How to Tell If You Have Intestinal Parasites and What to Do About That
How to Tell If You Have Intestinal Parasites and What to Do About That
There is a common misconception that intestinal parasites exist only in underdeveloped countries. While they are indeed more prevalent there, they are much more common than many people realize in developed countries as well. It's not a pleasant thought to consider yourself a host to a colony of intestinal parasites, but you are not alone. According to the World Health Organization, over 3 billion people suffer from some type of intestinal parasite, and not all of these individuals live in underdeveloped or impoverished nations.

What Are Intestinal Parasites?
Parasites are generally classified into many groups, but the two main types of intestinal parasites are helminths and protozoa.
-
Helminths are multicellular worms that cannot multiply in the human body, such as tapeworms, pinworms, and roundworms.
-
Protozoa, on the other hand, are single-celled organisms that can multiply inside the human body and can cause serious infections.
How Do You Get Intestinal Parasites?
Intestinal parasites are typically transmitted when a person comes into contact with infected feces (for example, through contaminated soil, food, or water). Other factors that can increase your risk include:
-
Visiting an area known to have parasites.
-
Poor hygiene and sanitation practices (for both food and water).
-
Having a weak immune system.
-
Handling animals.
-
Age factor (children and the elderly are more likely to get infected).
Once you are infected with parasites, the condition is contagious and can be easily passed to other people.
Why Are Intestinal Parasites Dangerous?
As the name suggests, parasites live inside us and feed off us. In places with high hygiene levels, parasites might not pose a great threat, but in poorer countries or areas with low hygiene and poor sanitary conditions, parasites can be a real life threat. When our intestines become a host to parasites, even the high levels of acid in the digestive tract may not fully protect our body. Our immune system then tries to defend itself, and the gut can become inflamed.
Intestinal parasites can prevent the proper absorption of food by the body and release toxins into the bloodstream and lymphatic system. Severe infections can cause a bowel obstruction, where the intestine is partly or completely blocked, preventing food, fluids, and gas from moving through the intestines normally. Severe infestation can also lead to anemia by causing bleeding in the intestines.
The challenge is that because there are so many types of parasites, they can cause a wide range of symptoms, and only a few of them are directly digestive in nature. So, if you've tried various treatments to relieve your symptoms without success, intestinal parasites could be the hidden cause of many unresolved health issues you're experiencing.

