
7 Resistance Band Ab Moves That Torch Belly Fat and Build Core Power
This variation transforms a simple bridge into a powerhouse move, strengthening not only your glutes but also your deep core muscles, lower back, and hip stabilizers.

According to the National Stroke Association, stroke is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States and one of the top causes of long-term disability among adults. Yet, many people aged 45 and older may have experienced a minor or silent stroke without knowing it.
Understanding the early warning signs, risk factors, and preventative actions could make the difference between full recovery and a lifetime of disability—or even death.
Let’s break down everything you need to know about stroke, including how to spot it, how to prevent it, and how to act fast if it strikes.
A stroke happens when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or significantly reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die within minutes.
There are two main types of stroke:
Ischemic Stroke – Caused by a blood clot blocking an artery in the brain (about 87% of all strokes).
Hemorrhagic Stroke – Caused by a burst blood vessel, leading to bleeding in or around the brain.
There’s also a third, milder type:
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) – Sometimes called a "mini-stroke", this is a temporary blockage that causes stroke-like symptoms but doesn’t lead to permanent damage. However, it’s a serious warning sign of a possible full-blown stroke in the future.
When brain cells die, the functions they control—like speech, movement, memory, vision, and balance—can be affected. The severity and outcome depend on:
The location of the stroke in the brain
The extent of damage
The speed at which treatment is received
Time is brain. Millions of brain cells can die each minute a stroke goes untreated.
Knowing the signs of stroke could save a life—maybe even your own.
| F | Face | Ask the person to smile. Does one side droop? |
|---|---|---|
| A | Arms | Ask them to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward or feel weak? |
| S | Speech | Ask them to repeat a simple sentence. Is their speech slurred or strange? |
| T | Time | If any of these are true, call 911 immediately. Time is critical! |
Sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the body (face, arm, or leg)
Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or understanding speech
Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
Sudden dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
A sudden, severe headache with no known cause
Trouble swallowing, or decreased reflexes
Nausea or vomiting, especially if paired with other symptoms
💡 If you're unsure whether someone is having a stroke, assume they are and get medical help immediately.
Several risk factors can increase your likelihood of having a stroke. Some are genetic, but many are lifestyle-related and preventable.
High blood pressure
High cholesterol
Diabetes
Obesity
Smoking
Physical inactivity
Excessive alcohol use
Sleep apnea
Heart disease (e.g., atrial fibrillation)
Illicit drug use (e.g., cocaine, meth)
Even seemingly minor conditions, if left untreated, can significantly raise your risk over time.
Want to lower your stroke risk dramatically? These evidence-based lifestyle changes can help you stay stroke-free and protect your long-term brain and heart health.
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week (e.g., brisk walking, cycling, swimming).
Benefits:
Lowers blood pressure
Improves circulation
Helps control weight
Reduces blood sugar
Excessive alcohol raises blood pressure and increases stroke risk.
👉 Stick to no more than 1 drink/day for women, and 2 drinks/day for men.
You don’t need to be ultra-slim to see benefits.
✅ Losing just 5–10% of your body weight can significantly lower cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure.
Especially if you’re being treated for:
High blood pressure
High cholesterol
Atrial fibrillation
Diabetes
💡 130,000 deaths annually in the U.S. are linked to not taking heart medications as prescribed.
Choose:
Fruits & vegetables (especially leafy greens and berries)
Whole grains
Lean proteins (like fish and legumes)
Healthy fats (olive oil, avocados, nuts)
Potassium-rich foods like bananas, potatoes, beans, and salmon also help regulate blood pressure.
👉 Dark chocolate (75%+ cocoa) in moderation may reduce stroke risk by up to 30%!
Smoking doubles your stroke risk. Even secondhand smoke is harmful.
Quitting today can lower your risk almost immediately.
Stimulants like cocaine and methamphetamine constrict blood vessels and raise stroke risk—even with first-time use.
Obstructive sleep apnea increases stroke risk up to 3-fold, especially in men.
Warning signs: loud snoring, daytime fatigue, breathing pauses during sleep.
Talk to your doctor about a sleep study or CPAP treatment.
Gum disease and poor oral hygiene have been linked to heart and brain issues.
Regular cleanings may reduce stroke risk by 13%.
Don’t ignore symptoms like:
Chest pain
Irregular heartbeat
Unexplained fatigue
Shortness of breath
Men, especially, often delay seeking help. Don’t "tough it out"—early action saves lives.
If you or someone near you shows signs of a stroke, do not wait to see if symptoms improve.
Call emergency services immediately and report:
The exact time symptoms began
The symptoms observed
Your location clearly
Doctors may run:
CT or MRI scans
Blood tests, including CPK (creatine phosphokinase), which may be elevated after a stroke
Some treatments, like clot-busting drugs (tPA), are only effective within 3–4.5 hours of symptom onset—delaying treatment can mean permanent disability or death.
Stroke is one of the few emergencies where public awareness can make a life-or-death difference.
Know the symptoms
Know the risk factors
Take action quickly
Share this with family and friends
🙌 For every 10 people who read this, one life might be saved. That could be your loved one—or even you.

