Eggplant The King of Vegetables
Eggplant, also known as aubergine, is a staple in many global cuisines. It’s rich in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients. However, not everyone benefits from including eggplant in their diet.
While it's generally safe for most people, certain individuals may experience adverse effects due to its specific chemical compounds and nutritional profile. If you fall into one of the groups below, you may want to reconsider how often—or whether—you eat eggplant.
1. 🩸 People With Anemia or Iron Deficiency
Eggplant contains compounds called anthocyanins, especially in the skin, which give it its deep purple color. While these are powerful antioxidants, they can also bind to iron molecules and inhibit the body’s ability to absorb iron from food.
-
❗ This can be problematic for individuals suffering from anemia or iron deficiency, as their iron absorption is already compromised.
-
Additionally, anthocyanins may reduce the absorption of zinc and copper, two other essential trace minerals for immune and metabolic health.
👉 Better Alternatives: People with iron deficiency should prioritize iron-rich foods like red meat, organ meats, lentils, and leafy greens combined with vitamin C-rich foods to enhance iron absorption.
2. 🤢 People With Sensitive Stomachs or Digestive Issues
Eggplant has a naturally "cooling" nature in traditional medicine systems like Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine. While cooling foods can be soothing in small amounts, consuming too much eggplant can irritate the stomach and may lead to:
-
Bloating
-
Abdominal pain
-
Loose stools or diarrhea
This makes it less suitable for people with sensitive digestive systems, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or chronic gastritis.
👉 Tip: If you have a delicate digestive system, limit your portion size or opt for well-cooked eggplant rather than raw or undercooked forms.
3. 🧠 People With Weak Digestion or Slow Metabolism
Eggplant has a tough, fibrous skin and a spongy interior that can soak up oil during cooking, making it heavier on the digestive system.
For those with:
-
Low digestive fire (slow metabolism)
-
Post-illness recovery
-
Or chronic digestive sluggishness
…eggplant can be difficult to break down and may cause discomfort, especially if eaten fried or heavily seasoned.
👉 How to Reduce Discomfort:
-
Peel the eggplant before cooking
-
Bake or steam instead of frying
-
Combine with warming spices like ginger, cumin, or black pepper to aid digestion
4. 🧬 People With Kidney Disease or Prone to Kidney Stones
Eggplants contain high levels of oxalates, which are naturally occurring compounds that can contribute to the formation of kidney stones, particularly calcium oxalate stones.
-
For individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD), hyperoxaluria, or a history of kidney stones, consuming high-oxalate foods like eggplant can increase the risk of recurrence.
👉 Note: It’s not just eggplant—other high-oxalate foods include spinach, beets, rhubarb, and nuts. If you have kidney concerns, speak with a nephrologist or registered dietitian to personalize your diet.
🔍 Final Thoughts
Eggplant is a versatile and nutrient-dense vegetable for most people, but it’s not ideal for everyone. If you belong to one of the following groups:
-
Have anemia or iron deficiency
-
Suffer from digestive sensitivity
-
Experience weak digestion
-
Deal with kidney issues or kidney stones
…it’s wise to either limit your intake or prepare it carefully to reduce potential side effects.
✅ When in doubt, consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine the best dietary choices for your unique health needs.
Would you like this turned into a social media post, infographic, or printable handout? Let me know!
News in the same category


3 Common Mistakes When Using Plastic Wrap That Can Cause Cancer and Are Often Made by Many People

What Do Vertical Nail Ridges Mean After 40

What Your Favorite Ice Cream Flavor Says About You

9 super effective 'anti-cluster' foods that help increase outstanding resistance

Drinking honey in the morning is good for digestion, but drinking it at 3 o'clock in the morning detoxifies the liver, making it twice as effective

Put this thing in a lemon and put it in the corner of the house. Once the mosquitoes go away, they won't come back

The Mystery of the Milk Bottle Dent

Easy Trick Will Defrost Your Car Window in Seconds

Drink 1 of these 5 drinks every morning and cancer will stay away 👇👇

Red beetroot: "Miracle drug" that cures many diseases but not everyone knows 👇👇

The refrigerator gasket is moldy, use this to clean it, it will be clean in just 5 minutes

How to make chicken mixed with Vietnamese coriander that the whole family will love

The fruit that grows in gardens and is rarely eaten turns out to be an autumn 'miracle drug', better than ginseng and bird's nest.

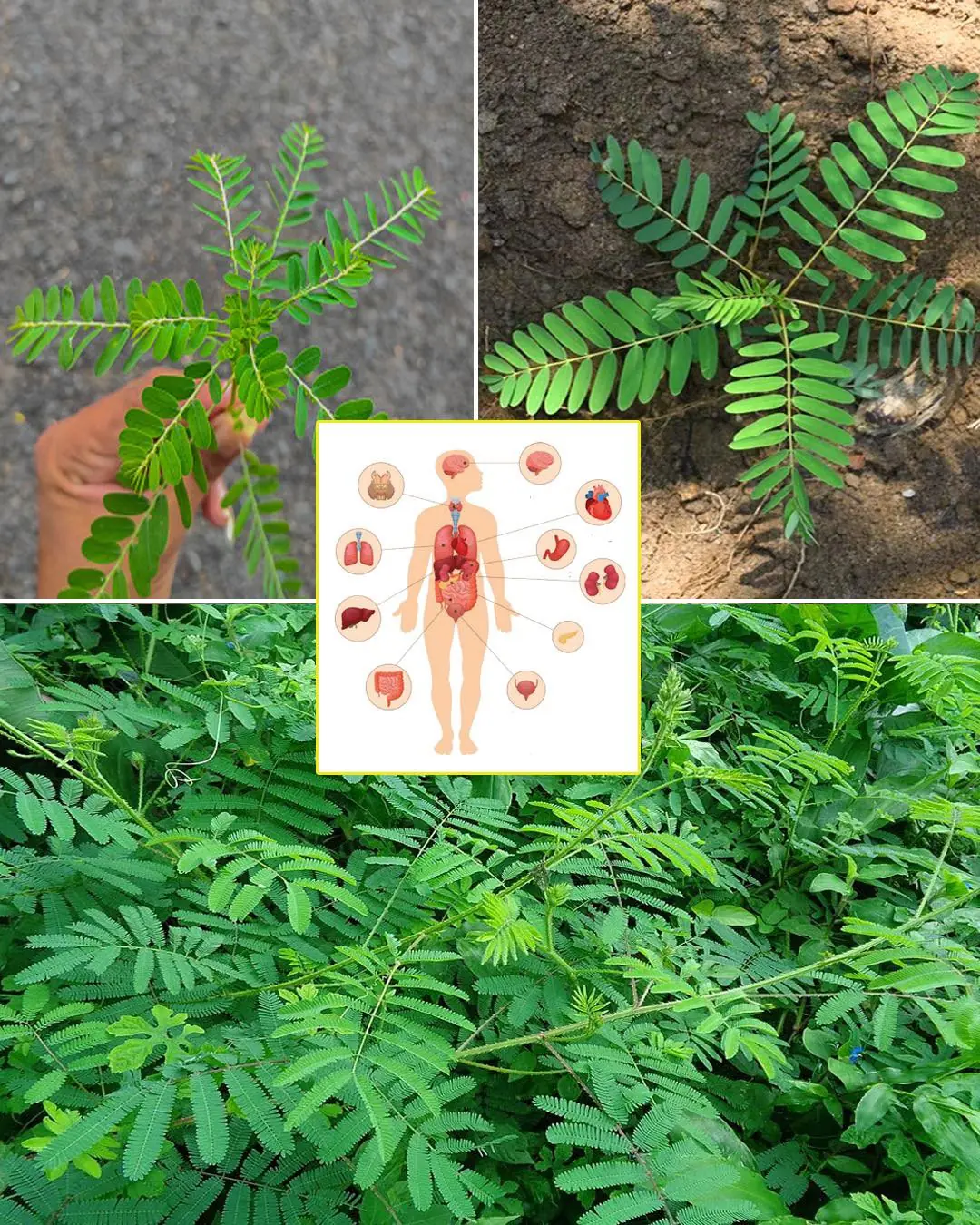
It's been a long time since I've seen this plant. It has good effects but is hard to find.

