The top 10 foods people use to keep their blood sugar steadier
Top 10 Foods to Control Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively often requires more than just medication—it involves making the right dietary choices. Here’s a guide to the top 10 foods that help control blood sugar levels, manage insulin sensitivity, and even aid in the reversal of type 2 diabetes while promoting overall well-being. If you want to learn about a simple habit that can further reduce post-meal glucose, read until the end!
Top 10 Foods to Control Diabetes
Number 10: Healthy Fats
Healthy oils and fats play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. Omega-3 fatty acids from sources like wild salmon and sardines, alpha-linolenic acid from flaxseed and walnuts, and monounsaturated fats from olive oil, nuts, and seeds help reduce inflammation. Studies have shown that a Mediterranean-style diet, rich in these healthy fats, can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease by up to 50%. It’s essential to avoid inflammatory vegetable oils such as soybean, sunflower, safflower, and canola oil, which have been linked to increased diabetes risk.
Number 9: Green Leafy Vegetables
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and cruciferous vegetables (such as cabbage and cauliflower) are packed with magnesium, which plays a key role in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. These vegetables also contain antioxidants, such as polyphenols and beta-carotene, which help lower oxidative stress—a contributing factor to many diabetes-related complications. Moringa, also known as drumstick leaves, is another powerful addition due to its magnesium and antioxidant content.
Number 8: Whole Grains
Unlike refined grains like white rice, whole grains such as brown rice and whole-grain bread help regulate blood sugar. Whole grains are rich in fiber, which not only improves insulin sensitivity but also prevents blood sugar spikes. Consuming whole grains has been shown to lower body mass index (BMI), which is directly linked to reduced diabetes risk. Maintaining a healthy body weight through proper nutrition can improve diabetes control by reducing the strain on your body’s insulin production.
Number 7: Coffee and Green Tea
Both green tea and coffee have beneficial effects on blood sugar regulation. Green tea, particularly due to its content of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), promotes insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscles, helping reduce blood sugar levels. Studies show that regular coffee consumption, whether caffeinated or decaffeinated, lowers the risk of type 2 diabetes by promoting weight loss and improving metabolic health, thanks to compounds like chlorogenic acid and quinides.
Number 6: Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate, particularly varieties with high cacao content, is a surprisingly beneficial food for people with diabetes. It helps improve insulin sensitivity thanks to its flavonoid antioxidants, which reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. These compounds also promote glucose breakdown and may improve circulation. Additionally, the magnesium in dark chocolate has a calming effect on the body, further supporting healthy blood sugar levels.
Number 5: Berries and Cherries
Berries like strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries, though sweet, have a minimal effect on blood sugar. They contain anthocyanins—antioxidants that enhance glucose uptake by cells and reduce inflammation. Berries also improve insulin secretion in obese individuals, which helps control blood sugar levels. Cherries, with their anthocyanin content, have been shown to boost insulin production by up to 50%, making them an excellent fruit choice for managing diabetes.
Number 4: Beans
Beans, including pinto, lima, and green beans, are packed with fiber and protein and have a low glycemic index (GI), making them ideal for managing blood sugar. Their high fiber content helps slow the rate of digestion, preventing blood sugar spikes. Beans also contain complex carbohydrates that digest slowly, keeping blood sugar levels stable and reducing hunger between meals. Add them to salads, sandwiches, or stews for a diabetes-friendly meal.
Number 3: Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are rich in fiber and flavonoids, including compounds such as hesperidin and naringin, that help lower blood sugar levels. These fruits also improve the uptake of glucose into muscle cells and fat cells, making them a powerful tool in diabetes control. The high vitamin C content boosts immunity and helps prevent complications associated with diabetes, like infections and heart disease.
Number 2: Nuts and Seeds
Nuts like walnuts and almonds, and seeds such as chia and fennel, are rich in fiber, healthy fats, and magnesium—all essential for managing blood sugar. Nuts and seeds are low in carbs but high in healthy fats, which help regulate blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity. Chia seeds, in particular, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which promote heart health while managing diabetes. Fennel seeds also have hypoglycemic properties, making them effective in lowering blood sugar levels.
Number 1: Avocados
Avocados are a diabetes superfood, rich in healthy monounsaturated fats, fiber, and vitamins. Their low sugar and carbohydrate content, combined with high fiber, slow the digestion of carbs and stabilize blood sugar levels. Additionally, avocados contain a unique compound called avocatin, which helps reduce insulin resistance and improve blood sugar control. Avocados are also excellent for weight management, making them an indispensable part of a diabetes-friendly diet.
Bonus Tip: Apple Cider Vinegar
In addition to including these foods in your diet, one effective strategy to manage post-meal glucose levels is consuming apple cider vinegar before meals. Research has shown that apple cider vinegar can reduce post-meal glucose by up to 34%, making it a simple yet effective addition to your daily routine.
These top 10 foods, when incorporated into a well-balanced diet, can significantly improve blood sugar control, help with weight management, and reduce the risk of diabetes complications. Always remember to consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing diabetes.
News in the same category


