
The ‘World’s D3adliest Food’ K!lls 200 People Annually — Yet 500 Million Still Can’t Resist It
Every year, over 200 people lose their lives to what experts call the “world’s d:eadliest food” — yet nearly 500 million people across the globe consume it regularly without incident. This paradox lies in a humble yet vital crop: cassava, a plant that has sustained communities for centuries but harbors a hidden danger if mishandled.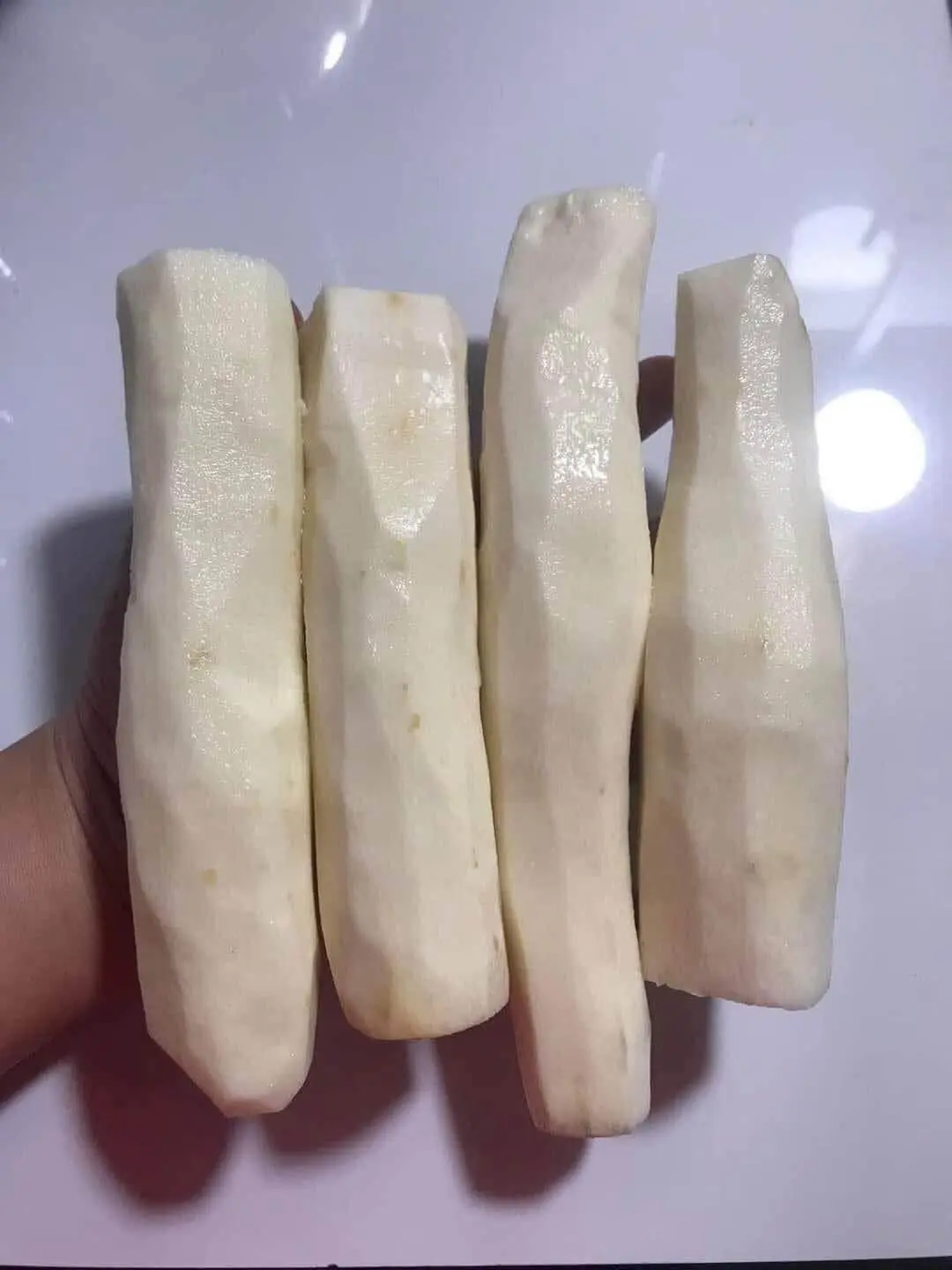
Cassava is both a plant and a major food source, cultivated on a mad:iessive scale, with hundreds of millions of tonnes produced annually. Native to South America, it has spread worldwide, becoming a d:ietary cornerstone in many tropical and subtropical regions. However, its danger lies in the fact that parts of the plant — including the stems, peel, and leaves — contain natural toxins that can generate hydrogen cyanide, a potentially lethal compound. For this reason, eating raw cassava is never safe.
