13 Subtle Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar and 9 Powerful Ways to Take Control of Your Health
13 Subtle Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar and 9 Powerful Ways to Take Control of Your Health
High blood sugar levels, the defining characteristic of Type 2 diabetes, often creep up quietly, presenting symptoms that are remarkably easy to dismiss or mistake for other, less serious conditions. This insidious nature means that a staggering 1 in 3 people living with diabetes are completely unaware of their condition. Ignoring these early, seemingly innocuous signs can lead to a cascade of dangerous and life-altering complications, including severe heart disease, irreversible nerve damage (neuropathy), and debilitating vision problems, even blindness.
This comprehensive article aims to empower you by illuminating the often-missed symptoms of elevated blood sugar levels – the crucial early warning signs of Type 2 diabetes. By recognizing these indicators, you can take proactive, timely steps to protect your health, prevent the onset of full-blown diabetes, and mitigate its potential long-term complications.
The good news is that with the right combination of dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, and, where necessary, medical interventions or medications, Type 2 diabetes can be effectively managed. This allows individuals to not only live a fulfilling life but also maintain optimal health and vitality.
In the first part of this article, we will delve into the specific early warning signs of diabetes, providing detailed explanations to help you identify them. In the second part, you will discover nine highly effective and actionable strategies to prevent Type 2 diabetes or manage pre-diabetes, enabling you to take definitive control of your health journey.
Understanding High Blood Sugar: The Early Warning Signs of Diabetes
Globally, the prevalence of diabetes is a growing concern. In 2013 alone, over 382 million people worldwide were living with diabetes, with an overwhelming 90% of these cases attributed to Type 2 diabetes. This metabolic disorder is fundamentally characterized by persistently high levels of sugar (glucose) circulating in the blood. This occurs either because the pancreas, the organ responsible for producing insulin, reduces its output of this vital hormone, or because the body's cells become resistant to insulin's effects, failing to respond to it properly. Insulin's primary role is to act like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose to enter and be used for energy, thereby balancing blood sugar levels. When this process falters, the following symptoms can begin to develop:
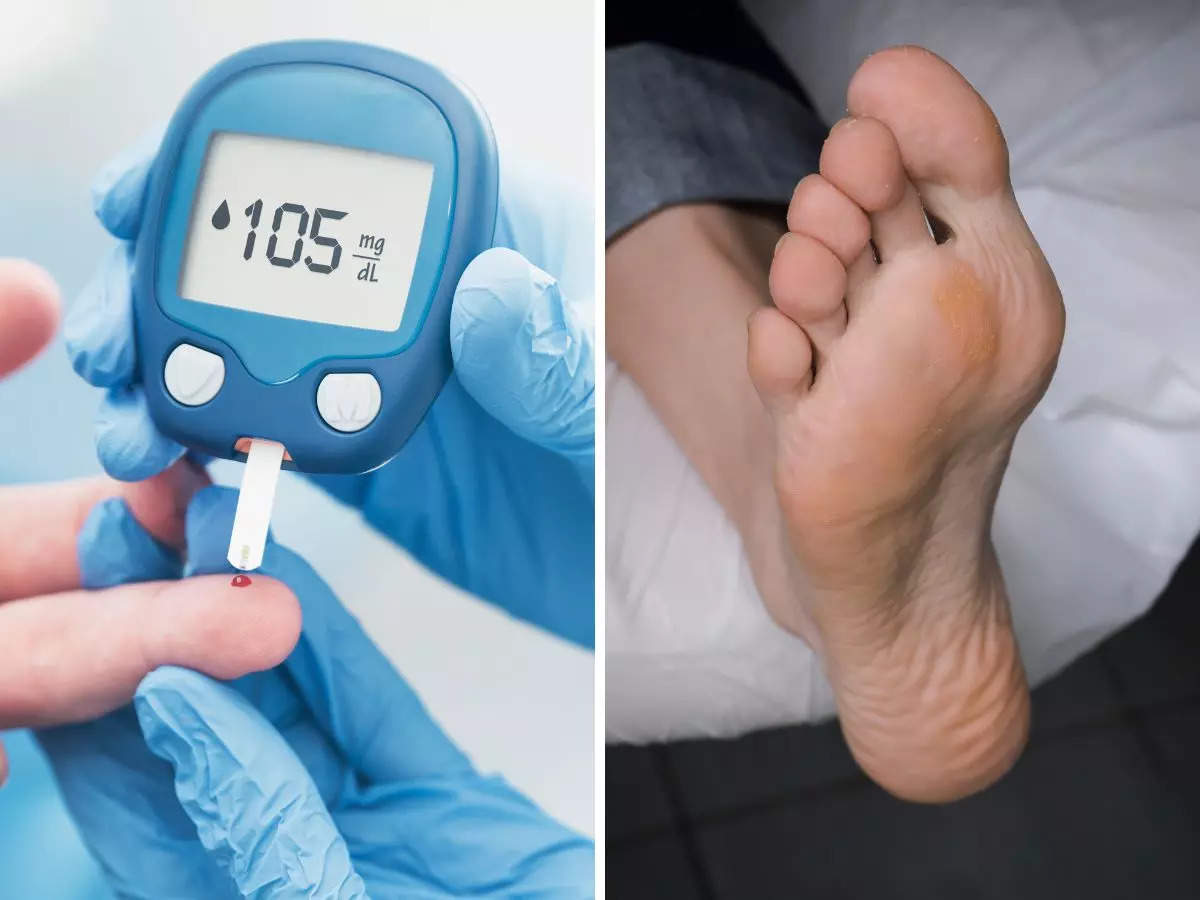
1. Frequent Urination (Polyuria): One of the most common and earliest indicators is a noticeable increase in the frequency of urination. If you find yourself needing to visit the restroom far more often than usual, especially waking up multiple times during the night (sometimes several times) to empty your bladder, this should raise a red flag. The kidneys, in an attempt to flush out the excess glucose from the bloodstream, begin working overtime, drawing more water from the body to excrete the sugar.
2. Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia): This symptom is directly linked to the previous one. As your body loses an increased amount of fluids through frequent urination, a powerful physiological response is triggered: an insatiable, constant need to drink. You may feel perpetually parched, no matter how much water you consume, as your body desperately tries to replenish its fluid levels.
3. Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): Despite consuming regular meals, individuals with high blood sugar may experience an abnormal and sudden urge to eat. This occurs because, even though there's an abundance of glucose in the blood, the body's cells aren't receiving enough of it for energy due to insulin resistance or deficiency. The cells essentially "starve," sending signals to the brain that result in persistent cravings, particularly for sugary foods.
4. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): A persistent lack of moisture in the mouth is another common symptom. This can be more than just an unpleasant sensation; it creates an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, significantly increasing the risk of various oral and dental problems. Gum diseases, in particular, are a known and serious complication of unmanaged diabetes, often linked to the dry, sugary environment in the mouth.