Key Symptoms of a Parasite Infection in the Body
-
Excessive food cravings or, alternatively, loss of appetite.
-
Weight loss.
-
Stomach pain.
-
Constipation, diarrhea, gas, or other symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
-
Blood sugar fluctuations.
-
Skin disorders, such as acute itching or pain around the rectum and other body parts, rashes, or other skin irritations.
-
Anxiety and depression.
-
Sleep disorders.
-
Pain or aching muscles or joints.
-
Fatigue and exhaustion.
-
Iron-deficiency or anemia.
-
Immune disorders with an excessive number of bacterial, fungal, or viral infections.
-
Diminished libido.
-
Bloody stools or light-colored stool.
-
Nausea or vomiting.
-
White specks in stool.
-
Sulfur burps.
If you are experiencing some of these symptoms, it's advisable to see your doctor.
How to Treat Intestinal Parasites
Treatment for intestinal parasitic infections can involve conventional medication or alternative medical approaches.
Conventional Medicine
If you suspect you have intestinal parasites, your doctor will be able to perform a stool test to confirm the infection and then prescribe medication most effective against the specific type of intestinal parasite identified.
Alternative Medicine
-
Herbs: Some commonly suggested herbal treatments include: garlic, goldenseal, barberry, anise, Oregon grape, wormwood, wormseed, black walnuts, curled mint, cloves, oregano, thyme, and olive leaf. Always consult a physician before taking any anti-parasite herbal supplement.
-
Supplements: Consult a physician before taking any supplements to ensure they don’t interfere with current medications.
-
Probiotics (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Saccharomyces boulardii, and bifidobacteria) help keep your digestive tract healthy, which discourages parasites.
-
Digestive enzymes help restore your intestinal tract to its normal state, making it inhospitable to parasites. Papain, an enzyme from the papaya plant, may help kill worms when taken 30 minutes before or after meals.
-
Vitamin C supports the immune system.
-
Zinc supports the immune system and is also used to heal stomach ulcers.
-
-
Homeopathic Treatments: Homeopathic remedies for parasite infections may include: Cina; Indigo; Spigelia; Podophyllum; Cuprum oxidatum nigrum; Teucrium; Sabadilla; Stanum.
-
Diet: A diet rich in raw garlic, pumpkin seeds, papaya seeds, pineapple, carrots, beets, and pomegranates can help to kill parasites.
-
In one study, researchers found that a mixture of honey and papaya seeds with plenty of water is good for flushing the system.
-
Consuming more fiber may help the body get rid of worms.
-
Avoid simple carbohydrates, such as refined foods, sweetened juices, and sugars.
-
Drink plenty of water to aid fecal elimination.
-
Temporarily avoid coffee and alcohol.
-
Consume foods rich in beta-carotene (a precursor for vitamin A), such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and squash. Vitamin A is thought to increase resistance to parasites.
-
Add spices such as turmeric and cloves, which can help fight parasites.
-
-
Intestinal Cleansing: This is a popular alternative approach that involves a high-fiber diet and supplements such as psyllium husks, citrus pectin, papaya extract, bentonite clay, activated charcoal, pumpkin seeds, beetroot, and flaxseed.
-
Food-Grade Diatomaceous Earth (DE): Food-grade diatomaceous earth is also a natural and effective way to eliminate internal parasites. A study published in the Journal of Poultry Science found that DE has the potential to be an effective treatment to help control parasites. Some people like to take a mixture of clove oil and wormwood along with food-grade diatomaceous earth to kill intestinal parasites. When buying diatomaceous earth, be sure to look for a brand that is food-grade, meaning that it is safe to ingest.
Preventing Infection
As previously mentioned, parasite infections are very contagious. You can easily pass parasite eggs onto anything or anyone you touch. Therefore, it is crucial to wash your hands and maintain good hygiene habits to reduce the chances of further transmission. Wash your hands thoroughly after going to the restroom and before eating or preparing food. If you travel overseas, pay close attention to the quality of drinking water and the hygiene of the food you consume, and wash fruits and vegetables well.
News in the same category


“I’ve Scanned 250,000 Brains”: These 5 Foods Can Make Your Brain Feel Younger in Just 2 Months

Avocado Seed Tea with Hibiscus Flower: The Homemade Remedy That Can Transform Your Health

