What Happens When You Eat 3 Whole Eggs Every Day…You’ll Be Surprised What It Does To Your Body!
A few years ago, many health organizations raised concerns about eggs because of their cholesterol content. For a while, eggs were lumped into the same “unhealthy” category as foods like coconut oil and avocados—once misunderstood but later redeemed by science.
(Updated June 21, 2024)
Today, nutrition experts largely agree: eggs are one of the most complete and nutritious foods you can eat.
While a large egg contains about 180–186 mg of cholesterol, your liver naturally produces 1,000 to 2,000 mg of cholesterol every day on its own. When you eat cholesterol-rich foods, your liver simply reduces its own production to balance levels. In other words, eating eggs doesn’t raise your total cholesterol—it just shifts the source.
So, should you eat more eggs? The answer, for most healthy people, is yes. Let’s look at seven science-backed reasons why eggs deserve a regular place on your plate.
1. Eggs Are Nutrient Powerhouses
When it comes to nutritional value, eggs are an all-in-one superfood.
Each egg delivers a wide range of essential nutrients, including vitamins A, D, E, B6, and B12, as well as thiamine, riboflavin, folate, iron, phosphorus, magnesium, and selenium (1). They also provide high-quality complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids your body can’t produce on its own.
In fact, nutritionists often use the egg as a “gold standard” for protein quality, since it’s so efficiently absorbed by the body. Few foods offer as much nutritional density for so few calories—about 70 to 80 calories per egg.
2. The Cholesterol Myth—Debunked
The biggest criticism against eggs has always been their cholesterol content. But science now tells a different story.
Eggs are rich in high-density lipoprotein (HDL)—the “good” cholesterol that supports brain and heart health. HDL helps your body produce vitamin D and regulate hormones like testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol (2,3).
Unlike low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which can build up in arteries, HDL acts like a cleaning crew, sweeping away excess cholesterol and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis (4,5).
For healthy individuals, regular egg consumption does not increase the risk of heart disease or stroke. In fact, studies show that people who eat eggs regularly often have better lipid profiles than those who avoid them.
However, individuals with diabetes may need to monitor intake, as excessive egg consumption could slightly increase cardiovascular risk (6).
The takeaway? You can confidently enjoy eggs as part of a balanced diet. The key to heart health isn’t cutting out eggs—it’s reducing sugar, avoiding trans fats, exercising regularly, and eating more vegetables (7).
3. Eggs Are Packed With Choline—Fuel for Your Brain
Choline is an essential nutrient that most people don’t get enough of, and eggs are one of the best natural sources.
Choline supports brain development, memory, and learning by helping produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter vital for mood regulation and cognitive performance (8). It also plays a major role in liver health, helping prevent fat accumulation.
This nutrient is especially critical during pregnancy—adequate choline intake supports fetal brain development and may help prevent birth defects. Yet, about 90% of Americans are deficient in choline, which may contribute to muscle damage and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (9,10).
A single large egg provides roughly 150 mg of choline, making it an easy and affordable way to boost intake.
4. Keeps Your Eyes Sharp
Eggs are also a rich source of lutein and zeaxanthin, two powerful antioxidants that protect your eyes. These carotenoids concentrate in the retina, where they help filter harmful blue light and reduce oxidative stress.
Regular egg consumption is linked to a lower risk of macular degeneration, the leading cause of blindness in older adults (11). They also help reduce cataract risk by up to 50% and improve night vision and overall visual clarity (12).
Interestingly, the fat in egg yolks actually enhances carotenoid absorption, meaning your body absorbs more lutein and zeaxanthin from eggs than from vegetables alone.
5. Excellent Protein for Muscle Growth and Repair

Two eggs contain roughly the same amount of protein as one serving of meat—about 12 grams—but with far less fat and acidity.
Many people eat only egg whites, believing the yolk is unhealthy, but this is a mistake. Half of an egg’s total protein is in the yolk (13), along with nearly all of its vitamins and minerals.
Protein from eggs supports muscle repair, growth, and recovery, making them ideal for athletes, older adults, and anyone looking to maintain lean muscle mass. Plus, they’re budget-friendly, portable, and easy to prepare in countless ways—from boiled to poached to scrambled.
6. Stronger Bones and Improved Calcium Absorption
Eggs naturally contain both vitamin D and calcium, the two essential nutrients your body needs to build and maintain strong bones (14).
Vitamin D boosts your ability to absorb calcium efficiently, while calcium itself supports blood clotting, muscle contraction, and nerve signaling (15). Together, they help reduce the risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures, especially in older adults who may be deficient in vitamin D.

7. Supports Weight Loss and Satiety
Despite their richness, eggs are relatively low in calories and incredibly filling. Their high protein content helps control appetite, keeping you full longer and reducing the urge to snack.
Studies published in both the Journal of the American College of Nutrition and the International Journal of Obesity found that people who ate eggs for breakfast consumed fewer calories throughout the day and experienced greater weight and fat loss compared to those who ate bagels or cereal (16,17).
Replacing a carb-heavy breakfast with eggs not only stabilizes blood sugar but also enhances metabolic function and helps reduce waist circumference over time.
Bottom Line
Eggs are not the enemy—they’re one of nature’s most balanced foods.
Rich in protein, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, eggs provide lasting energy and numerous health benefits for the brain, eyes, muscles, and bones. For most healthy adults, eating two to three eggs a day is perfectly safe and beneficial.
As long as your overall diet is balanced—low in sugar, high in fiber, and rich in whole foods—eggs can be a simple, delicious cornerstone of your nutrition plan.
News in the same category


