16 Warning Signs Your Blood Circulation is Poor and How to Improve It (Evidence-Based)
16 Warning Signs Your Blood Circulation is Poor and How to Improve It (Evidence-Based)
Do you frequently experience cold hands and feet accompanied by a persistent tingling sensation? These could be critical indicators of poor blood circulation. When blood flow in your body is compromised, it can lead to a cascade of health complications, ranging from dizziness and chronic fatigue to hair loss and even significant digestive upset.
Poor blood circulation is rarely a standalone issue; it's typically a symptom of an underlying health problem. Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, and smoking significantly elevate your risk of developing circulatory problems. These conditions often lead to the narrowing of arteries, which directly restricts vital blood flow throughout your body.
This comprehensive guide will help you identify the various signs and symptoms of poor blood circulation, understand its common causes, and discover effective strategies for improving your circulatory health. First, let's explore the critical role of healthy circulation and the dangers of its impairment.

The Crucial Role and Dangers of Poor Circulation
Your heart, nestled securely under your rib cage, is the powerhouse of your circulatory system, tirelessly pumping nutrient and oxygen-rich blood throughout your entire body. According to Dr. James Beckerman on WebMD, approximately 5 to 6 quarts (around 5 liters) of blood are constantly coursing through your vascular network. Since blood is responsible for delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to every tissue and vital organ, any reduction in circulation means that fundamental bodily functions will be impaired. Therefore, robust blood circulation is absolutely essential for maintaining overall health and fitness.
What is Poor Blood Circulation?
Poor blood circulation means that certain areas of the body, particularly the extremities like your hands and feet, do not receive an adequate supply of blood. While your heart efficiently pumps blood to your extremities, returning that blood "uphill" back to the heart and lungs requires significant effort. Factors like plaque buildup in your arteries, smoking, pregnancy, certain eating disorders, and significant weight gain can impede this flow, making it harder for your legs, arms, heart, and other crucial organs to receive sufficient blood.
Although poor circulation is more commonly associated with the elderly, it can lead to serious complications in people of all ages. Recognizing the signs early and actively seeking ways to improve blood circulation are paramount to preventing severe and irreversible damage to your brain, heart, liver, and limbs.

