Health 10/08/2025 19:34
Proven Inflammatory Foods to Avoid According to Science
News in the same category

Health 10/08/2025 19:26
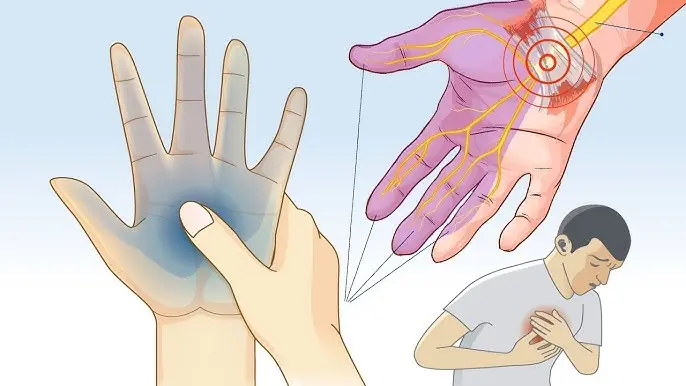
Waking Up with Numb or Tingling Hands: What It Really Means (Science Based)
Health 10/08/2025 19:19
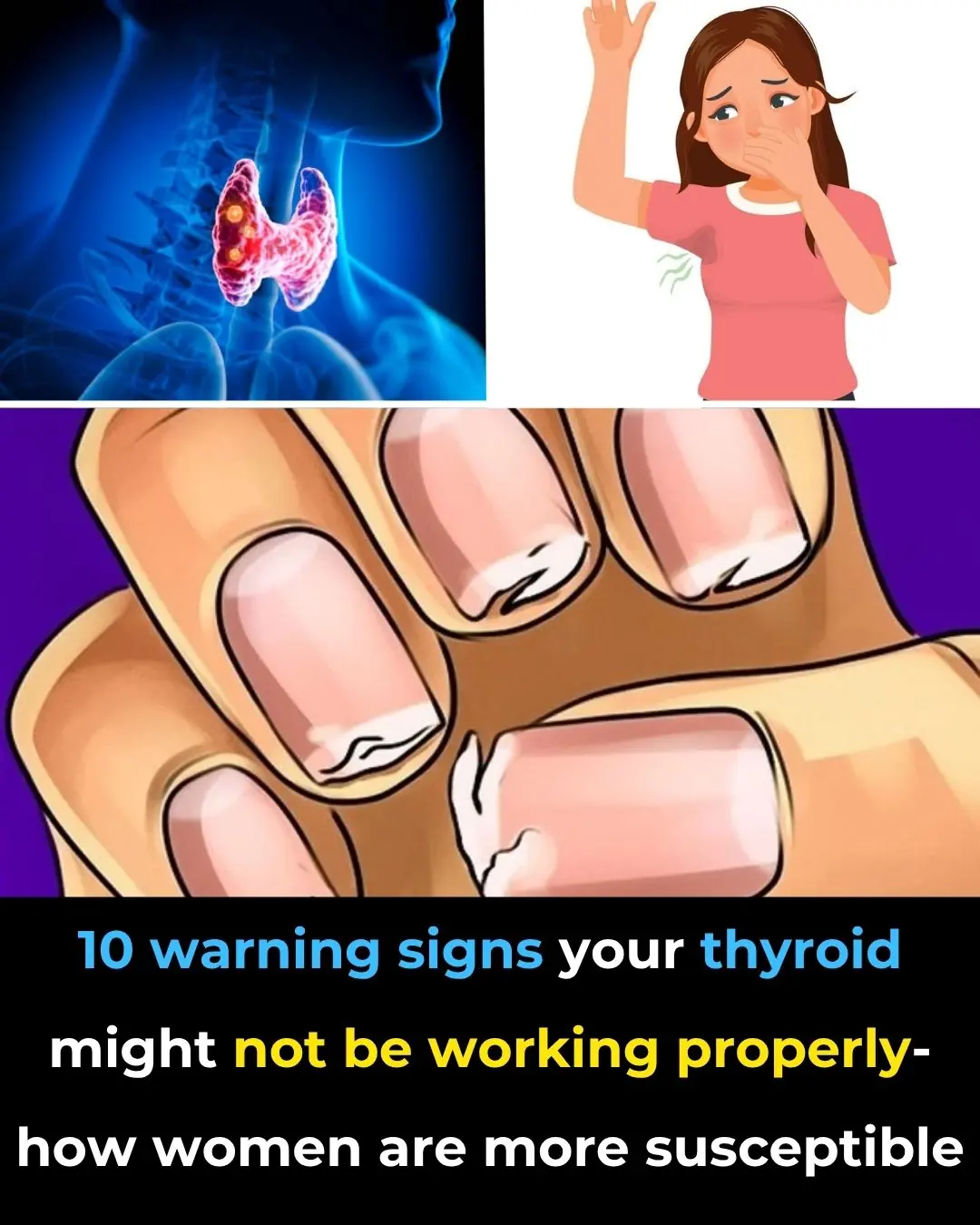
Thyroid Gland: How to Balance Its Hormones
Health 10/08/2025 15:57
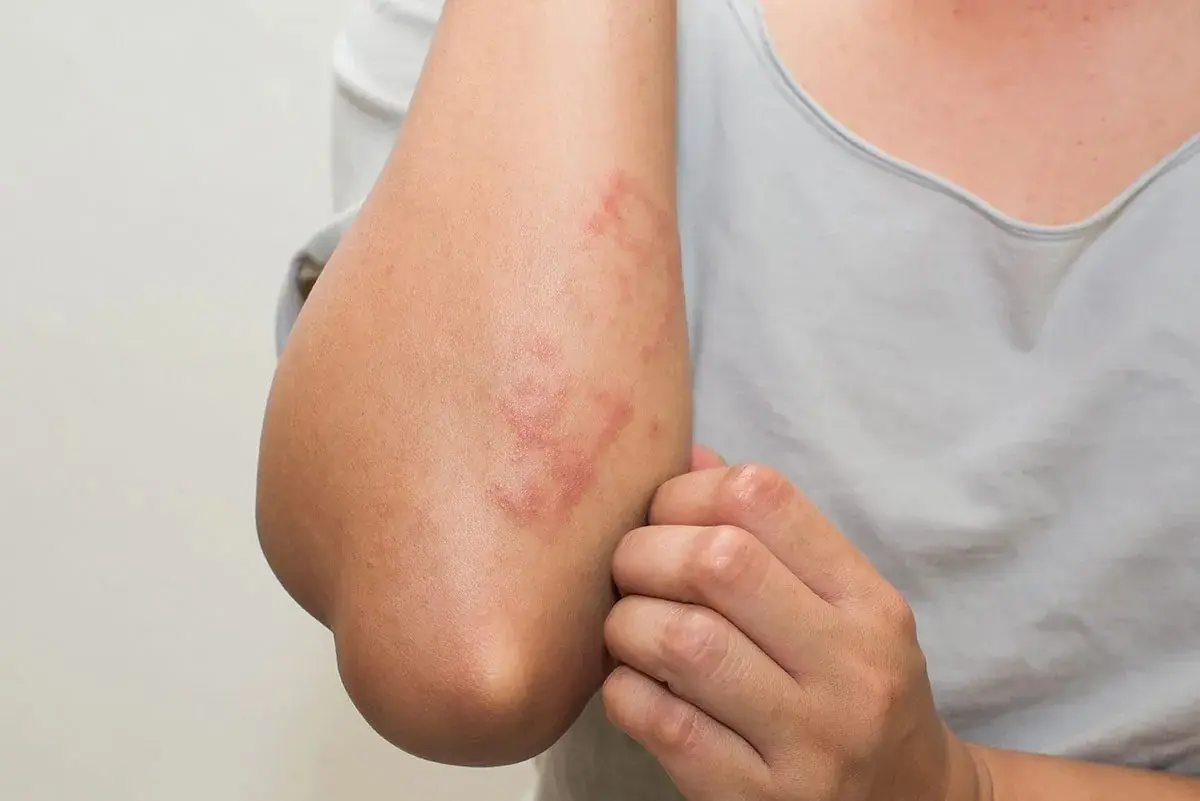
Gluten Intolerance Warning: Eczema and Other Hidden Signs Revealed
Health 10/08/2025 15:37