5 types of water good for your kidneys: Especially the first type, it's free and the more you drink it, the longer you live.

How to wash hair with betel leaf water helps reduce hair loss and makes new hair grow continuously

How to grow papaya in pots, fruit is heavy, big and sweet

Save millions of electricity bills every year by knowing how to clean this part of the rice cooker
News Post

Growing Wildflowers: A Mother’s Journey Through the Chaos
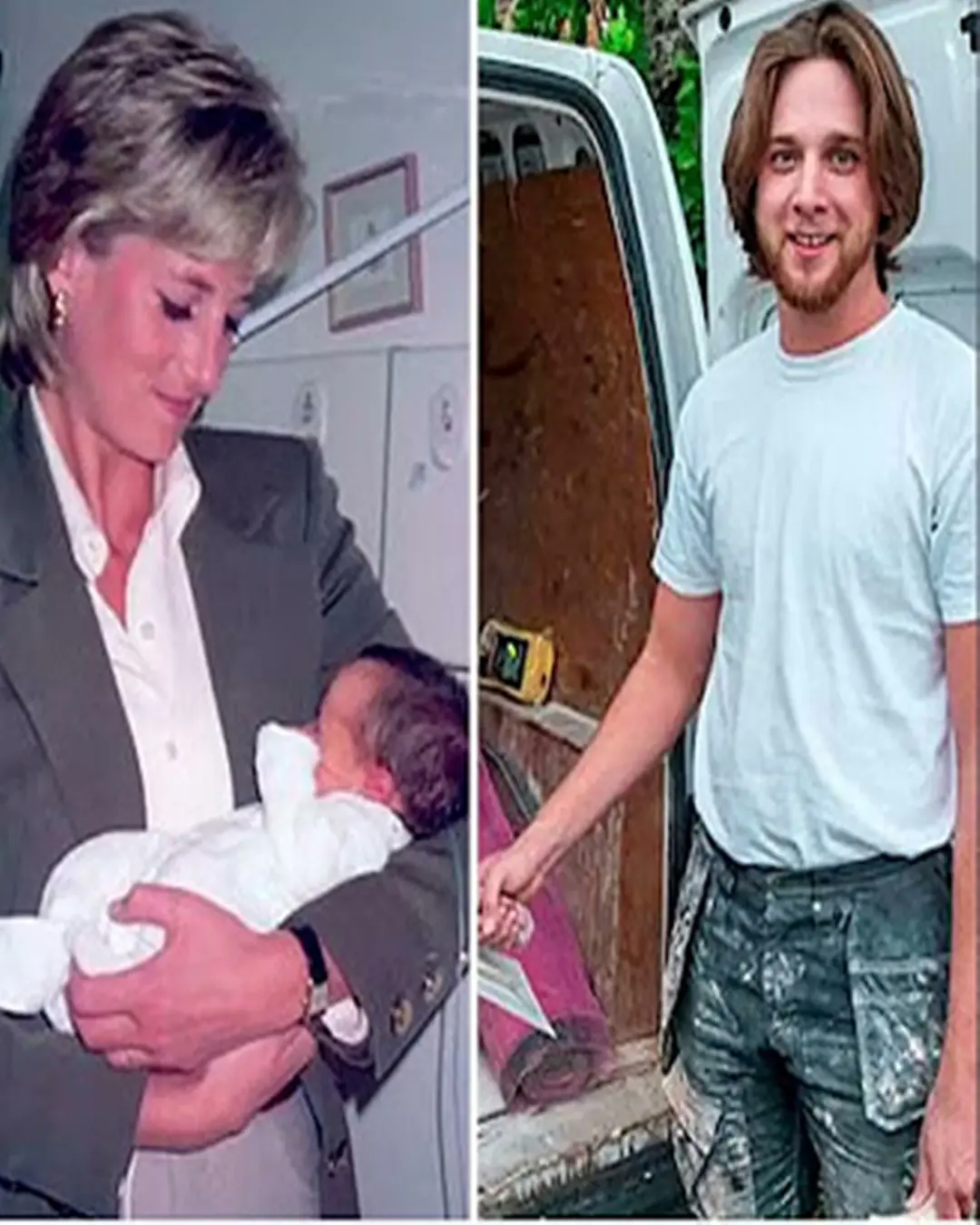