16 Critical Signs of Poor Blood Circulation
The signs of compromised blood circulation may not always be immediately obvious, but their long-term consequences can be severe. When the body's tissues and vital organs are deprived of an adequate blood supply, it can result in serious conditions such as blood clots, persistent swelling, a weakened immune system, and even cognitive impairments like memory loss.
Here are the many different symptoms of poor blood circulation. Depending on the severity of the weakened circulatory process, you may experience one or more of these indicators:
-
Numbness and Tingling in Limbs: One of the most common and recognizable symptoms of restricted blood flow is a sensation of numbness and/or tingling (often described as "pins and needles") in your hands and feet. Diabetes.co.uk notes that poor circulation frequently causes cold hands and feet alongside numbness, while Dr. Rob Hicks on WebMD corroborates the "pins and needles" sensation when limbs don't receive enough blood.
-
Impaired Cognitive Function: Your brain demands a constant and robust flow of blood to function optimally. Reduced blood flow to the brain can manifest as memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and diminished focus. The Journal of Geriatric Cardiology highlights that a reduction in cerebral blood flow, a drop in overall cardiac output, and blood pressure fluctuations are major contributors to cognitive deficits.
-
Digestive Issues: It might be surprising, but poor blood circulation can significantly impact your digestive system. Like all other bodily functions, the digestive tract requires a healthy blood supply to operate efficiently. The Cleveland Clinic reports that plaque buildup on blood vessel walls can restrict blood flow to the abdominal region, potentially leading to abdominal pain, diarrhea, or even bloody stools. In severe cases, this can become a life-threatening condition.
-
Loss of Appetite: Another less common but significant sign of circulatory problems is a unexplained loss of appetite. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute notes that certain rare diseases involving blood vessel inflammation can cause a lack of appetite. Since the gastrointestinal tract relies on adequate blood flow for digestion, poor circulation can disrupt this process and reduce hunger signals.
-
Fatigue: Your muscles require sufficient blood flow to function correctly and prevent fatigue. Slowed blood circulation throughout your body directly impacts your energy levels, causing you to feel tired more quickly as your heart works harder to compensate. Dr. Yu Shang on Medscape.com explains that a reduction in oxygen-rich blood reaching muscles can lead to fatigue. Individuals experiencing chronic fatigue or difficulty exercising may find that poor circulation prolongs recovery time after physical exertion.
-
Pain (Especially in Legs): Depending on the underlying cause of poor circulation, you may experience localized pain, most commonly in your legs or hands. Mayo Clinic doctors describe how extremely cold hands or feet might throb with pain as they warm up and blood flow returns. People with poor circulation in their legs often report an aching feeling in their calf muscles and feet, which typically worsens after prolonged sitting or standing.
-
Muscle Cramps: Beyond pain, poor blood circulation can also trigger muscle cramps. Various factors related to impaired circulation can stiffen muscles and induce cramping. Dr. William Shiel on eMedicineHealth.com states that poor circulation can lead to leg cramps. Moreover, inadequate delivery of essential nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium via insufficient blood flow can cause cramping in any muscle.
-
Discolored Skin: A tell-tale sign of insufficient blood reaching tissues is pale or even bluish skin (cyanosis). This discoloration isn't limited to just feet or hands; Mayo Clinic doctors indicate it can affect the color of your nose, lips, ears, and even nipples. Impaired circulation can also cause mottled skin (livedo reticularis), characterized by lacy patches of purplish discoloration.
-
Leg Ulcers: Circulatory problems can severely impede the body's natural healing process, leading to the formation of venous leg ulcers. According to Dr. Tim Kenny on Patient.info, these ulcers develop because blood cannot effectively flow back up the body, causing it to pool in the legs, leading to swelling, skin thickening, and damage.
-
Swelling (Edema): Swelling, particularly in the legs and ankles, is a common symptom of poor blood circulation, often referred to as edema. This occurs because poor blood flow from the legs back to the heart causes fluid to accumulate, forcing it from blood vessels into surrounding tissues. Swelling can also be a sign of heart disease, where the heart struggles to circulate enough blood. PubMed Health explains this mechanism, also noting that heart-related circulatory issues can cause abdominal swelling.
-
Hair Loss and Weak Nails: A lack of adequate blood flow to the scalp and other hair-bearing areas can lead to hair loss. Similarly, insufficient blood supply to the hands and feet can cause problems with your nails, such as brittle nails. The journal ePlasty reported that scalp massage, by increasing blood flow, can improve hair thickness. The Canadian Family Physician journal also published findings linking impaired circulation to brittle nails.
-
Angina: The narrowing of arteries, a direct consequence of poor circulation, can lead to angina. This is a serious heart condition characterized by left-sided chest pains and breathlessness, occurring when the heart muscle doesn't receive enough oxygen-rich blood. The journal Circulation identifies unstable angina as a symptom of "coronary circulation insufficiency."
-
Varicose Veins: Poor circulation can cause the veins under the skin, especially in the legs, to become twisted, swollen, and highly visible – a condition known as varicose veins. This is prevalent in individuals who stand for long periods. You might also notice smaller, visible veins resembling spider webs (spider veins). Symptoms can include pain after prolonged sitting or standing, and random itchiness. Varicose veins commonly appear near the feet and ankles and can become painful and itchy. PubMed Health explains that poor blood flow to the legs results in chronic venous insufficiency, which also causes legs to feel heavy, aching, itchy, and swell, leading to these unsightly knotted veins.
-
Weakened Immune System: Your body's ability to detect and effectively fight off pathogens is significantly impacted by poor blood circulation. The immune system's specialized cells, responsible for defending against infections, travel through the body via the circulatory system. When circulation is compromised, these vital immune cells may not be delivered quickly enough or in sufficient quantities, making you more susceptible to illnesses and causing wounds and injuries to heal much more slowly.
-
Cold Hands and Feet: One of the most immediate and common indicators of poor blood flow is consistently cold hands and feet, which feel significantly colder than the rest of your body. Optimal blood flow helps regulate body temperature, keeping it at a comfortable level. Impaired circulation interferes with this process, leading to chilly sensations, particularly in areas rich with nerve endings like the hands and feet. Mayo Clinic doctors confirm that peripheral artery disease, a common cause of poor circulation, often leads to cold extremities.