The World Health Organization (WHO) explains: “Cassava tubers contain a varying quantity of cyanogenic glucosides which protect the root against attack by animals and insects. Appropriate processing before consumption can reduce cyanogenic glucoside content of cassava. When high cyanogenic cassava is not processed correctly, high d:ietary cyanide exposure occurs.” Improper preparation can cause acute cyanide poisoning and lead to serious illnesses such as konzo — an irreversible condition characterized by sudden paralysis of the legs.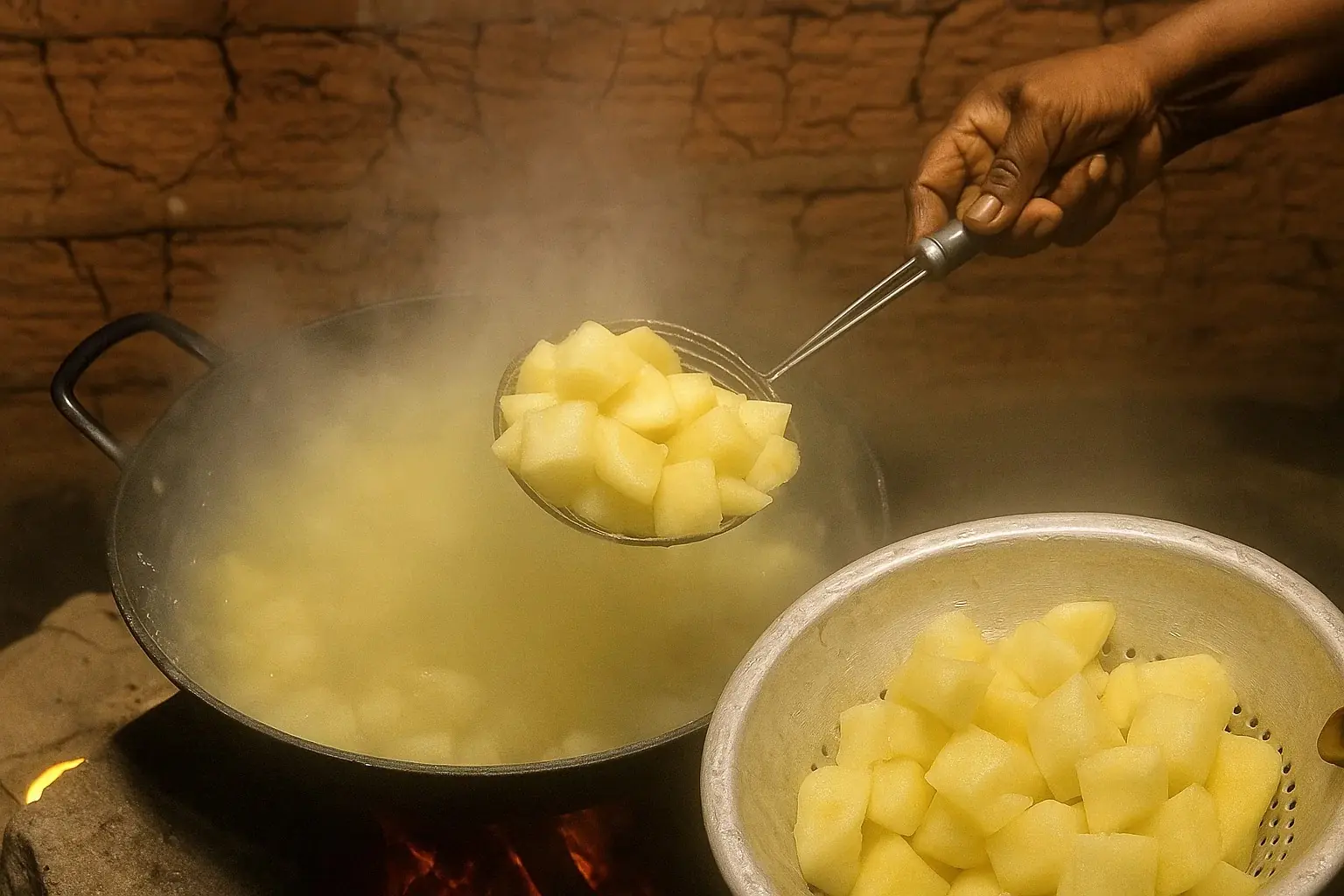
WHO further warns that “This often happens during times of famine and war… Konzo is a disease of extreme poverty. Konzo mostly occurs in epidemics, but sporadic cases are also reported.” Such outbreaks are most common in regions where bitter cassava varieties are consumed alongside a low-protein d:iet, which makes the body more vulnerable to the effects of cyanide.