The Baby in Princess Diana’s Arms
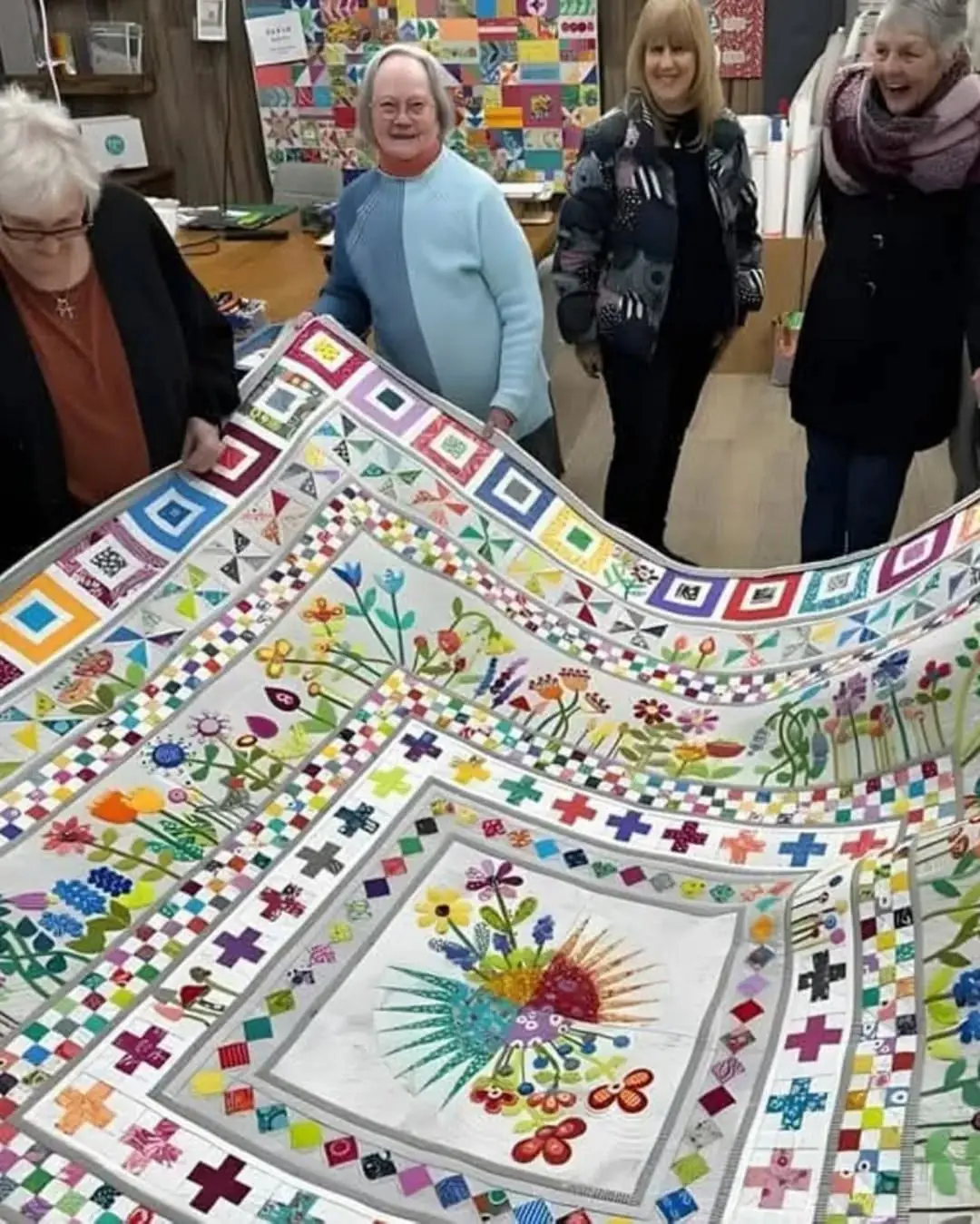

A Lifetime in Bloom: Lois Shows Us What Passion Truly Grows
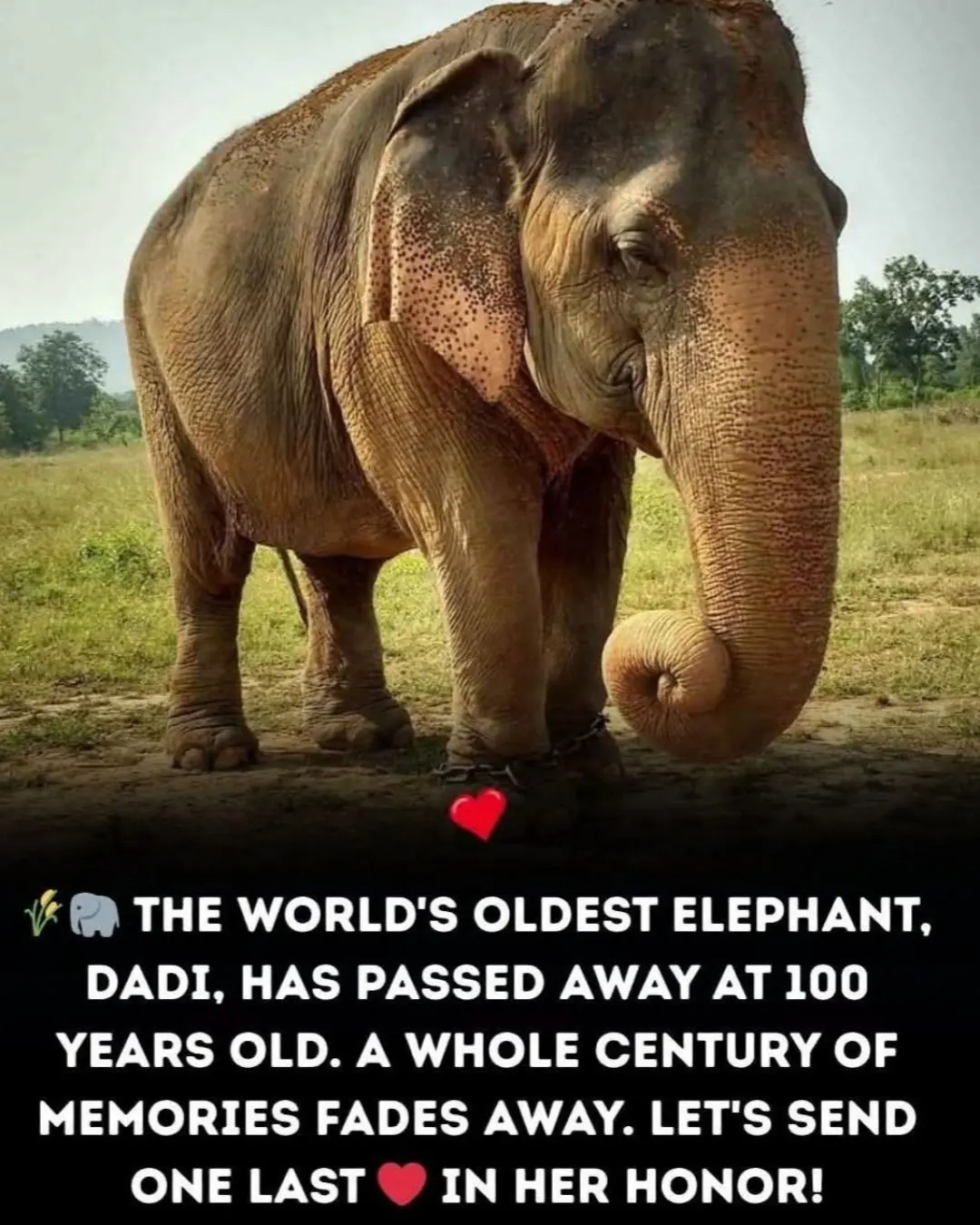

