
What To Know and Do About Pain Under Your Left Rib Cage
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/health-GettyImages-1337891278-b9484169749b482e9e802a0cdb5536b3.jpg)
Pain under the left rib cage is not always a sign of a serious medical condition, but it should not be ignored—especially if it is persistent, severe, or recurring. This area of the body contains several important organs, and discomfort may stem from something as simple as a muscle strain or gas, or from more serious conditions such as pancreatitis, kidney stones, or heart-related problems. Seeking medical advice is recommended if the pain does not improve or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
What Organs Are Located Under the Left Rib Cage?
Understanding which organs lie beneath the left rib cage—also known as the left hypochondriac region—can help narrow down potential causes of pain.
Key structures in this area include:
-
Spleen: Located just below the left rib cage, the spleen filters blood and plays an essential role in immune function and infection control.
-
Stomach: The upper portion of this muscular digestive organ sits under the left ribs and helps break down food.
-
Pancreas: Positioned behind the stomach, the pancreas produces digestive enzymes and hormones such as insulin that regulate blood sugar.
-
Left kidney: Found toward the back of the abdomen, the left kidney filters waste from the blood, regulates fluid balance, and helps control blood pressure.
-
Colon (large intestine): The descending colon runs down the left side of the abdomen and is responsible for absorbing water and moving waste toward the rectum.
In addition to these organs, the area also contains muscles, connective tissues, nerves, and blood vessels that support and protect internal structures.
Common Causes of Pain Under the Left Rib Cage
Pain beneath the left rib cage can range from mild and temporary to severe and life-threatening. Possible causes include digestive, musculoskeletal, and systemic conditions.
Digestive Conditions
Digestive issues are among the most frequent causes of pain in this area. Both short-term and chronic digestive disorders can lead to discomfort, including:
-
Gas: Swallowing air, eating quickly, drinking carbonated beverages, or consuming gas-producing foods (such as beans or cabbage) can lead to bloating, cramping, belching, and sharp pain.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Acid reflux can cause burning chest pain that may radiate to the left rib cage.
-
Constipation: Infrequent bowel movements can cause stool buildup in the colon, leading to cramping or pressure on the left side.
-
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): This functional digestive disorder causes abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, or a mix of both.
-
Ulcerative colitis (UC): A form of inflammatory bowel disease that may cause upper-left abdominal pain when inflammation affects the descending colon.
-
Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach lining can cause pain under the left ribs, along with nausea, bloating, indigestion, and early fullness.
-
Peptic ulcers: Open sores in the stomach or duodenum may cause a burning or gnawing pain beneath the rib cage that comes and goes.
Costochondritis
Costochondritis is inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone. Pain from this condition is often sharp and localized but may spread to the back or abdomen.
Symptoms typically worsen with movement, deep breathing, coughing, or sneezing. Pressing on the affected ribs may reproduce the pain.
Spleen Enlargement or Rupture
The spleen is protected by the left rib cage, but when it becomes enlarged (splenomegaly), it can cause a dull or aching pain in the upper left abdomen. Some people also feel full after eating small meals or experience pain that radiates to the left shoulder.
