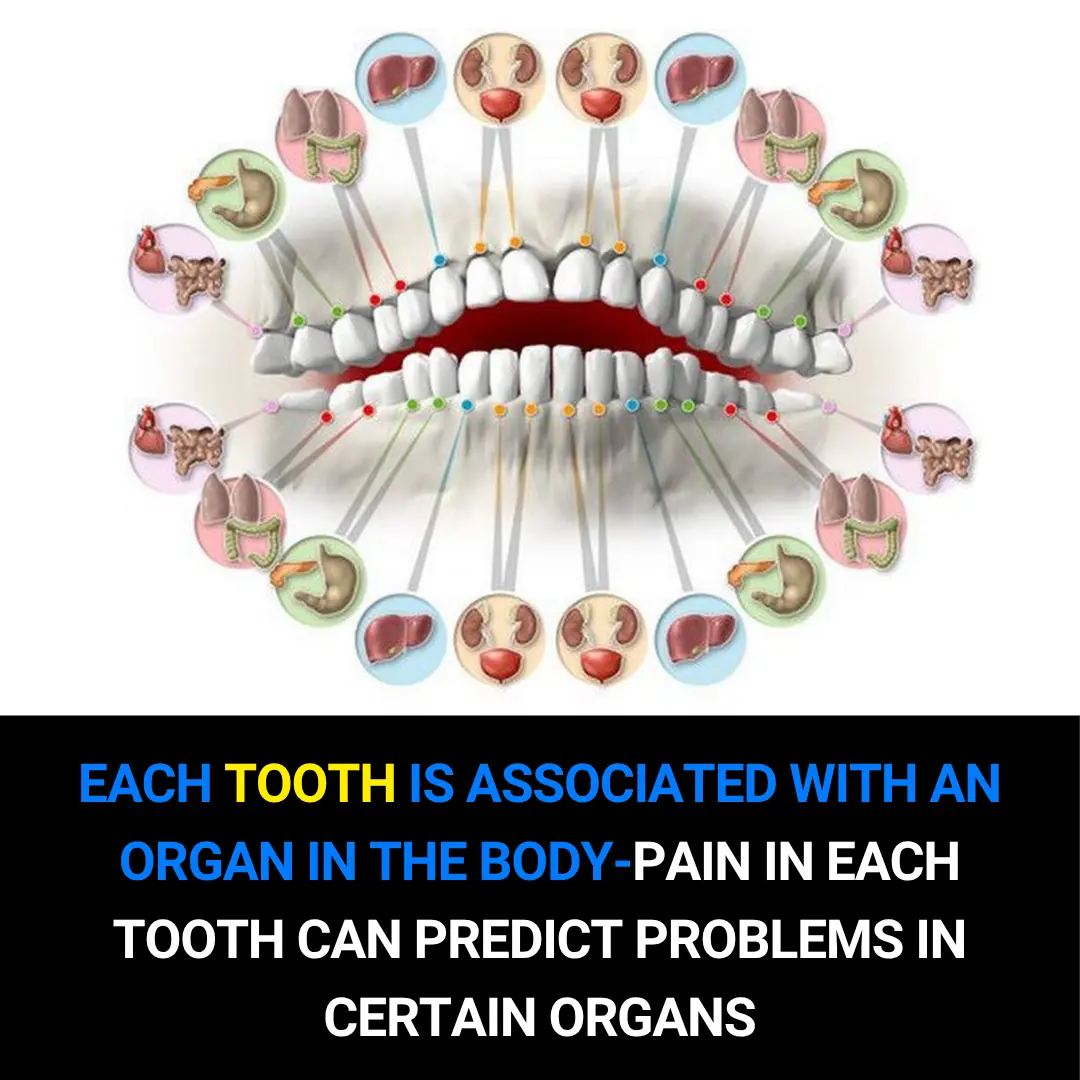
Each Tooth Is Connected to an Organ in the Body – How Tooth Pain May Reveal Hidden Health Problems
Dominika’s Fight for a Childhood Without Pain