Farewell to a Giant Soul: Vatsala the Elephant Passes at 100
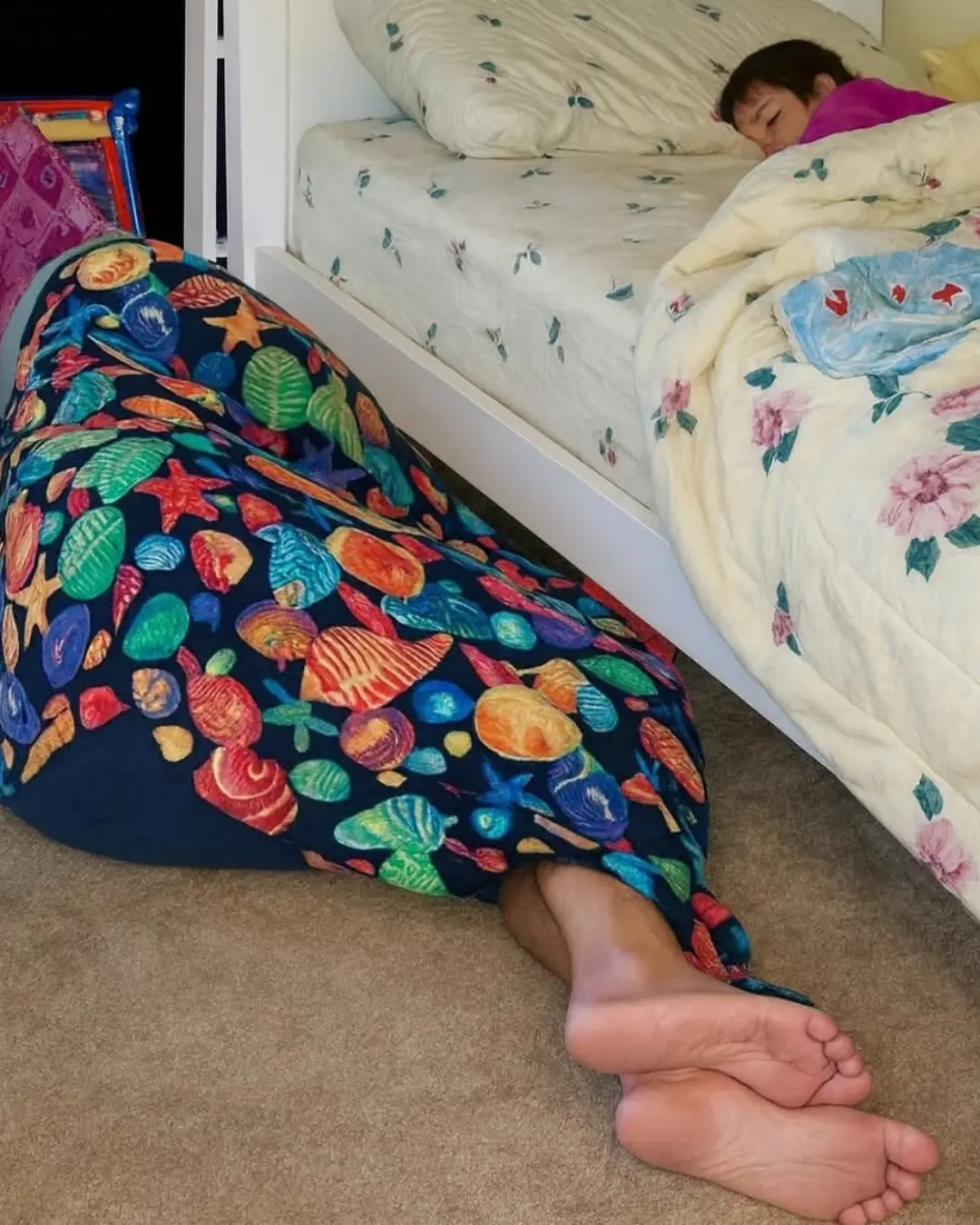

Keeping the Monsters Away: The Quiet Heroism of Foster Parents
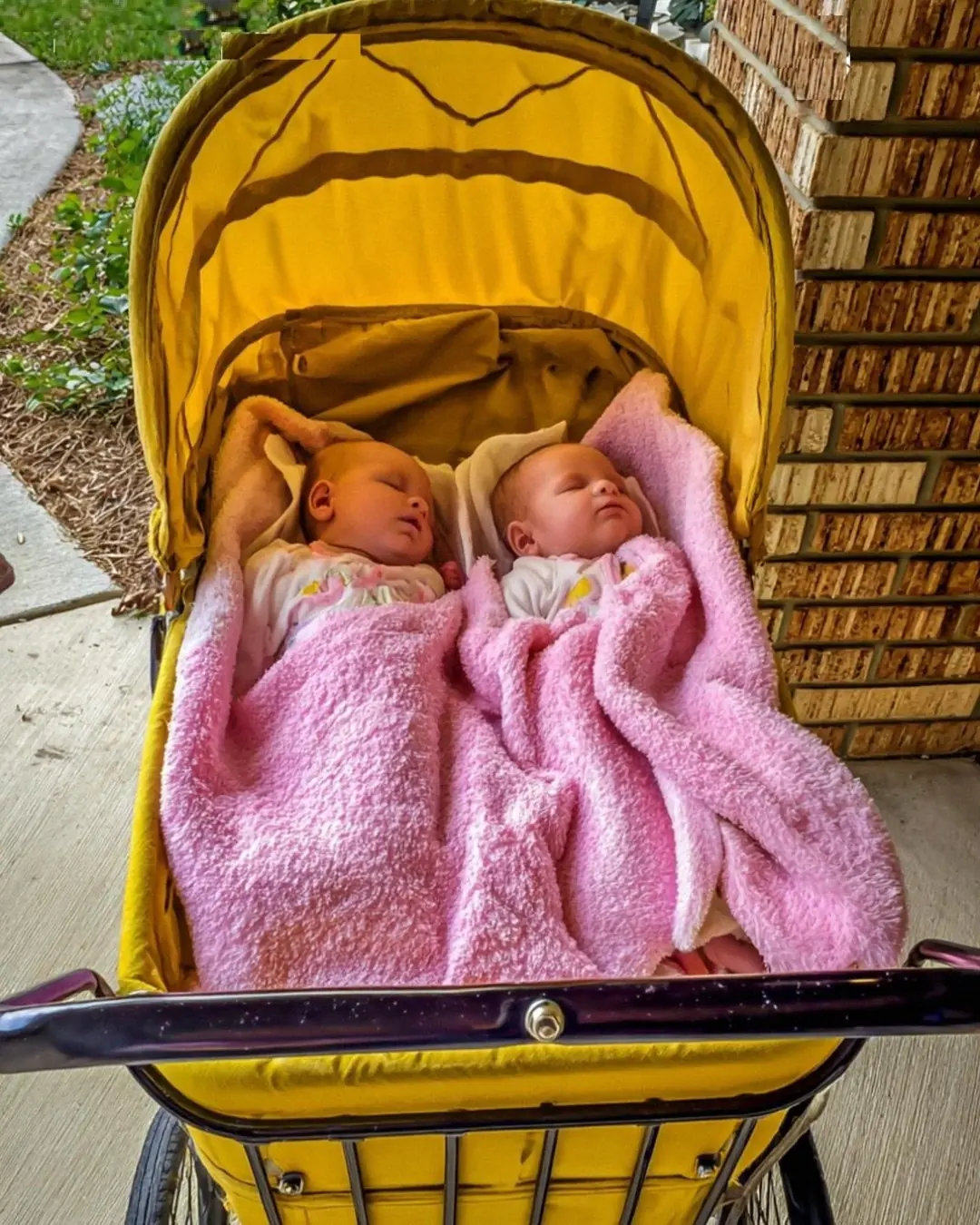

