What Is The Normal Blood Pressure For Each Age
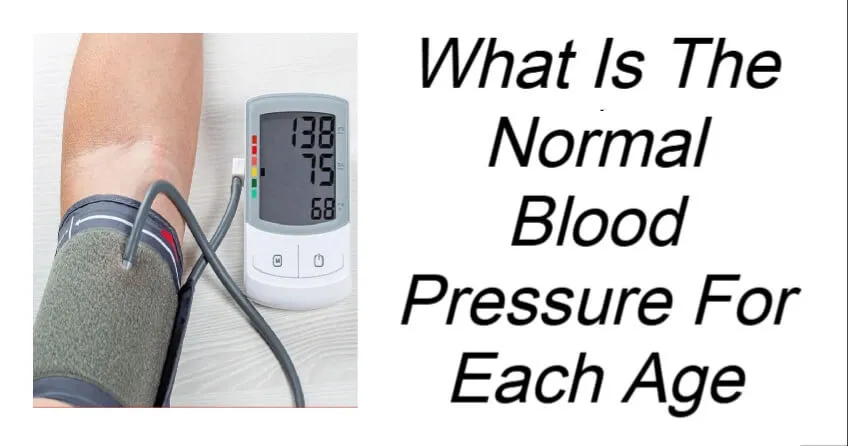
What Is Considered Normal Blood Pressure at Each Age?
Blood pressure is more than just a routine measurement during a doctor’s visit — it provides a valuable snapshot of how well your heart and blood vessels are functioning. As we grow older, understanding our blood pressure numbers becomes increasingly important because they can signal early warning signs of potential health concerns.
Knowing how blood pressure changes with age, and what is considered healthy for your stage of life, can help you make informed decisions that protect your heart and overall health for years to come.
Why Blood Pressure Matters
Blood pressure refers to the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps. These pressure levels offer a direct insight into your cardiovascular system’s health. Abnormal levels — whether too high or too low — can indicate underlying issues long before noticeable symptoms appear.
The often-cited “ideal” blood pressure is approximately 120/80 mm Hg, but what qualifies as normal can vary based on age, lifestyle, genetics, and other health conditions.
Below is a general guideline:
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic (Top) mm Hg | Diastolic (Bottom) mm Hg |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Less than 90 | Less than 60 |
| Optimal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 |
| Normal | 120–129 | 80–84 |
| Normal to High | 130–139 | 85–89 |
| High (Hypertension) | Greater than 140 | Greater than 90 |
A reading around 120/80 mm Hg is commonly viewed as typical for most healthy adults.
Average Blood Pressure for Children and Adolescents
Children's blood pressure varies more due to growth and development:
| Age Group | Systolic mm Hg | Diastolic mm Hg |
|---|---|---|
| Newborn to 1 Month | 60–90 | 20–60 |
| Infants | 87–105 | 53–66 |
| Toddlers | 95–105 | 53–66 |
| Preschoolers | 95–110 | 56–70 |
| School-Age Children | 97–112 | 57–71 |
| Adolescents | 112–128 | 66–80 |
Average Blood Pressure in Adults by Age and Gender
| Age Group | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| 18–39 years | 110/68 mm Hg | 119/70 mm Hg |
| 40–59 years | 122/74 mm Hg | 124/77 mm Hg |
| 60+ years | 139/68 mm Hg | 133/69 mm Hg |
These values show how blood pressure often trends upward with age due to natural changes in the cardiovascular system.
How Aging Affects Blood Pressure
As you grow older, the likelihood of developing high blood pressure (hypertension) increases. Common contributing factors include:
-
Stiffened arteries: Blood vessels naturally lose elasticity with age, making it harder for blood to flow efficiently.
-
Plaque buildup: Fatty deposits gradually accumulate in arteries, narrowing them and increasing pressure on vessel walls.
-
Changes in kidney and hormone function: The body becomes less efficient at balancing salt and fluid, affecting blood pressure control.
These age-related shifts explain why hypertension is one of the leading causes of heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, and vascular dementia.
How to Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure at Any Age
No matter your age, adopting supportive lifestyle habits can help maintain — and even lower — your blood pressure.
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight makes your heart work harder. Even small weight loss can yield measurable improvements in blood pressure.
2. Follow a Heart-Healthy Diet
Prioritize:
-
Fresh vegetables and fruits
-
Whole grains
-
Lean meats and fish
-
Low-fat dairy
Avoid or limit:
-
Excessive salt
-
Processed foods
-
Saturated and trans fats
-
High-sugar snacks
The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is one of the most researched and recommended eating patterns for blood pressure management.
3. Stay Physically Active
Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Movement keeps the heart strong and vessels flexible.
4. Stop Smoking
Tobacco damages blood vessel walls and raises blood pressure. Quitting leads to almost immediate cardiovascular benefits.
5. Drink Alcohol in Moderation
Regular heavy drinking raises blood pressure. Guidelines suggest:
-
Women: Up to 1 drink per day
-
Men: Up to 2 drinks per day
Final Thoughts
While rising blood pressure levels may be more common with age, they don’t have to be inevitable. By monitoring your numbers, making healthy lifestyle adjustments, and seeking guidance from a healthcare professional when needed, you can support your heart and live a stronger, healthier life.
If you haven’t checked your blood pressure lately, consider this a sign to do it today — small steps can make a powerful difference over time.
News in the same category


