
Energy Drinks May Cause Blood Cancer: New Research
In recent years, energy drinks have gained massive popularity among young adults, athletes, students, and professionals looking for a quick energy boost. Marketed as performance enhancers and mental stimulants, these beverages are often consumed without a second thought. However, emerging scientific research is beginning to reveal a darker side to these drinks. Alarmingly, new studies suggest that frequent consumption of energy drinks may be linked to a higher risk of developing blood cancer, a group of diseases affecting the bone marrow, lymphatic system, and blood-forming tissues.
Energy drinks typically contain high levels of caffeine, sugar, taurine, and various artificial additives. While these ingredients can temporarily increase alertness and physical stamina, they also put significant stress on the body’s metabolic and cardiovascular systems. Until now, most health concerns surrounding energy drinks have focused on heart problems, sleep disturbances, and addiction. However, recent research is drawing attention to the potential carcinogenic effects of these beverages—particularly in relation to hematological malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma.
Scientists believe that the risk may stem from the combination of synthetic chemicals and preservatives used in energy drinks. Some of these compounds, such as benzene derivatives, have already been associated with DNA damage and cellular mutations in laboratory settings. Additionally, excessive caffeine intake may disrupt normal cell cycles, promote oxidative stress, and weaken immune responses—all of which could increase the likelihood of abnormal blood cell development and, over time, cancer.
A 2024 study conducted by a team of oncologists and toxicologists from an international research institute investigated the long-term effects of energy drink consumption on rodents. The study found that animals given high doses of energy drinks over several months showed significant changes in bone marrow cell structure, along with early signs of leukemia. While animal studies are not always directly applicable to humans, they provide strong evidence that warrants further exploration.
Moreover, a growing number of epidemiological studies have observed higher incidences of blood-related cancers in younger populations who regularly consume energy drinks. Adolescents and young adults, whose bodies are still developing, may be especially vulnerable to the toxic effects of excessive stimulant and sugar intake. One concern is that energy drinks are often consumed alongside other harmful substances like alcohol and tobacco, potentially amplifying their negative health impacts.
Doctors and public health officials are now calling for stricter regulations on energy drink marketing, especially toward teenagers and children. Currently, many countries lack comprehensive policies to monitor the contents and advertising of these beverages. Some researchers advocate for warning labels similar to those found on tobacco products, emphasizing the potential long-term risks of consumption.
Another aspect worth noting is the behavioral dependency energy drinks can create. The constant desire for a quick boost can lead to overconsumption, which further increases exposure to harmful chemicals. When used daily over several years, the body’s natural energy regulation systems may become disrupted, leading to chronic fatigue, hormonal imbalances, and cellular damage.
It is important to clarify that occasional consumption of energy drinks is unlikely to directly cause cancer. However, when used excessively and habitually—especially by vulnerable individuals—the risks could become significant. As with many health concerns, moderation is key, and being aware of what we put into our bodies is the first step toward prevention.
In conclusion, while the link between energy drinks and blood cancer is still being actively researched, early findings are concerning enough to justify caution. Consumers should be mindful of the ingredients and frequency of their intake. Governments and health organizations must work together to raise awareness, enforce regulations, and conduct more extensive studies. Our health, especially when it comes to something as serious as cancer, should never be compromised for a temporary burst of energy.
News in the same category


Researcher Studies Over 200 Kids—Here’s What the Most Emotionally Intelligent Ones Had in Common

Scientists Bioengineer Tooth That ‘Grows’ in Place Like a Natural One And Feels Real

9-year-old dies after dental procedure

How to Get Rid of Muscle Soreness: Effective Home Remedies That Really Work
Natural Blood Thinners: Evidence-Based Foods, Supplements, and Vitamins for Healthy Blood Flow

How to Conquer Constipation: Your Guide to Effective Home Remedies

Simple, Natural Ways to Lower Cholesterol (and Why You Might Want To)

13 Subtle Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar and 9 Powerful Ways to Take Control of Your Health

Exercise Is ‘Better Than Drugs’ In Stopping Cancer From Returning After Treatment, Study Finds
Massaging The Neck And Face May Be Helping Flush Waste Out of the Brain

10 Things That Men May Find Unattractive About Women Over 50

How Long You Should Be Able to Stand on One Leg, According to Your Age

15 Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Dementia You Shouldn’t Ignore
10 Natural Ways to Calm Gum Irritation at Home