From Sidewalk to Forever: A Daughter’s Choice That Changed Everything
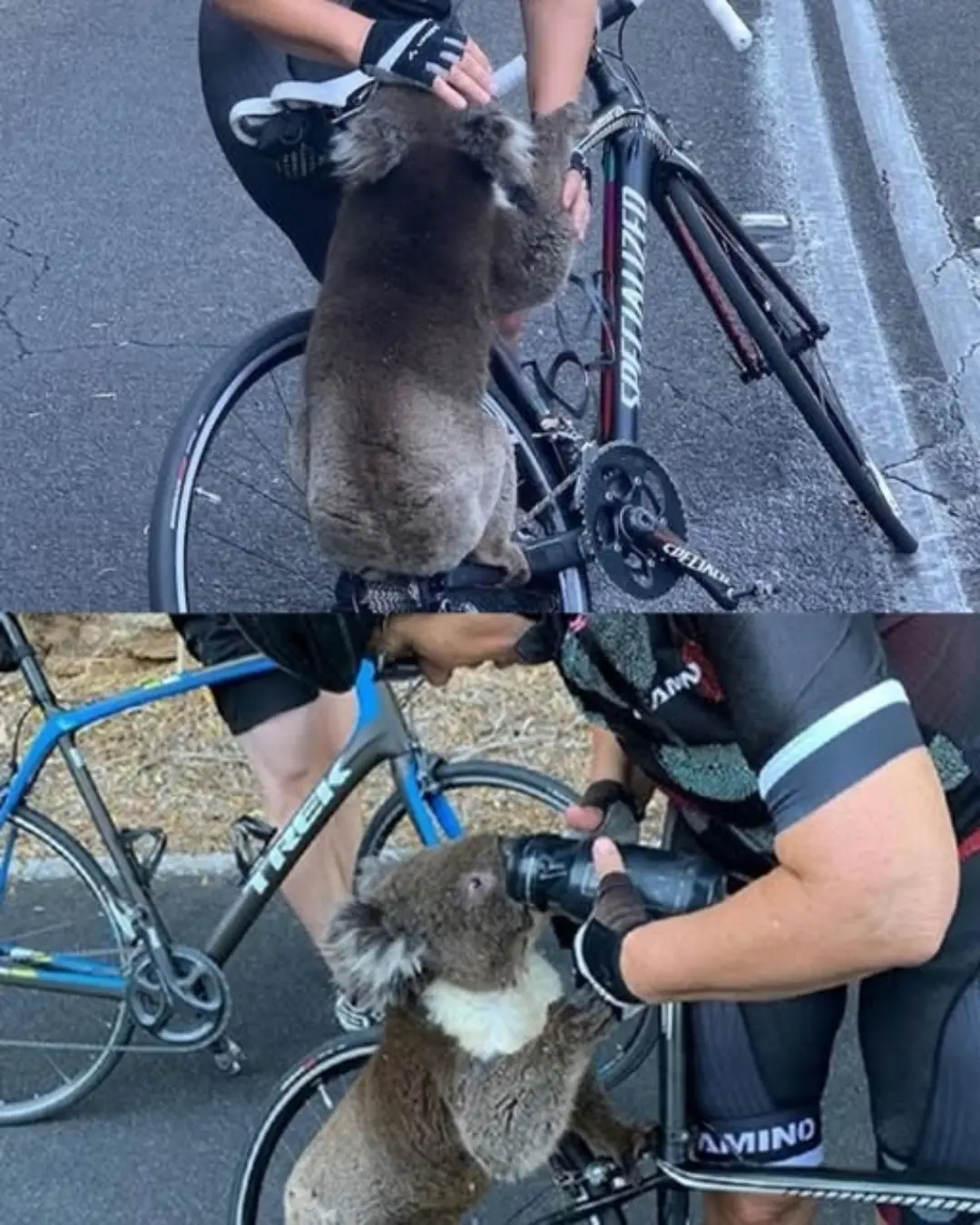

A Thirst for Life: Cyclists Halt Ride to Save Parched Koala in Australia’s Heatwave
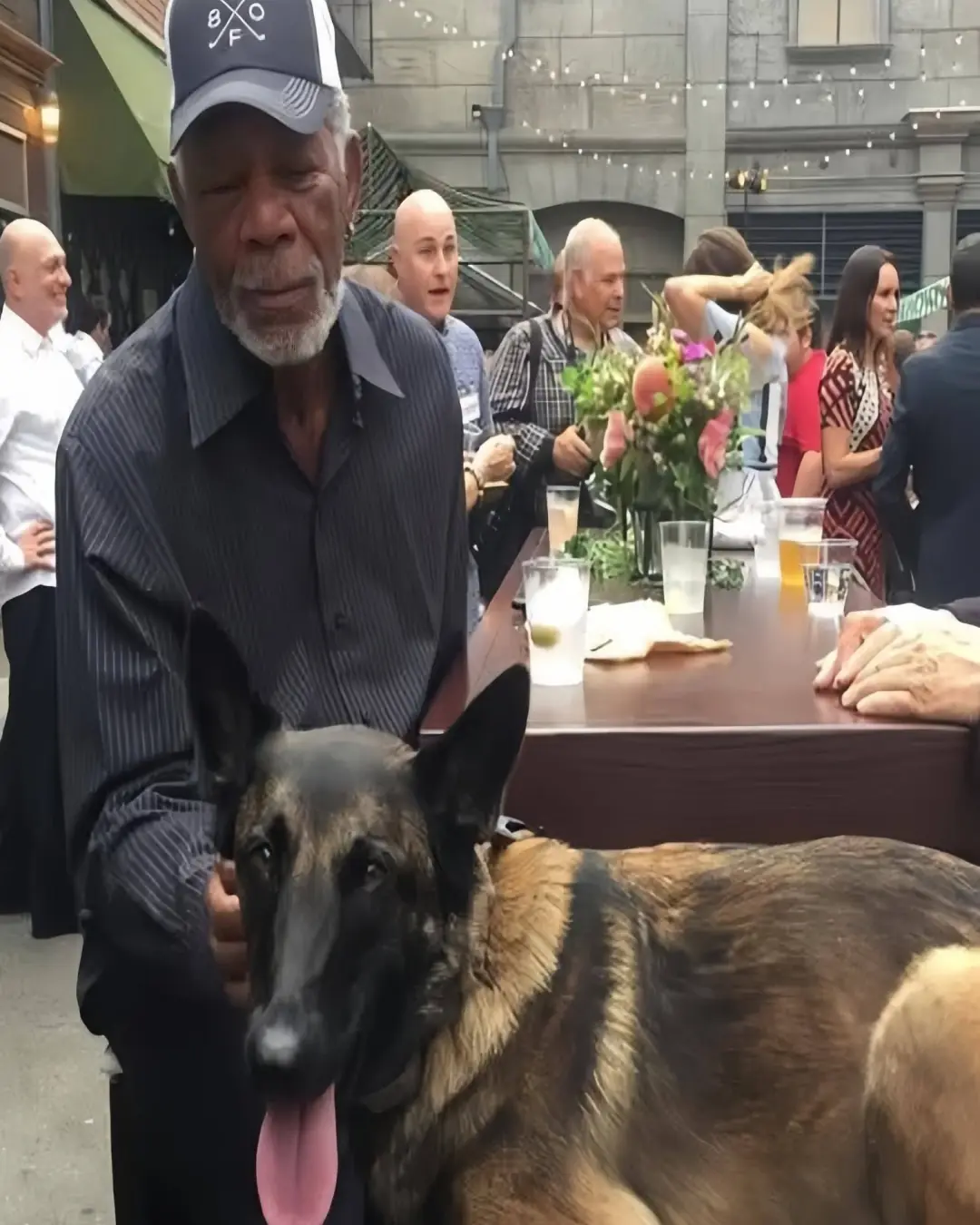

