
Say Goodbye to Leg Cramps: 8 Vitamins Every Senior Needs for Stronger Legs
Can you stand up from a chair without using your hands? Walk up a flight of stairs without feeling winded, wobbly, or unsteady? If you hesitated—or answered “not really”—these could be early signs of nutrient-related leg weakness, a silent condition affecting millions of adults over 50.
The good news? You can take control now by targeting the specific nutrients your body needs to restore strength, stability, and endurance in your legs.
Say Goodbye to Leg Cramps: 8 Essential Nutrients for Stronger, Healthier Legs After 50
These aren’t just your average multivitamin recommendations. These are targeted compounds, each playing a distinct and crucial role in your leg health. One improves nerve signaling to prevent cramps. Another rebuilds connective tissue. Combined, they create a powerful framework for regaining lower body strength and mobility.
Let’s dive into the top 8 vitamins and minerals every senior should consider.
8. Vitamin D – The Mobility Molecule
It’s no coincidence that many older adults struggle to rise from a chair. What most people think is just "aging" is often a vitamin D deficiency in disguise. In fact, up to 60% of adults over 50 have suboptimal vitamin D levels, which directly affects their leg strength and balance.
Vitamin D acts like a key that activates muscle function. It helps maintain muscle fiber integrity, and also supports bone density, giving your legs the structural stability they need to move confidently.
🧬 The Science: Studies from the American Geriatrics Society reveal that seniors who supplement with vitamin D are 23% less likely to fall than those who don’t.
✅ Optimal Daily Dose: 800–2000 IU, ideally in the D3 form (which is more bioavailable than D2).
✅ Best Sources:
-
15–20 minutes of midday sunlight
-
Fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel)
-
Vitamin D3 supplements taken with healthy fats
Pro Tip: Pair with magnesium and K2 to maximize absorption and bone support.
7. Magnesium – The Muscle Relaxation Master
If you’ve ever been jolted awake by a painful leg cramp, your body might be screaming for magnesium.
Magnesium is essential for relaxing muscles after they contract. When you’re low in magnesium, your muscles can become stuck in a tense, semi-contracted state, causing those sudden nighttime cramps or tightness during the day.
Magnesium also regulates nerve signaling and improves circulation to your leg muscles, ensuring they receive the oxygen and nutrients they need.
🧬 The Science: Magnesium helps balance calcium in muscle tissue. Without enough magnesium, calcium floods in and over-contracts your muscles.
✅ Recommended Daily Intake: 320–420 mg
✅ Top Sources:
-
Spinach and dark leafy greens
-
Pumpkin seeds
-
Dark chocolate
-
Magnesium glycinate supplements (most absorbable form)
Bonus Tip: Magnesium also improves sleep, which is critical for muscle repair.
6. Vitamin B12 – The Nerve Signal Protector

Muscle strength means little if your nerves aren’t firing correctly. If you’ve ever felt tingling, numbness, or unexplained weakness in your legs, you could be dealing with a vitamin B12 deficiency—a common but underdiagnosed issue after age 50.
B12 is responsible for maintaining the myelin sheath, the protective insulation around your nerves. When this sheath breaks down, signals between your brain and muscles get distorted, leading to coordination issues and fatigue.
🧬 The Science: Up to 43% of adults over 60 have low B12 levels, often misdiagnosed as arthritis or neuropathy.
✅ Best Absorption Methods:
-
Methylcobalamin (active form)
-
Sublingual drops or tablets
-
B12 injections (for severe deficiency)
✅ Note: B12 from food (meat, eggs) is harder to absorb with age due to reduced stomach acid.
Quick Fix: Add nutritional yeast to your meals for a tasty, B12-packed boost.
5. Collagen – The Tissue Rebuilder
Struggling to bend down or tie your shoes? That stiffness might be more than inflexibility—it could be collagen loss.
Collagen is the scaffolding protein that holds your joints, tendons, and connective tissue together. After age 50, collagen production plummets, leaving joints vulnerable to pain, wear-and-tear, and reduced mobility.
🧬 Types That Matter:
-
Type I & III – support muscle and tendon strength
-
Type II – rebuilds joint cartilage, especially in the knees and hips
✅ Best Ways to Replenish Collagen:
-
Bone broth (all types of collagen)
-
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides + vitamin C
-
Collagen-rich foods like chicken skin, sardines, and eggs
Did You Know? Collagen also improves skin elasticity and gut health—bonus benefits!
4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids – The Inflammation Fighter