The effortless daily trick people use to double their potassium

Aspirin saves lives— but here’s what most people still get wrong about it

7 powerful anti-cancer foods you should start including in your diet

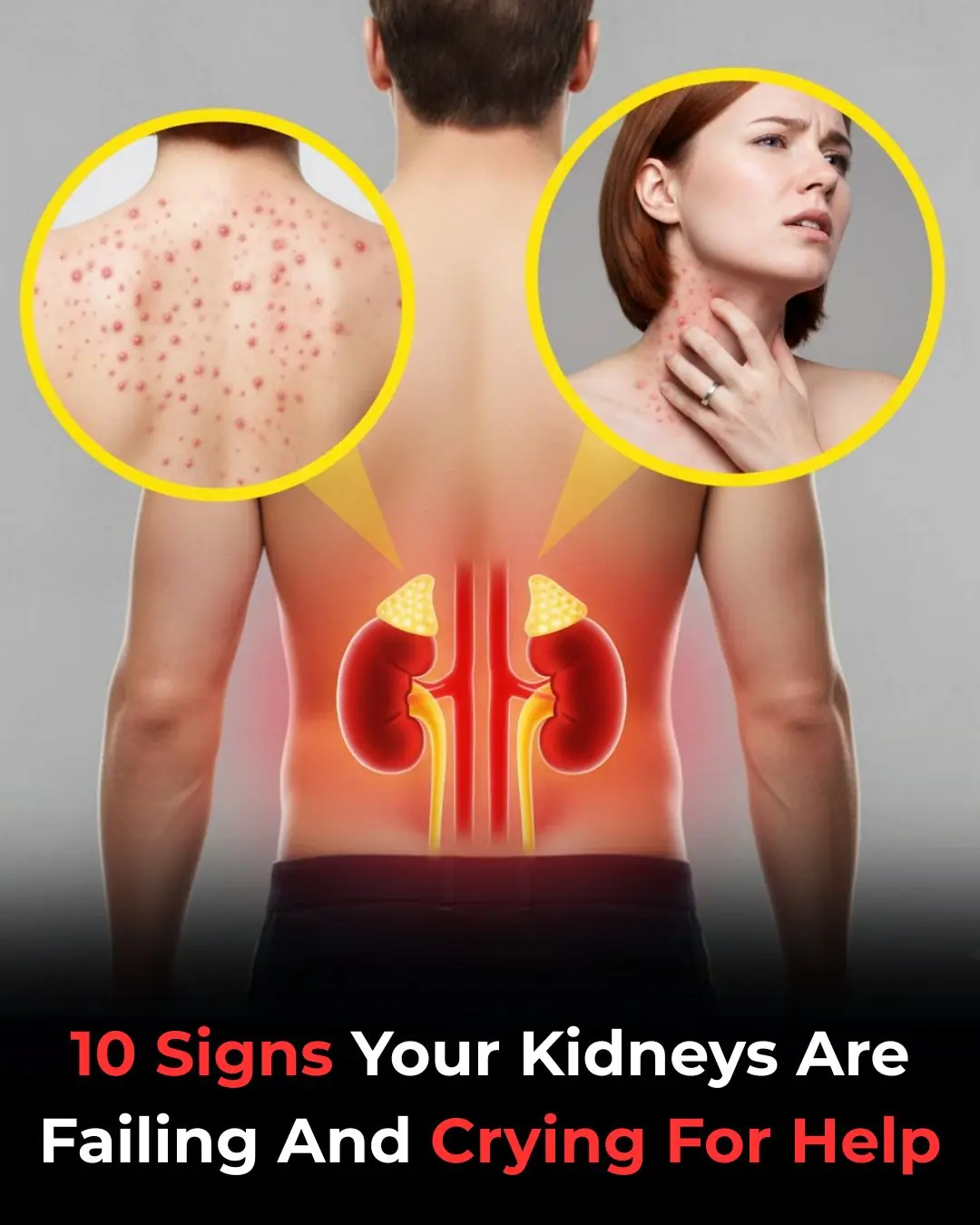
If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, the Body Will Show these 10 Signs

