10 Warning Signs It’s Time to Cut Back on Caffeine
Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed stimulants in the world, commonly found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, sodas, and even certain medications. For many, it serves as a reliable pick-me-up to stay alert and productive throughout the day. However, like many substances, too much of a good thing can backfire. Excessive caffeine intake can lead to a range of physical and mental health issues. Being aware of how your body responds to caffeine is key to maintaining balance and long-term wellness.
Here are ten warning signs that may indicate you’re overdoing it on caffeine — and that it might be time to scale back.
1. Frequent Headaches
While caffeine is known to offer temporary relief for headaches — and is even included in some over-the-counter headache medications — it can also cause them. Regular, high caffeine intake can lead to what's known as "rebound headaches," where missing your usual dose results in painful withdrawal symptoms. Additionally, because caffeine is a diuretic, it can lead to dehydration, another major trigger for headaches. If you’re relying on caffeine daily and experiencing frequent head pain, your habit may be the culprit.
2. Muscle Twitches or Spasms

Caffeine directly stimulates the central nervous system. When consumed in large amounts, it can cause your muscles to twitch involuntarily or even spasm. This is particularly due to its impact on electrolyte balance — especially magnesium and potassium, which are vital for healthy muscle contraction and relaxation. If you notice odd muscle movements or cramping, it may be worth cutting back and rehydrating.
3. Heightened Anxiety or Nervousness

Caffeine works by blocking adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation, making you feel more awake and alert. While that’s great in moderation, high doses can trigger or worsen anxiety symptoms, particularly in people who are sensitive to stimulants. Racing thoughts, restlessness, heart palpitations, and feelings of unease after caffeine consumption are clear red flags. If your mental state feels less calm than usual, caffeine might be playing a role.
4. Digestive Issues
Caffeine increases stomach acid production and can irritate the gastrointestinal lining. For people with sensitive stomachs or conditions like acid reflux or gastritis, this can lead to discomfort, bloating, heartburn, or even nausea. Some also report a coated or sour taste on the tongue, particularly with strong coffee or energy drinks. Reducing caffeine or switching to less acidic options like green tea may help ease symptoms.
5. Dry or Flaky Scalp
Caffeine has diuretic effects, which means it causes the body to expel more water. Over time, this can lead to dehydration, affecting the skin and scalp. A dry, itchy, or flaky scalp may be a subtle sign that you’re not staying properly hydrated — especially if your fluid loss is increased by excessive caffeine consumption. Hydrating with water alongside your caffeine intake can help, but moderation is key.
6. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
RLS is a neurological condition characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, usually in the evening or during rest. Caffeine’s stimulating nature can worsen these symptoms, making it more difficult to relax and fall asleep. Studies have shown that cutting back on caffeine can reduce the severity or frequency of RLS in some individuals. If you suffer from RLS, especially at night, try limiting or eliminating caffeine after midday.
7. Midday Energy Slumps
One of caffeine’s main appeals is its quick energy boost. However, it can also lead to sharp energy crashes as its effects wear off, leaving you feeling more drained than before. This cycle often leads to a dependency: more caffeine is consumed to overcome the slump, which perpetuates the pattern. Long-term reliance can actually decrease your body’s natural energy production, making you feel more tired without it.
8. Swelling or Inflammation

Though less common, some individuals may experience inflammation or swelling as a result of caffeine sensitivity. This can manifest as puffiness, joint pain, or bloating. Inflammation is the body’s natural immune response, and if triggered by caffeine, it may indicate an underlying intolerance or overexposure. If you notice increased swelling or water retention after consuming caffeine, it's worth investigating.
9. Trouble Sleeping or Insomnia
Because caffeine blocks adenosine — the brain chemical responsible for making you feel sleepy — it can severely disrupt your sleep patterns. Even consuming caffeine six hours before bedtime can interfere with falling asleep or staying asleep through the night. Poor sleep, in turn, leads to fatigue, prompting more caffeine use the next day — a cycle that can be hard to break. Consider cutting caffeine by the early afternoon to improve sleep quality.
10. Elevated Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Caffeine increases adrenaline production, which can cause your heart to beat faster and your blood pressure to rise. While this might not be a concern for everyone, those with heart conditions, hypertension, or heightened cardiovascular risk should monitor their intake closely. Persistent palpitations or feelings of a “racing heart” after drinking coffee or energy drinks should not be ignored.
Final Thoughts
Caffeine can be a valuable ally when used in moderation — boosting alertness, improving mood, and enhancing productivity. However, your body often sends clear signals when it’s had too much. Paying attention to these warning signs can help prevent chronic issues and keep you feeling your best.
If you're experiencing several of the symptoms listed above, try gradually reducing your caffeine intake, staying hydrated, and prioritizing rest. Sometimes, simply switching to decaf, herbal tea, or lower-caffeine alternatives can make a significant difference in how you feel day to day.
News in the same category


After Surviving 800 Snake Bites, This Man’s Blood Could Be the Universal Antivenom the World’s Been Waiting For

“Cases Are Exploding”: Living Near a Golf Course May Raise Your Risk of Parkinson’s, Study Warns

You’ll never see mosquitoes again if you do this

What to Eat to Boost Energy After 60: Key Foods for Vitality and Well-being.