Chronic leg stiffness isn’t always about muscle or joint damage—it’s often about inflammation. And inflammation is largely influenced by what you eat.
Most people consume too many omega-6 fats (found in processed foods) and too few omega-3s, which are potent anti-inflammatories.
🧬 How They Work: EPA and DHA (the key omega-3s) reduce inflammatory compounds like IL-6 and TNF-alpha that damage muscle tissue.
✅ Optimal Daily Dose: 1000–2000 mg EPA/DHA combined
✅ Top Sources:
-
Wild-caught salmon, sardines, and anchovies
-
Algae oil (vegan alternative)
-
High-quality fish oil with vitamin E
Bonus: Omega-3s also support heart, brain, and eye health—critical for overall aging well.
3. Zinc – The Muscle Maintenance Mineral
You can eat all the protein in the world, but without zinc, your body can’t build or maintain muscle.
Zinc acts like the project manager of your muscle-building crew. It’s essential for protein synthesis, testosterone production, and growth hormone regulation—all crucial for maintaining leg mass and strength as you age.
🧬 The Stats: Zinc deficiency affects 30% of older adults, leading to up to 40% less muscle strength.
✅ Recommended Intake: 15–30 mg per day
✅ Top Sources:
-
Oysters (highest zinc content)
-
Grass-fed beef
-
Pumpkin seeds
Pro Tip: Always take zinc with copper (2:1 ratio) to prevent imbalance.
2. Vitamin K2 – The Calcium Traffic Controller

Many people take calcium and vitamin D for their bones—but without vitamin K2, that calcium might end up in your arteries or joints, not your skeleton.
Vitamin K2 ensures calcium goes where it should—into your bones and teeth—and not into soft tissues.
🧬 How It Works: K2 activates proteins like osteocalcin, which bind calcium into bone, while blocking calcium buildup in blood vessels and joints.
✅ Ideal Daily Dose: 100–200 mcg (MK-7 form preferred)
✅ Best Sources:
-
Natto (fermented soybeans)
-
Grass-fed butter and ghee
-
Aged cheeses like gouda and brie
Did You Know? K2 works in synergy with vitamin D and magnesium for full-spectrum bone support.
1. Selenium – The Cellular Defender
Oxidative stress is like rust for your muscles—and selenium is your natural anti-rust mineral.
This trace mineral powers glutathione peroxidase, one of the body’s most potent antioxidant enzymes. It shields your muscle cells from free radical damage, reducing fatigue and helping preserve function well into your later decades.
🧬 Bonus Role: Selenium is also critical for thyroid health, which regulates metabolism and energy in every muscle in your body—including your legs.
✅ Recommended Daily Intake: 100–200 mcg
✅ Top Food Source:
-
Brazil nuts (just 1–2 per day meets your needs)
Pro Tip: Pair with vitamin E to amplify antioxidant protection.
How to Put It All Together
These 8 nutrients form a complete leg-strengthening system:
-
Vitamin D & Magnesium – Strength + relaxation
-
B12 & Collagen – Nerve health + tissue repair
-
Omega-3 & Zinc – Inflammation + muscle maintenance
-
Vitamin K2 & Selenium – Bone integrity + cellular defense
Sample Daily Routine:
-
Morning: B12 drop + vitamin D3 + zinc + selenium (with breakfast)
-
Lunch: Omega-3-rich meal (like salmon)
-
Evening: Bone broth or collagen supplement + magnesium before bed
Final Thoughts: Leg Weakness Isn’t Just "Aging" – It’s Often Deficiency
Leg weakness, cramps, instability, and fatigue are not inevitable. In most cases, they’re simply nutritional warning signs that your body is missing critical tools it needs to stay strong and mobile.
By making smart, intentional changes to your diet and supplementation routine, you can rebuild strength, improve balance, and regain the confidence to move freely—at any age.
Start small. Stay consistent. And remember: strength doesn’t vanish overnight, and it doesn’t come back that way either—but it can come back.
News in the same category

The Most Effective Natural Way to Remove Gallstones

4 hidden signs of iodine deficiency in your skin, hair & nails

Here's why you should never sleep with the bedroom door open. FIND OUT MORE IN THE COMMENTS ⬇️

The Purple Maguey Plant — Benefits and Traditional Uses
How to Naturally Kill The Bacteria That Causes Bloating And Heartburn
The Health Benefits of Fasting: How It Regenerates Stem Cells, Fights Cancer & Protects Your Heart

Bananas: The Common Fruit That Could Drastically Improve Your Health
Why People with Green Eyes Are So Fascinating
Eat Red Onions Daily and Watch This Happen

