
Skipping sleep can lead to a spike in immune cells linked to chronic inflammation.

The condition is associated with obesity and related health issues like diabetes and heart disease.
The study investigated the impact of even short-term sleep deprivation on healthy adults, aiming to understand the link between sleep, immune health, and conditions like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The research showed that obese individuals had lower sleep quality and higher levels of chronic low-grade inflammation compared to lean individuals.
Overweight and obese participants also showed increased numbers of non-classical monocytes, immune cells involved in inflammation, and higher levels of cytokines that induce rather than fight inflammation. Interestingly, the study showed that the inflammation caused by sleep deprivation is reversible with adequate sleep, suggesting that catching up on lost sleep can reduce the risk of chronic inflammation and related health conditions. Apart from contributing to obesity, lack of sleep weakens the immune response, making individuals more susceptible to illness and hindering recovery. During sleep, the body produces essential proteins called cytokines that fight infection and inflammation. Sleep deprivation reduces cytokine production and lowers levels of antibodies and infection-fighting cells. Most adults need 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night for optimal health, while children require varying amounts depending on their age. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment are key to achieving quality sleep.
News in the same category


Panic Attacks And Anxiety Have Been Linked To Certain Vitamin And Mineral Deficiencies

Woman reveals five colon cancer symptoms that should not be ignored

How To Get Rid Of Phlegm And Mucus In Your Throat And Chest On Your Own

Scientists Behind Early COVID Predictions Warn of New Virus in US That Could Endanger Humanity

10+ Foods to Help Lower Your Blood Sugar

9 Reasons Why You Should Be Eating More Dates

How to Naturally Cleanse the Lymphatic System to Fight Chronic Disease

The Datura Genus: A Beautiful but Deadly Plant You Should Avoid

Cancer Rates Are 82% Higher In Young Women Than In Men: ‘Something Broader Is Going On’

Scientists Behind Early COVID Predictions Warn of New Virus in US That Could Endanger Humanity