Top 5 Nutrients to Reduce Swelling in Feet and Legs

If you sleep with socks on, see what happens
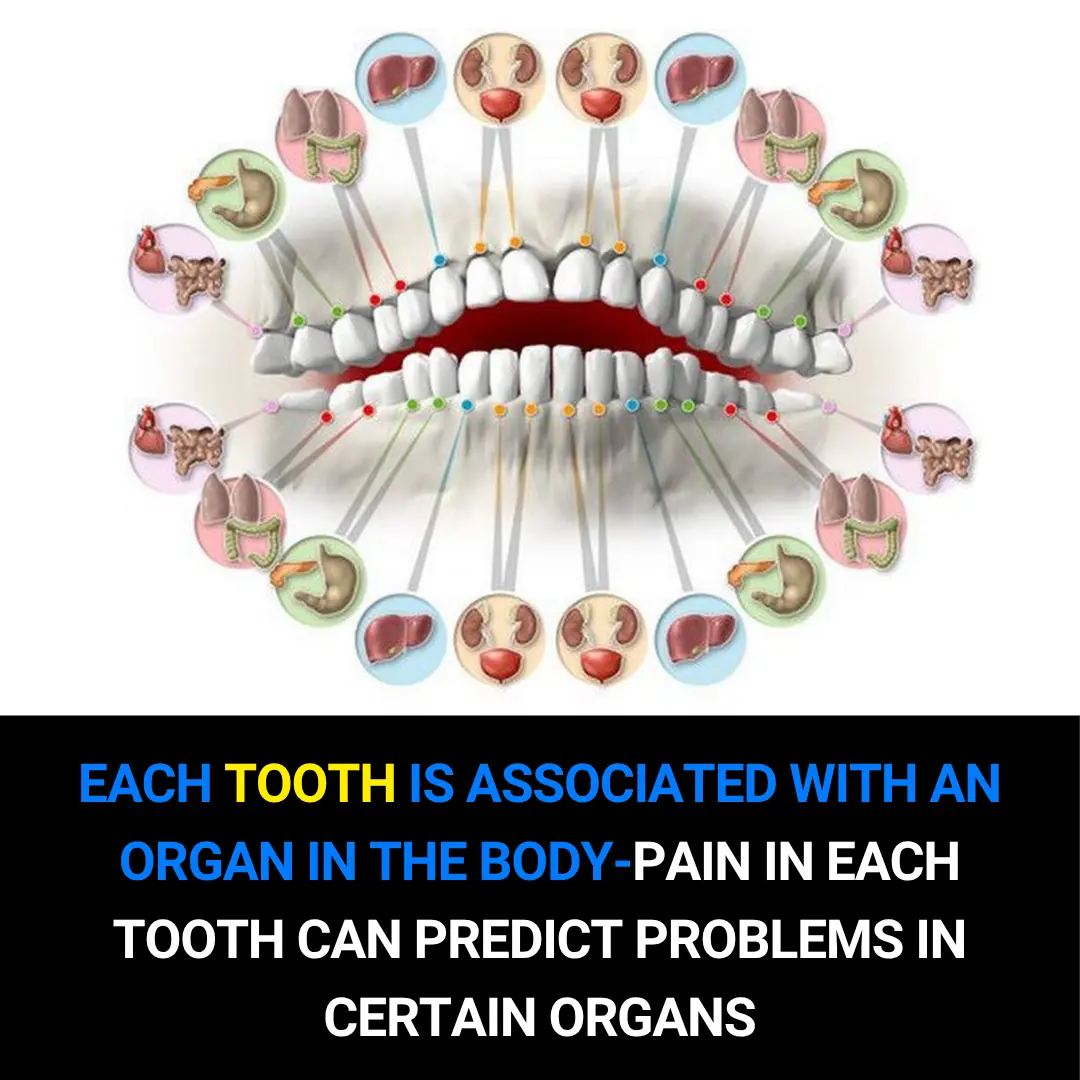
Each Tooth Is Connected to an Organ in the Body – How Tooth Pain May Reveal Hidden Health Problems

7 Heart-Healing Foods Your Cardiologist Won’t Tell You About

This Is What Happens To Your Body The Day You Stop Eating Bread

14 Symptoms of Liver Damage You Need to Know

17 Foods That Increase Magnesium And Prevent High Blood Pressure, Blood Clots And Muscle Fatigue

This Is What Happens to Your Body If You Eat Canned Tuna Every Day

Mix Castor Oil and Rosemary — The 7-Day Results Will Surprise You

This Is What Happens to Your Body the Day You Stop Eating Bread
14 Symptoms of Liver Damage You Need to Know

Prepare Ginger This Way to Prevent Cancer, Reduce Cholesterol, and Lower Blood Sugar Levels

How to effectively cleanse your lungs in just 72 hours

Scientists find a berry that can combat cancer, diabetes, and obesity

Doctors reveal that consuming pumpkin causes in...
🚨 The Silent Danger: Early Signs and Prevention of Colorectal Cancer

The shocking truth about blocked arteries—it’s NOT just fatty foods!

