The best way to lower blood pressure fast!
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a significant health concern that poses a major risk for severe conditions like stroke, heart attack, and kidney disease. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is crucial for overall well-being. Fortunately, there are various strategies to help reduce blood pressure, some of which can be effective almost immediately, without the need for medication. However, it's essential to remember that while these methods may provide quick relief, their effects are often short-lived and should be practiced regularly.
The good news is that there are natural approaches to lowering blood pressure that can be implemented into your daily routine. And, by addressing the root causes, it’s possible to lower your blood pressure long-term, potentially even preventing hypertension from becoming a chronic issue.
Three Effective Ways to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally
Here are three methods that have been scientifically proven to lower blood pressure, often within minutes:
-
Breathing Exercises: A Simple Yet Powerful Method

Breathing exercises are one of the easiest and most effective ways to lower blood pressure. Research, including comprehensive meta-analyses that combine results from multiple studies, shows that slow and controlled breathing can significantly reduce blood pressure. In fact, some studies suggest that the blood pressure reduction can be as high as 10 points (systolic).
The key to effective breathing exercises is to aim for a slower breathing rate—typically six to ten breaths per minute. This technique is often incorporated in practices such as yoga, and specialized devices, like respirators, are designed to help train you in controlled breathing.
One popular breathing technique is the 4-4-8 method, which works as follows:
-
Inhale deeply for 4 seconds.
-
Hold the breath for 4 seconds.
-
Exhale slowly for 8 seconds.
This method is sometimes called "box breathing" and has been linked to improved arterial stiffness, a key factor in managing high blood pressure. The mechanism behind its success lies in the stimulation of the vagus nerve, which is responsible for activating the body's "rest and digest" functions. Slow breathing helps to relax the heart rate and dilate blood vessels, leading to a decrease in blood pressure (Journal of Hypertension, 2021).
-
Isometric Exercise: A Surprising but Effective Approach

Isometric exercises, which involve holding a contraction of a muscle without movement, can also help lower blood pressure quickly. Though these exercises are not as effective for building muscle, studies have shown they can significantly impact blood pressure.
A common isometric exercise is the handgrip exercise. Here’s how to do it:
-
Use a handgrip strengthener or a dynamometer (a device used to measure grip strength), or simply grip a firm object such as a pillow.
-
Squeeze with about 20-30% of your maximum strength.
-
Hold the squeeze for 2 minutes, then rest for 1-3 minutes.
-
Repeat this process two or three times.
This exercise has been shown to lower both systolic (the top number) and diastolic (the bottom number) blood pressure. While the exact mechanism is not fully understood, it is believed that isometric exercises help improve artery function, increase elasticity, or cause blood vessels to dilate (Hypertension Research, 2020).
-
Addressing the Root Cause: Metabolic Health and Insulin Resistance