Lung Cleansing with a Powerful Natural Garlic Juice

7 Signs of Mini Stroke in The Elderly

This Kid has Eaten Almost No Refined Sugar Her Whole Life. This is What She Looks Like Today

Doctor Warns: Sleeping With A Fan On May Trigger Allergies And Respiratory Issues
News Post

Heartbreaking Voice Message From Pilot Before Crash Goes Viral — Here’s What He Said

Air India crash simulation reveals how sole survivor escaped death
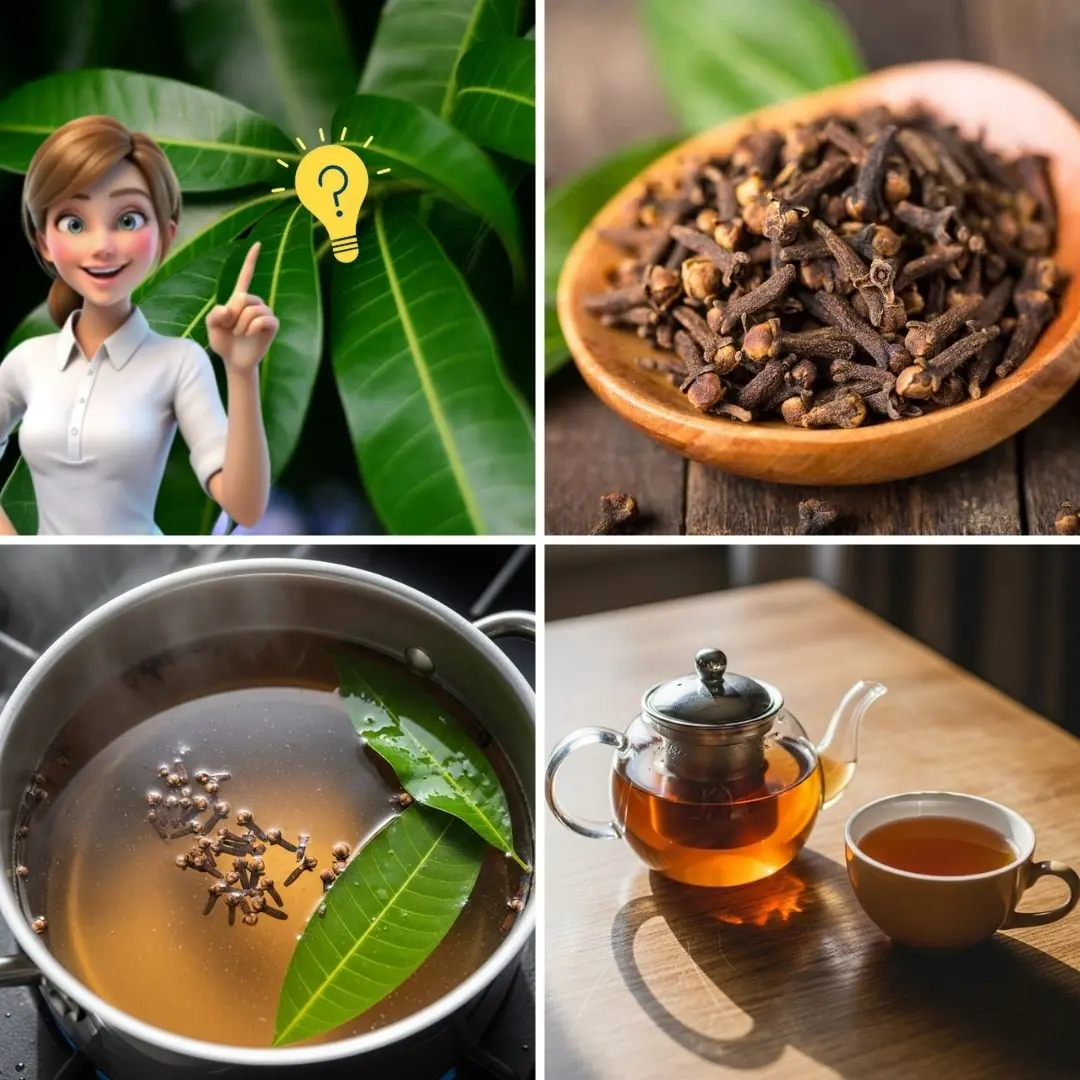