Boil bananas before bed, drink the liquid and you will not believe what happens to your sleep
News Post

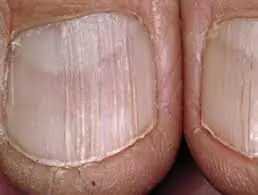
Vertical Nail Ridges? Here’s What Causes Them — and How to Fix It

The Unseen Heroes: A Rescue Dog's Loyalty That Saved My Life

Barrett’s Miracle: A Journey of Faith, Strength, and Prayer
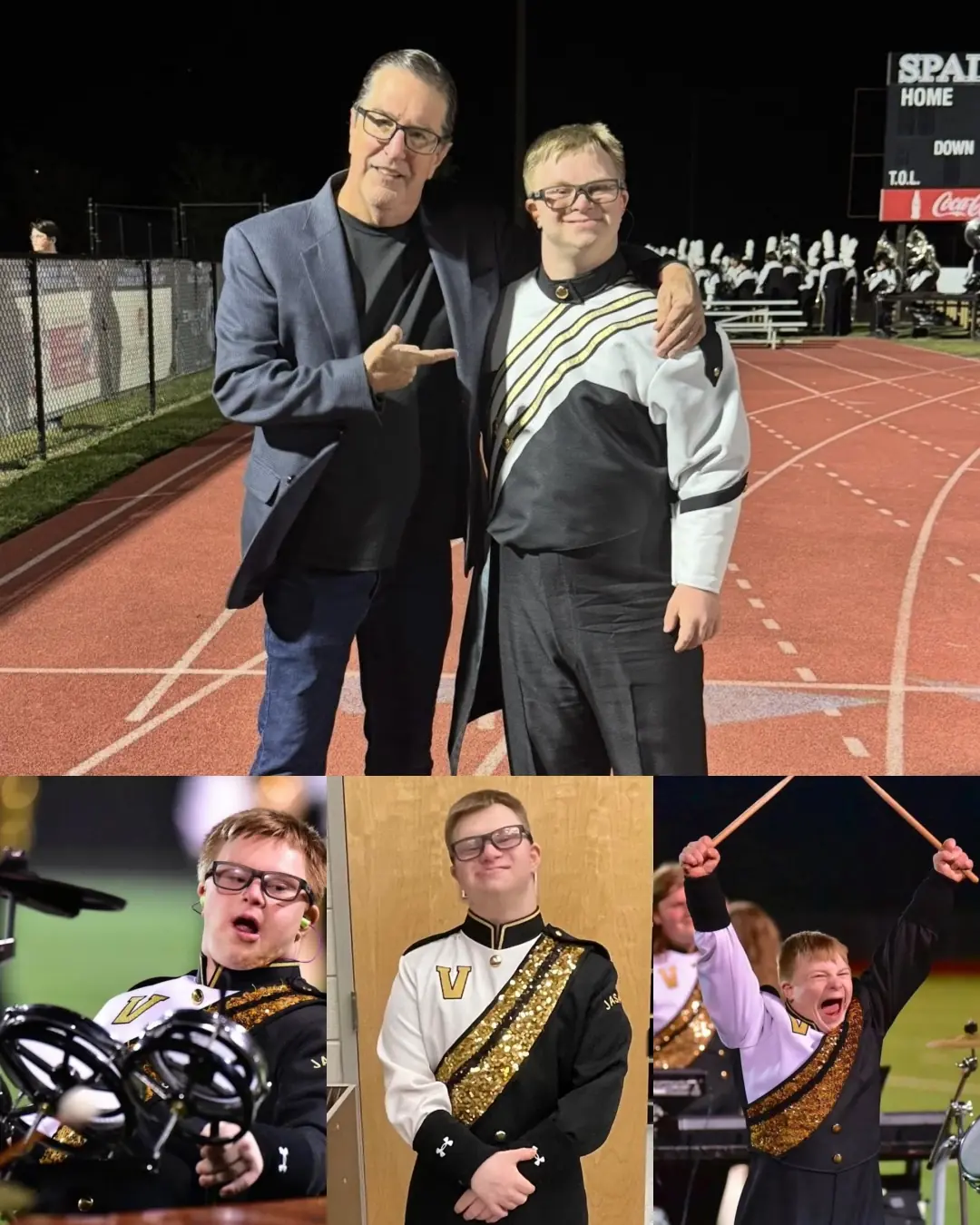