Despite these dangers, cassava remains a d:ietary lifeline for millions, especially in countries where it is more affordable and accessible than other staple foods. The key to its safe consumption lies in proper preparation — methods like peeling, soaking for up to 24 hours, and thorough cooking can drastically reduce toxin levels. In Venezuela, for example, El País reported that some residents fell ill or d:ied after consuming poorly prepared cassava during severe food shortages, when desperation led people to skip crucial safety steps.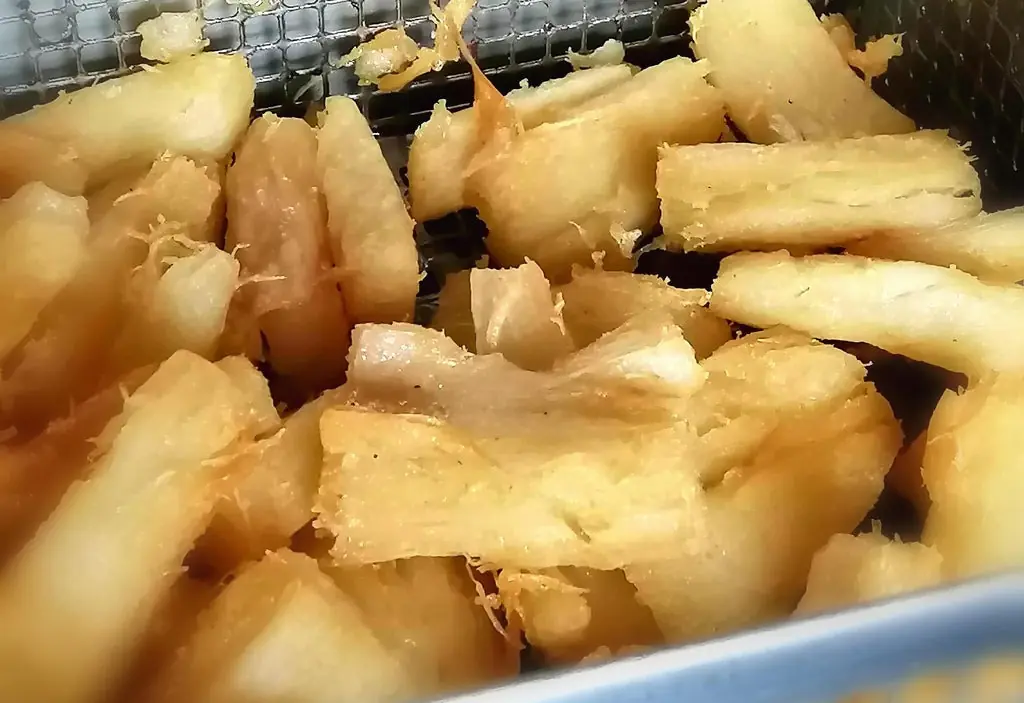
Cassava’s story is one of resilience and risk — a food that has sustained generations through scarcity and hardship, yet demands respect and caution in its preparation. For many, it is not just a meal, but a lifeline — one that must be handled with care to ensure it nourishes rather than harms.
News in the same category