5. Unexplained Weight Loss or Weight Gain: The body's inability to utilize glucose effectively can lead to paradoxical weight changes. When insulin can't get glucose into the cells for energy, the body perceives itself as starving and begins to break down muscle protein and fat stores for fuel. Rapid, unexplained weight loss (e.g., 10 to 20 pounds over a couple of months without intentional dieting) is a significant warning sign that demands further investigation. Conversely, the increased hunger and cravings for sugary foods can also lead to an unexpected weight gain for some individuals.
6. Fatigue: A pervasive, excessive tiredness is a hallmark symptom. This profound fatigue develops as the body constantly struggles to compensate for the cells' lack of available glucose for energy. Furthermore, sleep often gets interrupted by the urgent need to urinate, exacerbating the exhaustion. People frequently report lower energy levels, a chronic feeling of malaise, and it's not uncommon to also experience increased irritability and a generally low mood due to persistent discomfort and energy deficit.
7. Vision Problems: High blood sugar levels exert a detrimental effect on the eyes, particularly by changing the shape of the lens and the eyes themselves. As a direct result, vision becomes noticeably blurry, and some individuals may even report seeing occasional flashes of light or experiencing distorted vision. Initially, these changes to the eyes are often reversible if blood sugar levels are brought under control. However, if glucose levels remain elevated for a prolonged period, this can cause permanent and irreversible damage, potentially leading to severe eyesight loss or even blindness (diabetic retinopathy).
8. Headaches: A persistent or recurring headache can be an early indication of elevated blood sugar levels, a condition medically known as hyperglycemia. This symptom often worsens as the blood glucose levels climb higher and the condition progresses, indicating the body's struggle to cope with the metabolic imbalance.
9. Infections, Cuts, and Bruises That Do Not Heal: This is a classic and highly indicative sign of diabetes, directly stemming from blood vessel damage. Excessive amounts of sugar in the bloodstream harm the delicate veins and arteries, compromising their ability to efficiently transport blood, oxygen, and vital nutrients to areas that need repair and healing. As a result, even minor cuts, scrapes, or bruises take an unusually long time to heal, leaving the body vulnerable to prolonged infection.
10. Yeast Infections: Since bacteria and fungi thrive in an environment rich in sugar, individuals with high blood glucose levels are far more susceptible to various infections. Yeast infections, particularly those caused by Candida species (like vaginal candidiasis in women), become significantly more common and recurrent due to the increased sugar in bodily fluids.
11. Numbness and Tingling in Hands and Feet: This concerning symptom is a direct result of nerve damage, a condition known as neuropathy, which is strongly associated with diabetes (diabetic neuropathy). The tingling and numbness, often described as a "pins and needles" sensation, typically affects the hands and feet and can be accompanied by burning pain and swelling. If blood sugar levels are not effectively brought down and maintained within a healthy range, this nerve damage can become permanent, presenting a serious and debilitating complication of diabetes.
12. Skin Changes: High blood sugar can manifest visually through specific skin changes. One prominent sign is velvety dark skin, medically termed acanthosis nigricans, which typically appears in folds of skin such as the neck, groin, and armpit areas. Other unusual skin changes, rashes, or persistent itchiness, particularly around the vaginal or groin area, can also be indicators of underlying elevated glucose levels.
13. Sexual Dysfunction: Diabetes can also cause significant damage to the delicate blood vessels and nerves in the sex organs, leading to a range of sexual problems for both men and women. Women may experience vaginal dryness, pain during intercourse, and reduced libido. Men can encounter significant difficulties with erection (erectile dysfunction), with studies indicating that anywhere from 35% to 75% of men with diabetes may suffer from impotence.
If you are experiencing some or any combination of these symptoms, it is absolutely crucial to consult your doctor promptly. They can conduct necessary blood tests to accurately establish if you are indeed suffering from Type 2 diabetes or are at risk.