A Farewell to a Friend and His Passion for Music

Top 5 Nutrients to Reduce Swelling in Feet and Legs
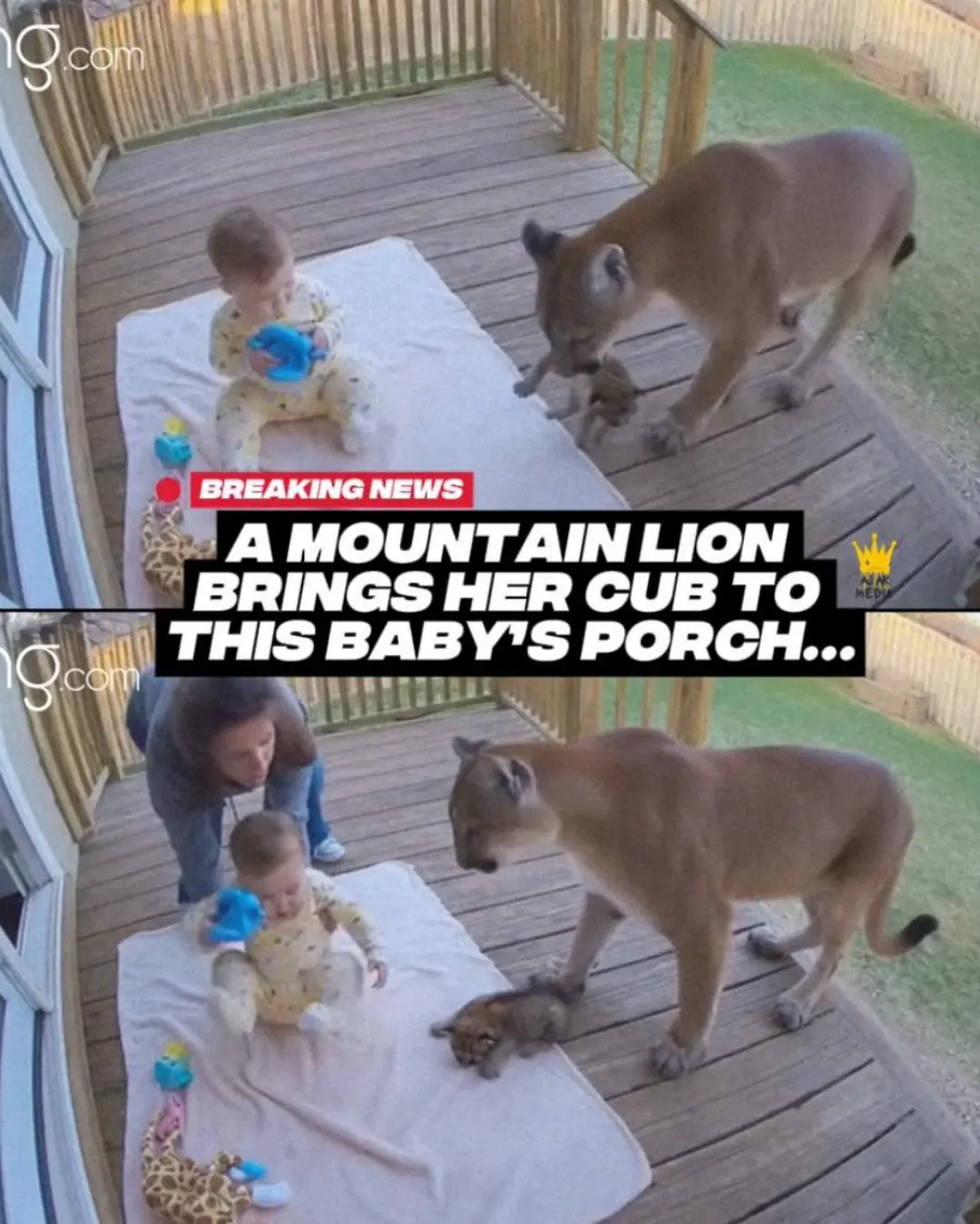

A Rare Encounter: The Moment a Mountain Lion Meets a Baby
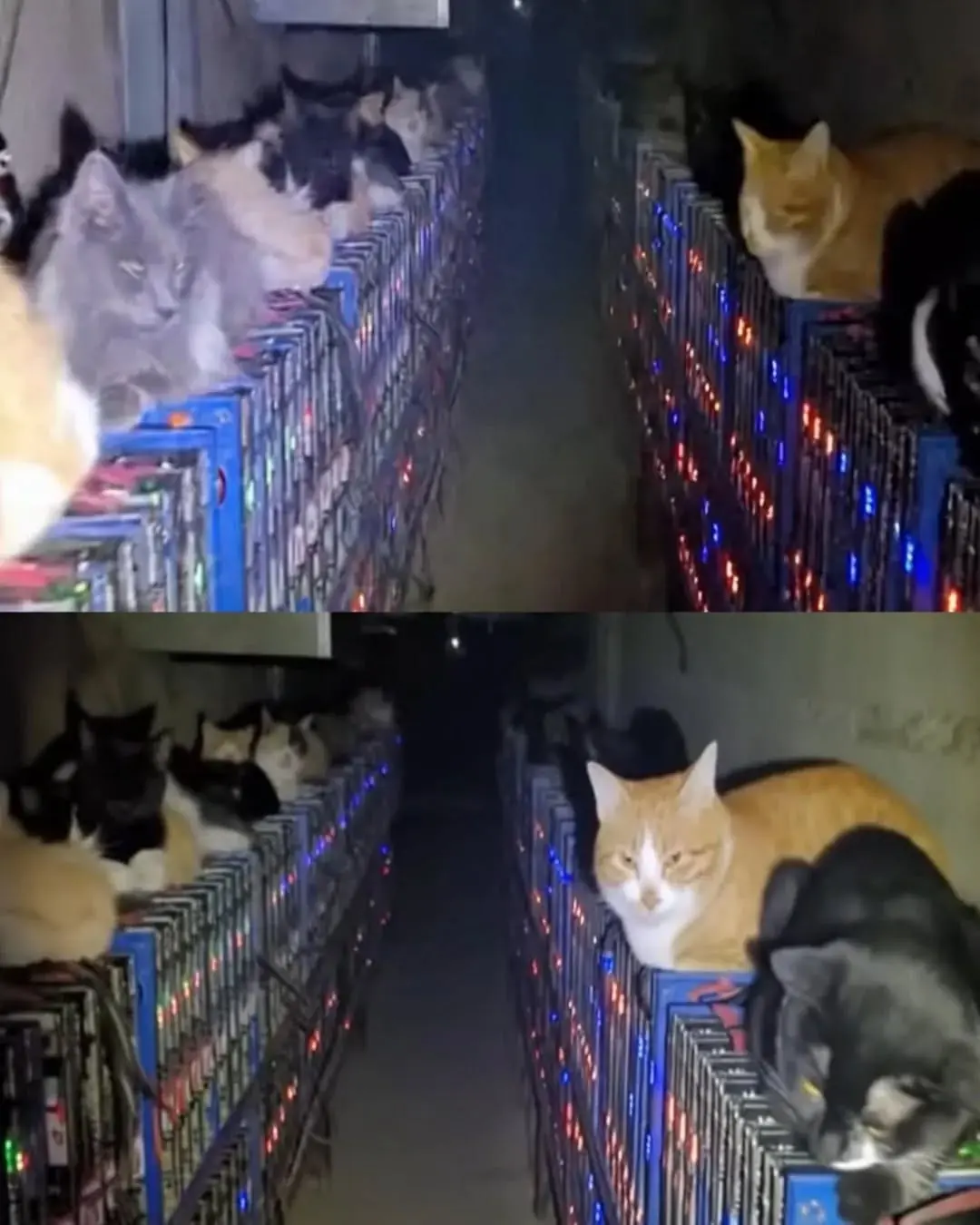