12 Health Hacks Doctors Rarely Share: Secrets for Optimal Health and Well-being

A Parade Moment That Became Global Joy

Nick Vujicic: Living Proof That the Human Spirit Knows No Limits

You’re Made of Stardust – Literally! 🌌🚀

Sea Levels Are Rising Faster Than At Any Time In 4,000 Years 🌍

Your Dog Might Actually Love You More Than Food
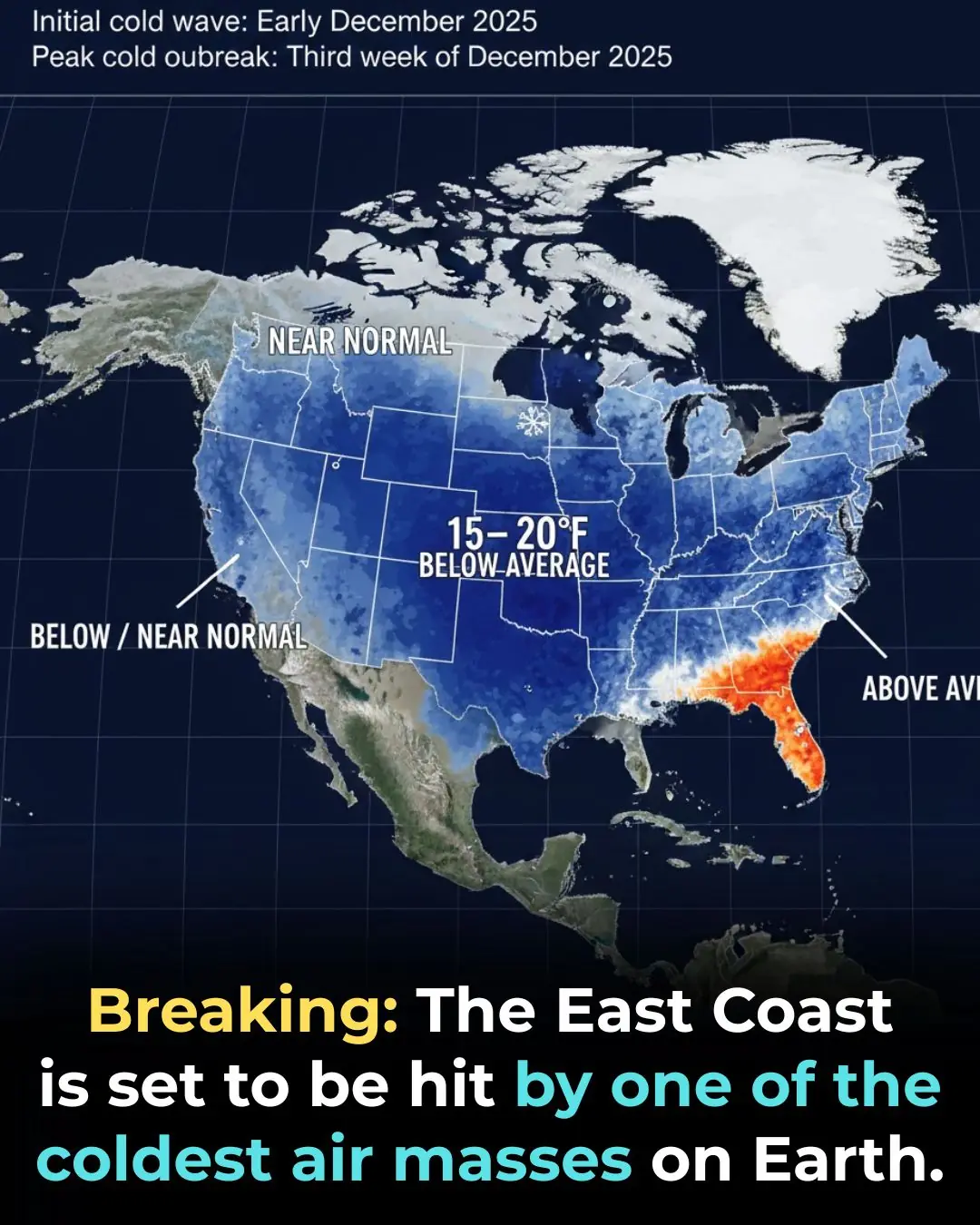
Deep Freeze Set to Slam the Eastern U.S. This December