This Brewery Is The Only Black-Owned Brewery In New York Brewing Its Beer On-Site

Joseph Deng Makes History as First Player From South Sudan to Sign a Professional MLB Contract
Meet The Specks, the Black Brother-Sister Duo Who Invented the Potato Chip

Meet Mr. & Mrs. Grady, Owners Of North Carolina’s Only Black-Owned Whole Hog Barbecue Smokehouse

Negro History Week: Here’s the True Story Behind Black History Month

10 Natural Foods That Outshine Supplements, According to Nutrition Experts

Why You Should Never Pour Boiling Water Down the Kitchen Sink

Button Mushrooms: A Humble Market Treasure Packed With 17 Times More Potassium Than Bananas

6 Foods That Never Expire If Properly Stored

Coronation Street follow-up: Will Driscoll in new grooming storyline as spoilers confirms more details of his secret

KRISTI NOEM RIPS ZACH BRYAN's NEW SONG CRITICIZING ICE ... He Responds to Backlash

‘Poop smears on the seat’: Delta reportedly apologizes after passenger endures cross-country flight next to ‘human biohazard’

Turning Point USA Announces Rival Super Bowl Halftime Show 'Anything in English' Option

Strictly star Ellie Goldstein addresses exit as she announces she and Vito will keep training together ‘until the final’

GBBO star Prue Leith reveals she’s tried weight-loss jabs: ‘I didn’t shed an ounce!’
🦶 Your Feet Are a "Blood Sugar Meter": Beware of Diabetes If You Frequently Experience These 5 Strange Symptoms

‘New Couple Alert’ on Hoda Kotb’s Photo With Kevin Costner at Super Bowl
Blurred Vision in One Eye and a Headache
News Post

‘They Described a Man I Never Met’: Comedian Roy Wood Jr. Tells Shannon Sharpe He Learned To Love Watching How His Absent Dad Treated Another Family

This Brewery Is The Only Black-Owned Brewery In New York Brewing Its Beer On-Site

Joseph Deng Makes History as First Player From South Sudan to Sign a Professional MLB Contract

Meet The Specks, the Black Brother-Sister Duo Who Invented the Potato Chip

Meet Mr. & Mrs. Grady, Owners Of North Carolina’s Only Black-Owned Whole Hog Barbecue Smokehouse

Negro History Week: Here’s the True Story Behind Black History Month

Buckingham Palace statement in full as King Charles removes Prince Andrew’s title

Has the Bermuda Triangle Mystery Finally Been Solved

Put the entire roll of toilet paper in the refrigerator
4 Types of Shoulder Pain That May Signal Dangerous Cancer — Don’t Mistake Them for Simple Joint Problems
6 Body Parts That Turn Black May Signal Cancer — Don’t Ignore Them

Serrated Leaf Motherwort: A Precious Herb with Many Benefits

Banana flowers and their little-known uses

Eat these 5 fruits to avoid magnesium deficiency, keep your heart healthy and your bones strong.

The Amazing Power of Caesalpinia pulcherrima (Peacock Flower)
White Bumps or Spots on Lips: Causes and Effective Treatments

Corn Silk: 30 Health Benefits and How to Use It

Turmeric Dosage: How Much You Actually Need for Arthritis, Cancer, and Other Diseases

Better Than Medicine? The Shocking Truth About Dates & Blood Sugar!