Top 8 Foods for Stronger Legs (Seniors, Eat Daily!)

He thought it was just an allergy, until the diagnosis proved otherwise
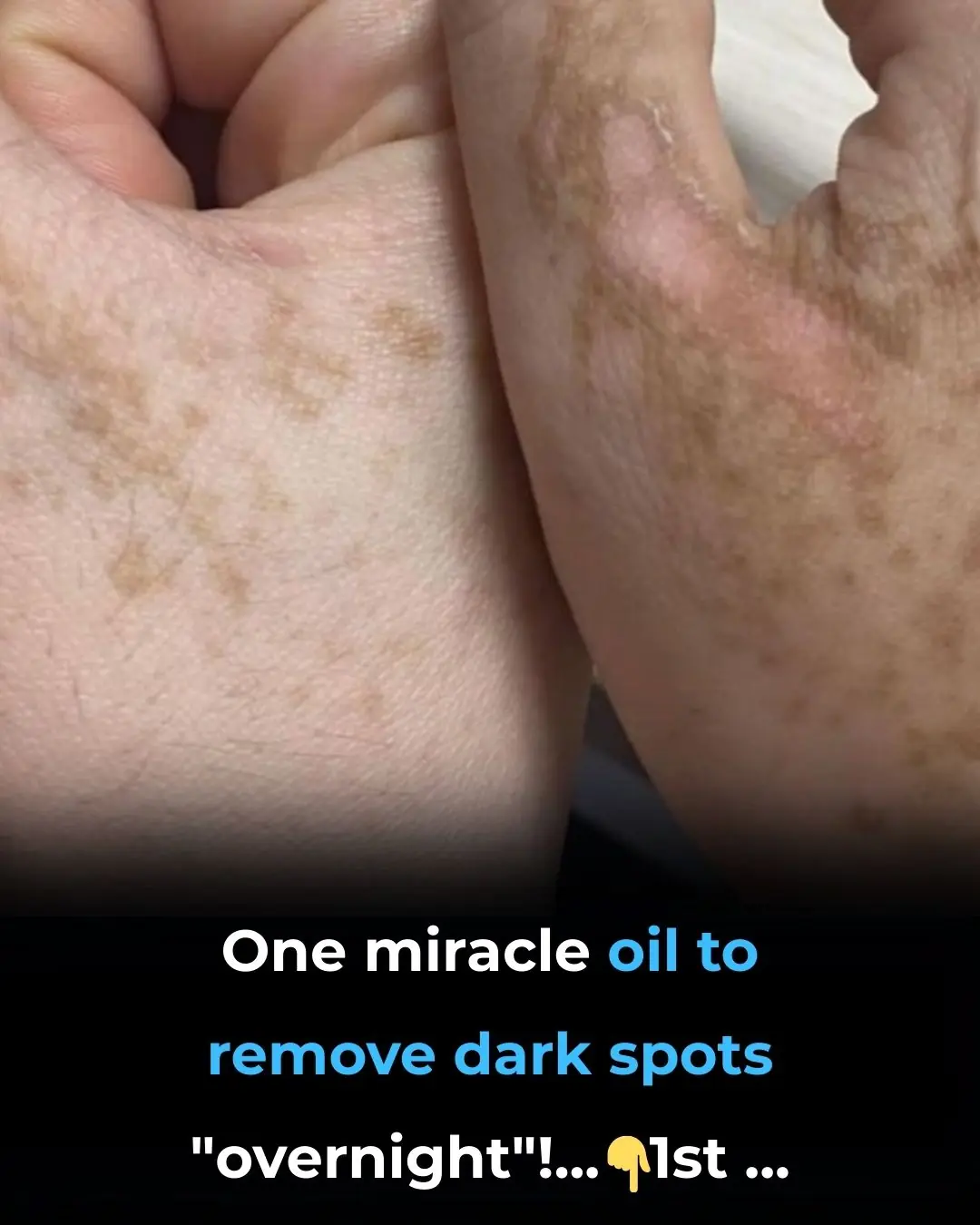
One Miracle Oil to Remove Dark Spots “Overnight”!