An Actor’s Greatest Role: Morgan Freeman Becomes a Guardian of Strays
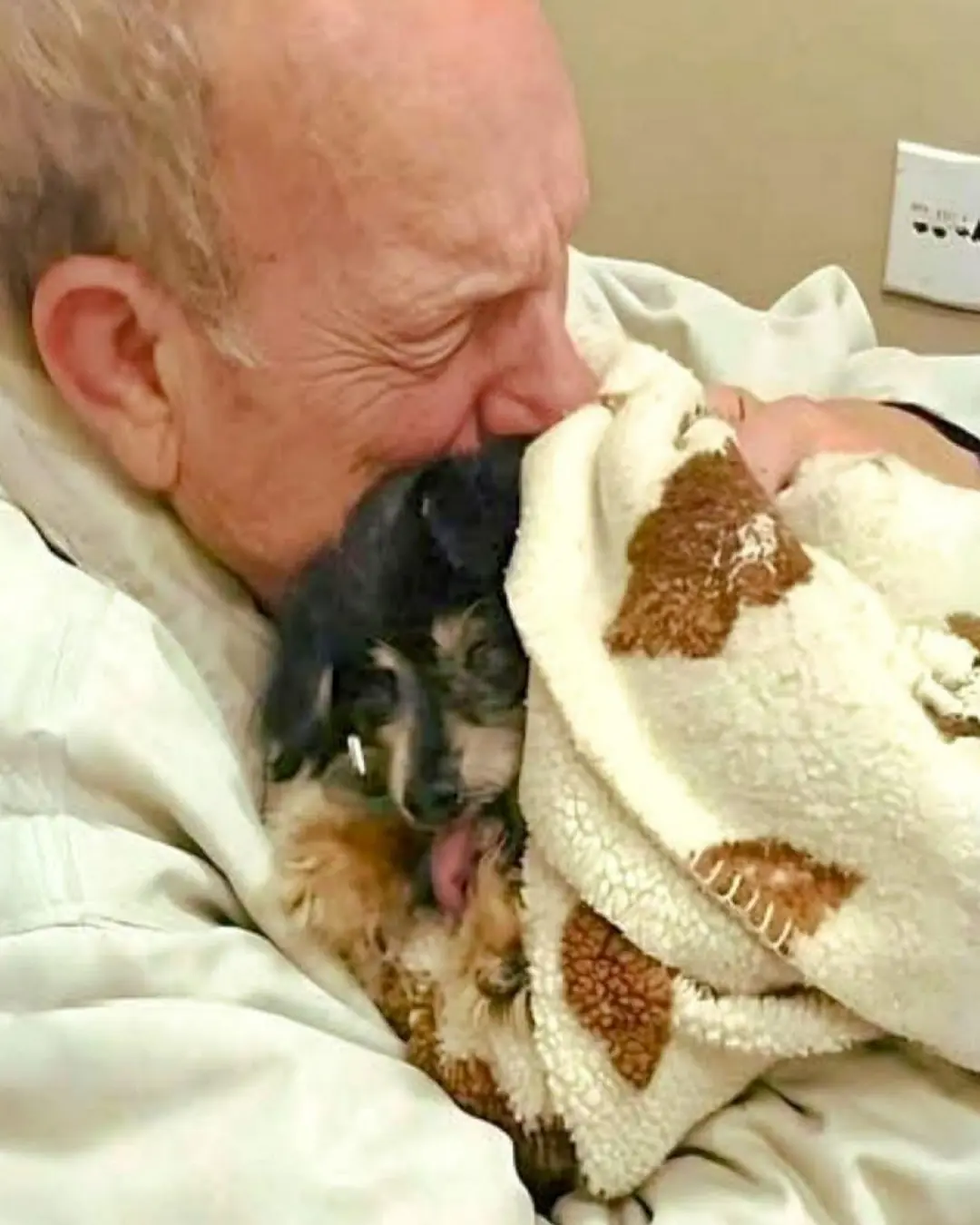

When a Celebration Became a Goodbye: A Daughter’s Farewell to Her Faithful Companion
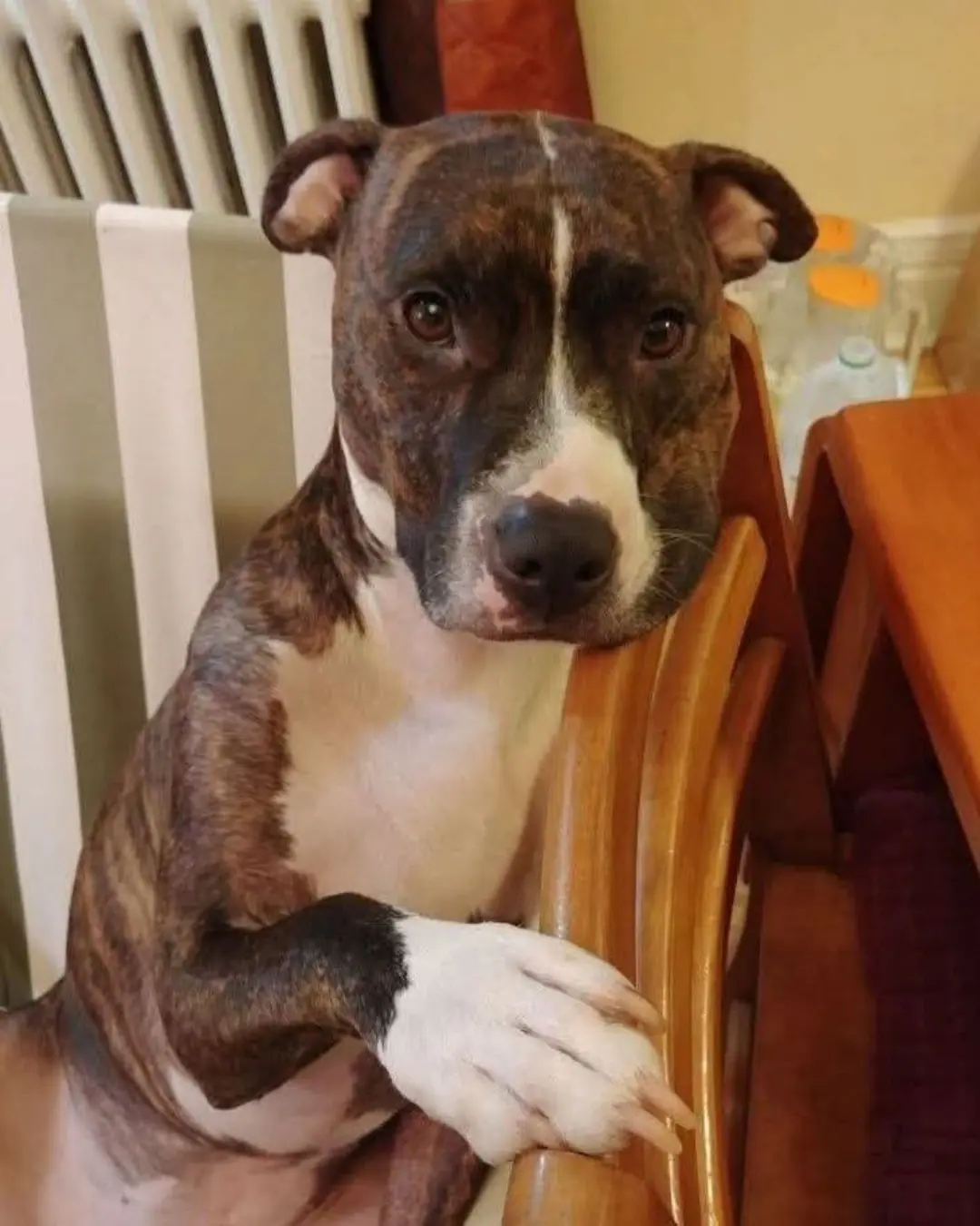