A ruptured spleen—often due to trauma—is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas, most commonly caused by gallstones or heavy alcohol use.
Acute pancreatitis usually causes severe upper abdominal pain that radiates to the back and may worsen after eating. Additional symptoms include fever, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, and abdominal tenderness.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that form when substances like calcium or uric acid become concentrated in urine. Dehydration and dietary factors increase risk.
Pain from kidney stones is often sudden and intense, starting in the back or side and radiating toward the lower abdomen or groin. The pain typically resolves once the stone passes.
Musculoskeletal Causes
Pain under the left rib cage can also result from issues affecting bones, muscles, or connective tissue, such as:
-
Slipping rib syndrome: A rare condition in which weakened ligaments allow ribs to move excessively, causing pain.
-
Rib fractures: Broken ribs cause pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing and may damage nearby organs.
-
Intercostal muscle strain: Overstretching or overusing the muscles between the ribs can lead to soreness, tenderness, and sharp pain.
Other Potential Causes
Less common but serious causes include:
-
Heart attack: May cause pressure-like chest pain that radiates to the abdomen, arm, jaw, or back.
-
Pleurisy: Inflammation of the lung lining that causes sharp or burning pain with breathing.
-
Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs that may cause chest pain, cough, fever, and shortness of breath—especially when the lower left lung is involved.
-
Aortic aneurysm: A dangerous bulge in the aorta that can cause sudden, severe chest or back pain.
-
Pneumothorax (collapsed lung): Air leakage around the lung causes sharp chest pain, breathing difficulty, and fatigue.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Some causes of left rib pain, such as gas or mild muscle strain, may resolve on their own. However, you should see a healthcare provider if the pain:
-
Persists for more than a few days
-
Worsens over time
-
Interferes with daily activities
-
Occurs with fever or breathing difficulty
Call emergency services immediately if the pain is accompanied by symptoms such as crushing chest pressure, pain spreading to the arm or jaw, dizziness, nausea, or shortness of breath, as these may indicate a heart attack.
How Is the Cause Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider will review your medical history, perform a physical exam, and ask detailed questions about your symptoms. They may listen to your heart and lungs, examine your abdomen, and check for tenderness or swelling.
Additional Tests
Depending on findings, diagnostic tests may include:
-
Blood tests to detect infection, inflammation, or heart damage
-
Imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRI
-
Endoscopy to examine the esophagus and stomach
-
Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy to evaluate the large intestine
-
Electrocardiogram (EKG) to assess heart function
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve home care, medication, procedures, or surgery.
Home Remedies
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers
-
Rest and activity modification
-
Gentle stretching
-
Ice or heat therapy
-
Dietary adjustments for digestive causes
Medical Treatments
-
Prescription medications (NSAIDs, acid reducers, immunosuppressants)
-
Shockwave therapy for kidney stones
-
Surgical intervention for severe conditions such as aneurysms or organ rupture
Quick Summary
Pain under the left rib cage can result from many conditions, including digestive disorders, musculoskeletal injuries, kidney stones, or problems involving the spleen, lungs, or heart. While some causes are mild, others require urgent care.
If you experience ongoing, severe, or unexplained pain, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
News in the same category