Several diagnostic tests are commonly used, and they often need to be repeated on separate occasions to provide a reliable diagnosis. The fasting plasma glucose test measures your blood sugar levels after an overnight fast (typically 8 hours). If your fasting blood sugar is consistently above 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) on two separate occasions, it indicates a diagnosis of diabetes. Of equal concern are slightly lower values, ranging from 100 to 125 mg/dL. This range is considered pre-diabetes, a critical warning stage where lifestyle interventions can often prevent the progression to full-blown diabetes.
9 Effective Steps to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes and Reclaim Your Health
Before individuals develop full-blown Type 2 diabetes, they almost invariably pass through a stage known as "pre-diabetes." During this period, blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to meet the diagnostic criteria for diabetes. Receiving a pre-diabetes diagnosis should not be a cause for despair but rather a powerful wake-up call and a valuable opportunity for proactive change.
Importantly, a pre-diabetes diagnosis does not automatically mean you will develop diabetes. This stage offers a crucial window where you have the time and the genuine possibility to correct unhealthy habits. Early and consistent lifestyle modifications can often return blood glucose levels to the normal range, effectively preventing the onset of Type 2 diabetes. The first and most impactful action you can take to improve your health is to shed unhealthy habits and diligently cultivate healthier ones.
Being diagnosed as pre-diabetic is, in essence, an invitation to initiate significant and beneficial lifestyle changes that can profoundly help prevent diabetes. Here are nine preliminary, yet essential, steps that provide an excellent starting point for improving your health and substantially reducing your risk of developing this chronic condition:
1. Be Physically Active: Incorporating more physical activity into your daily life is perhaps one of the most important and effective changes you can make to significantly reduce your risk of, or even prevent, Type 2 diabetes. If it's been a long time since you last engaged in regular exercise, begin gradually and safely. Small changes make a big difference: choose the stairs instead of the elevator, do stretching exercises while watching TV, or take a short walk during your lunch break.
Exercise is an integral part of any treatment plan for pre-diabetics because it has a direct, positive impact: it helps lower blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces excess body fat. An ideal training program generally recommends at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity, five times a week. If you can't carve out that much time at once, remember that shorter bursts of activity (e.g., three 10-minute walks) count equally and contribute to your overall fitness goals. Making physical activity a consistent part of your daily routine is a cornerstone of long-term health.
2. Lose Weight: Obesity, particularly abdominal obesity, is recognized as one of the primary drivers of Type 2 diabetes. The good news is that you don't necessarily need to lose dozens of pounds to see a significant difference and effectively prevent diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, reducing just 7% of your initial body weight can help reduce the risk of diabetes by an impressive 58%! The focus should be on sustainable, healthy weight loss to improve your body's response to insulin and regulate blood sugar, rather than resorting to extreme diets that may ultimately harm your health.
3. Don't Smoke: Smoking is a profound risk factor that extends far beyond lung health. Research, including a study published in 2012, has conclusively shown that smoking is strongly associated with increased insulin resistance and systemic inflammation. It significantly elevates the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and, for those already diagnosed, dramatically aggravates its complications. The evidence strongly suggests that avoiding smoking altogether is one of the most crucial ways for both diabetes control and preventing debilitating diabetic complications.
4. Improve Sleep Habits: The quality and quantity of your sleep play a surprisingly critical role in metabolic health. A compelling study from 2007 found that consistently short sleep duration (less than optimal) could be a significant risk factor for diabetes development. Subjects who reported sleeping 5 or fewer hours per night were almost twice as likely to develop diabetes over the follow-up period compared to those who consistently slept 7 hours.