Bella the Hero: How a Pit Bull’s Loyalty Saved a Life

No Matter How Dirty You Are, Absolutely AVOID These 7 “Dangerous Hours” When Washing Your Hair to Prevent Stroke, Sudden Illness, or Hospitalization Without Warning

3 Common Mistakes When Using Plastic Wrap That Can Cause Cancer and Are Often Made by Many People
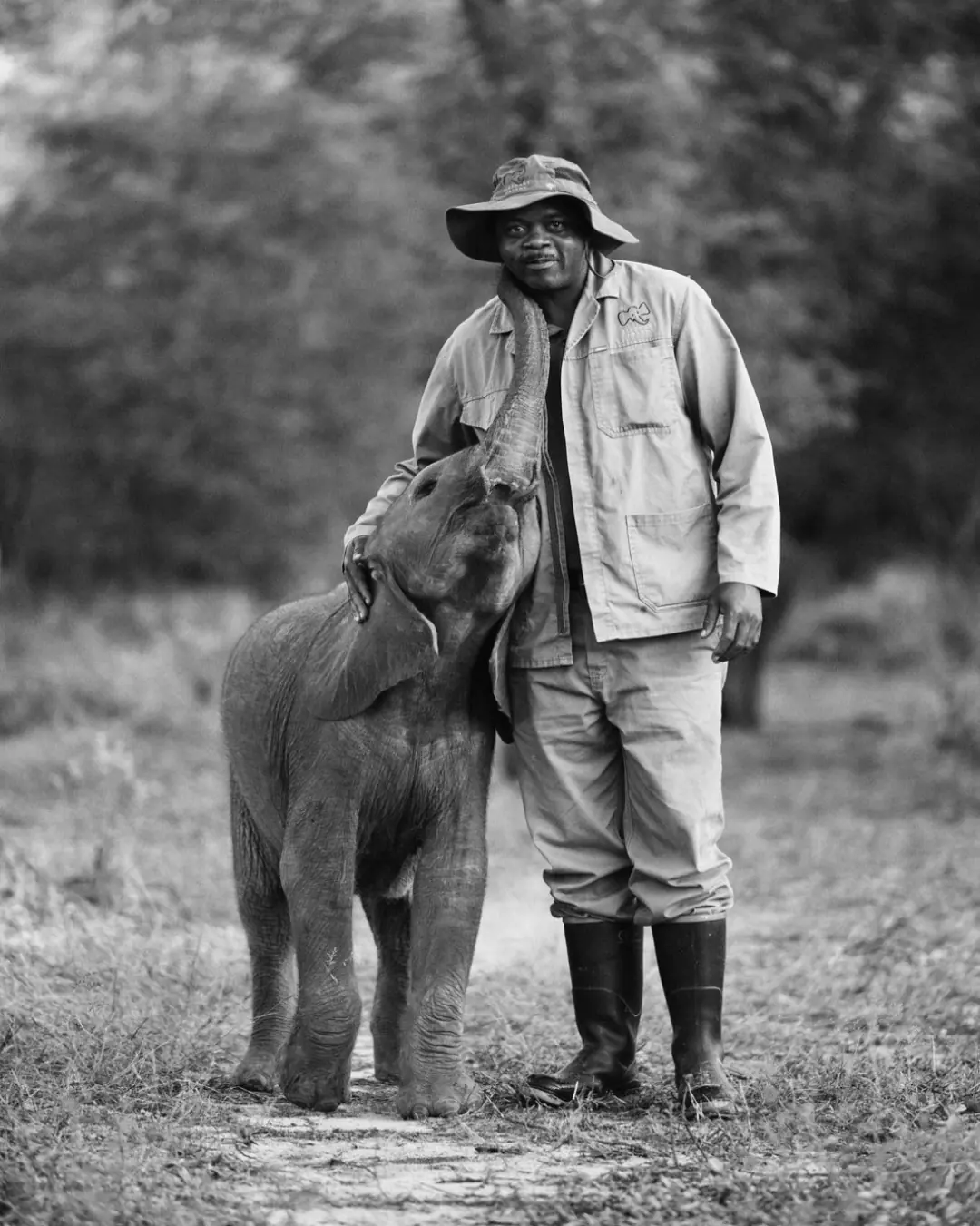