Advancing Clinical Excellence in IgA Nephropathy
What To Know About Chronic Kidney Failure

Could Your Magnesium Supplement Be Causing Side Effects?
Why Thick Toenails Happen, And How To Get Rid of Them

The military sleep method that can help you fall asleep in just two minutes

Surprising Health Benefits of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea)
Rising Deaths From Stomach Cancer: Doctors Warn — See These 4 Abdominal Signs and Seek Medical Care Immediately

Australia is replacing animal testing with smarter, humane science

Cracked Egg in Your Carton? Here’s When It's Safe to Eat—And When to Toss

Scientists Restore Natural Hearing Using Stem Cells in a Historic Medical Breakthrough
Morning Swelling in Kidney Disease: What Your Body Is Trying to Tell You
Cancer May Show These 2 Warning Signs at Night — Everyone Should Be Aware

Coffee Consumption May Slow Biological Aging in Severe Mental Illness

A French-made artificial heart brings new life to patients once dependent on donor transplants.
3 silent killers that make strokes deadly (warning signs)
You’d Be Surprised How Your Sleeping Environment Impacts Your Body and Mind
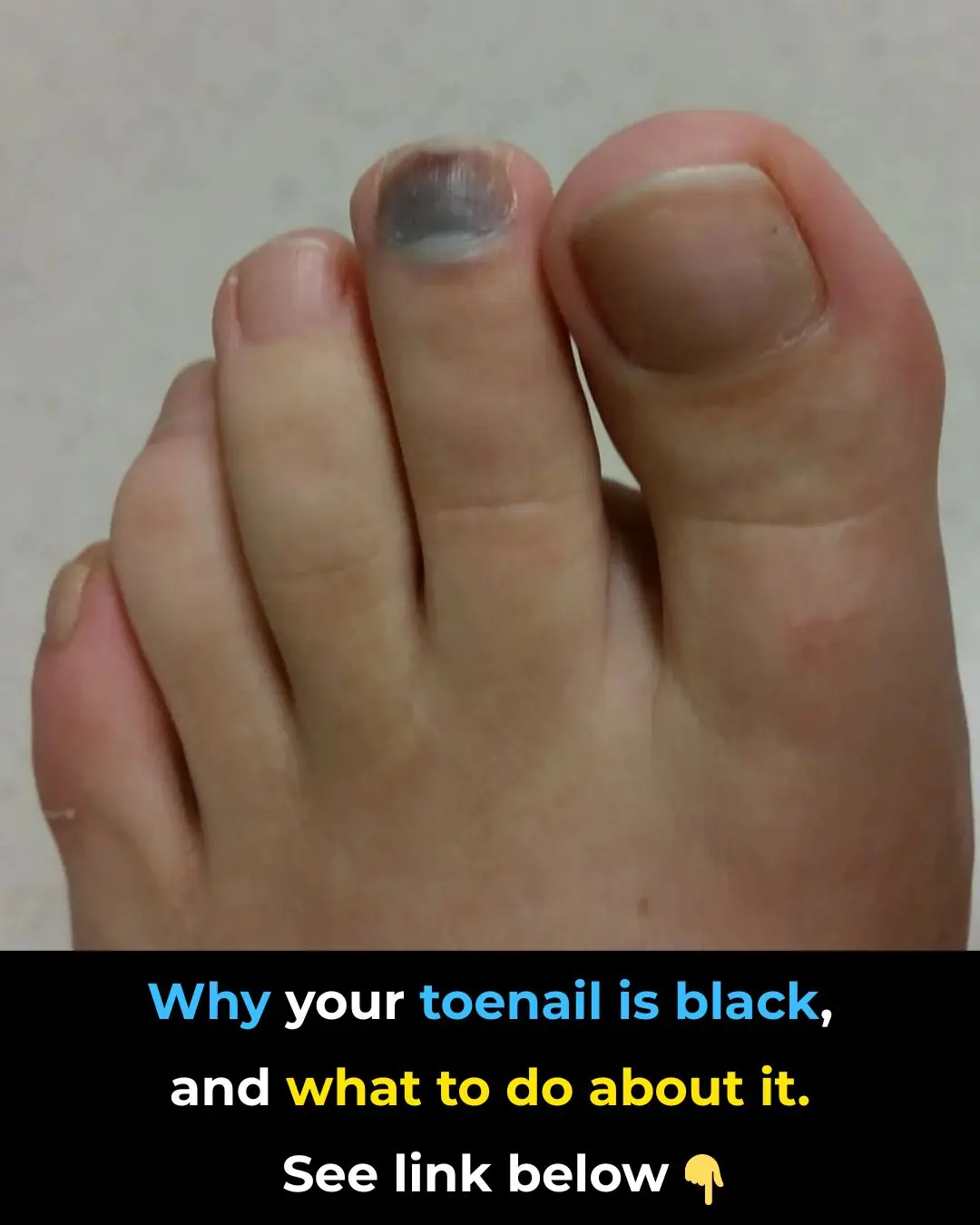
What Causes a Toenail To Turn Black?

7 Foods To Help You Live a Longer, Healthier Life
News Post

Which Fruits Should Cancer Patients Avoid and Which Should They Eat?