Nike Co-Founder Phil Knight Makes Historic $2 Billion Donation to Cancer Research

Dutch Engineers Tackle the Pacific’s Plastic Crisis with 600-Meter Ocean Vacuum
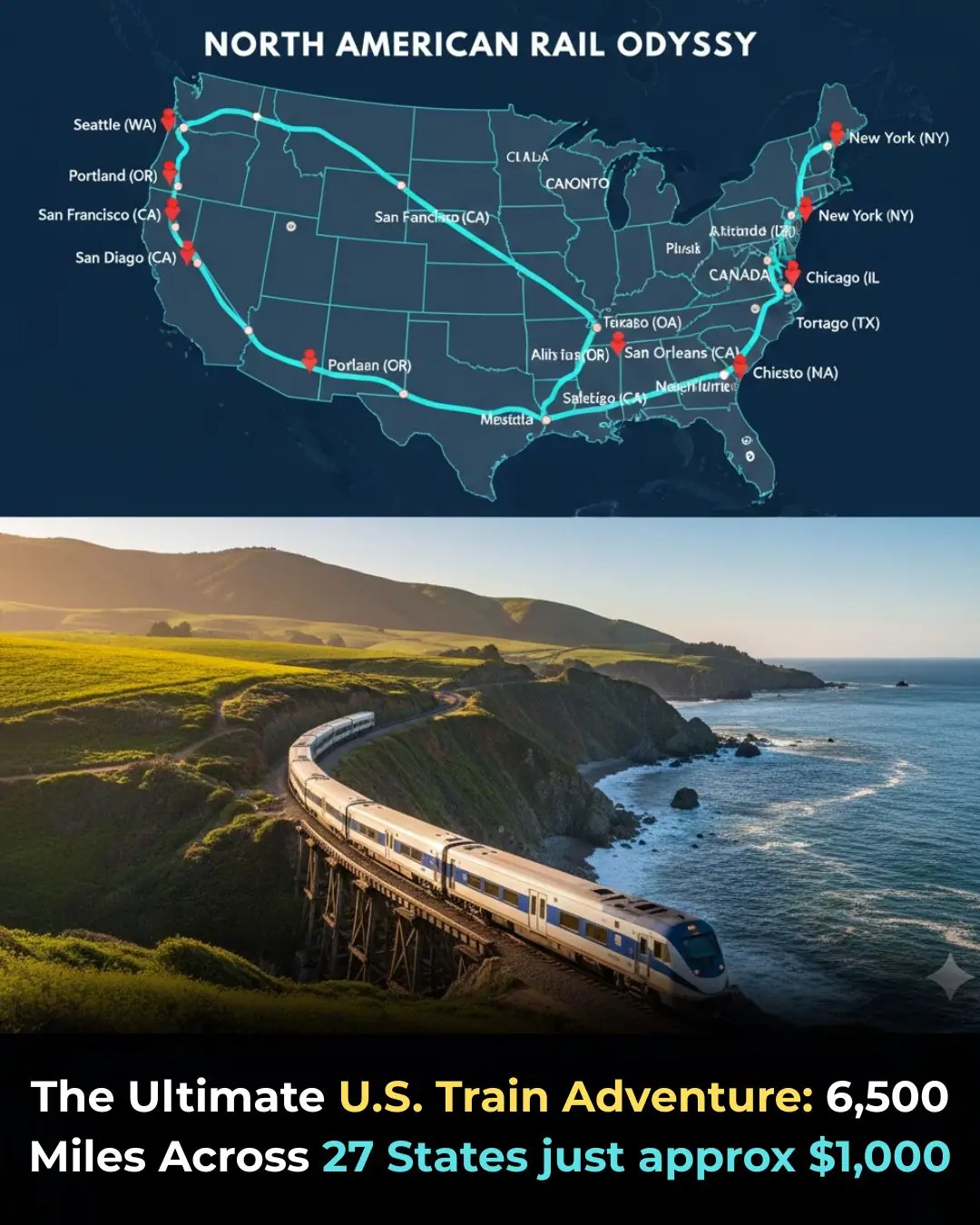
How to Take a Loop of the Entire U.S. by Train