Repurposed Cancer Drug Shows Promise in Slowing Parkinson’s Disease Progression
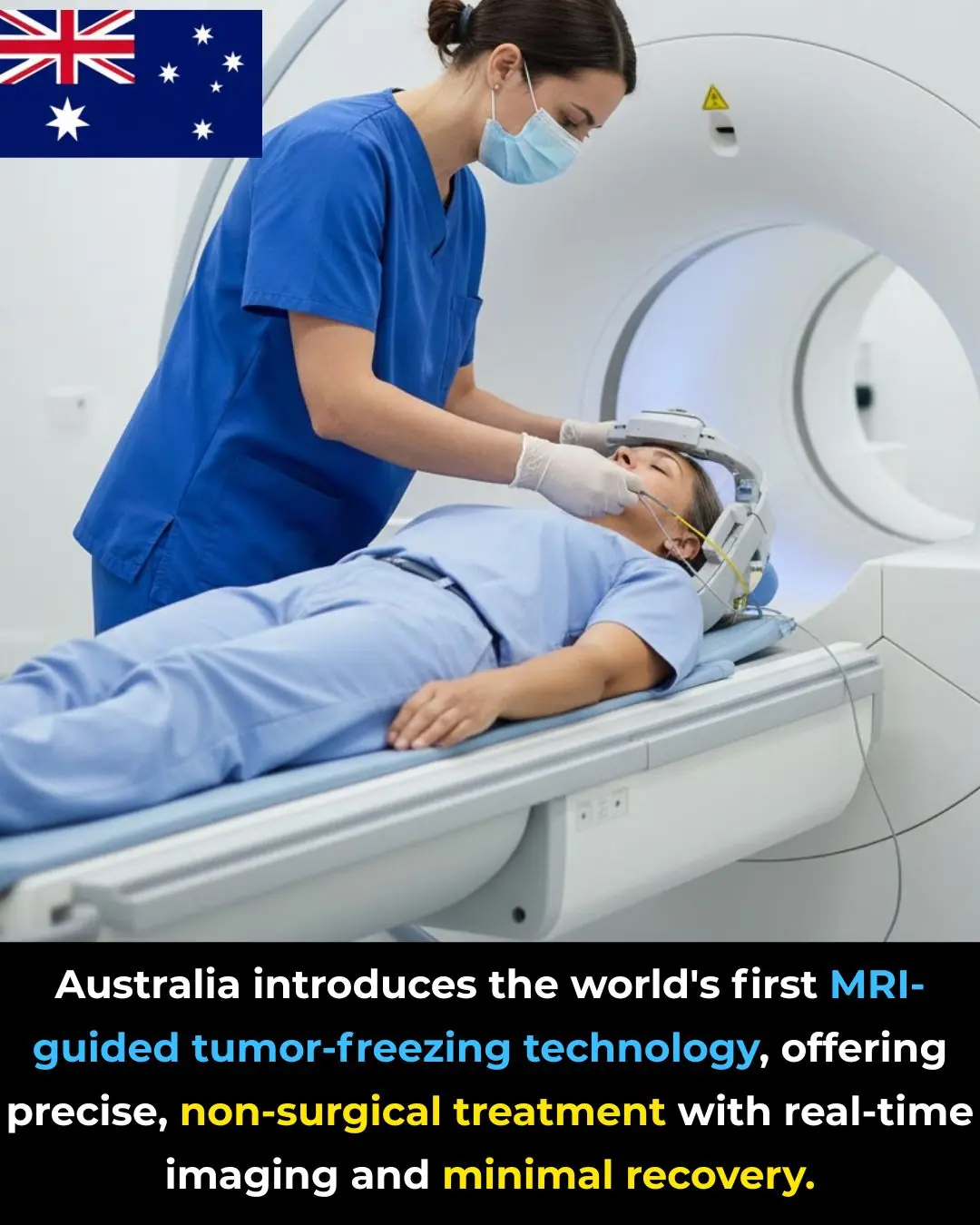
MRI-Guided Cryoablation: Australia’s Breakthrough in Non-Surgical Tumor Treatment

7 habits that make you look ugly...

If you're a woman with chin whiskers, pay attention. Here's what it means

🏠 8 Household Items That Could Be Affecting Your Health (And How to Check Them Safely at Home)

If your cat comes near your face while you sleep, this is happening in your life

10 Benefits of Drinking Rosemary Tea on an Empty Stomach

Red Bumps That Look Like Goosebumps

Reasons You Should Sleep 8 Hours a Day
🔥 Red Alert in Your Arteries! These 8 Secret Fruits Dissolve Silent Clots and Save Your Heart 💓