Advancing Clinical Excellence in IgA Nephropathy

3 types of fruits that are cheap in Vietnamese markets but are considered "pure gold" to protect health
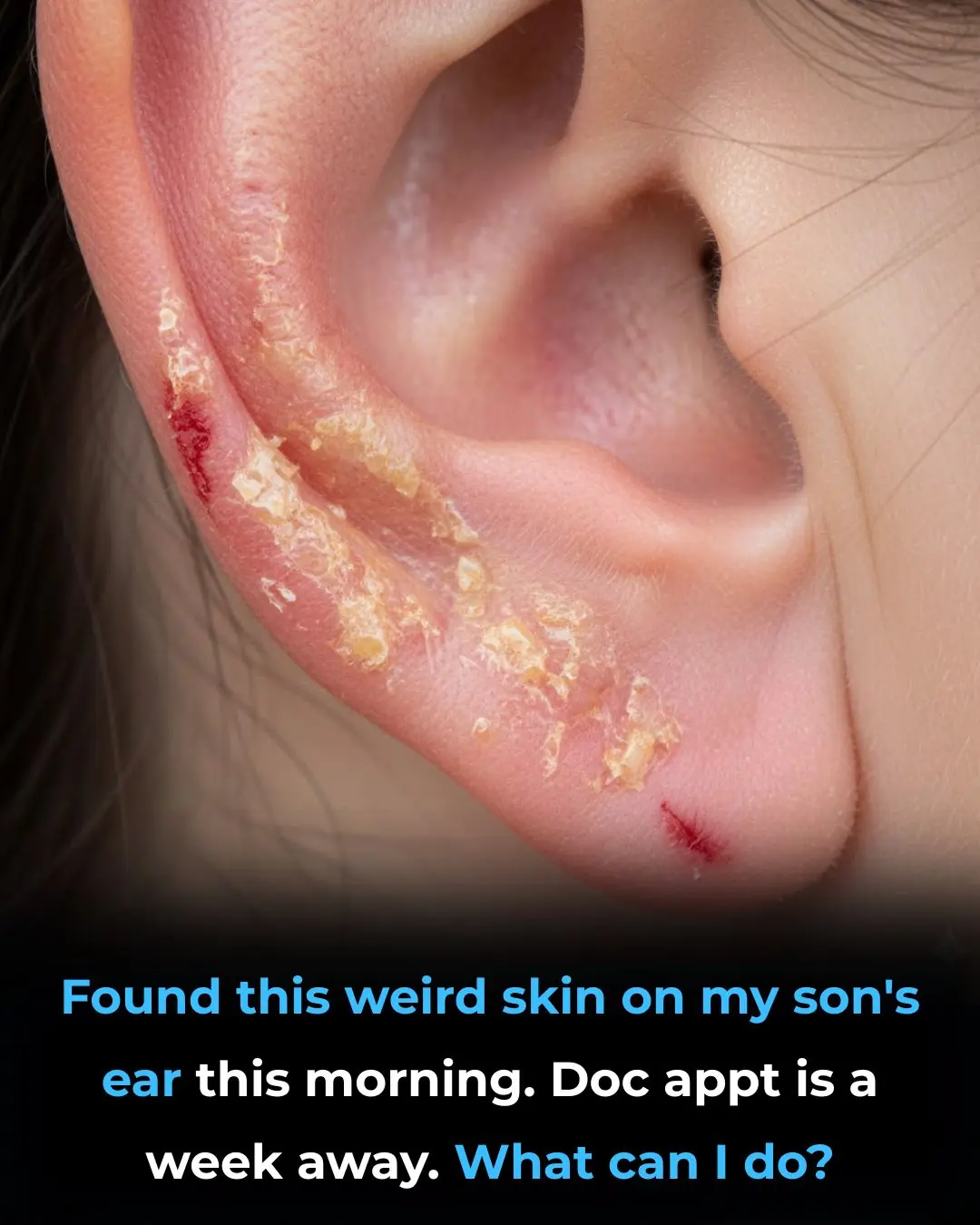
Found this weird skin on my son's ear this morning. Doc appt is a week away. What can I do?

My nana taught me this hack to get rid of dark circles in 5 mins with 0 work. Here’s how it works

What To Know About Chronic Kidney Failure

Could Your Magnesium Supplement Be Causing Side Effects?

Why Thick Toenails Happen, And How To Get Rid of Them

The military sleep method that can help you fall asleep in just two minutes
Garlic with Olive Oil Over 50: The Irreversible Body Reaction Everyone’s Talking About