-
Erectile Dysfunction (in men): Adequate blood flow is essential for achieving and maintaining an erection. Diabetes.co.uk lists erectile dysfunction as one of the potential signs of poor circulation in men.
Common Causes of Poor Blood Flow
Understanding the underlying cause of poor blood circulation is crucial for effective treatment. Sometimes, stimulating blood flow is all that's needed, while other times, it requires addressing a specific medical condition.
-
Being Overweight/Obesity: Maintaining a healthy weight is vital for a robust vascular system. Carrying excess weight places additional strain on your heart and directly reduces blood flow throughout your body. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases highlights that even losing as little as 10 pounds can significantly improve blood flow, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Obesity can also restrict blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of stroke.
-
Diabetes: Diabetes is a major cause of poor circulation, often leading to peripheral artery disease (PAD), which can impair blood flow to vital organs and the extremities. Individuals with diabetes must pay meticulous attention to foot care, as poor circulation in the legs drastically increases the risk of serious foot problems. Diabetes.co.uk explains that prolonged high blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and promote plaque buildup, emphasizing the importance of maintaining proper blood pressure and low cholesterol for healthy circulation.
-
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Damage to the nerves that control your cardiovascular system can result in insufficient blood flow to organs and other body parts. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases states that nerve damage can affect blood pressure and heart function, potentially leading to symptoms like dizziness, fainting, or lightheadedness – all warning signs of poor circulation.
-
Smoking: Smoking is a powerful risk factor for developing various vascular diseases, including severe symptoms of poor circulation. The detrimental effect of smoking on blood flow is primarily due to its promotion of plaque buildup in your veins. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute warns that this plaque restricts blood flow throughout the body, dramatically increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and heart attack.
-
Thyroid Disease: Thyroid disorders can also impact blood circulation, leading to reduced blood flow, particularly to the brain. The journal Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders reported that variations in thyroid function negatively affect cerebral blood flow (blood supply to the brain). Poor circulation is just one of many potential signs of a thyroid disorder.
-
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): PAD is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, causing them to narrow and restricting circulation. This affects not only blood flow to your legs but also to your brain, scalp, and heart. Mayo Clinic doctors confirm that PAD can cause leg numbness, cold hands and feet, hair loss, a weak pulse in the legs, and muscle cramping.
-
Raynaud’s Disease: Raynaud’s disease affects blood vessels, causing spasms that reduce blood flow to the hands and feet, leading to numbness and tingling in these extremities. While its exact cause isn't fully understood, Mayo Clinic doctors suggest that cold temperatures or stress trigger the arteries in the hands or feet to narrow significantly, limiting blood supply. Over time, blood vessels may thicken, further restricting flow.
-
Blood Clots: The formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel can restrict or completely cut off blood flow to specific organs and arteries. Dr. Benjamin Wedra on eMedicineHealth states that blood clots can form after surgery, periods of immobility, or due to plaque buildup. They are also commonly seen in pregnant women. Blood clots can become life-threatening if they dislodge and travel, potentially causing a heart attack if they reach the heart, or a pulmonary embolism if they enter the lungs, a serious cause of chest pain.
How to Improve Poor Blood Circulation
If you're experiencing signs of an insufficient circulatory system, there are many practical and natural ways to boost your blood circulation:
-
Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to strengthen your heart, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance blood flow throughout your body. Even moderate exercise, like brisk walking, can make a significant difference.
-
Massage: Therapeutic massage, particularly of the legs, can help stimulate blood flow and alleviate symptoms of poor circulation. It can also aid in improving the appearance and discomfort associated with varicose veins. Consider incorporating essential oils known for their circulatory benefits during massage.
-
Manage Stress Levels: Chronic stress negatively impacts blood flow, often diverting it from essential systems. Learning effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature, can significantly improve circulation to your brain and the rest of your body.
-
Quit Smoking: Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps you can take for your circulatory health. It directly improves blood flow through your veins, reduces plaque buildup, and strengthens your heart, significantly lowering your risk of heart disease, stroke, and heart attack.
-
Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet: Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains helps strengthen your heart and prevents the development of conditions that impair blood flow. Incorporating foods like ginger, known for its blood-thinning and circulation-boosting properties, can also be beneficial. Focus on reducing processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sodium.
-
Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake is crucial for maintaining blood volume and fluidity, allowing blood to flow more easily through your vessels. Dehydration can lead to thicker blood, making the heart work harder.
-
Elevate Your Legs: If you experience swelling in your legs and ankles due to poor circulation, elevating your legs above heart level for periods throughout the day can help fluid drain back towards your core, reducing edema.
-
Wear Compression Stockings: For those with varicose veins or chronic leg swelling, compression stockings can help by applying gentle pressure to the legs, encouraging blood flow back to the heart and reducing fluid pooling.
-
Warm Baths/Showers: Warm water can help dilate blood vessels, temporarily improving blood flow.
-
Regular Movement: Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing. If your job requires it, take frequent breaks to walk around, stretch, and move your legs to prevent blood from pooling.
By understanding the warning signs and adopting these proactive measures, you can significantly improve your blood circulation and enhance your overall health and well-being. Always consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan, especially if you experience severe or persistent symptoms.
News in the same category