Stray Cats Bring a Bitcoin Mine to a Standstill — And Melt Hearts in the Process

If you sleep with socks on, see what happens

Each Tooth Is Connected to an Organ in the Body – How Tooth Pain May Reveal Hidden Health Problems
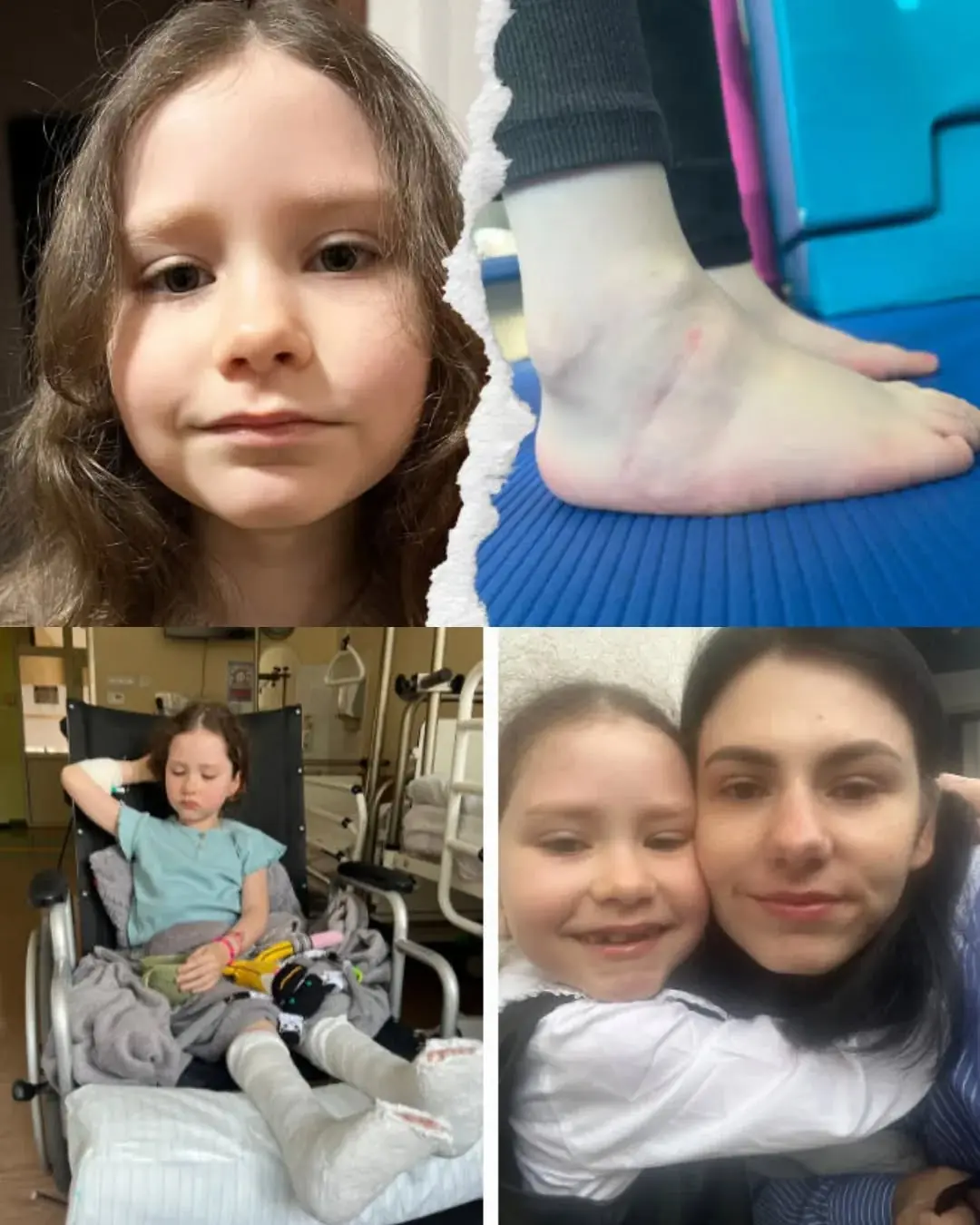
Dominika’s Fight for a Childhood Without Pain