While breathing and isometric exercises can provide temporary relief, the long-term solution lies in addressing the root causes of high blood pressure. One of the most common, but often overlooked, factors contributing to hypertension is metabolic disease, including insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes. These conditions lead to elevated glucose and insulin levels, which can directly affect blood vessels or lead to hormonal changes that negatively impact blood pressure.
To manage metabolic health and prevent high blood pressure from becoming a chronic issue, it’s important to make the following lifestyle changes:
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Blood Pressure Control:
-
Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major cause of heart disease, stroke, and hypertension. It is widely known to damage the cardiovascular system and exacerbate high blood pressure (American Heart Association, 2023).
-
Limit Alcohol Intake: While some studies suggest that moderate alcohol consumption may have a slight benefit for heart health, excessive drinking can raise blood pressure. For most people, it's best to limit alcohol intake to avoid its detrimental effects on blood pressure (European Society of Hypertension, 2022).
-
Avoid Processed Foods: Diets rich in processed and ultra-processed foods are linked to higher blood pressure and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. These foods often contain unhealthy fats, excessive salt, and added sugars that can disrupt metabolic function (World Health Organization, 2021).
Dietary Recommendations to Improve Blood Pressure:
-
Reduce Carbohydrates: Specifically, cutting back on processed carbohydrates like sugary cereals can significantly help lower blood pressure. A focus on foods with a low glycemic index (GI) and a good carbohydrate-to-fiber ratio is essential for managing hypertension.
-
Follow the DASH Diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is specifically designed to reduce high blood pressure. It emphasizes eating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while minimizing sodium intake by avoiding processed foods (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, 2022).
Exercise and Physical Activity:
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is one of the best ways to manage and lower blood pressure. A combination of aerobic exercise (like jogging or cycling), resistance training (such as weightlifting), and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) has been shown to have the most significant effect on reducing blood pressure over time. Although exercise may temporarily raise blood pressure during activity, it helps to lower it in the long run (American College of Cardiology, 2023).
Sleep and Stress Management:
Good sleep hygiene is essential for managing high blood pressure. Poor sleep quality is strongly linked to elevated blood pressure and metabolic disorders. A consistent routine of sufficient, high-quality sleep can make a big difference in your overall health.
Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression are also major contributors to high blood pressure. While stress management techniques such as relaxation exercises or deep breathing can help alleviate symptoms, addressing the underlying causes of stress is critical for long-term relief.
Supplements to Aid Blood Pressure Reduction: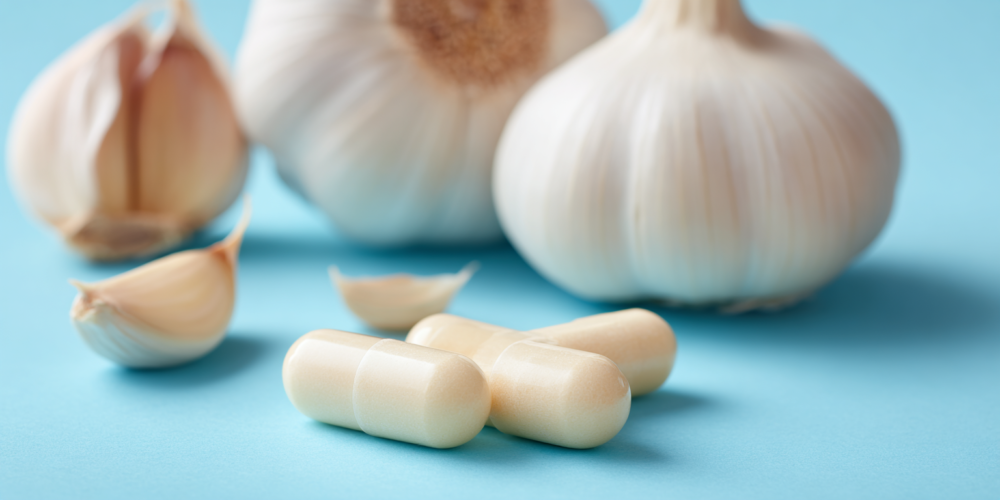
Although lifestyle changes are the most important factor in lowering blood pressure, certain supplements may offer additional benefits. Some research supports the use of the following supplements:
-
Vitamin C: Taking 500 mg daily has been shown to reduce systolic blood pressure by about 3 points and diastolic pressure by 1.5 points (American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2021).
-
Garlic: Daily garlic intake (300-960 mg) can reduce systolic blood pressure by around 4 points (Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 2020).
-
Citrulline: Supplementing with 3-9 grams daily can help increase nitric oxide production, which relaxes and dilates blood vessels, potentially lowering blood pressure by 2-4 points (Clinical Science, 2022).
The Importance of Accurate Blood Pressure Measurement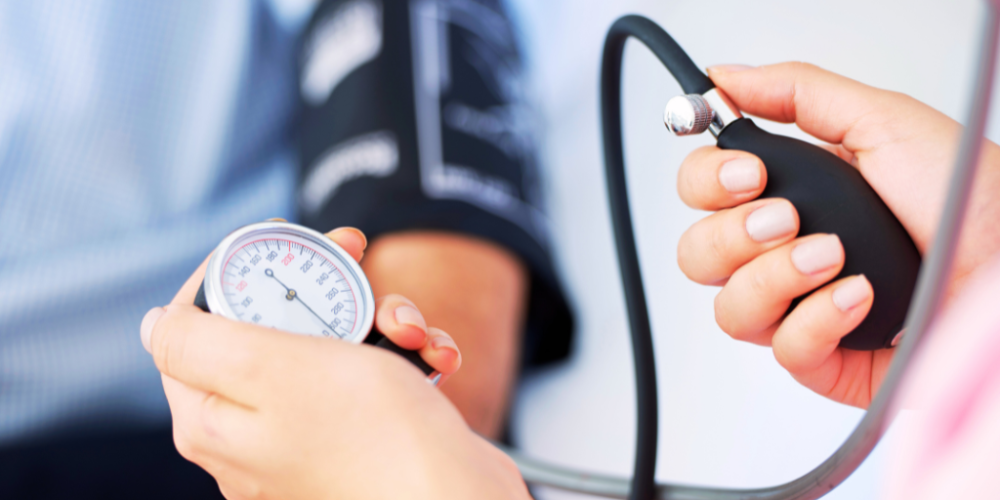
Accurate blood pressure readings are essential for monitoring and managing hypertension. One common mistake that leads to inaccurate measurements is improper technique. It’s crucial to follow the correct procedures when measuring your blood pressure at home. If your blood pressure is only elevated at the doctor's office, it may be due to white coat hypertension, a phenomenon where stress or anxiety causes a temporary spike in blood pressure. Tracking your blood pressure at home can provide a more accurate picture of your health.
By combining these strategies—breathing exercises, isometric exercises, dietary changes, regular physical activity, improved sleep, stress management, and targeted supplements—you can significantly lower your blood pressure and improve your overall health.
Sources:
-
Journal of Hypertension, 2021
-
Hypertension Research, 2020
-
American Heart Association, 2023
-
European Society of Hypertension, 2022
-
World Health Organization, 2021
-
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, 2022
-
American College of Cardiology, 2023
-
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2021
-
Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 2020
-
Clinical Science, 2022
News in the same category