People with Cancer Often Share 8 Morning Signs—Especially Clear After Age 40
5 Foods That Tumors Hate: Eat These Often for Better Health
Scientists Warn of a Silent Epidemic: Men’s Testosterone Levels Are Plummeting — And Here’s Why

Scientists Found The Hidden Factor Behind the Global Infertility Crisis, And It’s Terrifying

🍵 The Quiet Power of Cinnamon Tea: A Simple Sip for Natural Balance

How to Make the Perfect Pineapple, Turmeric, Carrot, and Lemon Juice: Your Ultimate Homemade Immune Boost Drink
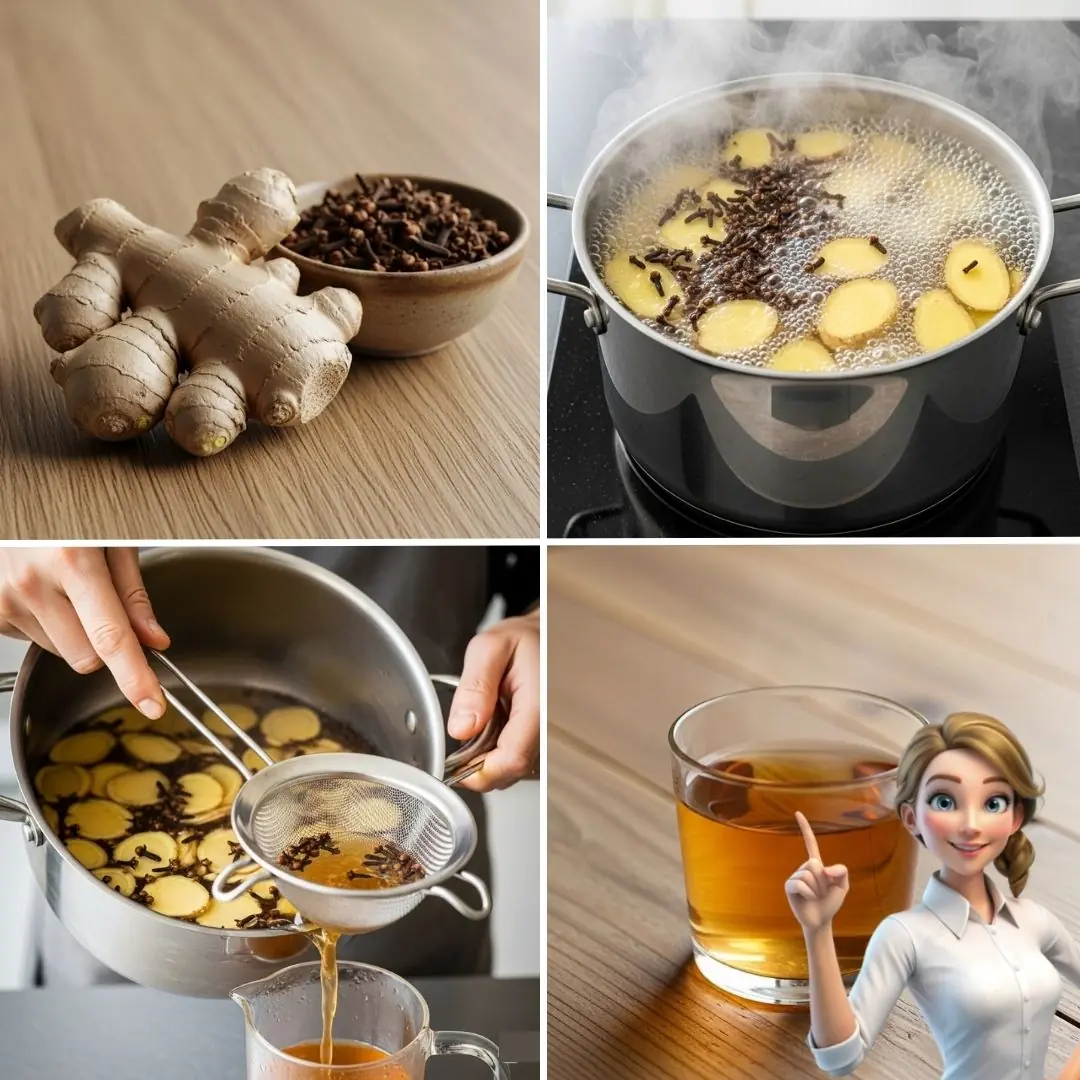