This variation transforms a simple bridge into a powerhouse move, strengthening not only your glutes but also your deep core muscles, lower back, and hip stabilizers.

It’s about making gradual, sustainable swaps—cutting back on processed foods, replacing saturated fats with healthier ones, and prioritizing fiber-rich, nutrient-dense ingredients.



He thought he was strong and healthy, but one morning at work, his body gave in without warning. By the time he reached the hospital, it was too late. His story serves as a chilling reminder that what you eat for breakfast could quietly determine your ris

Your eyes do more than reflect emotions; they can also reveal critical clues about your overall health. Subtle changes in appearance, color, or vision may sometimes be early warning signs of dangerous cancers developing elsewhere in the body — long befo

The influence of a husband’s habits on his wife’s well-being is far greater than many couples realize. Small daily choices — whether neglecting exercise or lighting a cigarette — can quietly accumulate into significant health risks over time.







Could a simple vaccine hold the key to protecting the brain against one of the most feared diseases of aging?
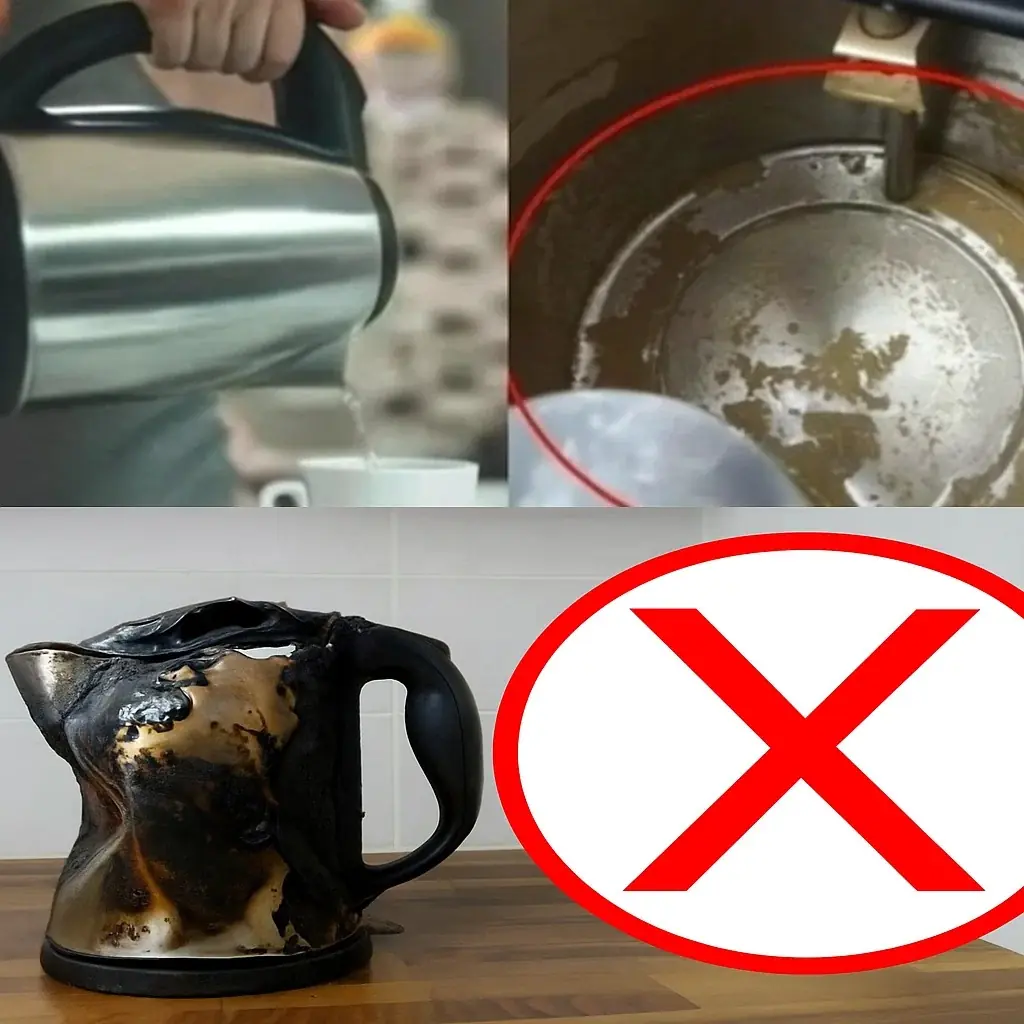



Electric kettles are found in nearly every modern home, making it quick and easy to boil water for tea, coffee, or instant meals. But shocking warnings from health experts reveal that some kettles may release dangerous substances into the water you drink

Struggling with premature gray hair in your 20s or already noticing streaks of silver in your 30s and 40s? Don’t panic. While gray strands can feel like a dreaded sign of aging, nature offers surprising, inexpensive solutions that can help you regain yo

This variation transforms a simple bridge into a powerhouse move, strengthening not only your glutes but also your deep core muscles, lower back, and hip stabilizers.