Why There's A Growing Trend Of Straight Men Dating Trans Women
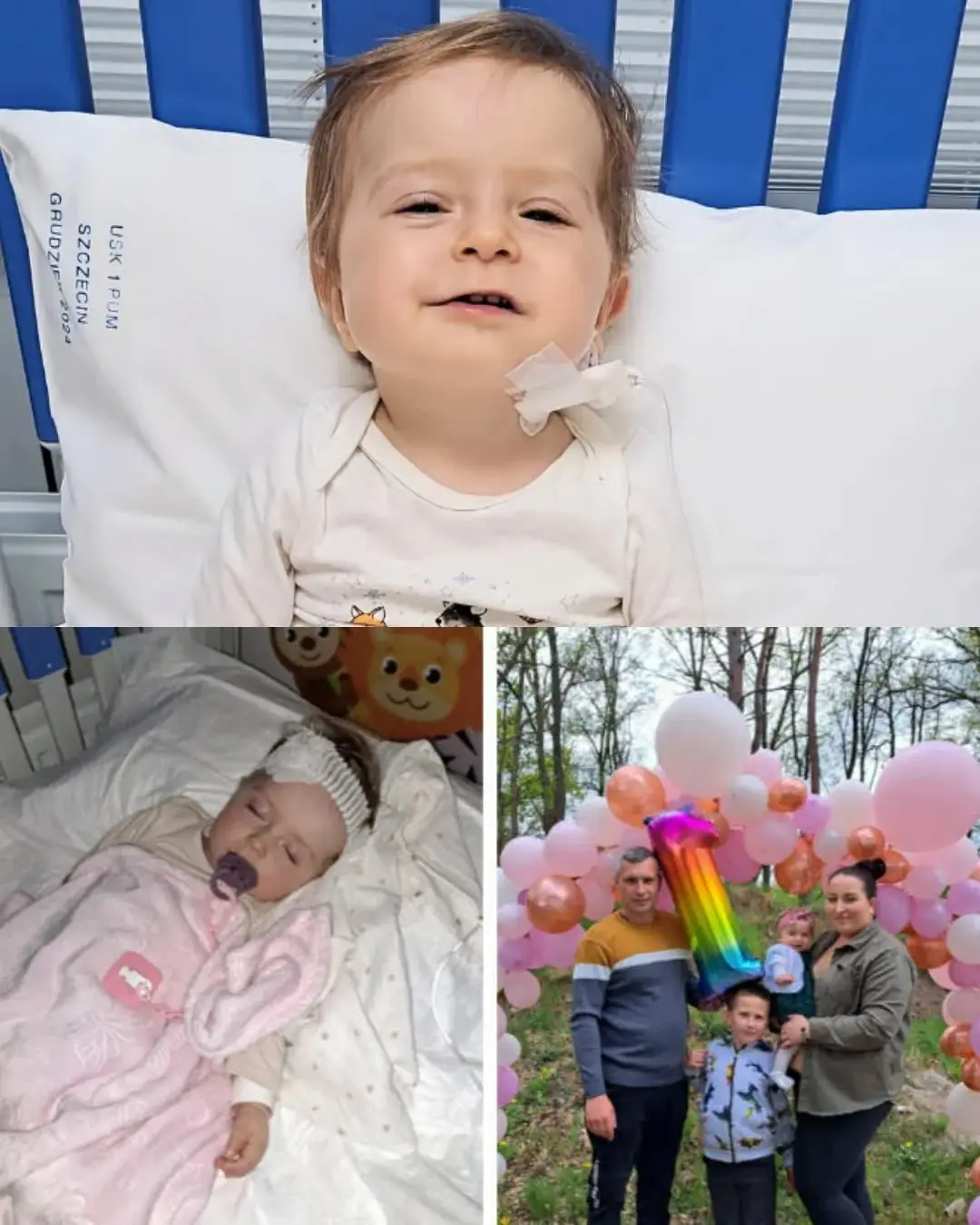
Michalinka’s Fight for Life: A Tiny Body, a Giant Spirit
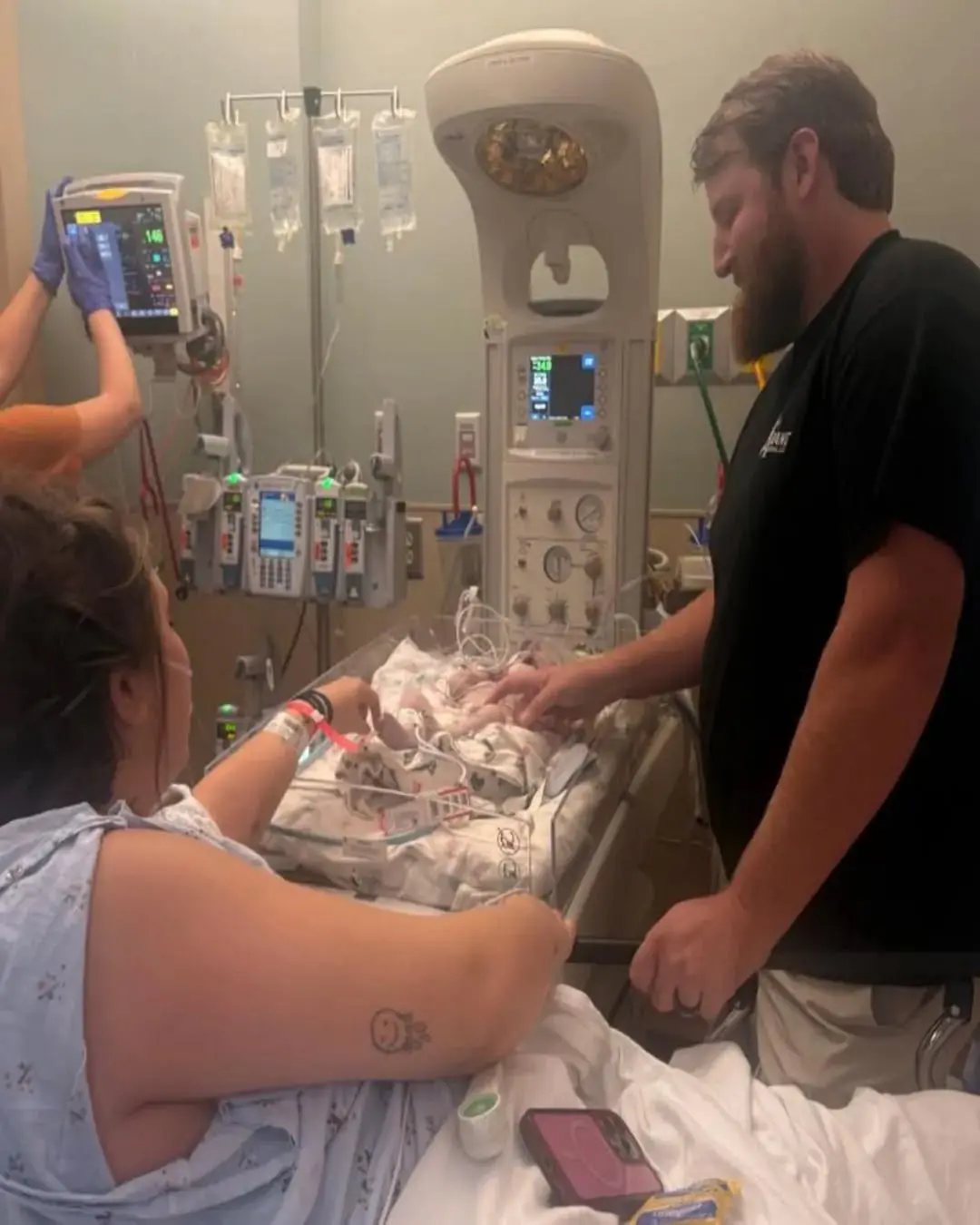
A Miracle in the Making: Baby Harlan’s Fight for Life
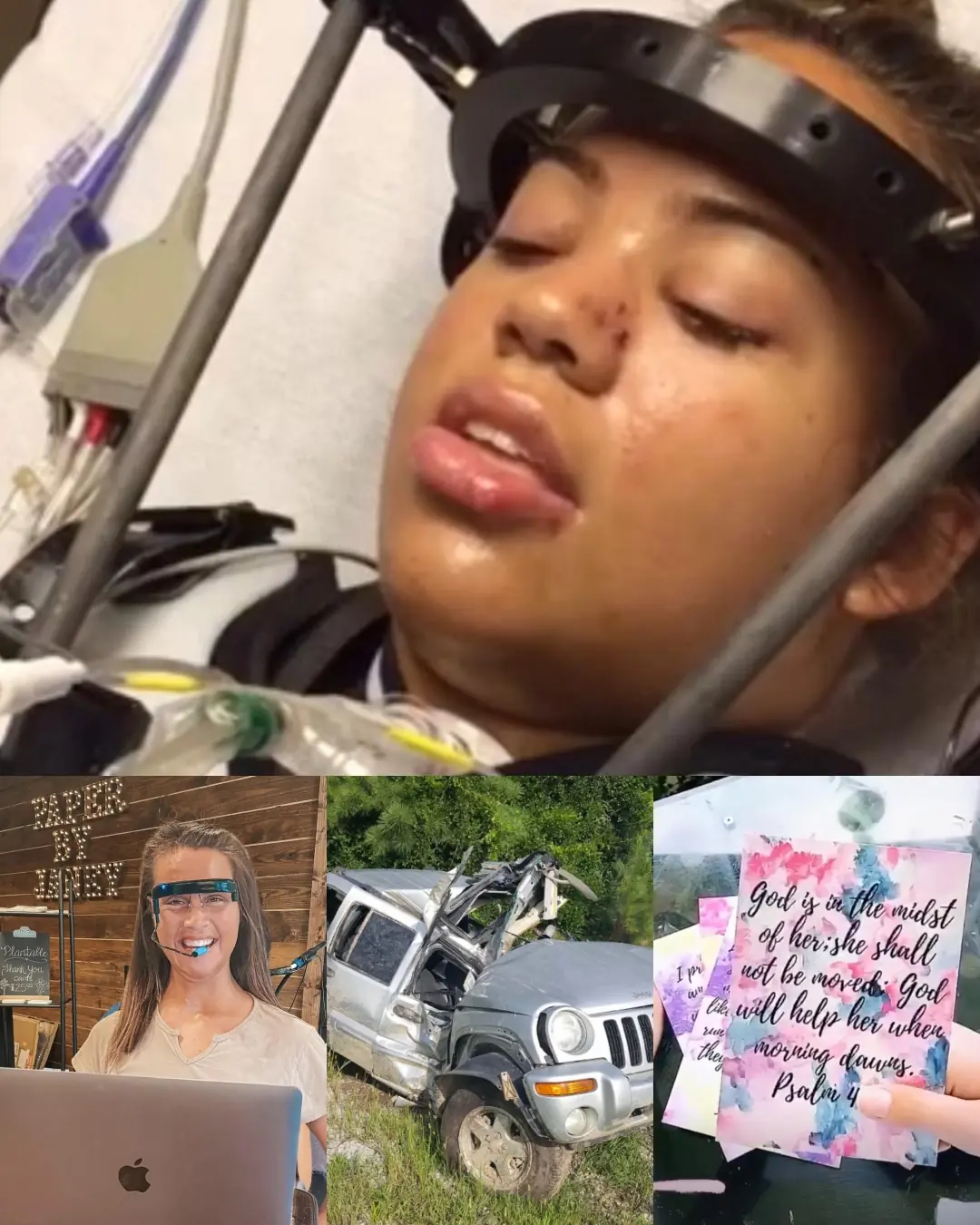