Simple Cloves and Ginger Recipe for Wellness

Nature’s Candy Unleashed: The Jaw-Dropping Health Hacks of Dates You NEED to Know!
Banish Throat Mucus: Effective Home Treatments for a Clearer Throat (Evidence-Based)

Beat the Bloat: 8 Common Causes of Abdominal Bloating and Evidence-Based Solutions

Doctor Frank Suárez's Natural Recipe: Eliminate Diabetes, Poor Circulation, Fatty Liver, Pancreas Problems, High Blood Pressure, Knee Pain, and Even Cancer

Juniper (Juniperus communis): Benefits and Uses

4 Common Habits You Must Change Immediately When Using Air Conditioning to Protect Your Respiratory Health
If Your Body Shows These 5 Signs, It Could Be a Warning of Kidney Disease or Impending Kidney Failure
"2 Pains and 1 Yellow” – Warning Signs That Silent Liver Cancer Is Progressing: Being Negligent May Cost Your Life

Warning: Your Sushi Might Carry a Japanese Tapeworm – What You Need to Know About Salmon Safety

TikToker Unknowingly Records Near-Death Encounter After Picking Up One of Earth's Deadliest Creatures

Travel Influencer Unknowingly Films Terrifying Encounter with World's Deadliest Jellyfish
News Post

Here’s Why Cabin Crew Sits On Their Hands During Take Off and Landing

Surprising Reasons Why You Should Spread Salt

The First Communication Between Two Humans in Dreams Has Been Achieved – This Is How It Works

Am I Wrong for Cutting Off My Daughter’s Friends and Pulling Her from Soccer Camp?
A father decides to pull his daughter from soccer camp and cut her ties with two friends he deems "ghetto," but when family pressures him to reconsider, he starts questioning his actions. Is he wrong?

AI Is Set to Replace 41% of Jobs in the Next Five Years

MY HUSBAND CANCELED OUR DREAM VACATION FOR HIS MOTHER - MY REACTION WENT VIRAL!
“No, I’m going to Thailand, not to your mom’s garden beds,” I refused to go to the dacha, and my husband got offended.

The Miracle Child: The Baby Who Changed Everything at Saint Thorn Medical Center
A mysterious baby born with an unusual heartbeat starts to change the lives of everyone around him. From medical staff to nurses, his presence brings hope, awe, and a chilling sense of wonder.

The Dress That Could Make or Break My Career – And Why I Said No to My Niece’s “Special” Gift
A career-driven woman refuses her niece's offer to sew her a dress for a big event, leading to family tension. Is she being too harsh, or is her decision about professionalism and self-respect?

RELATIVES OVERSTAY THEIR WELCOME – BUT WHAT THEY DISCOVER IN GRANDMA'S HOUSE WILL CHANGE EVERYTHING!
— You’ve been coming to stay in my house for the third month now, maybe that’s enough? — I couldn’t hold back, looking at the relatives’ suitcases.

The boss’s daughter got a job as a cleaning lady to uncover the director’s scams

When Family Dynamics Clash: The Birthday Cake Dispute
A woman stands her ground over her daughter's birthday cake, facing pressure from her sister-in-law and family. Will she keep her decision, or choose peace over principle?
MY FIANCÉE M0CKED MY DE@D MOTHER AT OUR REHEARSAL DINNER - WHAT I DID NEXT CANCELED THE WEDDING
I'm 33, and until recently, I was engaged to Lydia, a woman I honestly thought I'd spend the rest of my life with. I met her about six years ago through mutual friends at a cookout. She had this great smile, was quick with a joke, and we just clicked.

Study Reveals: Your Body Remembers Trauma, Even After the Mind Has Let Go

Revenge Ink: How I Taught My Fiancé and His Mother a Lesson They'd Never Forget
When my fiancé’s mother told him to leave me for a richer woman, I devised the perfect plan for a dramatic and unforgettable revenge. Here’s how I got back at them with a lesson they’ll never forget.

Man Sentenced After Stowing Away On 120 Flights By Masquerading As Flight Attendant

5 Drinks That Can Help Dissolve Kidney Stones and Aid Easy Elimination

People with Cancer Often Share 8 Morning Signs—Especially Clear After Age 40

5 Foods That Tumors Hate: Eat These Often for Better Health

People Stunned After Learning The True Meaning Behind ‘SOS’ — It’s Not What You Think