Here's The Truth Behind This Scar On People's Upper Left Arm
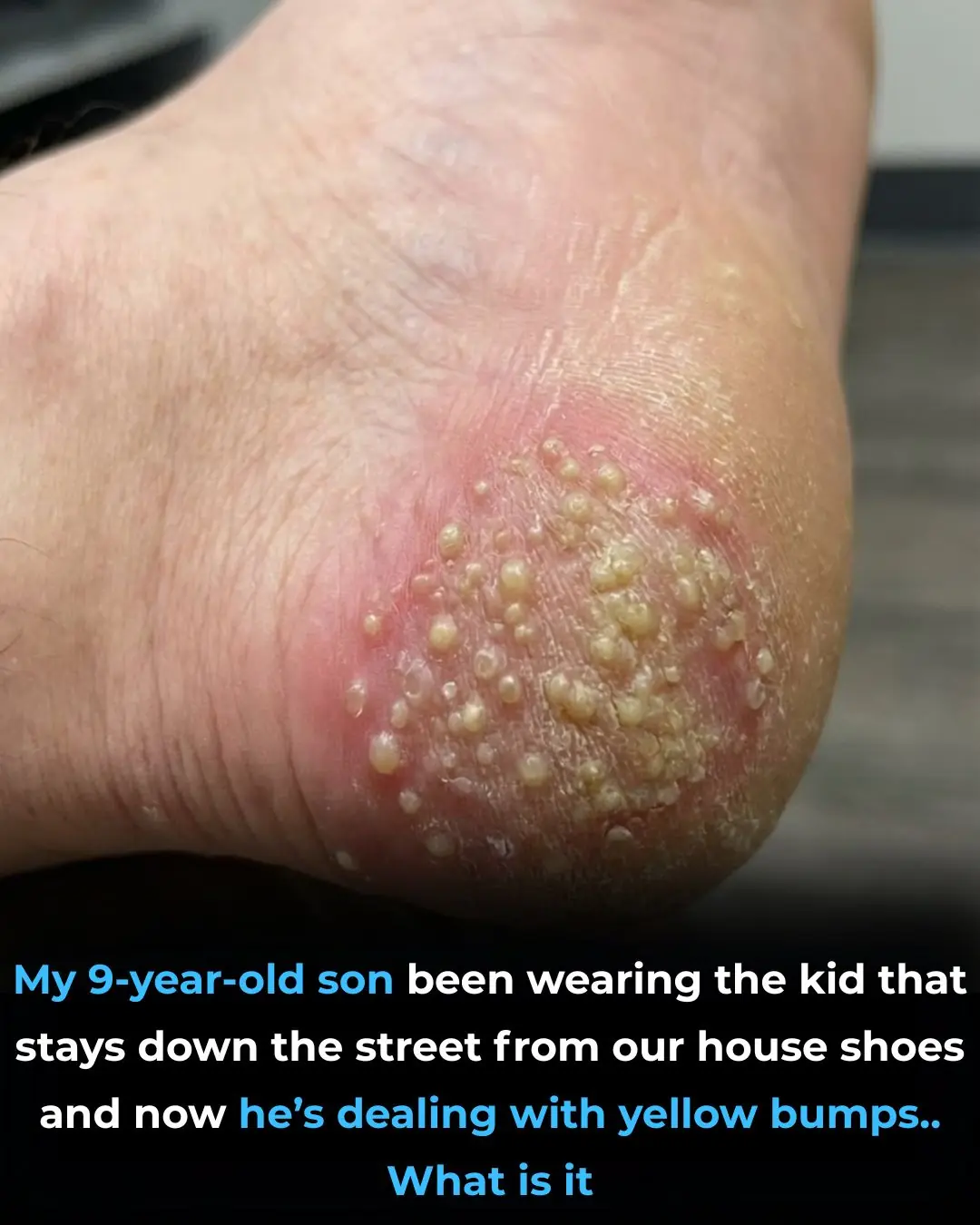
These are the consequences of wearing used…

Early Menopause

The Powerful Plant That Can Support Well-being: Discover the Benefits of Greater Burdock Root