Your Body Is Begging You to Notice These High Blood Sugar Warnings
Health 10/08/2025 15:28
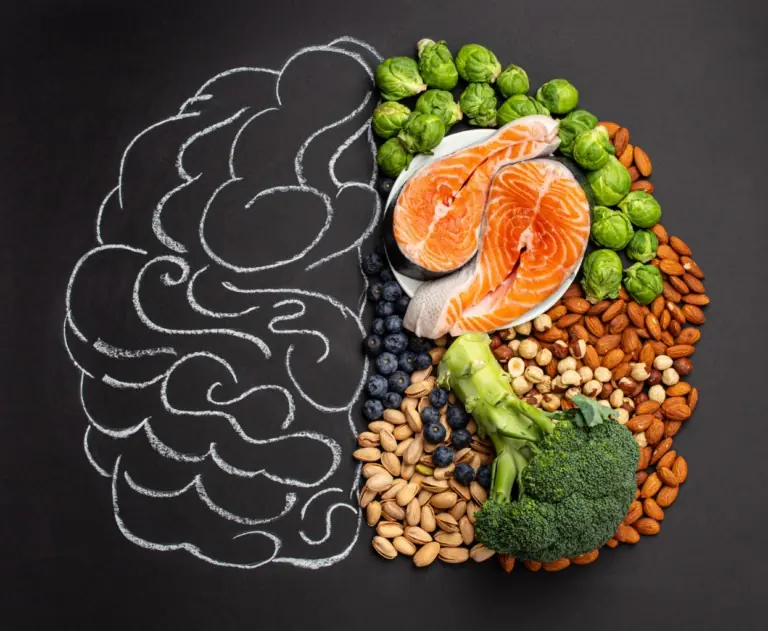

