
The secret to growing lemons in pots with lots of fruit.

Lemons are widely used in daily life. You can use them to make refreshing drinks, enhance the flavor of dishes, clean household items, or even as part of your beauty routine—such as for hair care or exfoliation.
Growing a lemon tree at home is not only practical but also adds a touch of greenery to your living space. Even if you don’t have a large garden, you can successfully grow lemons in pots. With just a few simple techniques, lemon trees can thrive and produce abundant fruit regardless of where they are planted.
Best Time to Plant Lemons
Lemon trees can be planted at any time of the year, but the ideal periods are February–March and July–August or October. During these months, temperatures and humidity conditions are optimal for strong growth and better fruit production. Planting at the right time helps the tree adapt quickly and reduces the risk of slow development.
Choosing the Right Soil
Soil quality has a major influence on how well lemon trees grow. Lemons prefer soil with a pH between 5.5 and 7. Loamy, well-aerated, nutrient-rich soil is ideal. If your soil is too heavy or compacted, you can improve it by mixing in organic matter such as compost, coconut coir, or sand to increase drainage. Good soil structure helps the roots breathe and reduces the risk of root rot.
Selecting the Right Pot
When growing lemons in containers, choosing the right pot is essential. Terracotta pots are highly recommended because they are breathable and drain better than plastic pots, helping prevent waterlogging. The pot should be about 25% larger than the plant’s root ball so the roots have room to expand.
It’s also advisable to repot the tree every two years. Choose a slightly larger pot each time to accommodate the growing root system. Winter is the best season for repotting because the tree’s growth rate slows down, minimizing stress on the plant.
Choosing the Right Lemon Variety
Although some people grow lemons from seeds, this method usually takes several years before the tree produces fruit—and sometimes the fruit quality is unpredictable. For quicker and more reliable results, buy grafted or nursery-grown seedlings. These young trees are more vigorous, disease-resistant, and capable of bearing fruit much sooner.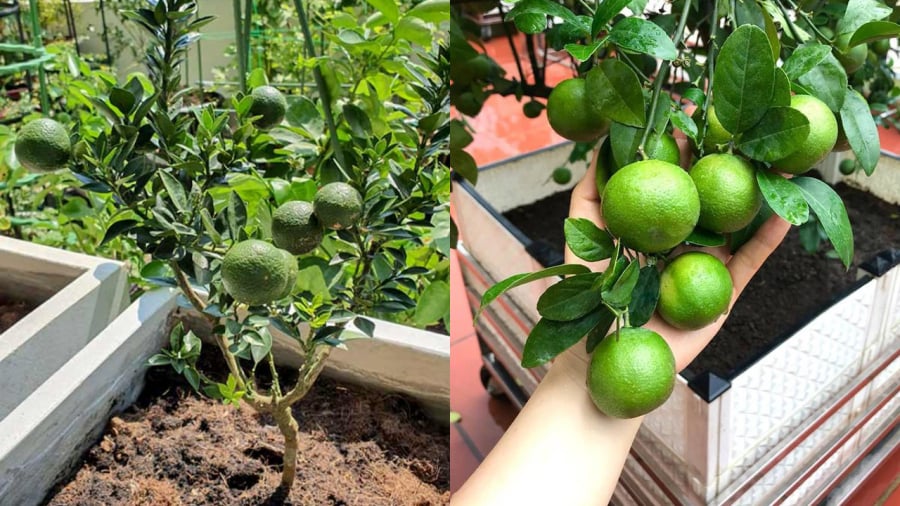
Light Requirements
Lemon trees are sensitive to cold temperatures and strong winds, so it’s best to place them in areas with plenty of sunlight and good air circulation. Ideally, the tree should receive at least 7–8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Placing the pot in south-, east-, or west-facing areas helps ensure the plant gets enough light. The more sunshine it receives, the healthier the tree will be and the more fruit it will produce.
Watering Properly
Water management plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy lemon tree. Overwatering or underwatering can both cause fruit drop and even lead to withering. If the soil becomes too dry, salt can accumulate and damage the roots.
To check whether the tree needs water, insert your finger 2–3 cm into the soil. If it feels dry, it’s time to water. On hot or windy days, you may need to increase watering frequency. However, always avoid soaking the soil—moist but not soggy is ideal.
Adding a layer of mulch such as straw or dried leaves on the soil surface can also help retain moisture and keep the roots cool during hot weather.
Fertilizing
Lemon trees have high nutrient demands, especially during peak growth periods. February–March and August–October are the months when the tree grows most vigorously. During these times, apply fertilizer once a month.
For potted lemon trees, use a balanced fertilizer such as 18-18-18. Additionally, applying potassium-rich fertilizer when the tree is flowering will help improve fruit setting and increase fruit quality. Organic fertilizers like compost or worm castings may also be added periodically to enrich the soil.
Pruning Branches and Roots
Pruning helps the lemon tree stay compact while encouraging more fruit production. This can be done during the growing season. Remove weak, thin, or diseased branches to redirect nutrients toward stronger parts of the plant.
Some shoots may grow directly from the main trunk and consume valuable nutrients. These should also be trimmed. When repotting, you can lightly prune the roots to stimulate growth and improve flowering and fruiting.
Regular pruning improves airflow, prevents pests, and keeps the tree looking attractive as a home decoration.
News in the same category


