Surprising Link: Marriage May Increase Dementia Risk, New Study Finds
🧠 Surprising Link: Marriage May Increase Dementia Risk, New Study Finds

A groundbreaking 18-year study published in Alzheimer's & Dementia has revealed a surprising connection between marital status and the risk of developing dementia. Conducted by researchers from Florida State University and the University of Montpellier, the study tracked over 24,000 dementia-free adults aged 50 and older, uncovering that married individuals may have a higher likelihood of developing dementia compared to their unmarried counterparts.
📊 Study Overview
The research followed participants for up to 18 years, collecting data on their health, lifestyle habits, and cognitive function. The findings indicated that approximately 22% of married individuals developed dementia during the study period, while only about 13% of those who were divorced or never married experienced the same outcome. These results persisted even after adjusting for factors such as age, health conditions, lifestyle choices, and genetic predispositions.
🧩 Understanding the Findings
While the study's findings challenge the long-held belief that marriage universally protects against cognitive decline, researchers suggest that the quality of social connections plays a more significant role in brain health. A 2022 study published in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience found that individuals with strong social networks—regardless of marital status—had better cognitive health and a lower risk of dementia. This suggests that fostering meaningful relationships and staying socially active are crucial for maintaining brain function as we age.
🧠 Implications for Brain Health
The study's results highlight the importance of social engagement in promoting cognitive health. For married individuals, maintaining a robust social network outside of the marriage may provide additional cognitive benefits. Conversely, unmarried individuals might be more inclined to cultivate diverse social relationships, potentially offering protective effects against dementia.BioTech Info Center+1PMC+1
Moreover, the research underscores the need for healthcare providers to consider marital status and social connections when assessing an individual's risk for dementia. Encouraging patients to build and maintain strong social ties could be an effective strategy in dementia prevention and overall brain health promotion.
✅ Conclusion
In conclusion, while marriage has traditionally been associated with various health benefits, this extensive study suggests that it may not offer the same protective effect against dementia as previously thought. Instead, the quality and breadth of an individual's social connections appear to be more influential in safeguarding cognitive health. As we continue to explore the complex factors influencing brain health, fostering meaningful relationships and staying socially engaged emerge as vital components in the fight against dementia.
News in the same category

🧠 The Meninges: The Silent Layers That Protect Your Brain

8 Subtle Signs Angels Might Be Near Your Home

Why Your Hard-Boiled Eggs Have a Green Ring—and How to Prevent It

Soap Left on Plates? British Dishwashing Method Sparks International Debate
Medicine Breaks New Ground as Ultrasound Builds Tissue Without Surgery

A Heartbreaking Survival Trick: How a Stray Cat Learned to Hide His Pain

Bears Turn Honey Theft Into a Surprising Taste Test in Turkey

Scientists Say Your Butt Shape May Say More About Your Health Than You Think
The Rare Condition That Makes Human Bones Slowly Vanish

A Hidden Consequence of Tick Bites You Should Know About

Smoking, Obesity, and Hypertension: The Leading Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer

When Blue Wings Return: A Second Chance for the Spix’s Macaw

Three Friends, One Hive, and a Very Bad Idea

Measles Cases Hit 30-Year High in the US, Raising Urgent Public Health Concerns

Why Skipping Housework on New Year’s Day Might Bring You Good Luck

Millie Bobby Brown’s Reaction to Eleven’s Ending Goes Viral After Stranger Things Finale

Baby Name Expert Predicts the Most Popular Naming Trends for 2026

No Fines, No Enforcement: How Trust Worked During Japan’s Toll System Failure

This “Easy” Puzzle for Kids Is Completely Stumping Adults
News Post

She Thought He Was Just a Cop—Until She Found the Key That Changed Everything

I Married a Rich Old Man to Save My Father—On Our Wedding Night, He Removed His Mask

She Didn’t Come Home for 10 Years—Then She Heard the Pilot’s Voice and Broke Down in Tears

My Husband Planned a Romantic Dinner for His Mistress—So I Reserved the Next Table and Brought Her Husband

My Husband Was Cheating—and the Pool Gave Him Away

He Walked Into Court With His Lover—Then the Judge Spoke, and Everything Became Hers
🚨 Recurrent Yeast Infections? STOP Doing These Things Immediately!
Doctors Are Amazed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast

Dust cinnamon lightly on your lips. It works so fast it feels wrong
He Is the Least Likely to Have This Health Problem, According to Researchers

Longevity doctor who ‘reversed his biological age’ shares advice for people over 30

Doctors warn 5 everyday habits are slowly killing your kidneys
Eliminate Mucus, Phlegm in the Throat and Nose, and Rhinitis Naturally: Powerful Home Remedies
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast
Eat Garlic Daily, But Avoid These 8 Common Mistakes That Ruin Its Benefits
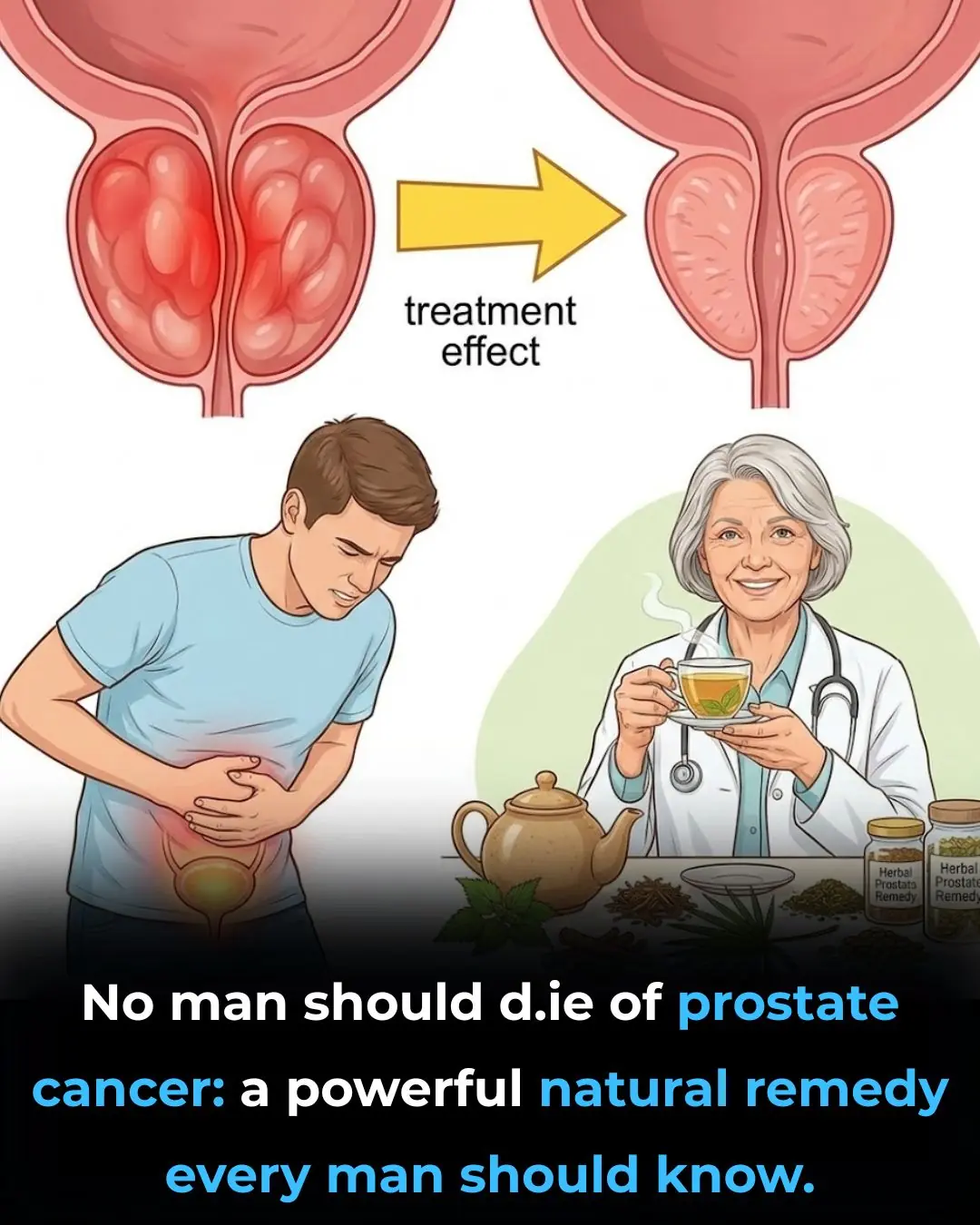