Research Reveals 12 Powerful Foods to Boost Your Brain, Improve Memory, and Make You Smarter
Health 10/08/2025 15:20

Proven Benefits of Watermelon and Watermelon Juice Including Nutrition Facts (Science Based)
Health 10/08/2025 14:35

Proven Health Benefits of Okra That Are Based On Science (Including Nutrition Facts)
Health 10/08/2025 14:30

What Causes a Heart Attack? 13 Health Conditions to Watch For
Health 10/08/2025 13:14
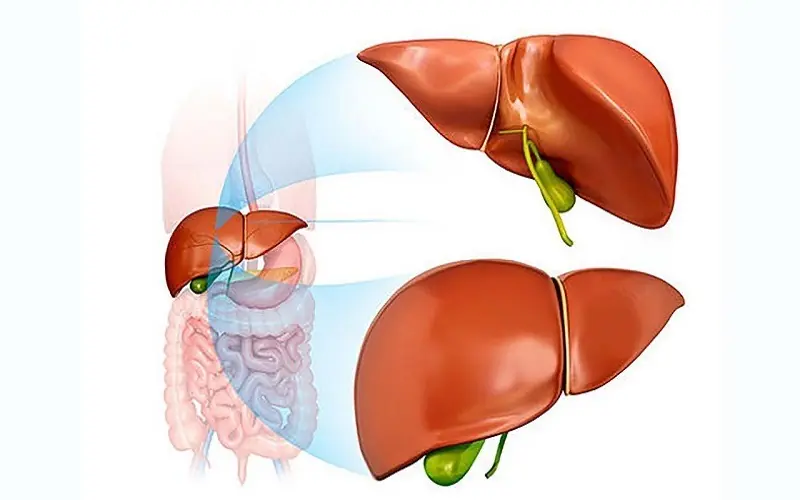
10 Proven Foods to Stimulate Your Liver and Remove Toxins Fast
Health 09/08/2025 18:01
Scientists Reveal How to Cleanse Your Colon Fast Using Just 2 Simple Ingredients
Health 09/08/2025 17:54
Doctors Urge: Stop Eating These 6 Foods That Fuel Cancer Growth
Health 09/08/2025 17:43

Sleeping Naked: 8 Surprising Benefits
Health 09/08/2025 16:58

8 Habits That Could Damage Your Brain (According to Research)
Health 09/08/2025 16:33

What Causes Belly Fat: Foods that Cause Belly Fat and Other Causes of Belly Fat
Health 09/08/2025 16:28
10 Warning Signs of Cervical Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore
Health 09/08/2025 16:21
4 Common Causes of Body Pain on the Right Side
Health 09/08/2025 15:31
7 Early Signs Your Heart May Be in Danger – Don’t Ignore #3!
Health 09/08/2025 15:24

Discover the Power of Rosemary: Nature’s Potent Pain Reliever & Healing Herb
Health 09/08/2025 14:01
News Post

A Quiet Act of Kindness That Restored My Faith in Humanity.
Life stories 10/08/2025 19:29