The #1 seed flour people over 60 use for steady energy and strength

Stop adding butter — eat these 3 foods instead for faster weight loss

Doctors warn: before a heart attack your body will warn you of these 7 RED flags

Foods to Eat if You Need to Poop – The Best Natural Laxatives to Relieve Constipation
This is what happens to your body when you stop having intimate relationships

Remember The ‘3 Don’ts’ After Meals And ‘4 Don’ts’ Before Bed To Prevent Strokes At Any Age

The Power of Citrus Pith: The Hidden Layer Packed With Health Benefits

Powerful Health Benefits of Pineapple You Should Know

7 Powerful Bay Leaf Benefits for Heart Health and Smoother Blood Flow

Stop Counting Calories — The “100g Protein Rule” That Boosts Energy and Crushes Cravings

10 Supplement Combinations You Should Never Take Together
News Post

Signs of kidney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis!

Eyes as a Window to Heart Health: New Study Reveals How Eye Exams Can Detect Early Cardiovascular Risks

Revolutionary ALS Discovery: Immune System’s Role in Disease Progression Opens New Treatment Possibilities

The Heart as a 'Little Brain': Exploring Its Impact on Emotions, Decision-Making, and Mental Health

Groundbreaking Study Maps Brain Regions Linked to Dyslexia, Uncovering Connections to ADHD and Pain

Harnessing Anger and Passion for Purposeful Action

How Two Children Created the Perfect Birthday With Creativity Instead of Cash

How to Make Your Stainless Steel Pots Shine Like New and Choose Sweet, Juicy Oranges

Just tried this and whoa

Beer on the Window Sill: A Simple Trick With Surprising “Magic” Benefits

How to Make Rose Water at Home Using Fresh Rose Petals

You are doing it all wrong. Here's the right time to eat tomatoes

Mexico City Ends 500 Years of Bullfighting in Landmark Animal-Welfare Vote

Try This Method: Clean Your Floors Just Once a Week—They Stay Shiny, Fresh, and Dust-Free

10 Foods That Help Beat Fatty Liver: Nutrition Experts Recommend Eating Them Daily

The effortless daily trick people use to double their potassium
Revolutionary Light-Based Cancer Treatment Offers Precision and Fewer Side Effects

The Second Life of Lions — Finding Freedom After Rescue.

Aspirin saves lives— but here’s what most people still get wrong about it
