New Discovery: Protein AP2A1 May Hold the Key to Reversing Aging at the Cellular Level
New Discovery: Protein AP2A1 May Hold the Key to Reversing Aging at the Cellular Level
A groundbreaking new study has uncovered a protein that could revolutionize our understanding of aging — and potentially how we fight it. Scientists have identified AP2A1, a protein that plays a critical role in how cells age and, more importantly, how they might reverse the aging process.
As we age, many of the cells in our body begin to function less efficiently. One common sign of cellular aging is an increase in cell size. These enlarged, non-functioning cells contribute to many age-related diseases, but until now, the reason behind this change was poorly understood.
AP2A1 and Its Surprising Role in Aging
The researchers focused on human fibroblast cells, which are commonly used in aging studies because they mirror many of the changes seen in older cells. They found that AP2A1 activity was significantly higher in aging cells, especially in parts of the cell that help maintain its structure and shape.
What’s more intriguing is what happened when scientists reduced AP2A1 levels. The aging cells began to shrink back to a more youthful size and regain function, essentially reversing some of the hallmarks of aging. Conversely, when AP2A1 levels were increased in younger cells, those cells aged faster, showing clear signs of decline.
Effects Seen Across Multiple Cell Types
This wasn’t a one-time fluke. The study found similar results in other types of cells, including those artificially aged by UV radiation or drugs. That means AP2A1’s role in aging could be much broader than previously thought.
The researchers also discovered that AP2A1 works closely with another protein called integrin β1. Integrin β1 is responsible for helping cells anchor themselves to their environment, a key part of maintaining cellular structure. The duo of AP2A1 and integrin β1 strengthens the cell’s internal support system — specifically along structures called stress fibers — allowing the cells to stay more firmly attached.
This stronger attachment may be the reason aging cells become larger, as it helps lock them in place and makes them more resistant to change.
Could Controlling AP2A1 Reverse Aging?
This discovery suggests a powerful new possibility: regulating AP2A1 levels could be a way to control or even reverse cellular aging. Unlike other theories that propose aging happens randomly, this study points to a more targeted, structural process — one that could potentially be interrupted or reversed with the right treatment.
The implications of this are enormous. If scientists can find safe ways to manipulate AP2A1, it might lead to future therapies for age-related diseases, improved cell regeneration, and even anti-aging treatments that work at the root cellular level.
Conclusion: A Promising Step Toward Anti-Aging Therapies

The discovery of the AP2A1 protein and its impact on aging cells opens the door to a new era in anti-aging research. It highlights the potential to not only slow down the aging process but possibly reverse it at the cellular level. While more research is needed, especially in live organisms, this study represents a major step forward in understanding how aging works — and how we might one day stop it.
Stay tuned — the future of anti-aging science just got a lot more exciting.
News in the same category


AVOID Bananas If You Suffer From These 5 Health Problems!

Doctors reveal how many times you should be able to swallow in 30 seconds to be 'healthy' and the results are shocking

Crockpot Sausage and Potatoes

A New Type of Drink Found to Help 'Push Back' Cancer: It’s Not Tea or Coffee

Not So Impossible Cheeseburger Pie

35-Year-Old Man’s Sore Throat Turned into Cancer After 5 Chemotherapy Sessions—Doctor Urges: Throw These 2 Things Out of Your Fridge

Eight Early Symptoms Found in 23% of Cancer Patients: Warning Signs That Should Not Be Ignored

Doctors forced to apologize after 32-year-old woman given hysterectomy to treat 'tumor on her ovary' but biopsy showed no signs of cancer

Liquid Gold Tea: A Natural Remedy for Inflammation

Caramel Apple Fudge

Mozzarella Fried Cheese Bites: Cheesy, Crunchy, and Irresistible

You are doing it all wrong. Here's how to drink 8 glasses of water each day
A new type of Artificial Intelligence can detect breast cancer 5 years before diagnosis
Why Vitamin D Is Essential for More Than Just Bone Health