Avoid Ginger If You Have THESE Health Problems

The step-by-step plan to drop 30 pounds quickly in 2025

Got High Blood Pressure? Try This 2-Ingredient Tea!
The Best Natural Remedies to Treat and Prevent Varicose Veins Effectively

People Who Do This Every Morning Have Better Circulation and More Energy
12 warning signs of poor circulation in your legs.

Treating Nail Fungus Naturally

7 ways to protect your heart during the winter months
Unexplained Bruising on Your Body: Causes and Treatments

Coconut water: Is It Good for You, Nutrition, Benefits, Side Effects (Science Based)

Lose just 1 gram of fat in your pancreas – and your diabetes may reverse, study finds

Doctors warn about 7 overlooked prostate cancer signs you should never ignore

Top 5 Veggies to Detox Your Arteries and Prevent Heart Attacks!
Untreated sleep apnea may nearly double your risk of Parkinson’s, major study finds
Warning Signs Your Magnesium, Potassium and Calcium Levels Are OFF and How To FIX It!

You are doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to relieve leg cramps at night
Few Know This Trick To Stop Uric Acid Crystals From Destroying Joints
WHAT IS THROMBOSIS? SYMPTOMS AND HOW TO PREVENT IT
News Post

What Happens If You Eat 4 Whole Eggs Every Day for 30 Days?

Thicker Thighs Linked to Lower Risk of Heart Disease and Diabetes, Study Finds
Breakthrough Drug Offers Hope for Restoring Vision by Repairing Nerve Insulation

Avoid Ginger If You Have THESE Health Problems

Nobel Prize-Winning Discovery of Autophagy: The Body’s Self-Repair Mechanism
Dietary RNA: A Key to Slowing Cellular Aging and Promoting Longevity

The Role of Fish Oil Supplementation in Enhancing Fat Loss and Muscle Growth: A Scientifically Supported Approach

Dandelion Root Extract Shows Potential to Eliminate Up to 95% of Cancer Cells in 48 Hours

Meet the Solar-Powered Sea Slug: The First Animal Known to Photosynthesize!

13-Year-Old Boy's Heartwarming Act of Sacrifice: Buying His Mother a Car Through Hard Work and Compassion

Living With a Rare Condition, a 25-Year-Old Faces One of Life’s Hardest Decisions

Simple Ways to Reduce Nighttime Wake-Ups and Improve Sleep Quality.

Aretha Duarte Makes History As First Black Latin American Woman To Climb Mount Everest

Doctors reveal the #1 supplement to reduce dementia risk

The Coffee Photo That Survived the War.

Issa Rae Opens New ‘Downtown Dough’ Pizzeria in L.A.

From Hardwood Hero to Human Inspiration: The Legacy of Rodney Rogers.

The step-by-step plan to drop 30 pounds quickly in 2025

The Weight Bryce Couldn’t Carry Alone.