The #1 Kitchen Mistake That’s Making Your Family Sick (And Ruining Your Food)

🏠 8 Household Items That Could Be Affecting Your Health (And How to Check Them Safely at Home)

Subtle Signs You’re Not Drinking Enough Water

Beets The Superfood That Actually Lives Up to the Hype

I have absolutely no idea! Let's see why.
A Traditional Natural Compress for Joint and Tendon Comfort

The Surprising Health Benefits of Coffee

Simple Ways to Slow Wrinkles and Keep Your Skin Glowing

Here’s what the letter ‘M’ and the crescent moon on the palm of your hand truly signify

The Easy Trick to Make Stainless Steel Sparkle

Why Some People Put Water Bottles Outside Their Homes

🥦 3 Vegetables That Support Cancer Prevention — Backed by Science

Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer

The Best Time To Drink Pomegranate Juice for Better Blood Pressure and Muscle Recovery
What Is Stomach Cancer?
What Is the Adam’s Apple
I spent a couple of nights at my friend’s previous apartment and saw these unusual bumps
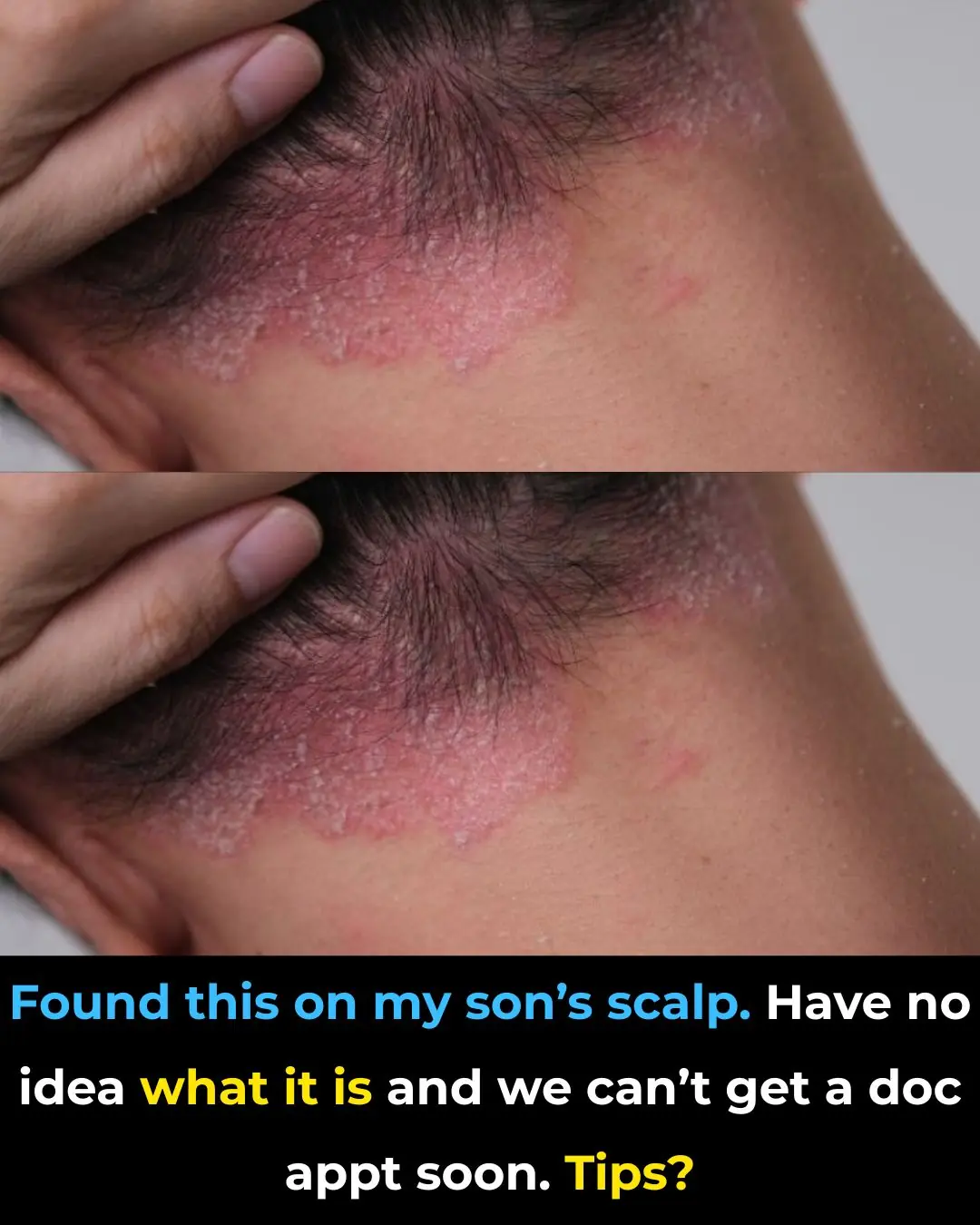
Found this on my son’s scalp. Have no idea what it is and we can’t get a doc appt soon. Tips?
News Post
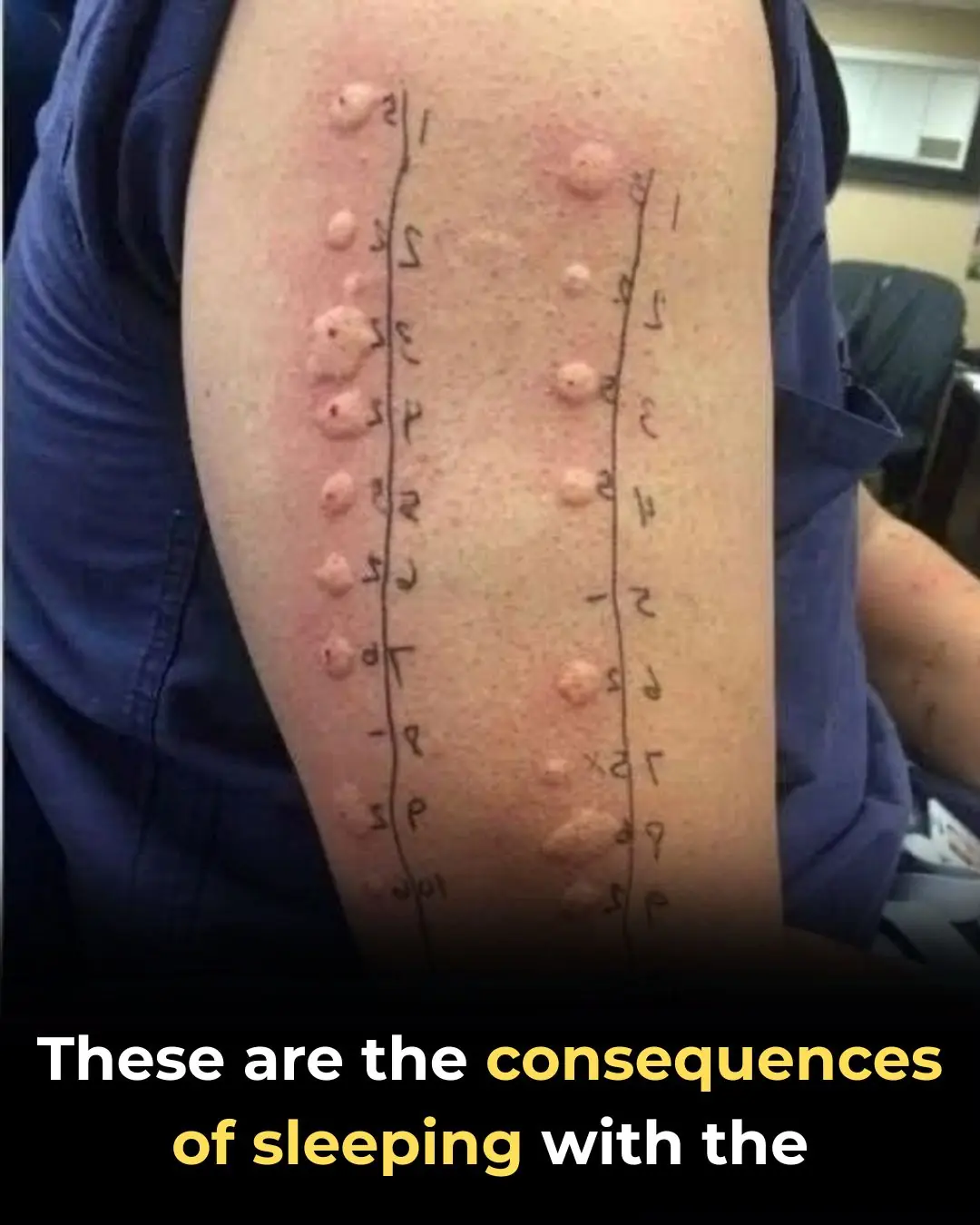
More Than a Moment: Understanding the Layers of Intimacy
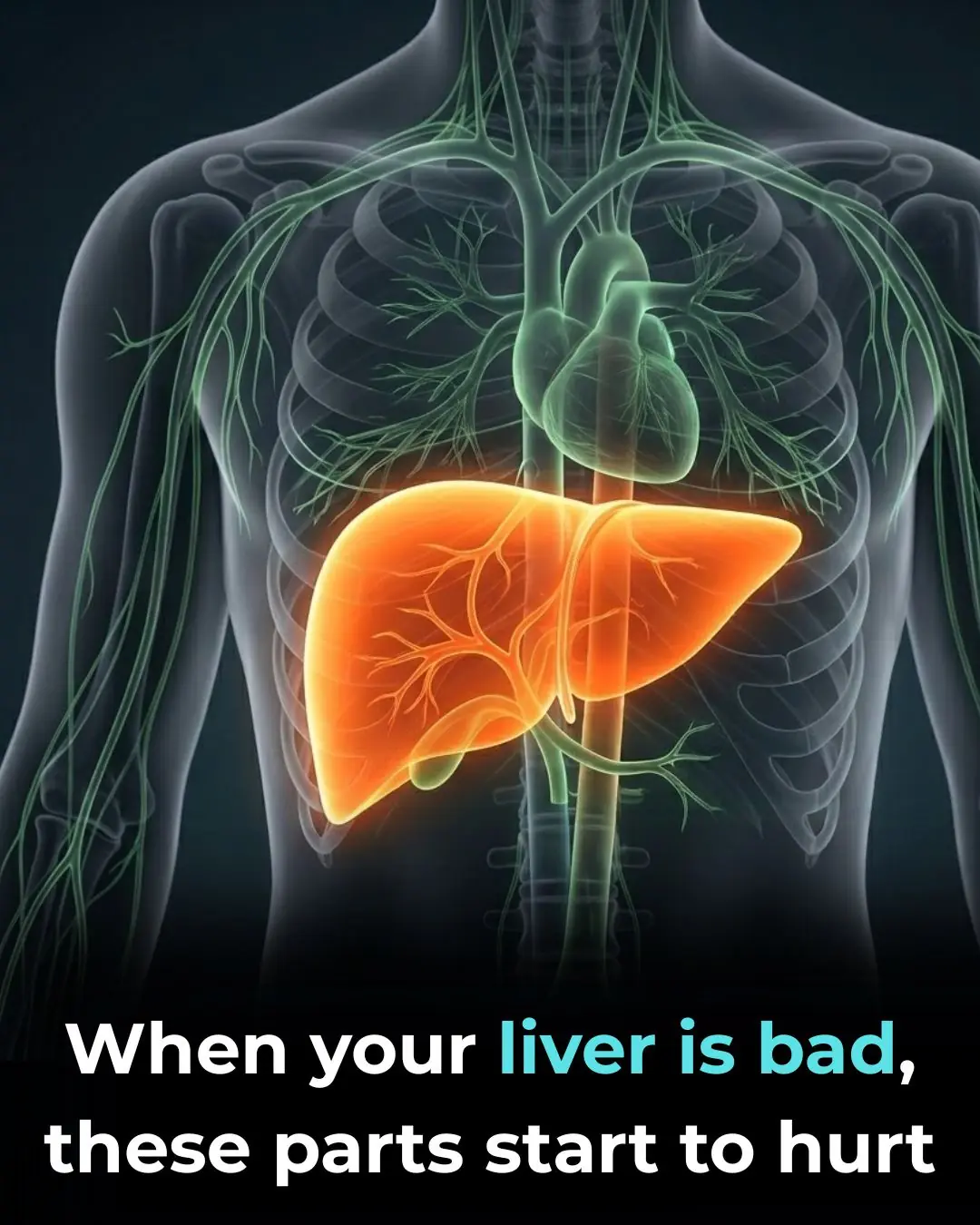
When your liver is bad. Please check if this is correct.