What’s the Line Between Normal and Abnormal Nighttime Urination?
Effective Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain
The #1 FASTEST way to reverse fatty liver naturally
10 Unusual Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Constantly Too High
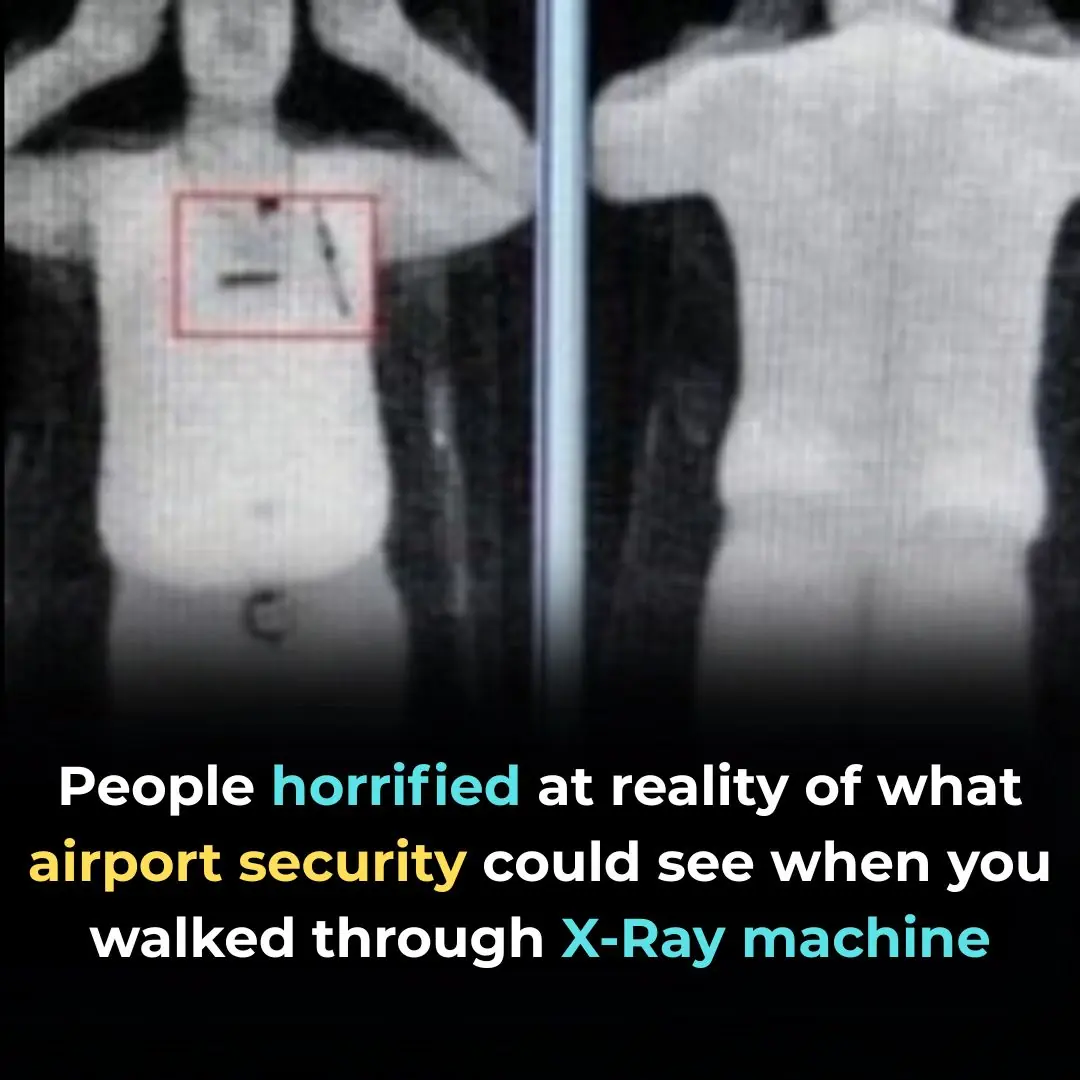
Horrifying Reality Of What Airport Security Are Able To See

Garlic, Onion & Olive Oil: The Ancient Trio That May Naturally Soothe Varicose Veins
Garlic, onion, and olive oil are humble ingredients with extraordinary benefits for circulation and vein health.
12 Powerful Herbal Teas to Naturally Lower Uric Acid and Ease Gout Pain
These teas work best alongside healthy lifestyle choices—balanced nutrition, hydration, and regular activity.

