
Groundbreaking Nanoparticle Technology Reverses Parkinson’s Disease in Stunning Study
In a remarkable leap forward for medical science, researchers have developed a nanoparticle-based therapy that has shown the potential to reverse the effects of Parkinson’s disease in laboratory studies. This revolutionary technology could represent a turning point in the treatment of one of the world’s most challenging neurodegenerative disorders.
Parkinson’s disease affects over 10 million people globally, with symptoms ranging from tremors and stiffness to severe difficulties with movement and speech. It is caused by the gradual death of dopaminergic neurons in the brain—nerve cells that produce dopamine, a chemical crucial for coordinating movement. Current treatments focus on managing symptoms through medications like Levodopa, but these do not halt or reverse the progression of the disease. Until now, a true cure has remained elusive.
The new breakthrough comes from a collaborative team of scientists from several leading universities, who developed a nanoparticle delivery system capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier—a protective shield that prevents many drugs from reaching the brain. This has long been a significant obstacle in treating neurological conditions. Using specially engineered biodegradable nanoparticles, the researchers were able to transport a therapeutic compound directly to the damaged areas of the brain in mice models of Parkinson’s disease.
What makes this study so groundbreaking is the ability of the nanoparticles not only to stop the progression of Parkinson’s disease but actually to reverse its symptoms. After treatment, the mice showed significant recovery in motor function, along with restored dopamine levels and improved brain activity. In essence, the damaged neurons appeared to regenerate or reactivate, something previously thought to be nearly impossible in adult brains.
According to the lead author of the study, published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, the therapy “represents a paradigm shift in how we approach neurodegenerative diseases.” Unlike traditional drugs, which often struggle to reach the brain and can have widespread side effects, the nanoparticle method allows for targeted, precise treatment. The particles can be designed to release their payload slowly and only in specific brain regions, greatly increasing their effectiveness and reducing the risk of harmful side effects.
While the research is still in the preclinical stage, the results have sparked global excitement and hope. Human trials are already being planned, with researchers cautiously optimistic that similar effects can be observed in people. If successful, this technology could not only help Parkinson’s patients but also pave the way for treating Alzheimer’s disease, ALS, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological conditions that have long resisted effective treatment.
However, experts warn that there are still many challenges ahead. Scaling up the production of these nanoparticles, ensuring long-term safety, and confirming their effectiveness in human brains will require time and rigorous testing. Nevertheless, the potential is undeniable.
This groundbreaking study illustrates the enormous possibilities that nanotechnology holds for medicine. What once seemed like science fiction—a cure for a chronic brain disease—may now be within reach. As scientists continue to explore this new frontier, millions of Parkinson’s patients around the world could one day benefit from a treatment that not only manages their symptoms but truly heals their brains. The future of neuroscience has never looked more promising.
News in the same category

A recent study has uncovered a key switch in aging—and it all comes down to a structure inside your cells called the nucleolus

ScienceScientists Say Viral Infections Could Be The Hidden Cause Of Alzheimer’s — 30 Years Of Research Now Validated
🧄🌿 Natural Remedy for Leg Pain, Rheumatism, Varicose Veins & Arthritis with Cloves and Garlic

White Clover (Trifolium repens): 15 Benefits and Homemade Uses
Breakthrough Protein Combo Could Heal Heart Damage and Regenerate Organs
Head Injuries May Reactivate Dormant Viruses and Trigger Alzheimer’s-Like Brain Damage
How Blood Production Changes After 70: New Research Reveals a Surprising Shift
What Is Acid Reflux? Causes, Symptoms, and How to Prevent GERD

AI and Eye Scans: A Breakthrough in Fast, Accurate ADHD Diagnosis
Early Signs of Heart Disease: What Chest Pain, Shortness of Breath, and Swollen Legs Could Mean

This Psychedelic Root from Brazil May Be Able to Treat Depression

Researchers Reveal How Long It Takes To Grow Muscle When Lifting Weights

Waking Up After 6 Hours of Sleep? Here's Why—and Whether It’s Enough
How Your Gut Bacteria Influence Your Mood, Thoughts, and Mental Health

The Hidden Cost of Anger: How One Minute of Rage Can Weaken Your Immune System for Hours

7 Benefits of Papaya Seeds & How to Consume Them Correctly

Cinnamon Tea: A Timeless Beverage for Health and Wellness
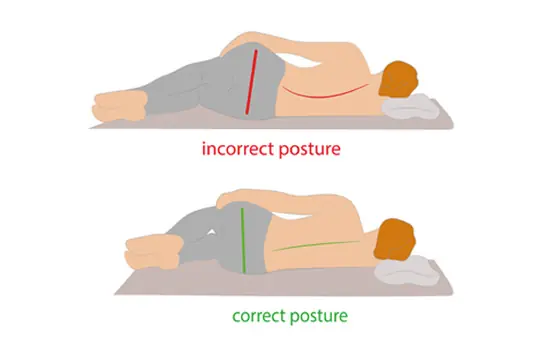
How Sleeping on Your Left Side Can Boost Your Health, According to Science
News Post

Lung Cleansing with a Powerful Natural Garlic Juice

A recent study has uncovered a key switch in aging—and it all comes down to a structure inside your cells called the nucleolus

ScienceScientists Say Viral Infections Could Be The Hidden Cause Of Alzheimer’s — 30 Years Of Research Now Validated

Greece Rocked By Massive Earthquake As Tsunami Warning Sparks Panic

Sun Unleashes Monster Flare As Scientists Say Earth Could Be Hit By Massive Solar Storm Tomorrow

🧄🌿 Natural Remedy for Leg Pain, Rheumatism, Varicose Veins & Arthritis with Cloves and Garlic

Modern House Fires Burn Faster: Why You May Have Only 3 Minutes to Escape

White Clover (Trifolium repens): 15 Benefits and Homemade Uses

A Mom of 7 Demanded My Deaf Grandpa Get Out of the Elevator—So I Brought Her Back to Reality

Could the Sahara Desert Power the Entire World with Solar Energy?

Breakthrough Protein Combo Could Heal Heart Damage and Regenerate Organs

Head Injuries May Reactivate Dormant Viruses and Trigger Alzheimer’s-Like Brain Damage

How Blood Production Changes After 70: New Research Reveals a Surprising Shift

My Ex-husband Got Our House, Car and All Our Money After Divorce – I Laughed Because That Was Exactly What I Planned

My Husband Cheated on Me With Secretary, Then Karma Crushed Him Back

My Husband Didn't Meet Me at the Hospital Discharge with Our Newborn – When I Found Out His Reason, I Went Pale

Mom of Quintuplets Can’t Pay For Groceries, Voice behind Says, ‘Your Bill Is Already Covered’

Drunk Bees? How Fermented Nectar Affects Honeybees in Australia
How Small Earth Is in the Universe—And Why That Should Inspire Us