From Tragedy to Triumph: The Unbreakable Spirit of Janey Carter
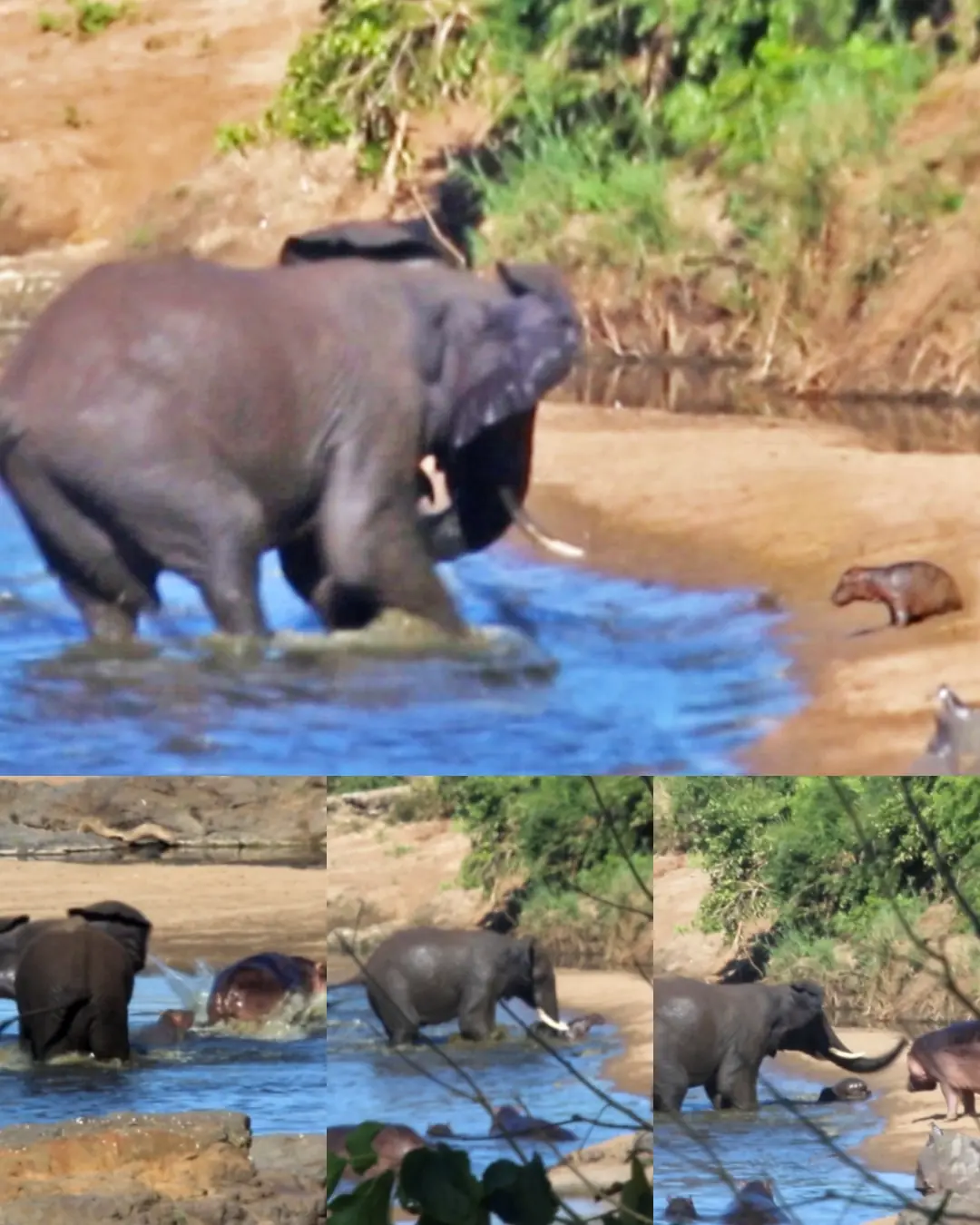

A Battle of the Wild: The Confrontation Between a Raging Elephant and a Baby Hippo

7 Heart-Healing Foods Your Cardiologist Won’t Tell You About

Never Clean Your Light Switch with Water: Here’s a Trick to Make It Spotless

Bad Habits After Doing Laundry That Can Make Your Whole Family Sick! Many People Overlook This Detail

Don’t Throw Away Your Used Balm Jar – Here’s a Super Useful Way to Reuse It That Every Family Needs
