
The Quiet of Blue Whales: How Climate Change is Affecting Whale Behavior and Ecosystems
Recent acoustic monitoring off the coast of California has revealed a significant shift in the behavior of blue whales, one of the largest and most majestic creatures on Earth. Over a six-year study period, researchers found that male blue whale vocalizations dropped by approximately 40%. This decline is not a random occurrence; it is closely linked to a series of environmental changes, most notably the effects of a prolonged marine heatwave that occurred over several years, commonly referred to as “The Blob.” This unusual climate event disrupted the abundance and behavior of krill, the primary food source for these massive marine mammals.
The marine heatwave, which significantly altered the marine ecosystem, caused changes in the distribution and availability of krill in the affected areas. Krill are essential to blue whales, as they rely almost exclusively on dense swarms of these tiny crustaceans for sustenance. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA, 2023), these heatwaves can alter ocean temperatures, currents, and productivity, leading to shifts in food availability for marine species, including whales.
Because blue whales have extremely high energetic demands, the scarcity of krill during this period made foraging far more difficult. As a result, these whales had to expend more energy searching for food, leaving them with less to invest in other vital behaviors such as singing. Blue whale songs play an important role in communication, mating, and territory marking. However, the decrease in vocalizations suggests that the whales are struggling to allocate energy for such activities due to the increased energy required for survival.
This decline in singing is not just an isolated anomaly—it serves as an important warning signal of broader ecosystem stress. Scientists interpret reduced vocal activity as a sign of several potential issues within the marine environment. Reduced singing can indicate that the whales are spending more time foraging, likely in an effort to find food in an environment where it has become more scattered and less abundant. Additionally, it could reflect less successful feeding or even decreased reproduction rates, as the energy spent on survival may take precedence over reproductive behaviors. As University of California marine biologist Dr. Elizabeth Henderson explains, “The drop in vocalizations is a clear indication that these whales are under increasing ecological pressure, and it reflects larger shifts happening in the ocean.”
In addition to the immediate impacts on blue whales, the decrease in their vocal activity highlights potential disturbances in the ocean food web. The krill population, which serves as a foundational food source for many marine species, is itself sensitive to changes in water temperature and oceanic conditions. As marine ecosystems become more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, shifts in the behavior of keystone species like the blue whale offer a glimpse into the broader health of the ocean. According to National Geographic (2023), the interconnectedness of marine species means that disruptions at the top of the food chain can have cascading effects throughout the entire ecosystem.
The significance of this discovery goes beyond simply understanding whale behavior. It underscores the need for continued research on how climate change and marine heatwaves impact marine species and ecosystems. By closely monitoring species like the blue whale, scientists are gaining valuable insights into how marine environments are changing and how these shifts may affect biodiversity, food webs, and ecosystems globally. Conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change on marine environments will be crucial in preserving not only the blue whale population but the delicate balance of the ocean's ecosystems.
In conclusion, the reduced vocal activity of male blue whales is a clear and alarming indicator of worsening conditions in the ocean environment. While these majestic creatures are not currently facing extinction, the effects of The Blob and other marine heatwaves point to the urgent need for action to protect marine life. As Dr. Brian Silliman of Duke University states, “This phenomenon represents a canary in the coal mine, signaling broader ecological disruptions that require our immediate attention and action.”
News in the same category


Transforming Oil into Green Prosperity: The Success of Norway’s Sovereign Wealth Fund

Maximize Broccoli's Cancer-Fighting Power: The Simple Trick That Boosts Sulforaphane Formation

Hidden Fungi in Your Nose: A Surprising Cause of Allergies and Asthma

From Dialysis to Remission: How New Drugs Are Changing the Fight Against Chronic Kidney Disease

The Hidden Beauty of Grass: Discovering Smiling Faces Under the Microscope

The Arrival of Mosquitoes in Iceland: A Sign of Shifting Ecosystems and Public Health Risks

PP405: A Promising New Drug That Could Revolutionize Hair Loss Treatment by Reactivating Dormant Hair Follicles

Astronomers Capture Groundbreaking Image of New Solar System Formation

Denmark's 'Rolling Grocer' Initiative Brings Fresh Food and Community Connection to Rural Seniors

Mosquitoes Discovered in Iceland for the First Time: A Warning of Climate Change Effects

Denis Vashurin: The Man Who Appears as a Teenager Despite Being in His 40s

M.K. Prakasan: The Teacher Who Swims 12 km Daily to Educate Students in Kerala

Belgian Prodigy Laurent Simons Earns PhD in Quantum Physics at Just 15 Years Old

Revolutionary Cancer Treatment: Activating Immune Structures Within Tumors to Shrink Cancer and Prevent Relapse

Linking Digestive Health, Vitamin D, and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Pathway to Cognitive Health