Seniors: This Castor Oil + Baking Soda Trick Is Blowing Doctors’ Minds!
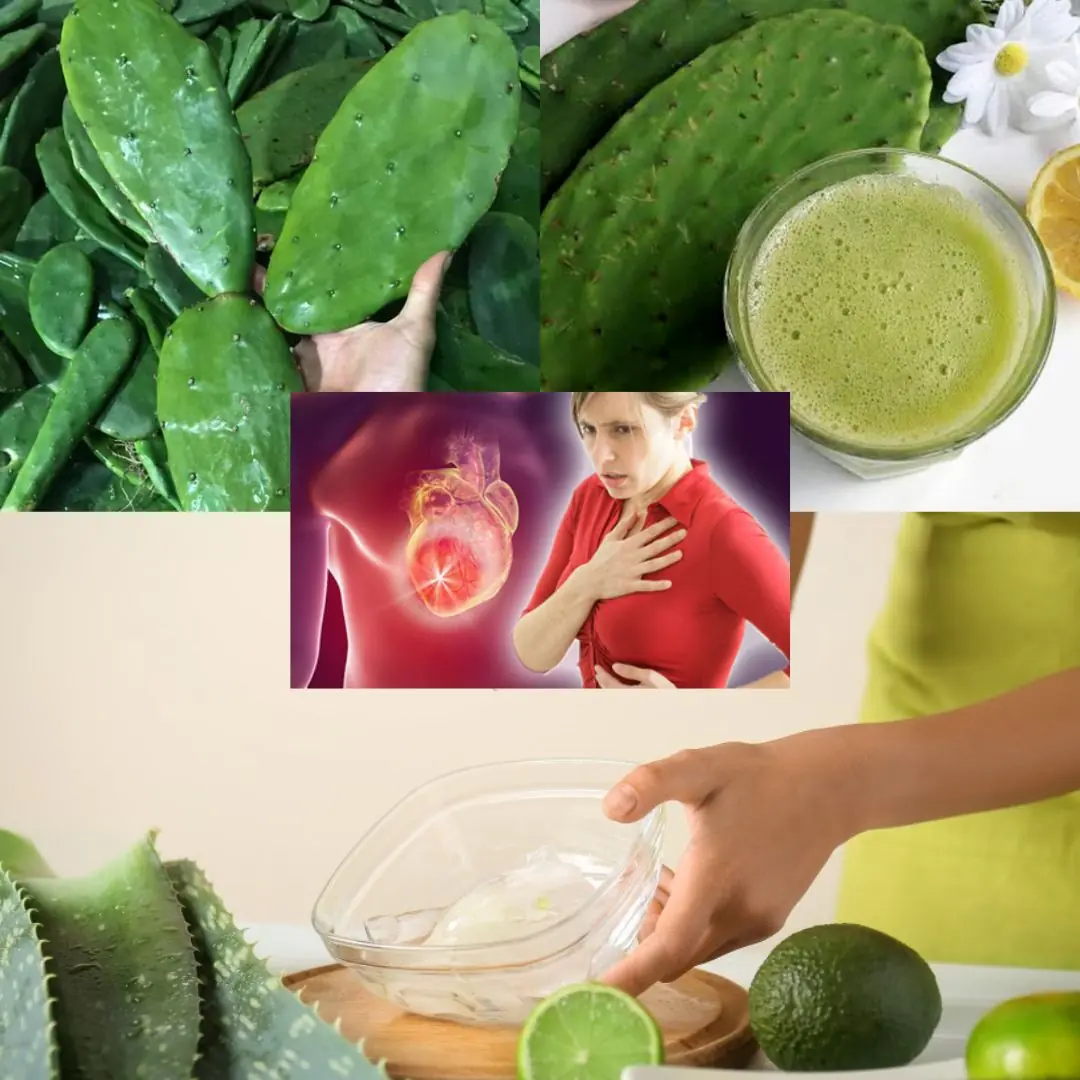

Lemon and Nopal Remedy: A Natural Boost for Your Body
65-Year-Old Man Dies at 11 PM: Doctor Warns Never to Drink These 4 Types of Beverages Before Bed – No Matter How Thirsty You Are
People at Risk of Cancer Often Show 3 Unusual Signs in the Neck – Even One Is a Health Warning
News Post