A person who regularly doesn't get enough sleep will find it significantly more challenging to lose weight, and their body's ability to use insulin efficiently will be compromised. It is highly advisable to adopt good sleep hygiene habits: aim to go to bed and wake up at consistent times every day, even on weekends; create a relaxing bedtime routine to wind down before turning off the lights; and strictly avoid excessive television viewing or smartphone use right before bedtime, as the blue light can disrupt melatonin production. If you frequently struggle with falling asleep, consider avoiding caffeine after lunch, and explore natural remedies or relaxation techniques.
5. Get Support: Embarking on lifestyle changes like weight loss, adopting a healthy diet, and increasing physical activity is significantly easier and more sustainable when you have a strong support system. Surround yourself with people who genuinely support and encourage your efforts. For example, consider joining groups that include individuals with similar health goals (e.g., a weight loss support group, a local running club, or a community fitness class). Leveraging these communities can provide motivation, accountability, and a sense of shared purpose, helping you to pursue a healthy lifestyle and avoid mental and physical "breaking points" that often lead to relapse.
6. Improve Your Diet: Your dietary choices have a monumental impact on your risk of developing diabetes. Consuming an unhealthy diet rich in red and processed meats, unhealthy trans and saturated fats, excessive added sugars, and highly processed foods will dramatically increase your risk. Instead, shift your focus towards a plant-based diet, emphasizing an abundance of fresh vegetables, especially non-starchy varieties like spinach, broccoli, carrots, green beans, and leafy greens.
Actively add foods rich in dietary fiber to your daily menu. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety. Choose whole grain foods over refined and processed grains (e.g., brown rice instead of white rice, whole wheat bread instead of white bread, oats instead of sugary cereals). Fruits are also highly recommended, despite some concerns among pre-diabetics and diabetics about their natural sugar content. The American Diabetes Association, however, emphasizes that overall, fruit consumption is encouraged as part of a balanced diet, especially when considering the glycemic index to guide food choices.
7. Reduce Stress Levels: Chronic stress is a powerful, yet often underestimated, risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. A significant research study published in PLoS One in 2017 concluded that persistent psychological stress is a strong independent predictor for the development of Type 2 diabetes. The research highlighted that improving mental health and actively reducing chronic stress levels may not only lower the growing incidence of Type 2 diabetes but also lead to better glycemic control for those already affected. Implementing stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can be profoundly beneficial.
8. Visit Your Doctor Regularly: People diagnosed as pre-diabetic sometimes underestimate the importance of frequent visits to their physician. However, consistent medical monitoring, typically on a frequent basis of every three to six months, is of paramount importance. Regular check-ups allow your doctor to track your progress, monitor your blood sugar levels, and provide ongoing guidance. If your situation is improving and your numbers are moving in the right direction, receiving reassurance from your doctor can be incredibly motivating. Conversely, if your condition does not improve, or even worsens, your doctor will be able to help get you back on track, offer specific tailored advice, or provide necessary medication if lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient.
9. Commit Yourself: Perhaps the most crucial key to the success of this entire process is unwavering commitment to changing your lifestyle. You need to foster a deep understanding that the journey will not be perfect every single day; there will be setbacks, temptations, and moments of weakness. Change takes time, patience, and consistent effort. However, you must commit to doing the very best you can most of the time.
Recognize that crises, challenges, and slip-ups are an inherent part of any significant process of change. You need to take this into account, allow yourself to experience these moments without self-condemnation, learn from them, and then purposefully choose to come out better and stronger on the other side. Your commitment is your most powerful tool in taking control of your health.
News in the same category