The 400-Year-Old Greenland Shark: A Living Witness to Centuries

The Hidden Dangers of Long-Term Energy Drink Consumption

Frozen Time Capsule: Scientists Reveal Ancient Antarctic Landscape
News Post
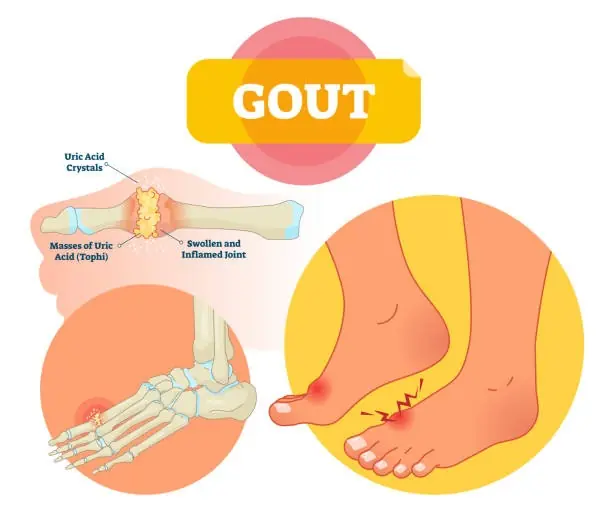
Few Know This Trick To Stop Uric Acid Crystals From Destroying Joints
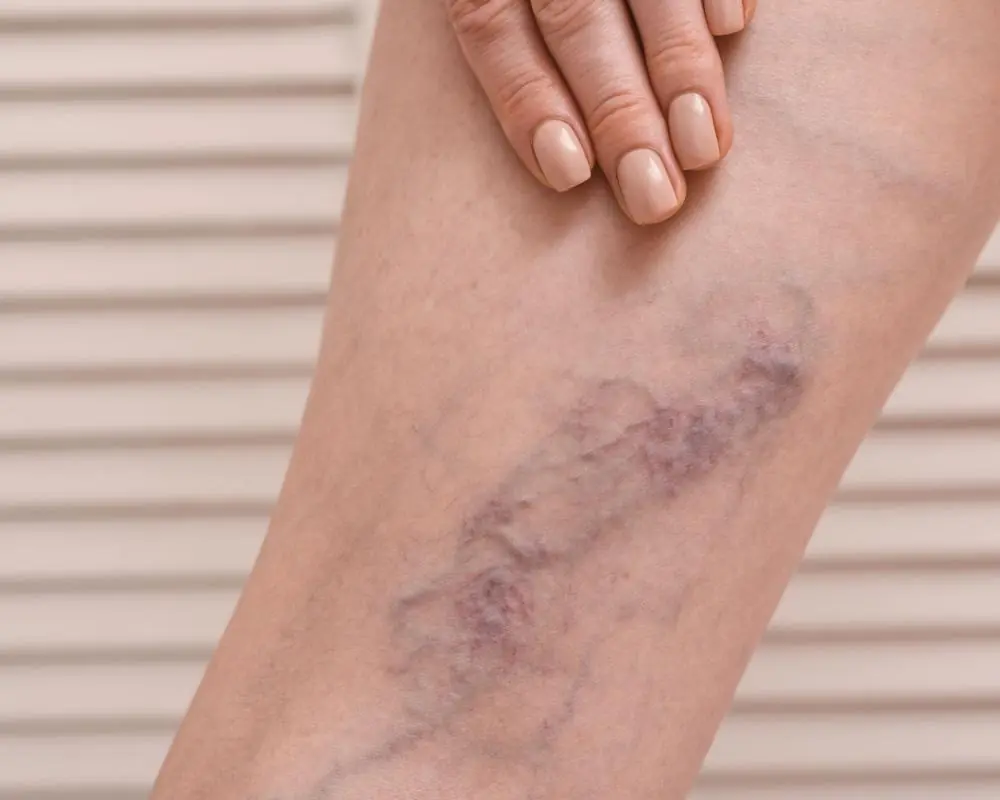
WHAT IS THROMBOSIS? SYMPTOMS AND HOW TO PREVENT IT

Natural Eyelash Growth Remedies – Oils, Serums & Home Treatments

From Space to Earth: The Science Behind Felix Baumgartner’s Record-Breaking Jump

Transforming Oil into Green Prosperity: The Success of Norway’s Sovereign Wealth Fund

Maximize Broccoli's Cancer-Fighting Power: The Simple Trick That Boosts Sulforaphane Formation

Hidden Fungi in Your Nose: A Surprising Cause of Allergies and Asthma

From Dialysis to Remission: How New Drugs Are Changing the Fight Against Chronic Kidney Disease

The Hidden Beauty of Grass: Discovering Smiling Faces Under the Microscope

The Arrival of Mosquitoes in Iceland: A Sign of Shifting Ecosystems and Public Health Risks

PP405: A Promising New Drug That Could Revolutionize Hair Loss Treatment by Reactivating Dormant Hair Follicles

Astronomers Capture Groundbreaking Image of New Solar System Formation

Denmark's 'Rolling Grocer' Initiative Brings Fresh Food and Community Connection to Rural Seniors

Mosquitoes Discovered in Iceland for the First Time: A Warning of Climate Change Effects

Denis Vashurin: The Man Who Appears as a Teenager Despite Being in His 40s

M.K. Prakasan: The Teacher Who Swims 12 km Daily to Educate Students in Kerala

Belgian Prodigy Laurent Simons Earns PhD in Quantum Physics at Just 15 Years Old

Revolutionary Cancer Treatment: Activating Immune Structures Within Tumors to Shrink Cancer and Prevent Relapse