Natural Prostate Remedy: An Effective Herbal Option for Urinary Health
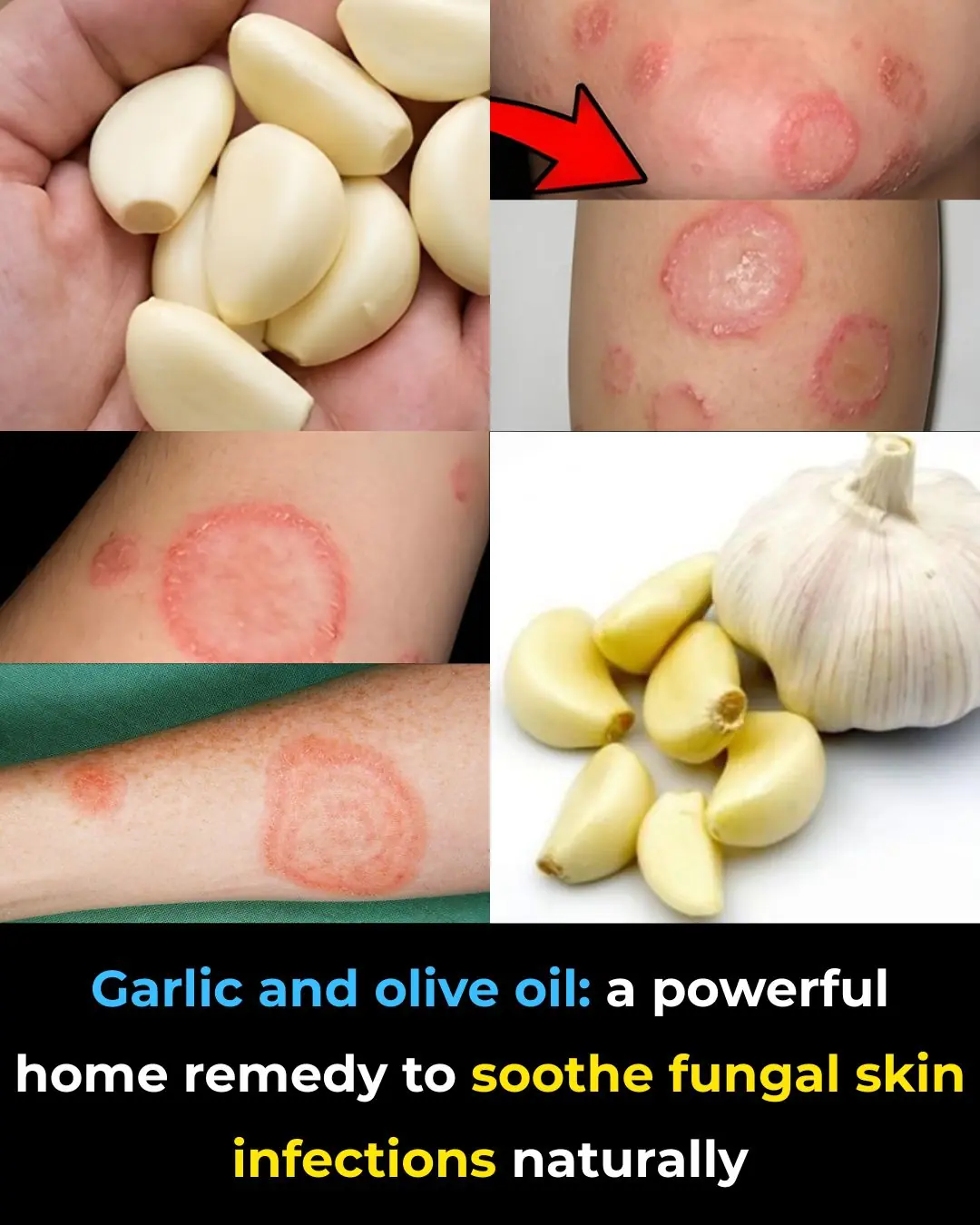
Garlic and Olive Oil: A Natural Way to Soothe Annoying Fungal Skin Infections at Home
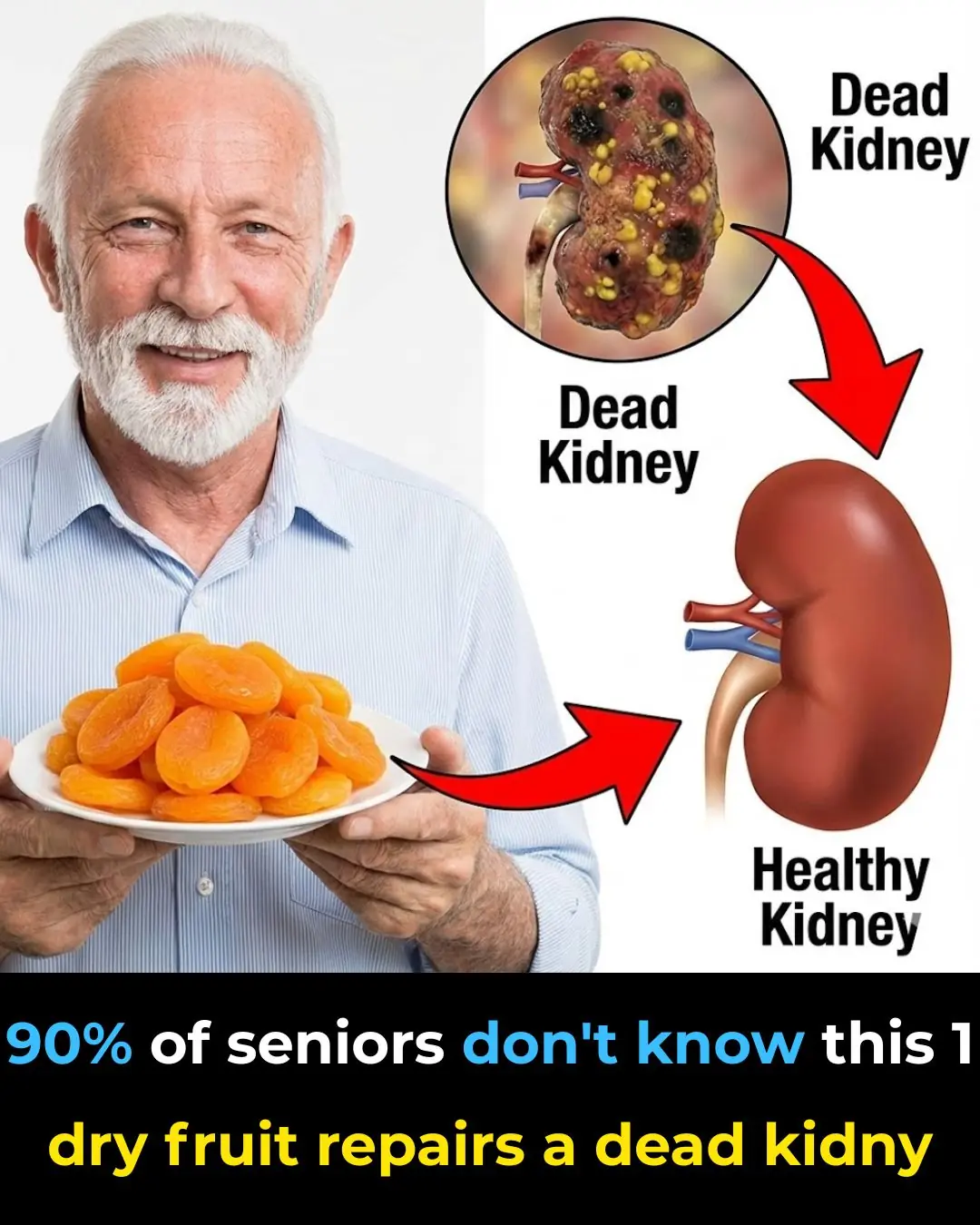
Top 5 Dried Fruits to Explore for Supporting Kidney Health After Age 60