Experts Warn Avoid These 4 Foods If You Want to Live Longer

A Natural Drink to Support Healthy Knees

Vegetables That Help Support Kidney Health
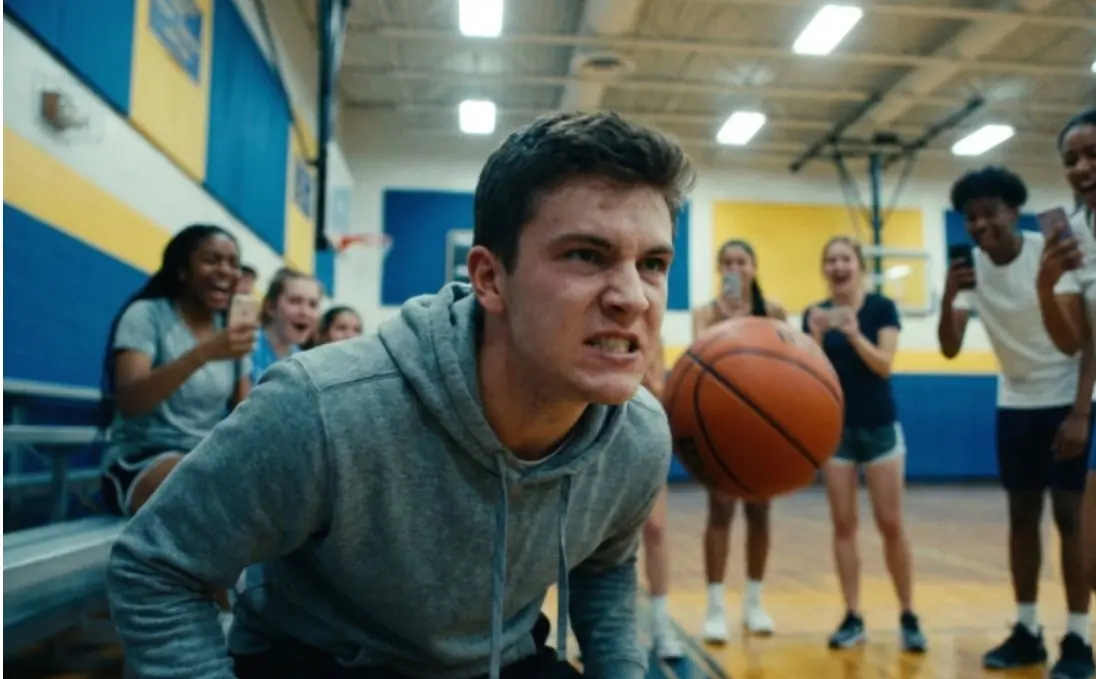
They Thought It Was Just a Joke in the Gym. That Single Throw Changed Everything

Restore Clear Vision Naturally: The Hidden Power of Oregano for Eye Health

How to Make Okra Water to Naturally Support 17 Aspects of Everyday Health

The Bridesmaid Spilled Wine and Called Her “A Poor Little Bird.” Then the Best Man Put a Crown on the Bride.