Discover How Baking Soda Could Transform Your Skin’s Appearance in Minutes – Even After 70!
What Happens When You Add Just 2 Garlic Cloves a Day to Your Routine – Even After 50!
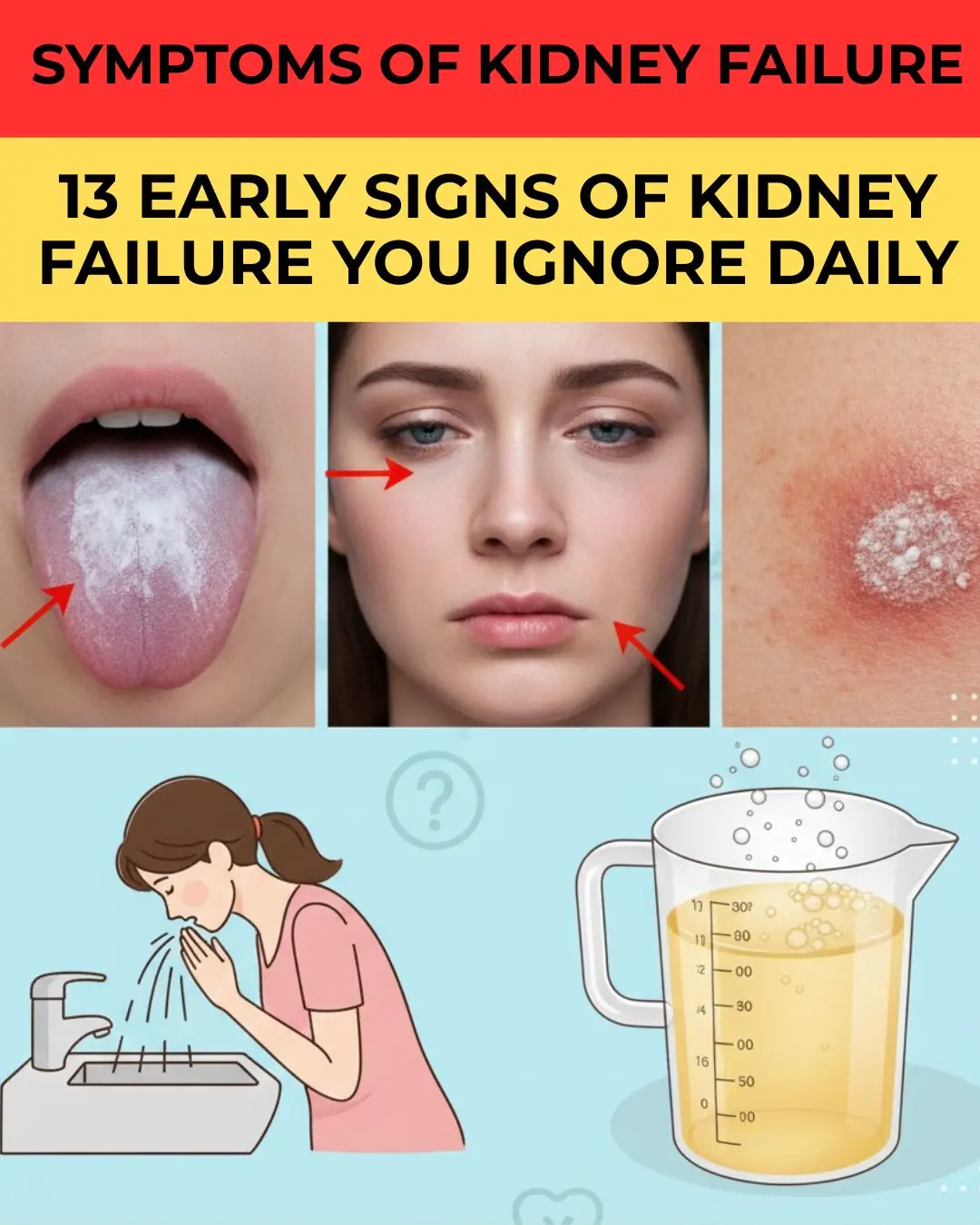
13 Subtle Signs Your Kidneys May Need Attention
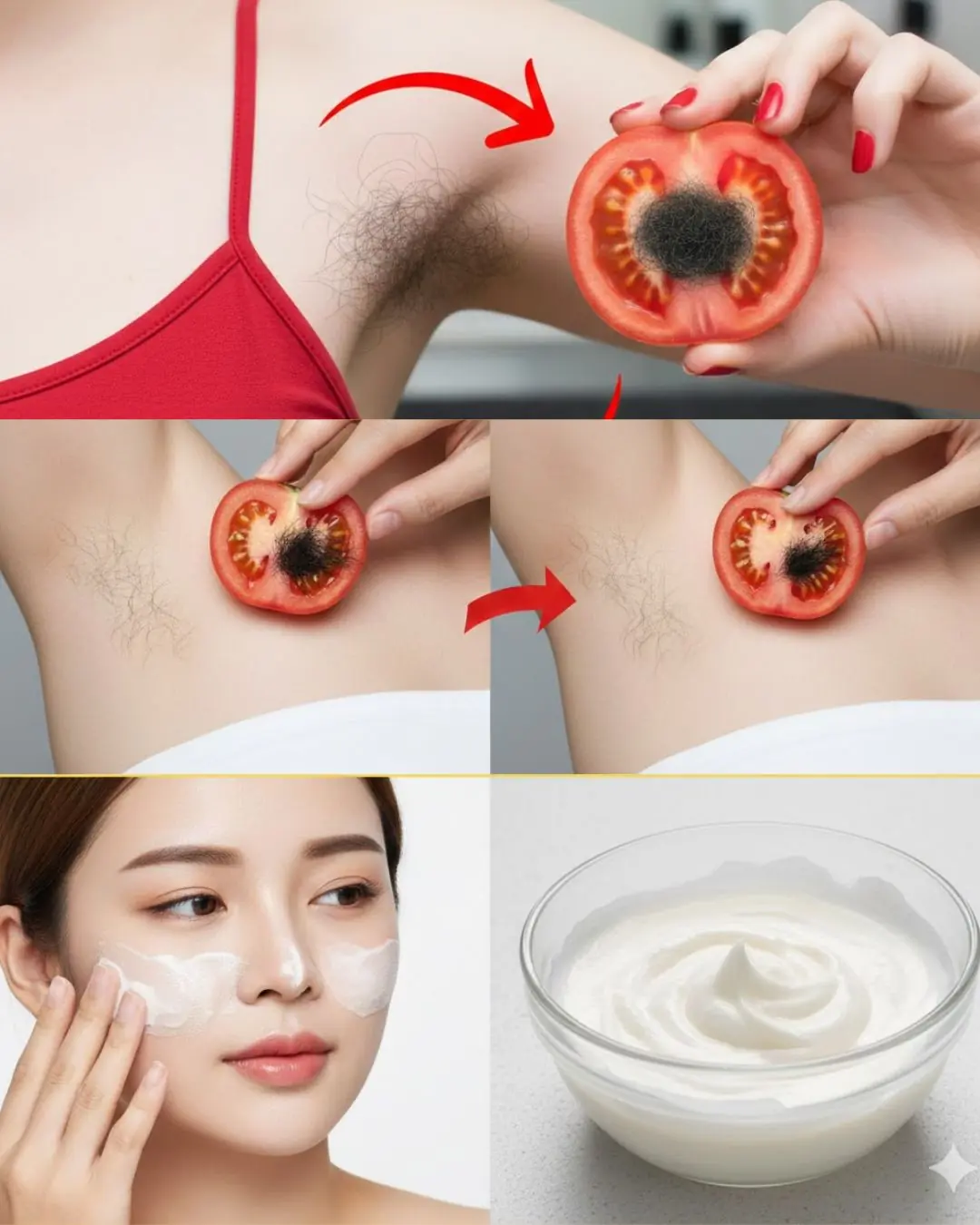
Stop Shaving? Exploring Popular Home Remedies for Hair Removal

Discover the Hidden Power of Ginger Oil: Why Women Over 65 Are Seeing Thicker, Darker Hair Naturally

Top 10 Foods That May Help Reduce Frequent Nighttime Urination (Nocturia)

Why Toothpaste and Baking Soda Aren’t the Answer for Wrinkles and Dark Spots – And What Might Help Instead

James Webb Space Telescope Reveals Hidden Mid-Infrared Flares from the Milky Way’s Central Black Hole

New Vision Correction Technique Reshapes the Cornea Without Surgery