10 Natural Ways To Eliminate Parasites You Almost Certainly Have

21 Signs of Magnesium Deficiency: How to Tell If You’re Running Low
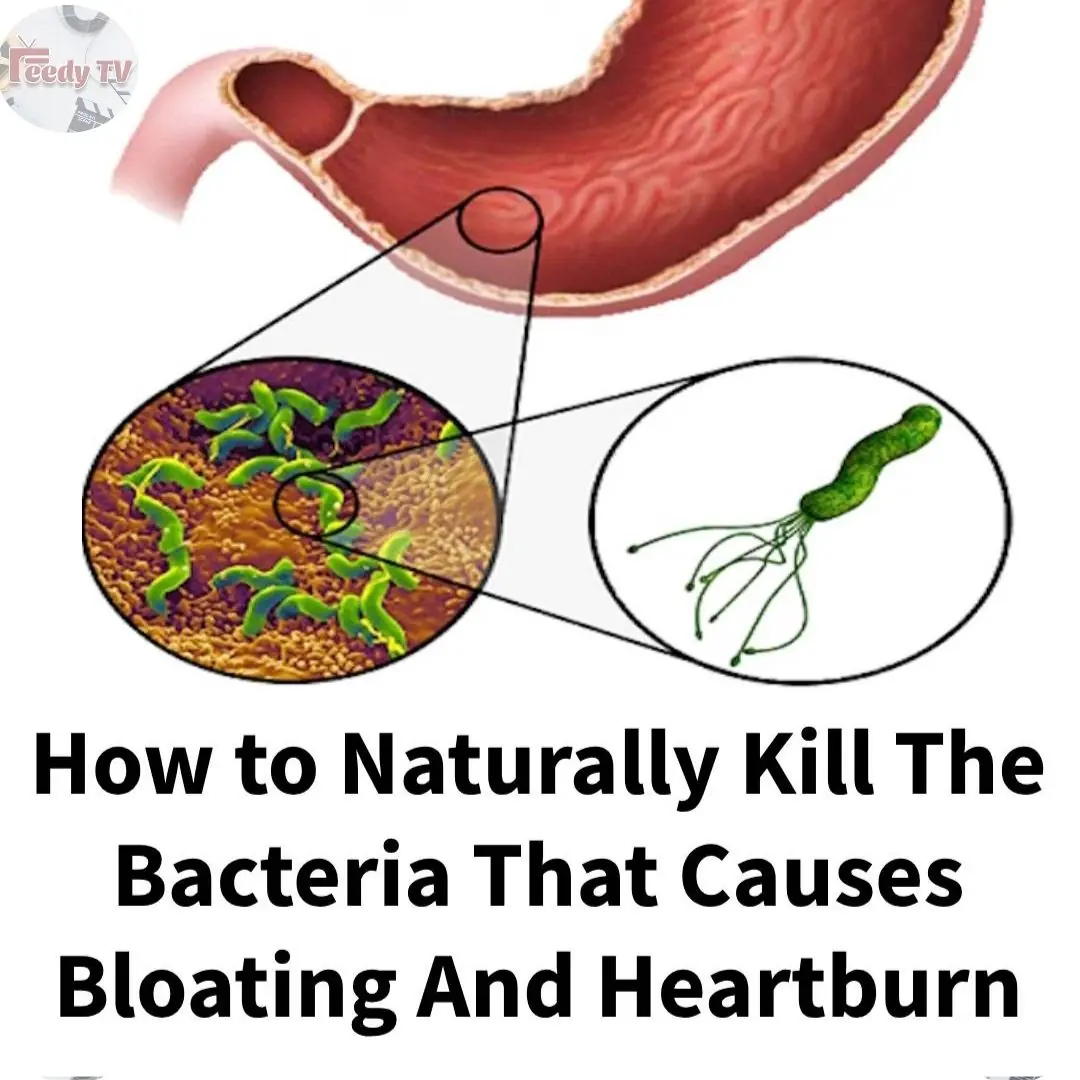
How to Treat H. Pylori (Helicobacter Pylori) Naturally Without Antibiotics
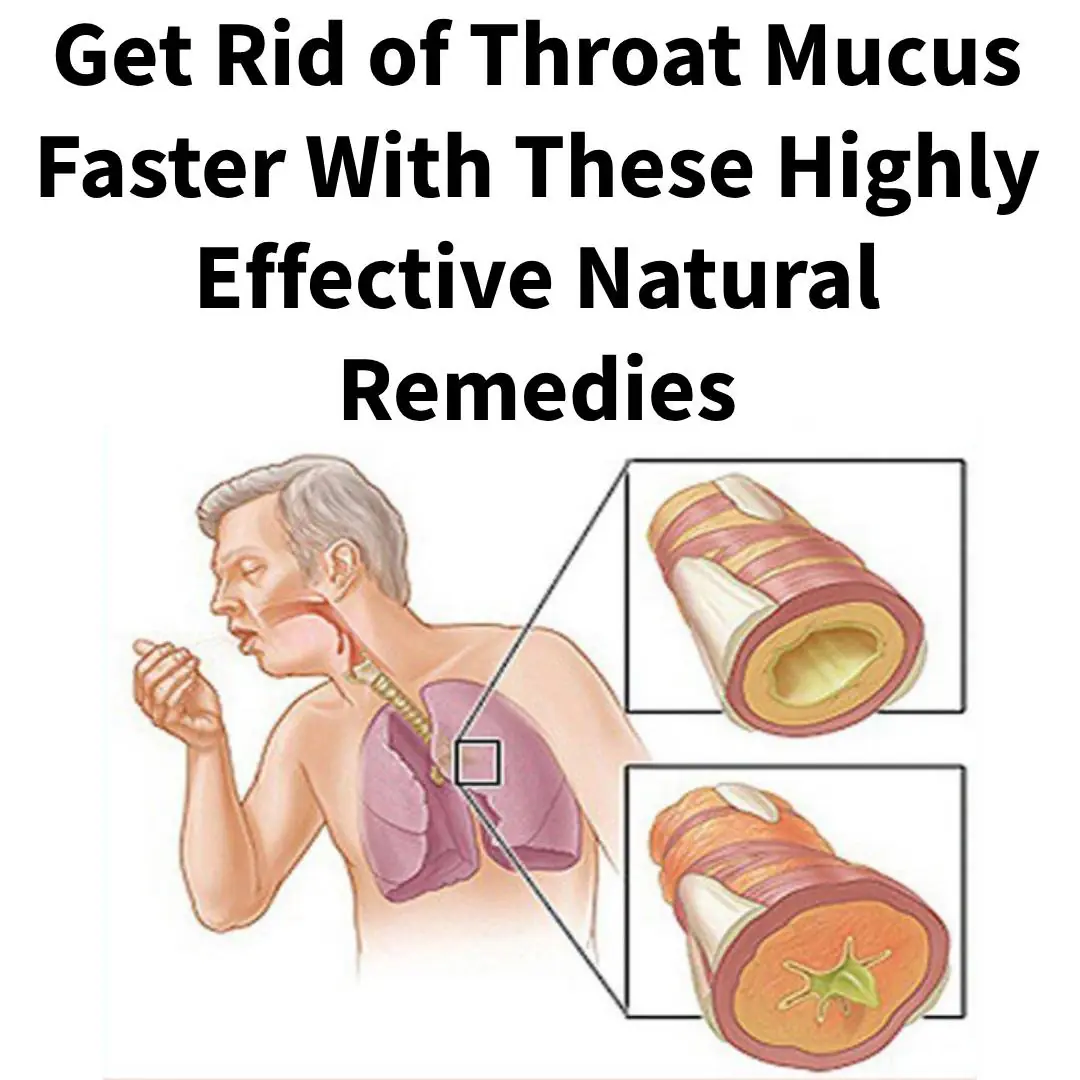
Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments (Evidence Based)