A Kiss from Joy: The Language of Love Between Elephants and Humans

What Do Vertical Nail Ridges Mean After 40
A Brave Fight for Life: Kuba’s Battle Against Ewing’s Sarcoma
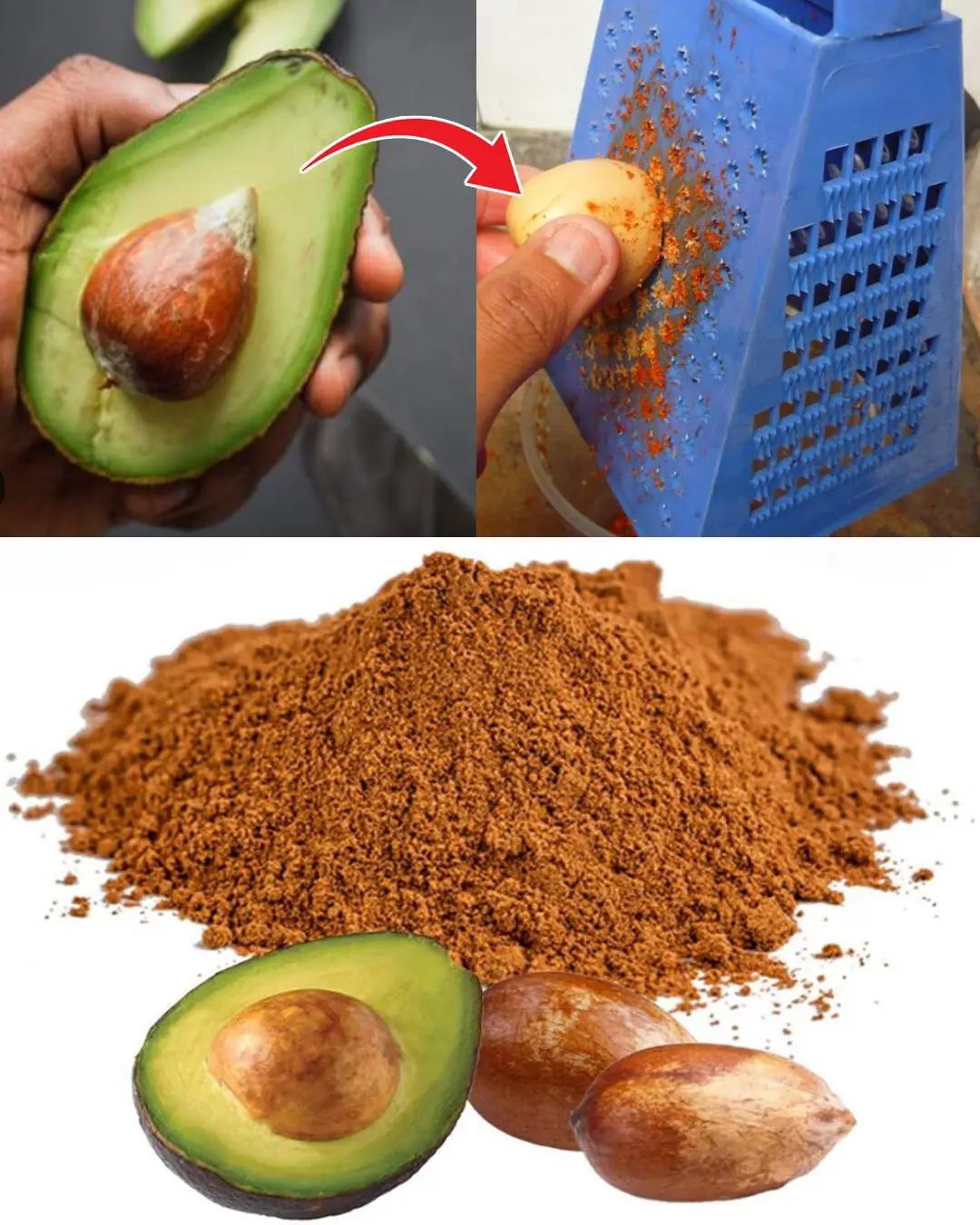

Avocado Seeds Benefits: 7 Reasons to use them
9 Signs You’re Actually Going Through Menopause (Even If You Didn’t Realize It)
Morning Detox Elixir: Olive Oil, Lemon & Ginger – The Natural Cleanse You Need Daily
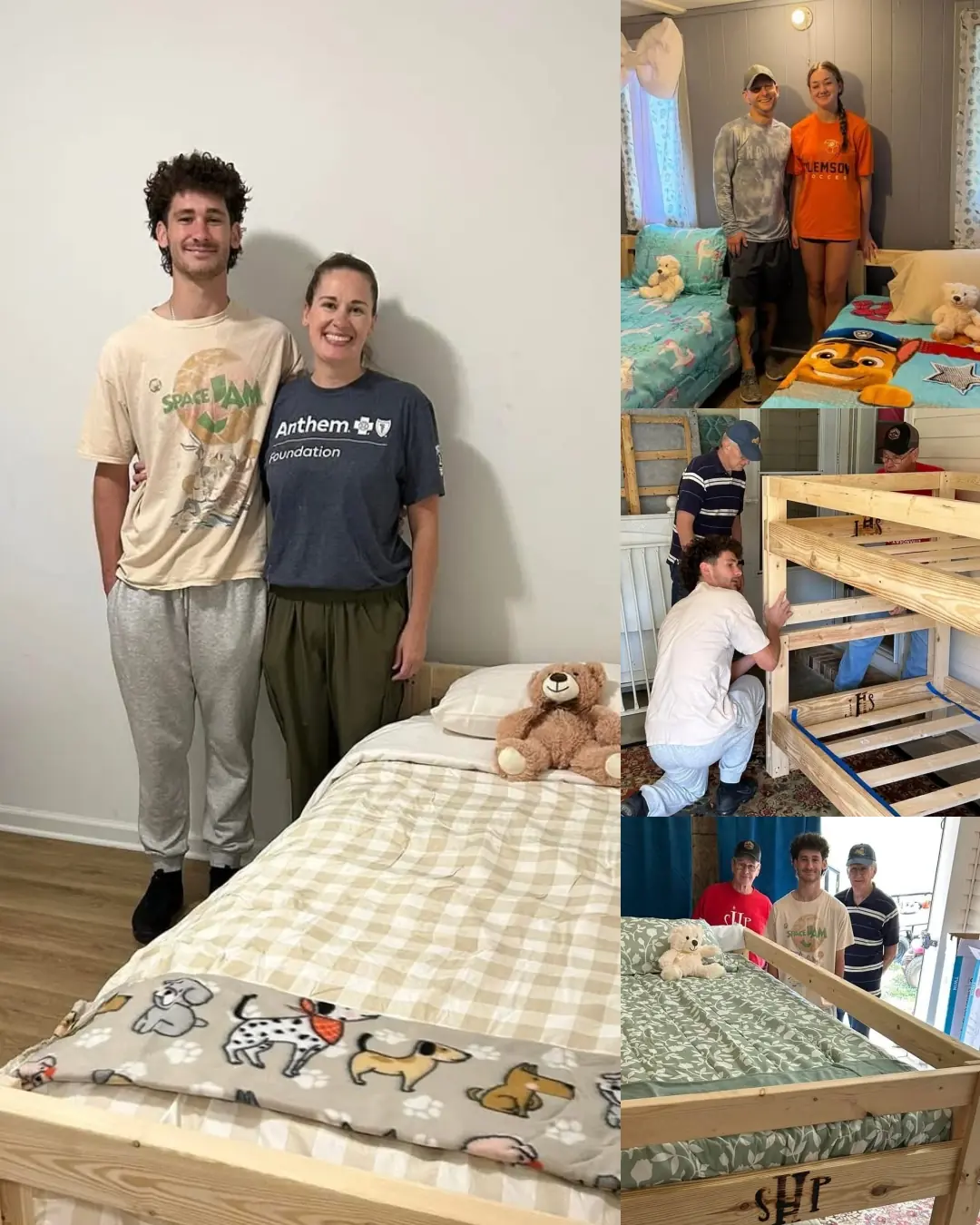

Nine Children in Dawsonville Get the Gift of a Bed, Comfort, and Peaceful Sleep