Mango Leaf and Clove Tea: A Gentle Herbal Support for Daily Wellness
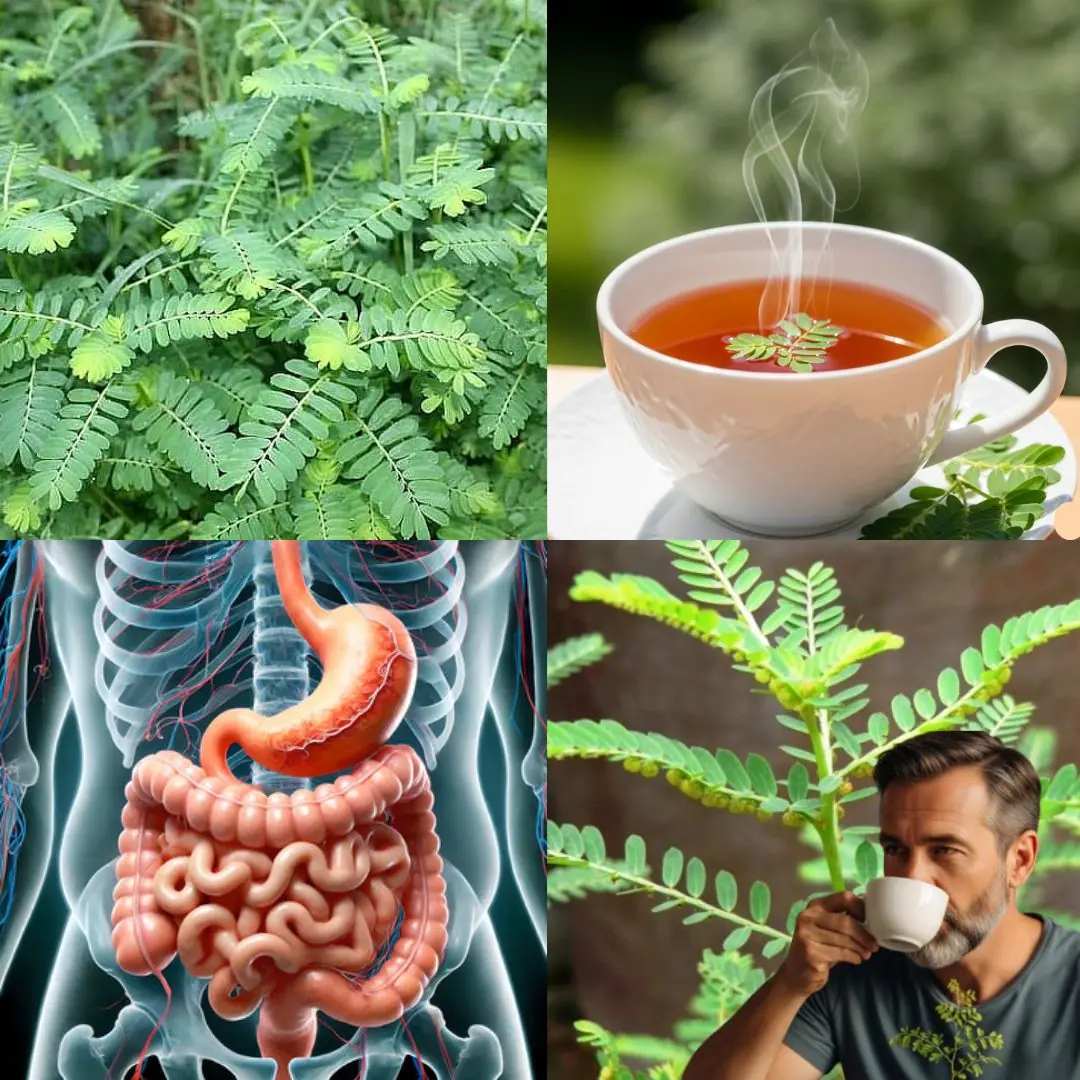