It’s about making gradual, sustainable swaps—cutting back on processed foods, replacing saturated fats with healthier ones, and prioritizing fiber-rich, nutrient-dense ingredients.

With flaxseed gel, you’re not just applying moisture—you’re giving your skin the building blocks it needs to repair, renew, and glow from within.

With just two simple household ingredients, you can try a gentle, budget-friendly, and surprisingly effective solution at home.

Packed with anti-inflammatory, detoxifying, and soothing properties, cabbage is more than just a kitchen staple — it’s a hidden healing ally.

A single bowl of salt might seem insignificant, but its impact on your fridge — and your household — is anything but small.


he peel is not harmful; in fact, it carries unique benefits. By using ginger correctly and storing it properly, you can unlock its full potential for boosting immunity, improving circulation, and keeping your


Plastic wrap is undeniably convenient, but it must be used correctly. Missteps like reusing, heating, or buying low-quality products can gradually harm your body.

He thought he was strong and healthy, but one morning at work, his body gave in without warning. By the time he reached the hospital, it was too late. His story serves as a chilling reminder that what you eat for breakfast could quietly determine your ris

Your eyes do more than reflect emotions; they can also reveal critical clues about your overall health. Subtle changes in appearance, color, or vision may sometimes be early warning signs of dangerous cancers developing elsewhere in the body — long befo

The influence of a husband’s habits on his wife’s well-being is far greater than many couples realize. Small daily choices — whether neglecting exercise or lighting a cigarette — can quietly accumulate into significant health risks over time.