Why There's A Growing Trend Of Straight Men Dating Trans Women
Michalinka’s Fight for Life: A Tiny Body, a Giant Spirit
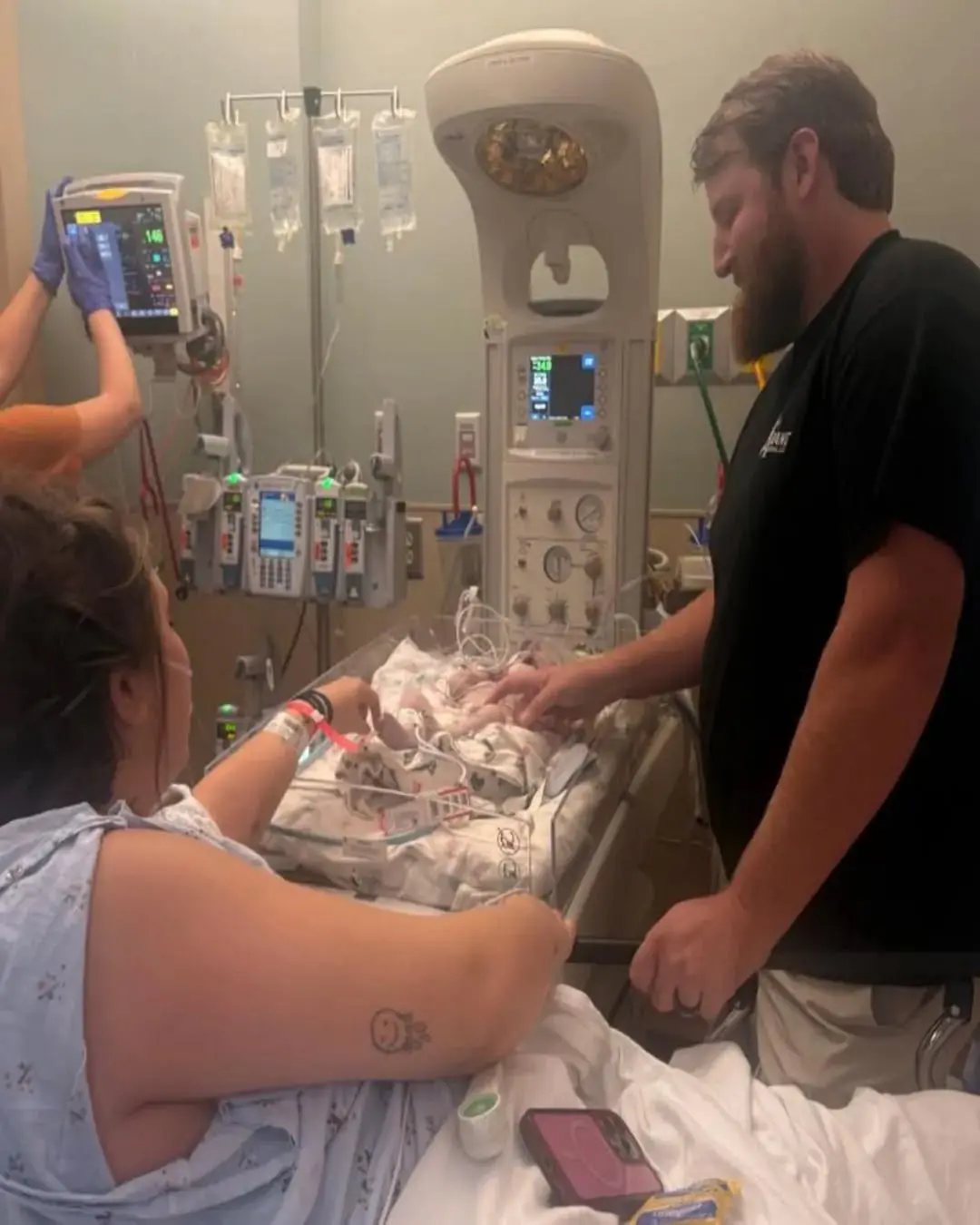
A Miracle in the Making: Baby Harlan’s Fight for Life
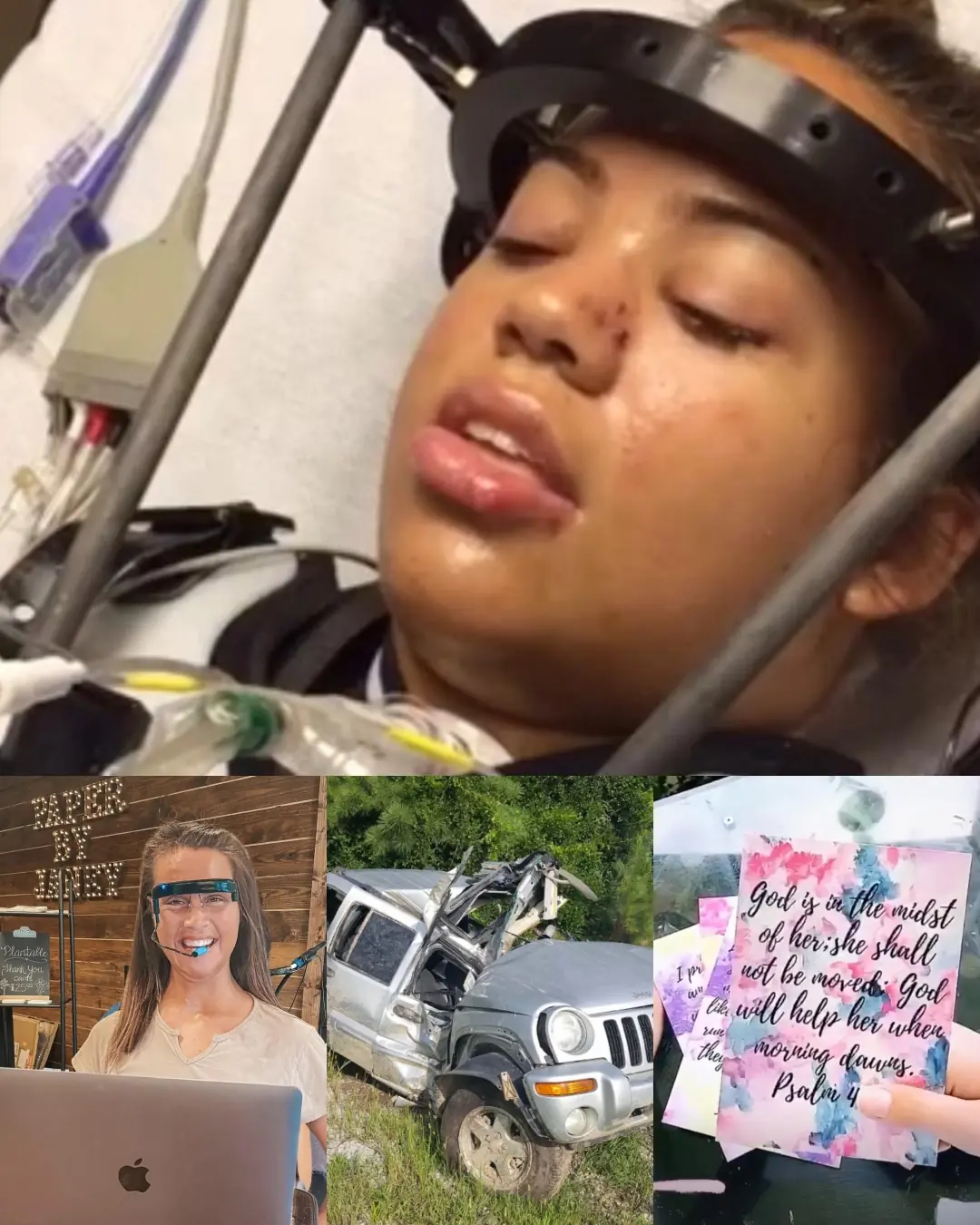
From Tragedy to Triumph: The Unbreakable Spirit of Janey Carter

A Battle of the Wild: The Confrontation Between a Raging Elephant and a Baby Hippo

7 Heart-Healing Foods Your Cardiologist Won’t Tell You About

Never Clean Your Light Switch with Water: Here’s a Trick to Make It Spotless

Bad Habits After Doing Laundry That Can Make Your Whole Family Sick! Many People Overlook This Detail

Don’t Throw Away Your Used Balm Jar – Here’s a Super Useful Way to Reuse It That Every Family Needs