The Stonebreaker Plant (Phyllanthus niruri): Nature’s Natural Remedy for Liver and Kidney Health
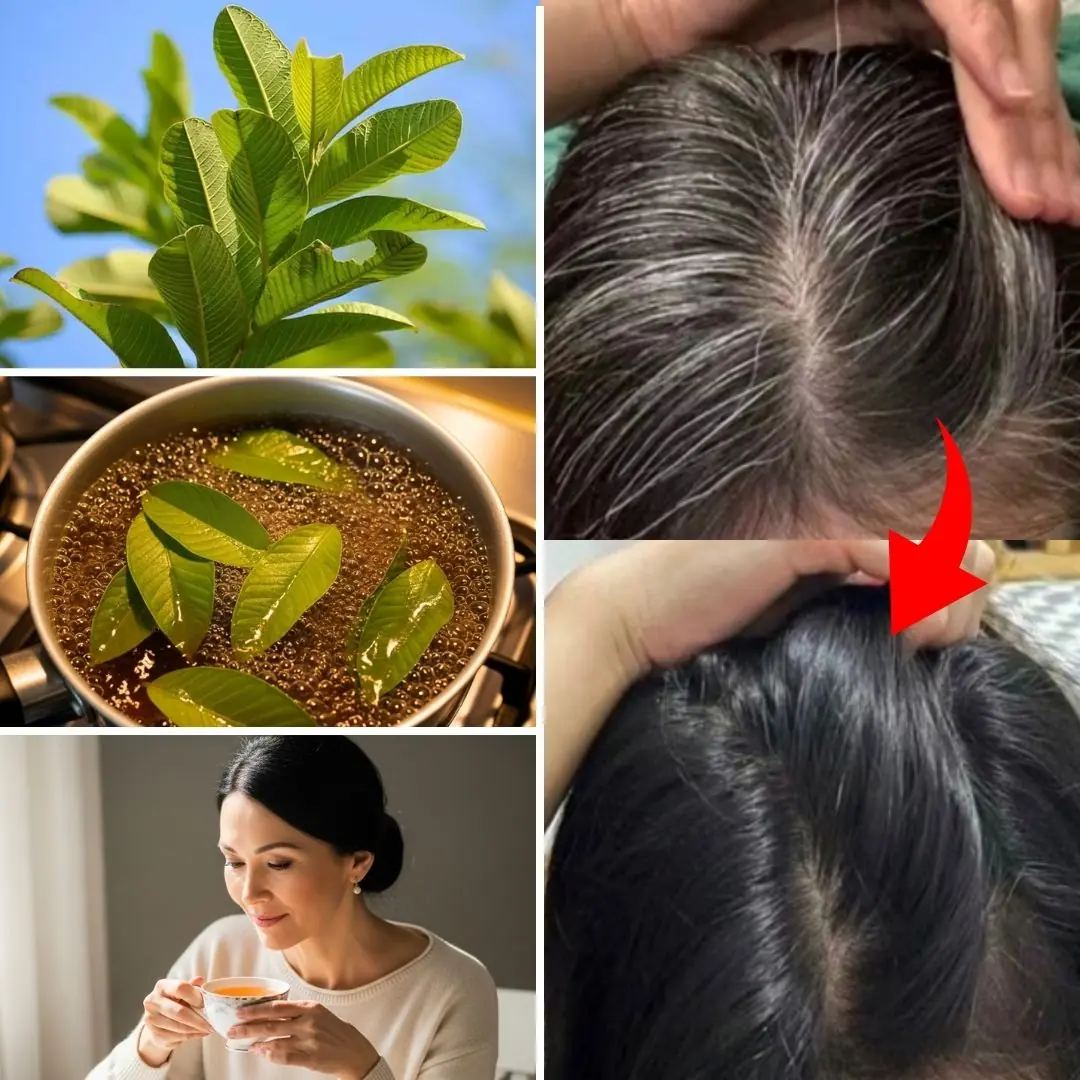

Can Guava Leaves Help with Gray Hair and Hair Growth? Exploring Natural Solutions

Increased Screen Exposure In Kids Linked to Anxiety, Aggression, and Self-Esteem Issues, Study Says

Researcher Studies Over 200 Kids—Here’s What the Most Emotionally Intelligent Ones Had in Common

Scientists Bioengineer Tooth That ‘Grows’ in Place Like a Natural One And Feels Real

Why There’s a Growing Trend of Straight Men Dating Trans Women

9-year-old dies after dental procedure

Air India pilot’s terrifying last words have been made public

Why You Should Avoid Seat 11A on Your Next Flight – Here’s What You Didn’t Know

Man Releases Chilling Never Seen Before Footage of Twin Tower Collapse

Masterful Painting Of Jesus By 8-Year-Old—Says She Saw The True Face Of Jesus

The Powerful Trio of Lemon, Apple, and Ginger: A Simple Blend That May Support Skin, Hair, and Vision