She Struck the “Janitor Bride” in Church—Then the Pastor Dropped to His Knees

Folha-da-Vida (Kalanchoe): The Garden Plant Many People Have—but Few Know How to Use

Don’t Toss That Avocado Pit: Practical Tips, Nutritional Insights, and Smart Uses You Should Know

The Secret of Red Onion: A Simple Kitchen Recipe That May Support Metabolic Balance

The Day Respect Was Conditional

He Dumped Filthy Water on Me at Thanksgiving—Then the Mayor Pulled Up
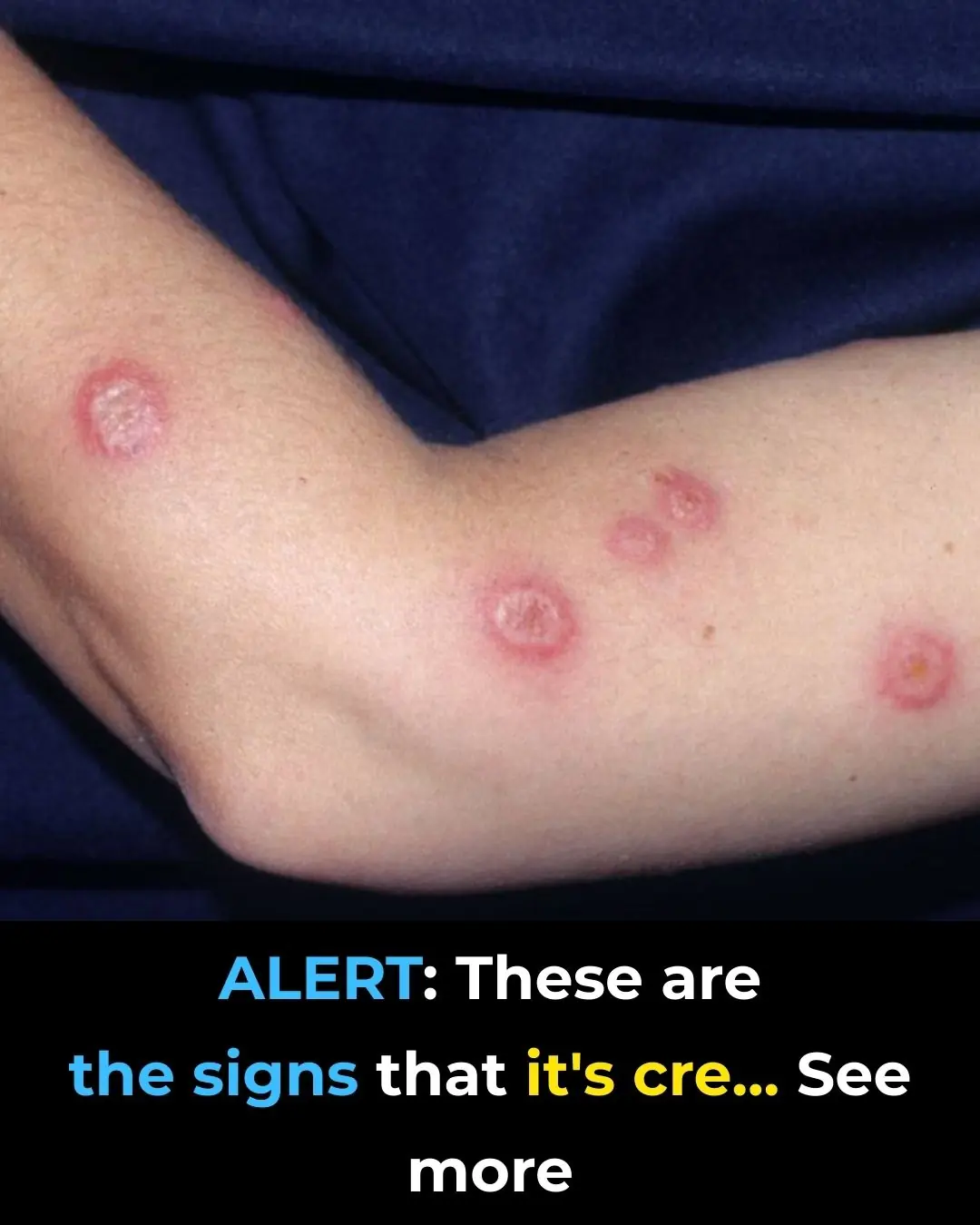
ALERT: These are the Signs of Sweet Syndrome
Doctors reveal that cassava consumption causes...

Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast
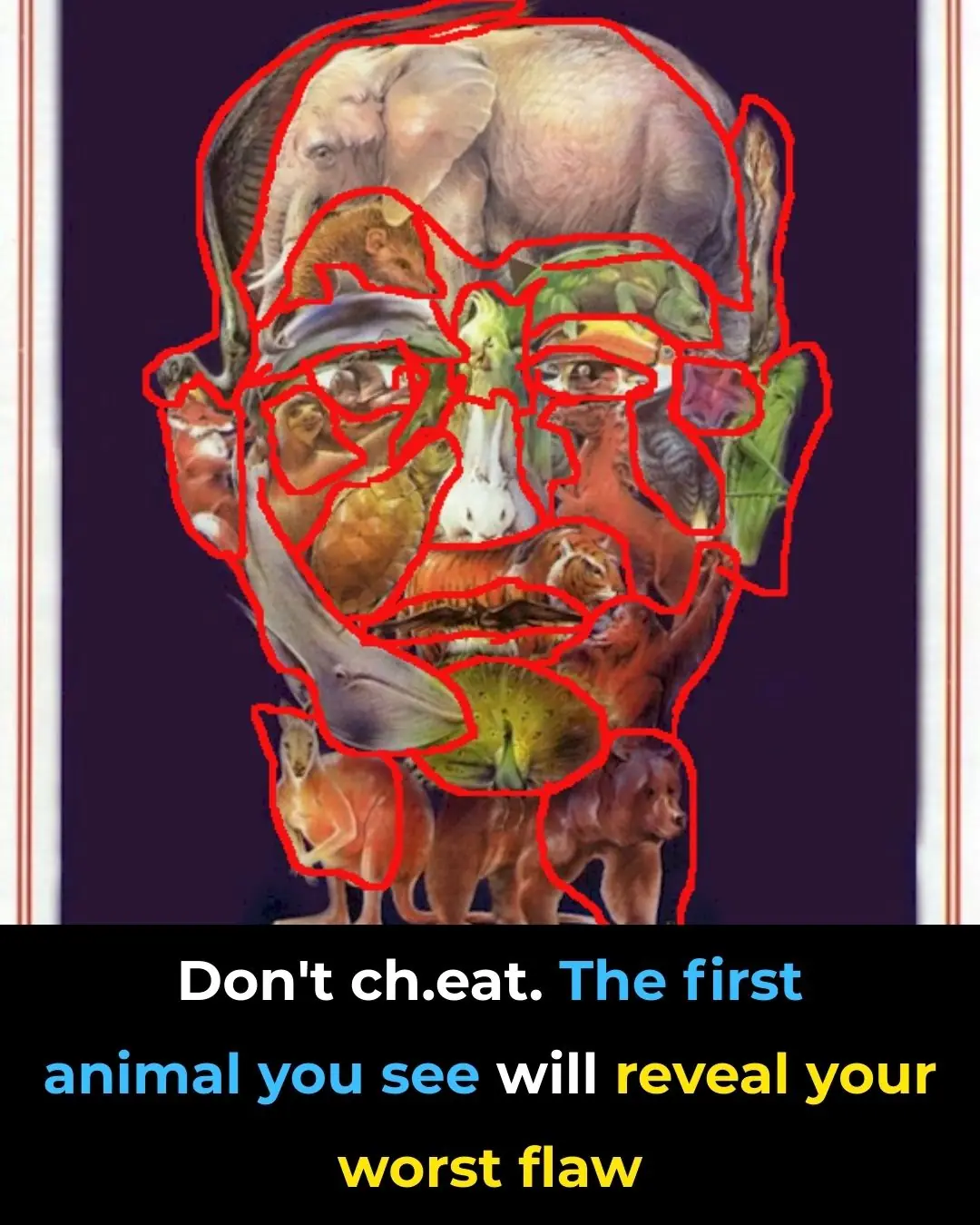
What the First Animal You See Reveals About Your Hidden Flaw