7 Kinds of Pain That Shouldn’t Be Ignored

Man Ate a Slug After Being Dared by His Friends Leading to a Tragic End
Off The RecordA Tiny Tree Was Discovered Growing Within A Man’s Lung

8 of the Best Anti-Cancer Foods. It’s Time to Start Adding them to Your Diet
News Post

I Accidentally Saw My Pregnant Daughter with My 48-Year-Old Best Friend at a Restaurant
Elliot's world shatters when he sees his estranged, pregnant daughter with his best friend, Joshua. Misunderstandings explode into accusations, and an accident leaves Joshua unconscious. As secrets unravel, Elliot faces the painful truth of his actions.

Drink Cumin Tea Every Day: Here’s What Happens to Your Body!

Vaseline, Carrot & Cucumber – Instantly Smooth Wrinkles in Just 3 Minutes! Even at 70! ✨🥕🥒

Glow Naturally with Simple Garlic Skincare Remedies That Work Wonders

Abandoned Puppy Becomes the Angel a Grieving Old Man Prayed For

I Visited My Late Father's House for the First Time in 13 Years and Found a Bag in the Attic with a Note for Me

6 Celebrities Who Passed on Their Looks to Their Grandchildren – Photo Comparison

My Wife Abandoned Me and Our Twins, Leaving Nothing but a Note – 10 Years Later, I Saw Her on the Street and Couldn't Believe My Eyes

My Best Friend Invited All His Friends and Their Plus-Ones to His Wedding, Except My Girlfriend – I Was Shocked to Learn Why

Someone Wrote 'Hope She Was Worth It' on My Car – But I Never Cheated, and My Wife Was Always by My Side

I Bought My Dream Home – Then My Husband's Family Decided to Move In Without Asking

After a Life-Threatening Childbirth, My Husband Wants to Kick Me and Our Baby Out Because of His Mother — Story of the Day

Every Time My Husband 'Works Late,' He Ends up at the Same Address – So I Drove There Myself
For weeks, Caleb's late-night deliveries led him to the same house. At first, I ignored it. But when I saw his location there again — and again — doubt took hold. Was there someone else? Desperate for the truth, I followed him. But when the door opene

Drink to Lose Belly Fat in 5 Days & Get a Flat Stomach Fast! 🔥 (Flat Stomach Drink)

The Body Knows When Death is Near, and It Begins in Your Nose

Coconut Oil and Baking Soda The Dynamic Duo for Gorgeous Skin

DIY Rice Face Mask Recipes To Get Rid Of Wrinkles And Fine Lines For Skin Whitening

Mix Vaseline with Egg and You Will Be Shocked! If Only I Knew This Earlier! 🥚✨

What Happens When You Drink Warm Turmeric Water Every Morning for Two Months?