Homemade Natural Remedies: Traditional Drinks and Recipes That Support Your Well-Being
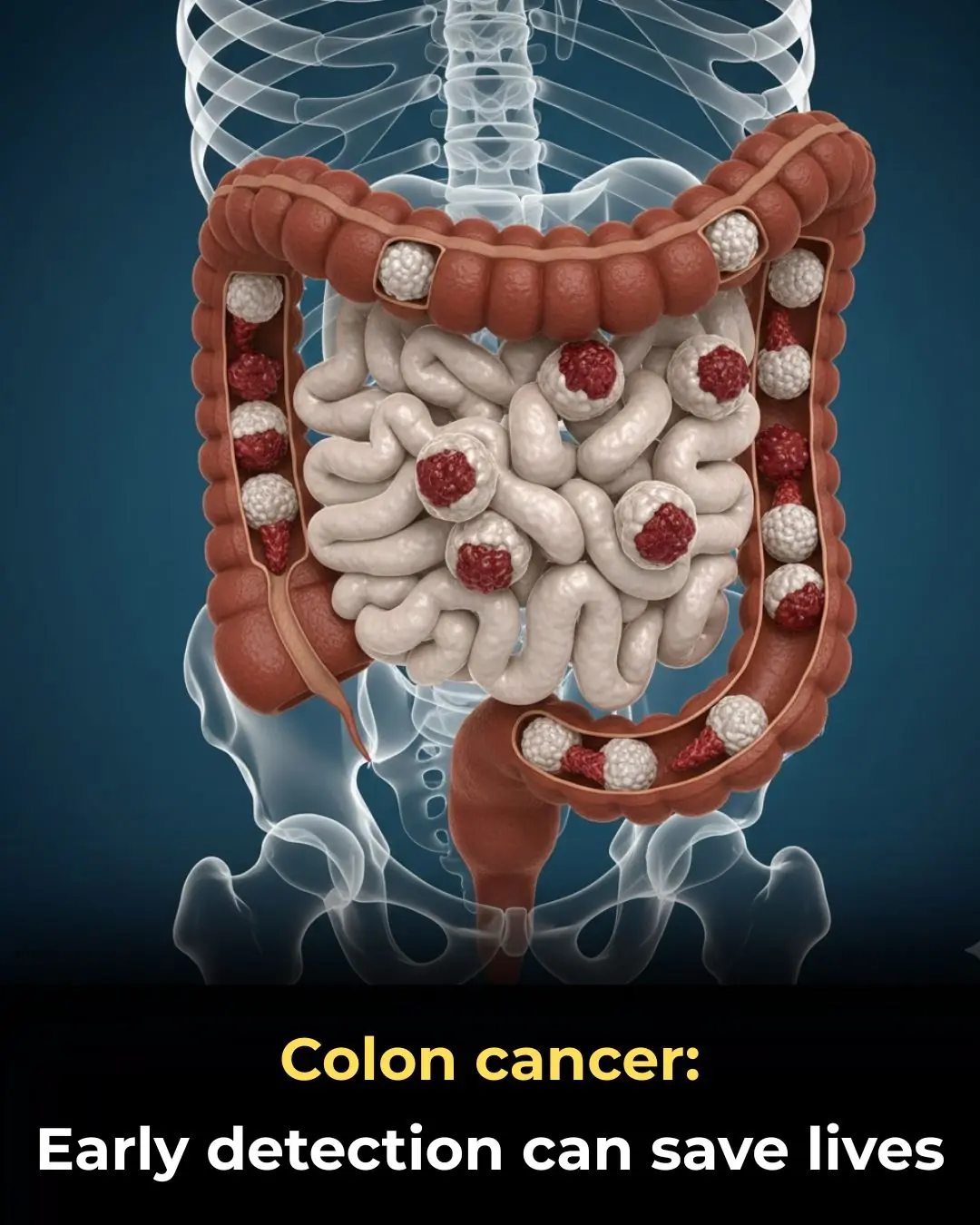
What Is Colon Cancer and Why Early Detection Can Save Lives
🩺 Gastritis: What It Is, Common Symptoms, Causes, and How to Care for Your Stomach
News Post

Spiny Amaranth (Amaranthus spinosus): Benefits, Risks, and Safe Uses

“I’ve Scanned 250,000 Brains”: These 5 Foods Can Make Your Brain Feel Younger in Just 2 Months

Avocado Seed Tea with Hibiscus Flower: The Homemade Remedy That Can Transform Your Health

A Businesswoman Scolded a Beggar for Touching Her Car — Then Saw His Bracelet

The Truth Behind the Wall — Max Knew It All, but No One Listened.

AFTER 15 YEARS OF RUNNING MY BUSINESS IN THE UK, I RETURNED TO GEORGIA AND FOUND MY DAUGHTER LIVING AS A MAID IN THE $4M MANSION I LEFT HER.

FATE STEPS IN

THE NIGHT IN CORRIDOR C

WRONG GIRL. WRONG BROTHER.

How to detect pork sausage contaminated with borax? Here are 6 simple tips.
Stepmother Forced Poor Orphan To Marry Poor Man But They Knew He Was A Billionaire

Billionaire Sees His Poor Employee Feeding Disabled People, What He Did Next Made Her cry

She Was Married Against Her Will — Life Took an Unexpected Turn

Billionaire had a one night stand with her, months later he saw her stranded and begging in the rain

They Mocked Her for marrying A Mad Man – Unaware He is a Billionaire in Disguise

Seven Months Pregnant, Left at a Bus Stop With One Loaf of Bread… Until a Stranger Stopped

My Sister Just Gave Birth—But My Husband Took One Look at the Baby and Whispered, “Call the Police.”

I Threw My Wife’s Daughter Out Because She Wasn’t My Blood—Ten Years Later, the Truth Destroyed Me

Eight Years After Her Daughter Vanished, a Mother Recognized Her Face Tattooed on a Stranger’s Arm