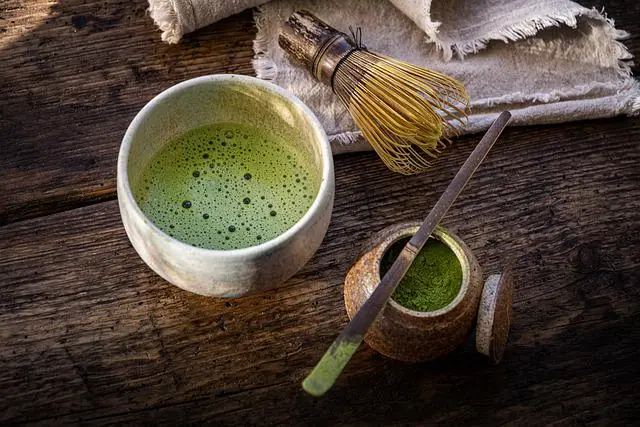
Proven Health Benefits of Matcha Green Tea: Weight Loss, Cancer and More (Evidence Based)
Health 10/08/2025 19:26

A Boy Named Shayden Just Wanted One Thing: A Friend — Can We Help?
Life stories 10/08/2025 19:21

Waking Up with Numb or Tingling Hands: What It Really Means (Science Based)
Health 10/08/2025 19:19
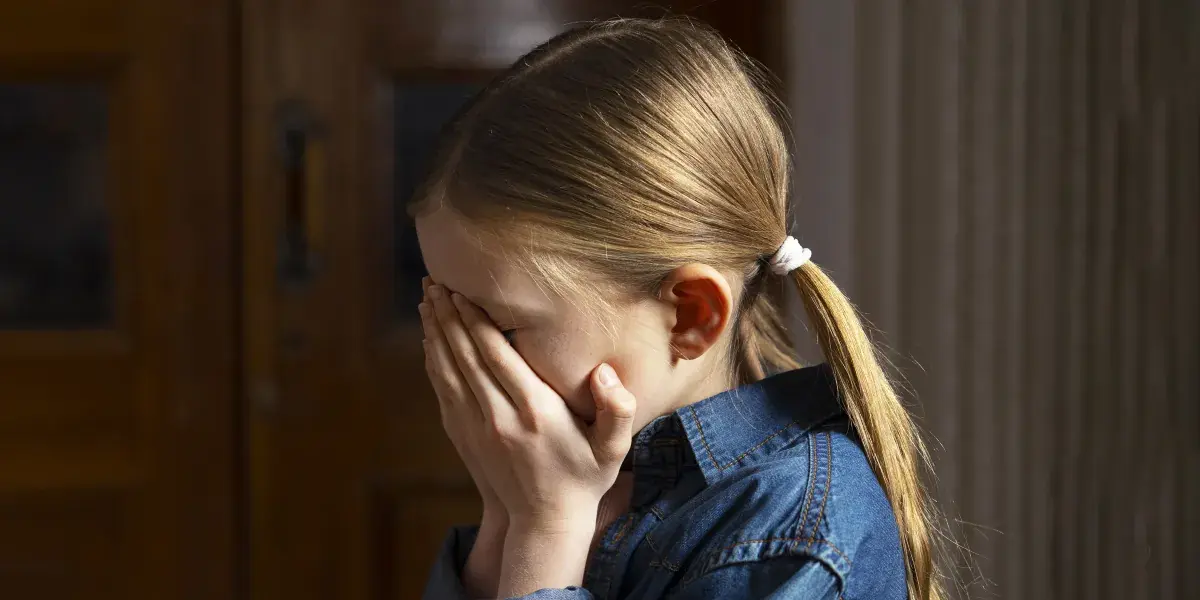