The surprising benefits of drinking apple cider vinegar before bed
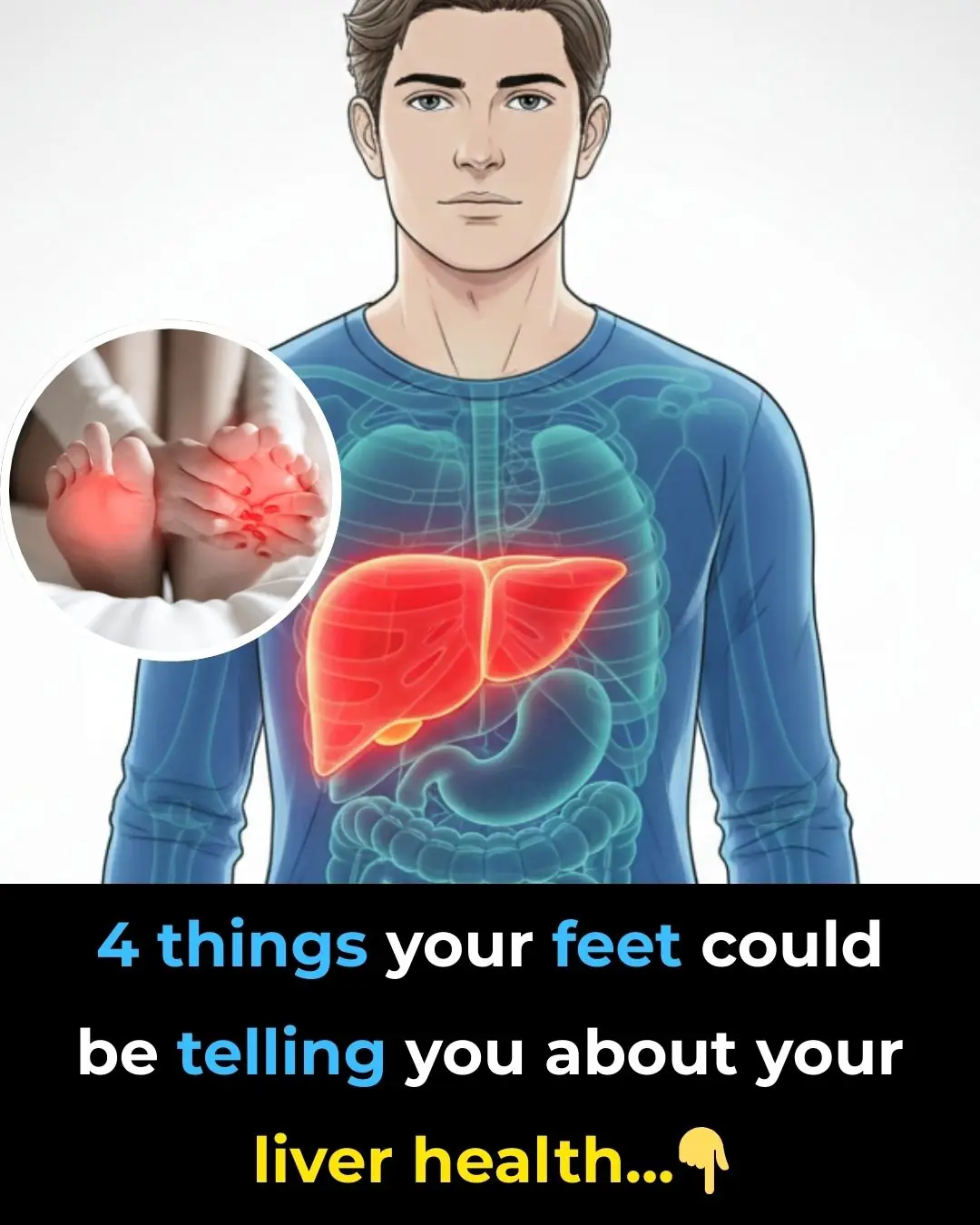
4 Things Your Feet Could Be Telling You About Your Liver Health
News Post

Forget 10,000 steps: Scientists prove 7000 steps gives you ‘almost identical’ life-saving benefits

The Most Effective Natural Way to Remove Gallstones

4 hidden signs of iodine deficiency in your skin, hair & nails

Objects People Were Confused About Their Purpose

Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear

What are the benefits of aloe vera? Here are 11 uses of aloe vera for health and skin

Just by looking at the spot on the crab's shell, 100% of the meat is packed to the brim, with my husband and children praising it non-stop.

These familiar fruits help improve sleep, especially number 1, which is both affordable and delicious.

Goosegrass: Health Benefits and Uses
7 Benefits of Chewing Raw Garlic on an Empty Stomach

Here's why you should never sleep with the bedroom door open. FIND OUT MORE IN THE COMMENTS ⬇️

Don’t Wash Your Wooden Cutting Board with Soap When It’s Moldy: Try This Simple Method to Make It Spotless in Just 5 Minutes

Mixing Essential Balm with Toothpaste: A Handy Tip Everyone Should Know, Both Men and Women Will Want to Follow Once They Discover It

They Call It the Blood Sugar Remover: The 100-Year Remedy That Heals Kidneys, Cleans Cholesterol, and Fights Diabetes Naturally

Top 5 Amazing Tips for getting rid of Blackheads and Whiteheads

14 Items to Throw Away Right Now

Group finds spiky creatures in nest – shocked when they realize what they are

The Purple Maguey Plant — Benefits and Traditional Uses

How to Naturally Kill The Bacteria That Causes Bloating And Heartburn