Homemade Vanilla Dessert Cream

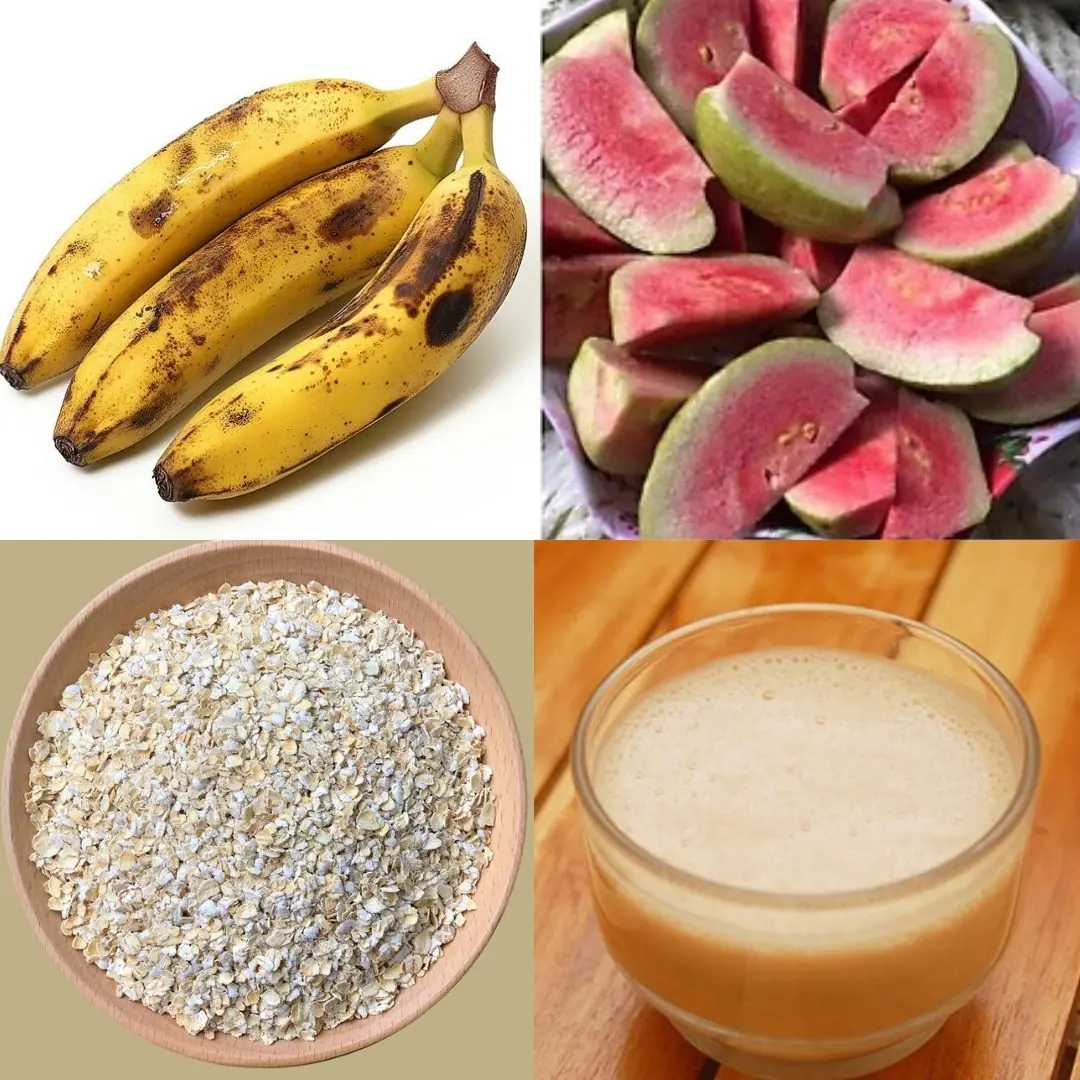
Oatmeal and Guava: A Natural Remedy for Leg Cramps, Diabetes, and High Blood Pressure

AVOID Bananas If You Suffer From These 5 Health Problems!

My Greedy In-Laws Tried to Get Rid of Our Sick Mom, but She Brilliantly Taught Them a Lesson

I Got Back from a Work Trip and Found My House Completely Empty

3 Eye-Opening Stories About Husbands Who Didn't Appreciate Their Devoted Wives – And the Important Lessons They Learn in the End

Doctors reveal how many times you should be able to swallow in 30 seconds to be 'healthy' and the results are shocking

14 Fish You Should Consider Never Eating
40+ Weird Signs That Lead To a Cancer Diagnosis

Pudding Cool Whip Frosting

NASA’s Mars Rover Uncovers Mysterious Spheres On The Planet’s Surface, Leaving Experts Baffled

Depressing find at the bottom of the Mariana Trench is a warning to the world

Crockpot Sausage and Potatoes

People Freaked Out After Spotting Creepy Hidden Face in Group Photo

A New Type of Drink Found to Help 'Push Back' Cancer: It’s Not Tea or Coffee

This One Everyday Habit Is Draining Your Electricity Bill — And No One Talks About It

Not So Impossible Cheeseburger Pie

35-Year-Old Man’s Sore Throat Turned into Cancer After 5 Chemotherapy Sessions—Doctor Urges: Throw These 2 Things Out of Your Fridge

Eight Early Symptoms Found in 23% of Cancer Patients: Warning Signs That Should Not Be Ignored