Drink Cloves and Cinnamon Before Bed? The Results May Surprise You
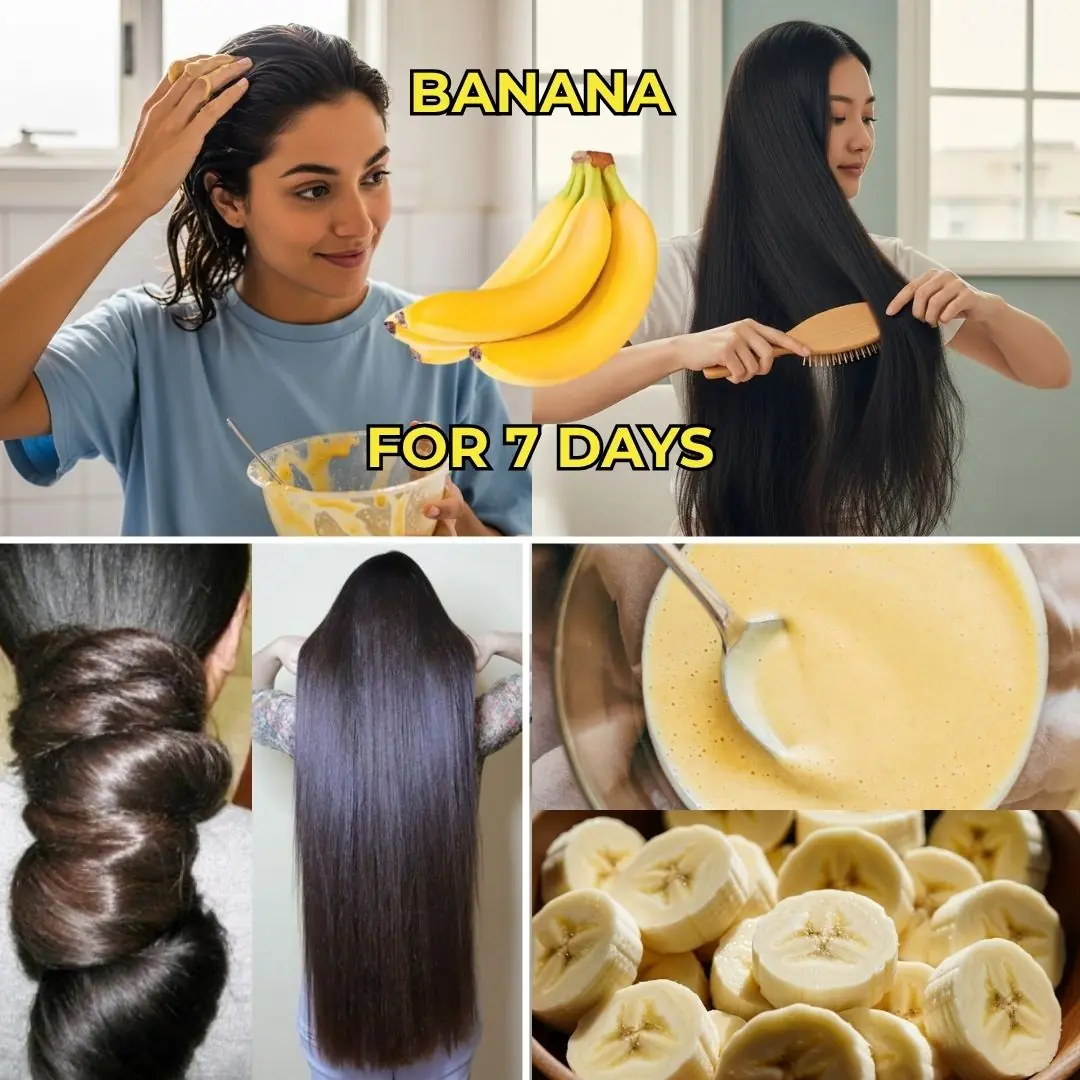

Hair Thinning? Try This Unique Combo to Support Hair Growth Naturally

The Ultimate Drink for Women’s Wellness: Watermelon Juice with Carrot, Beetroot, and Ginger

THIS HEALS YOUR THYROID IN JUST 3 DAYS! | Barbara O'Neill’s Clove Soak Formula
