Why Is One Knee Swollen but Not the Other?

Noticing that just one of your knees is swollen—while the other remains completely normal—can be concerning. While swelling in both knees often suggests a systemic or chronic condition like rheumatoid arthritis, swelling isolated to one knee typically points to a localized issue. Knowing the possible causes of one-sided knee swelling can help you determine whether it's a minor issue you can manage at home or a more serious condition that requires medical evaluation.
1. Injury or Trauma
One of the most common reasons for swelling in a single knee is injury or overuse. The knee is a complex joint that bears a lot of pressure and is vulnerable to both acute injuries and wear-and-tear damage. Sometimes, the injury is obvious—like a fall or sports-related impact—but other times, it results from repetitive strain and develops gradually.
Common causes include:
-
Ligament sprain or tear (such as ACL or MCL injuries)
-
Meniscus tear
-
Patellar dislocation
-
Bone bruise or fracture
Swelling from trauma often develops quickly, sometimes within hours, and may be accompanied by sharp pain, limited range of motion, stiffness, or a sensation of the knee "giving out."
2. Bursitis
The knee contains several small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion the joint and reduce friction. When one of these bursae becomes inflamed—often due to repeated kneeling, direct impact, or prolonged pressure—it can lead to prepatellar bursitis, commonly known as “housemaid’s knee.”
This typically causes visible swelling at the front of the knee and may feel tender or warm to the touch. While not usually dangerous, it can be uncomfortable and limit movement.
3. Infection (Septic Arthritis)
A joint infection is a serious and potentially dangerous cause of one-sided knee swelling. Known as septic arthritis, this condition occurs when bacteria enter the joint space, leading to rapid inflammation and fluid buildup.
Symptoms include:
-
Sudden swelling and intense pain
-
Redness and warmth around the knee
-
Fever, chills, or general malaise
This condition requires immediate medical treatment—often hospitalization, antibiotics, and joint drainage—to prevent permanent damage.
4. Gout or Pseudogout
If the knee swells up quickly and becomes extremely painful—especially during the night—the cause might be gout or pseudogout. These are forms of arthritis triggered by the buildup of microscopic crystals in the joint:
-
Gout is caused by uric acid crystals
-
Pseudogout involves calcium pyrophosphate crystals
Both typically affect only one joint at a time and can come on suddenly. The affected joint may also be red, warm, and difficult to move. These flare-ups can resolve on their own but often require medication to manage symptoms and prevent recurrences.
5. Localized Osteoarthritis
Although osteoarthritis often affects both knees over time, it can begin in just one—particularly if that knee has sustained an injury in the past or bears more of your body weight due to posture or biomechanics.
In this case, swelling tends to be:
-
Mild to moderate
-
Worse after physical activity or long periods of standing
-
Accompanied by stiffness, especially in the morning or after rest
Over time, wear and tear of the joint cartilage leads to inflammation and fluid buildup.
6. Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms at the back of the knee, often due to underlying joint problems like arthritis or a cartilage tear. It can make the knee feel swollen, especially when bending or extending the leg fully.
Although not always painful, the cyst may burst, causing sharp pain and swelling in the calf—sometimes mistaken for a blood clot. Ultrasound or MRI can confirm the diagnosis.
7. Blood Clot or Circulatory Issue
While uncommon, a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)—a blood clot in the leg—can cause swelling around the knee or lower leg. This is more likely if the swelling is accompanied by:
-
Pain in the calf
-
Warmth or redness in the leg
-
Shortness of breath (in severe cases)
A DVT is a medical emergency and needs immediate intervention to prevent serious complications like a pulmonary embolism.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical attention if:
-
The swelling appeared suddenly and is severe
-
The knee feels hot, red, or painful to touch
-
You have a fever or chills
-
You can’t walk or bear weight on the knee
-
Swelling persists for more than a few days without improvement
Delaying treatment can lead to worsening of the condition or permanent joint damage, especially in cases of infection, gout, or significant injury.
Final Thoughts
While having one swollen knee isn't always cause for alarm, it's not something to ignore either. The cause might be as simple as a minor sprain or as serious as an infection or blood clot. Monitoring the symptoms and getting timely medical advice are key to avoiding long-term complications. Taking care of your knees today ensures they’ll keep supporting you well into the future.
News in the same category

Early Signs of Liver Damage You Shouldn’t Ignore

Wrinkles Aren’t Just a Sign of Aging – Here’s What’s REALLY Causing Them

This is World’s ‘Most Lethal’ Food That Claims 200 Lives Annually

The danger of storing this in the refrigerator: a common habit that can affect your health

There is one thing you must unplug every time it rains or thunders

Just one spoon and you’ll run to the bathroom

A1c Testing in EDs Can Spot Undiagnosed Diabetes Cases
Recurring UTIs? 9 Proven Nonantibiotic Solutions

10 powerful plants to eliminate excess mucus and phlegm naturally
Spot these 10 warning signs of a stroke one week before
How to Get Rid of Worms in Humans

Proven Foods to Beat Gas and Bloating and Flatten Your Stomach

How to Make Lavender Lemonade to Help Get Rid of Headaches and Anxiety
1 shot to open arteries instantly (prevent heart attack & stroke)
5 early signs of poor circulation & how to boost blood flow
High Blood Pressure Drug Linked to Heart Failure, Study Shows

1 food for heart attack, hypertension, stroke and cholesterol?
Beta-Blocker Dos and Don’ts
News Post