8 Foods That Help Eliminate Cancer Cells
How to Tell If You Have Intestinal Parasites and What to Do About That

Scientifically Proven Health Benefits of Avocado and Avocado Seeds
An Eye Specialist Explains What To Do If You Begin To See “Floaters”

10 W@rning Signs It’s Time to Cut Back on Caffeine

5 Early Signs of Colon Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore
Scientists Discover Body’s ‘Kill Switch’ Capable of Destroying Cancer Cells

Native American High Schooler Discovers Cancer-Fighting Properties in Traditional Chokeberry Pudding

Be Careful If You’re Farting More Than 25 Times a Day—It Might Be a Sign Your Body is Trying to Warn You
Passing gas up to 25 times a day can be considered normal - but when you notice a sudden increase, especially if it's paired with discomfort or other symptoms, it's time to tune in.

The Healing Benefits of Cloves: Natural Remedies for Improved Wellness

13 Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar and 9 Ways to Take Control of Your Health
If You Have These Tiny Red Dots On Your Arm, Do Not Ignore The Warning Signs

The Truth About “Old Person Smell”: What Causes It And How To Get Rid Of It

Scientifically Proven Health Benefits of Lemons (Including Lemon Water)
News Post

Consciousness Is Not Confined to the Brain, But Is Connected To The Whole Universe, Scientists Say

After Surviving 800 Snake Bites, This Man’s Blood Could Be the Universal Antivenom the World’s Been Waiting For

“Cases Are Exploding”: Living Near a Golf Course May Raise Your Risk of Parkinson’s, Study Warns

11 Heartbreaking Signs Your Dog Is Nearing the End—And How To Give Them The Love They Deserve

Why McDonald’s Removed The Clown From The Company Image

You’ll never see mosquitoes again if you do this

What to Eat to Boost Energy After 60: Key Foods for Vitality and Well-being.

9 Chilling Stories of Third Man Syndrome: When an Unseen Presence Aided Survival in Disasters

Experts Are Drawing Attention To A Disturbing Noise That People Produce Just Before They Die

A Young Woman Was Found Dead During A Long-Distance Bus Journey—With 26 iPhones Glued To Her Body

8 Foods That Help Eliminate Cancer Cells

Hacker with 30 years experience reveals the one thing we need to be worried about in the future

Man who spent 10,000 Bitcoin on two pizzas in 2010 could've been eye-wateringly well off today

How to Tell If You Have Intestinal Parasites and What to Do About That

Scientifically Proven Health Benefits of Avocado and Avocado Seeds

An Eye Specialist Explains What To Do If You Begin To See “Floaters”
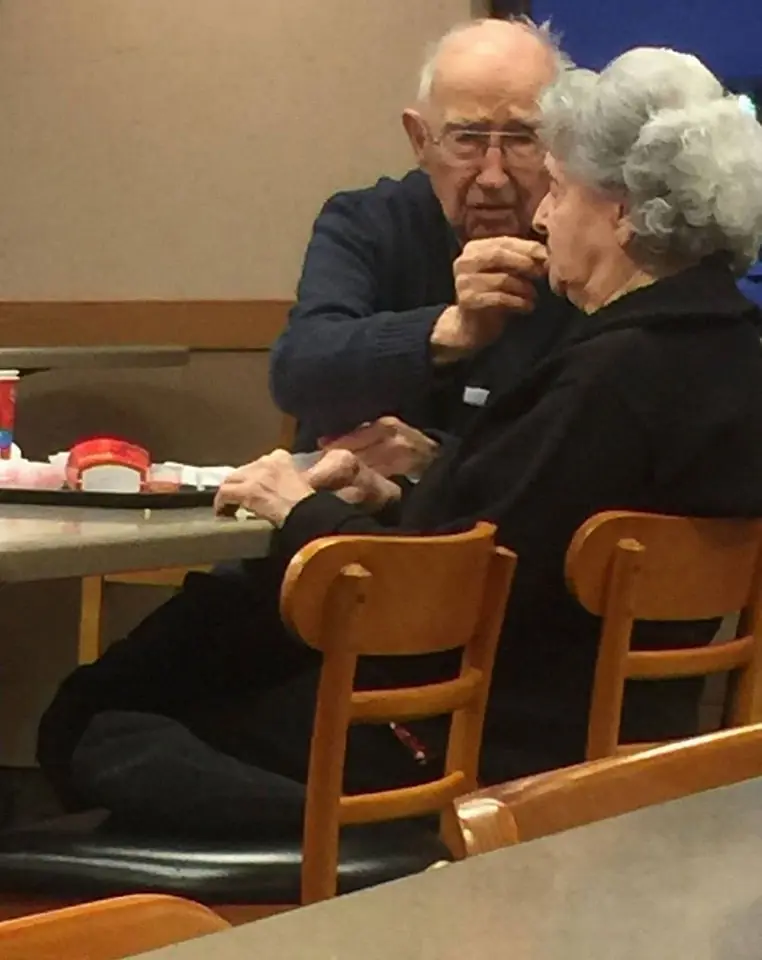

A Double Cheeseburger and 75 Years of Love.
It was just a regular evening at Wendy’s. I had stopped in for a quick bite—nothing fancy, just a double cheeseburger, fries, and a moment of peace before heading home.

My Own Daughter Stole My Retirement Savings to Buy a House for Herself