My MIL Kicked My 6-Year-Old Daughter Out of My Nephew’s 7th Birthday Party – When I Found Out Why, I Had to Teach Her a Lesson
Life stories 10/08/2025 19:11
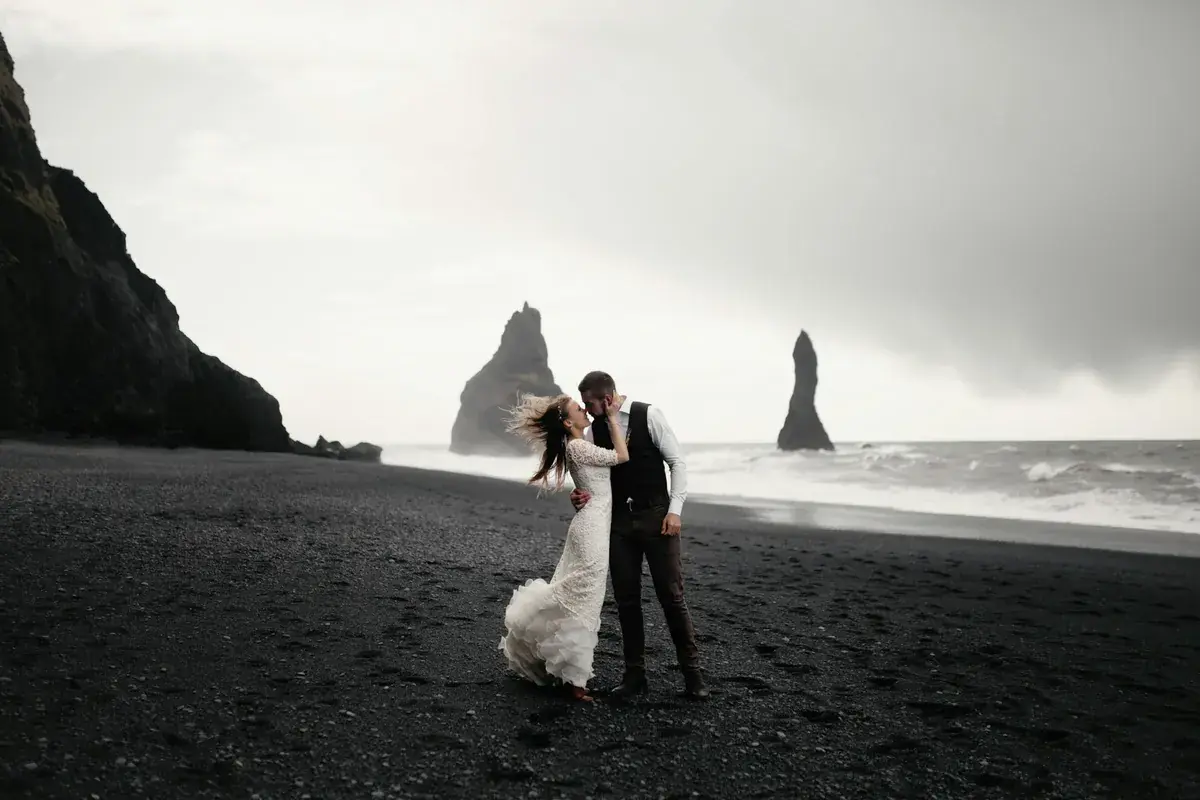

One Day My FIL Snapped, 'Did You Forget Whose House You're Living In?' — I Felt Humiliated and Had to Str!ke Back
Life stories 10/08/2025 19:03

Amazon's forgotten $500,000,000 deal that 'killed' Toys 'R' Us in 'cruel' move
News 10/08/2025 19:03

The real reason why nobody has ever found human remains inside the Titanic wreckage
News 10/08/2025 19:02
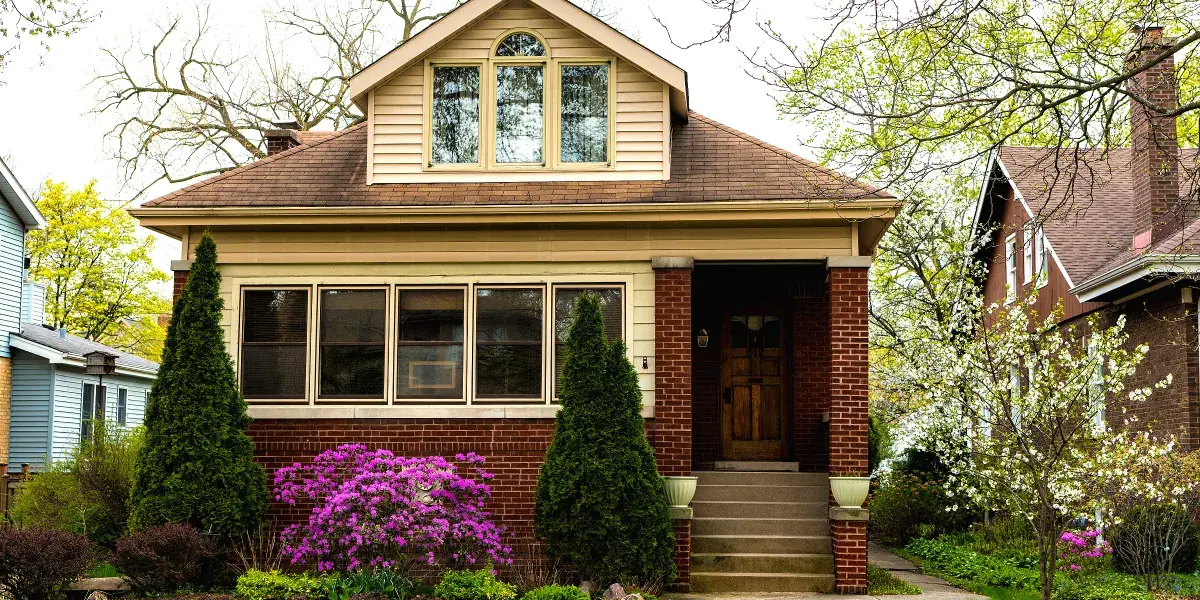