The Quiet Rise of Everyday Health-Tracking Technology
The Hidden Toll of People-Pleasing: How Emotional Suppression Can Trigger Autoimmune Disorders

The Pudu: The World’s Tiniest Deer and Its Role in South America's Forest Ecosystems

Deep Water Cycle: Scientists Discover Hidden Ocean Beneath Earth's Surface

Mexico City’s Sweeping Bullfighting Ban Marks Major Shift in Cultural and Animal-Welfare Policy

Los Angeles County Erases $180 Million in Medical Debt for 39,000 Residents

The 2025 Atlantic Hurricane Season Intensifies: A Heightened Risk for Major Storms

Europe Faces Unprecedented Heatwave: Rising Temperatures Strain People, Infrastructure, and Agriculture

Revolutionary Light-Based Cancer Treatment Offers New Hope with High Success Rate
News Post

CCF Tea to Burn Belly Fat

DIY Lip Balm with Vaseline and Beetroot: A Natural, Moisturizing Solution for Soft, Pink Lips

Coffee Gel For Eye Wrinkles

Coffee For Instant Skin Brightening

Japanese 4 Steps Glow Secret

30 minutes treatment for dark lips

How to Make a DIY Aloe Vera Night Cream for Glowing Skin

Rice Water Toner To Get Skin That Shines Like Diamond

Salon like Keratin Treatment at Home

Experts reveal the top 7 Shampoos to tackle hair loss effectively

10 Surprising Beauty Hacks You Never Thought You Could Do With Baby Powder

DIY Night Serum For Radiant Skin

Top 8 Foods to Clean and Restore Your Liver Naturally

The Ancient Secret Seed That Revolutionized Wellness: Unlocking the Power of Hibiscus and Cloves

Garlic Remedy for Removing Moles and Skin Tags Naturally: What Works and What to Know

Fibromyalgia: The Hidden Energy Crisis Behind Your Pain, Fatigue, and Sleepless Nights

The Hidden Oil That Sparks Her Desire and Rekindles Your Marriage

Unlock the Ancient Secret of Peach Tree Resin: 15 Life-Changing Benefits You’ll Wish You Knew Sooner

Aloe Vera & Cinnamon: The Traditional Duo That Naturally Supports Your Health, Vitality, and Vision