Researcher Studies Over 200 Kids—Here’s What the Most Emotionally Intelligent Ones Had in Common

Scientists Bioengineer Tooth That ‘Grows’ in Place Like a Natural One And Feels Real

9-year-old dies after dental procedure

How to Get Rid of Muscle Soreness: Effective Home Remedies That Really Work
Natural Blood Thinners: Evidence-Based Foods, Supplements, and Vitamins for Healthy Blood Flow

How to Conquer Constipation: Your Guide to Effective Home Remedies

Simple, Natural Ways to Lower Cholesterol (and Why You Might Want To)

Exercise Is ‘Better Than Drugs’ In Stopping Cancer From Returning After Treatment, Study Finds

Energy Drinks May Cause Blood Cancer: New Research
Massaging The Neck And Face May Be Helping Flush Waste Out of the Brain

10 Things That Men May Find Unattractive About Women Over 50

How Long You Should Be Able to Stand on One Leg, According to Your Age

15 Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Dementia You Shouldn’t Ignore
10 Natural Ways to Calm Gum Irritation at Home

Lung Cleansing with a Powerful Natural Garlic Juice

7 Signs of Mini Stroke in The Elderly

This Kid has Eaten Almost No Refined Sugar Her Whole Life. This is What She Looks Like Today

Doctor Warns: Sleeping With A Fan On May Trigger Allergies And Respiratory Issues
News Post

Increased Screen Exposure In Kids Linked to Anxiety, Aggression, and Self-Esteem Issues, Study Says

Researcher Studies Over 200 Kids—Here’s What the Most Emotionally Intelligent Ones Had in Common

Scientists Bioengineer Tooth That ‘Grows’ in Place Like a Natural One And Feels Real

Why There’s a Growing Trend of Straight Men Dating Trans Women

9-year-old dies after dental procedure

Air India pilot’s terrifying last words have been made public

Why You Should Avoid Seat 11A on Your Next Flight – Here’s What You Didn’t Know

Man Releases Chilling Never Seen Before Footage of Twin Tower Collapse

Masterful Painting Of Jesus By 8-Year-Old—Says She Saw The True Face Of Jesus

The Powerful Trio of Lemon, Apple, and Ginger: A Simple Blend That May Support Skin, Hair, and Vision

Drink Cloves and Cinnamon Before Bed? The Results May Surprise You

Hair Thinning? Try This Unique Combo to Support Hair Growth Naturally

The Ultimate Drink for Women’s Wellness: Watermelon Juice with Carrot, Beetroot, and Ginger

THIS HEALS YOUR THYROID IN JUST 3 DAYS! | Barbara O'Neill’s Clove Soak Formula

8 Herbal Teas That Lower Blood Pressure and Unclog Arteries (Doctors Never Say This!)

15 Powerful Foods to Relieve Acid Reflux Fast – The Ultimate Anti-Acidity Diet Guide

Health Benefits of Cayenne Pepper: 20 Surprising Wellness Secrets

DIY Brow Boosting Serum: Your 5-Minute Secret to Fuller, Bolder Brows

How to Get Rid of Muscle Soreness: Effective Home Remedies That Really Work