Bizarre truth behind viral Tennessee truck stop that's impossible to visit

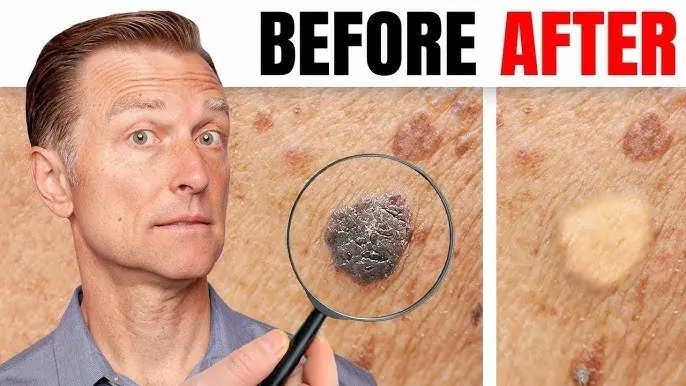
You Won’t Believe How Easy It Is To Get Rid Of Warts And Skin Tags With This Trick

Early Signs of Liver Damage You Shouldn’t Ignore

Wrinkles Aren’t Just a Sign of Aging – Here’s What’s REALLY Causing Them

Drift Off in Under Two Minutes with This Military-Approved Sleep Technique

This is World’s ‘Most Lethal’ Food That Claims 200 Lives Annually

The danger of storing this in the refrigerator: a common habit that can affect your health

There is one thing you must unplug every time it rains or thunders

Just one spoon and you’ll run to the bathroom

A1c Testing in EDs Can Spot Undiagnosed Diabetes Cases

Recurring UTIs? 9 Proven Nonantibiotic Solutions

10 powerful plants to eliminate excess mucus and phlegm naturally

Spot these 10 warning signs of a stroke one week before
🦷 Understanding Tooth Decay and Remineralization

🧄 Health Benefits of Eating Raw Garlic Daily
🌿 Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica): 17 Remarkable Benefits You Should Know
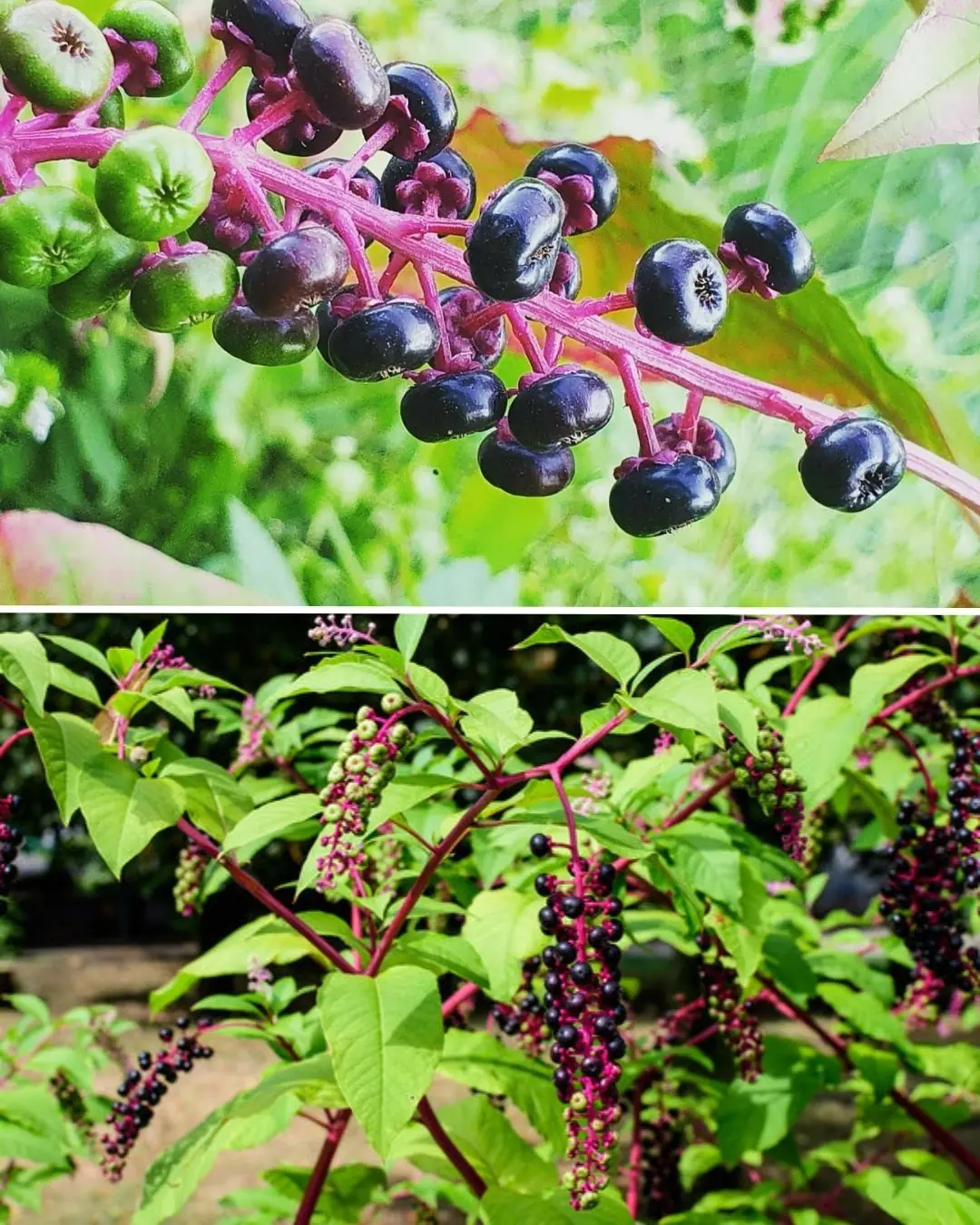

Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana): A Toxic Plant to Avoid

Aloe Vera and Clove Toner: A Natural Remedy for Aging Signs