My Parents Kicked Me Out for Refusing to Attend Their Dream College — Five Years Later, They Got a Lesson They’ll Never Forget
Life stories 10/08/2025 18:58
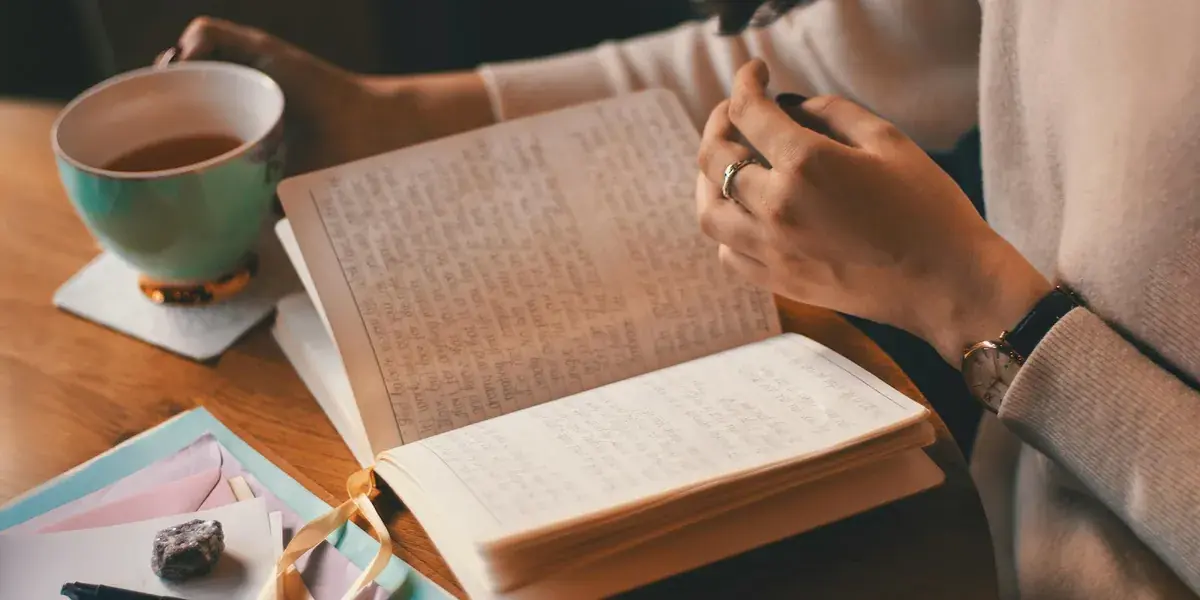

I Thought My Daughter Was Just Going Through a Phase, but Her Journal Exposed a Truth I Wasn't Ready for – Story of the Day
Life stories 10/08/2025 18:50

Scientists Reverse Aging of a 53-Year-Old’s Skin Cells to That of a 23
Facts 10/08/2025 16:00

Thyroid Gland: How to Balance Its Hormones
Health 10/08/2025 15:57

Gluten Intolerance Warning: Eczema and Other Hidden Signs Revealed
Health 10/08/2025 15:37

Your Body Is Begging You to Notice These High Blood Sugar Warnings
Health 10/08/2025 15:28

Research Reveals 12 Powerful Foods to Boost Your Brain, Improve Memory, and Make You Smarter
Health 10/08/2025 15:20

The Dog Who Never Ran Away Again.
Life stories 10/08/2025 15:06

Officer’s Quick Fix Turns Routine Call into a Viral Moment of Kindness.
Life stories 10/08/2025 15:02

My son brought a psychiatrist home to have me declared legally incompetent.
Life stories 10/08/2025 14:57

“Mom, why are you interfering in my family? You broke up your son with his wife, you broke up my brother, and now you’ve come for me?!” the daughter protested to her mother, jabbing trembling fingers at her phone.
Life stories 10/08/2025 14:53

