Doctor reveals what really happens to your body when you go under anesthesia

For many people, the idea of undergoing surgery is understandably nerve-wracking. While tomophobia — the fear of surgery — is relatively well-known, there’s a lesser-known but very real phobia called anesthesiophobia: the fear of anesthesia itself.
Unlike general surgical anxiety, anesthesiophobia centers on specific concerns: losing control, waking up during surgery, or perhaps the most terrifying thought of all — never waking up. While these fears can feel overwhelming, especially for individuals with anxiety or panic disorders, medical professionals work diligently to ensure patient safety, comfort, and peace of mind.
Still, the fear of the unknown can be powerful. Fortunately, Dr. Daniel Medel, a practicing anesthesiologist, is helping demystify the process. In a popular YouTube video, he explains what really happens when you’re “put under” — and why it’s a lot more fascinating (and less frightening) than Hollywood would have you believe.
Anesthesia: Why We Use It and What It Does
There are countless reasons someone might need anesthesia — from major procedures like open-heart surgery to routine treatments like wisdom tooth extraction. The primary purpose? To block pain signals from reaching the brain and prevent the physical and psychological trauma of being conscious during invasive procedures.
Dr. Medel explains that anesthesia is essentially a “reversible off switch” for the nervous system. But rather than flipping a single switch, it's more like dimming multiple systems — pain perception, memory, consciousness, and motor control — all at once.
“It’s not quite sleep, and it’s definitely not death,” Medel says. “The best way I can describe general anesthesia is like time travel — but only forward.”
The Three Types of Anesthesia
Dr. Medel breaks down anesthesia into three major categories:
-
Local Anesthesia – Used to numb a small, specific area. Commonly applied for minor procedures like mole removal or dental work.
-
Regional Anesthesia – Blocks sensation in a larger region of the body, such as an arm, leg, or the lower half during childbirth (e.g., epidurals).
-
General Anesthesia – This is the full knockout. You’re unconscious, your muscles are relaxed, and you won’t remember a thing.
These forms may be used independently or in combination, depending on the procedure and patient needs.
The Three Components of General Anesthesia
General anesthesia isn’t a single drug or a one-step process. It involves a carefully orchestrated mix of three core elements:
-
Analgesia: To block or significantly reduce pain.
-
Amnesia: To prevent the brain from forming memories of the experience.
-
Muscle Relaxation: To immobilize the body, allowing surgeons to operate safely and precisely.
These elements are custom-tailored for each patient, adjusted moment by moment by the anesthesiologist during the procedure.
What Happens Inside the Brain? It’s Not Just "Sleep"
One common misconception is that general anesthesia is just a deeper kind of sleep. But as Dr. Medel explains, brain scans tell a very different story.
While sleep involves predictable brain cycles — such as REM and non-REM stages — general anesthesia disrupts or even completely halts these patterns. Dr. Medel likens it to a series of network outages in the brain, where normal neural communication is interrupted.
In essence, your brain is taken offline in a controlled, reversible state.
What About Waking Up During Surgery?
One of the most common fears — and sources of anesthesiophobia — is intraoperative awareness, when a patient becomes conscious during surgery. This is extremely rare, affecting roughly 1 or 2 people per 1,000 receiving general anesthesia, and often occurs in specific, high-risk scenarios.
Modern monitoring techniques, including real-time vital signs and brain activity, make it easier than ever for anesthesiologists to detect subtle signs of consciousness and adjust medications accordingly.
Dr. Medel stresses that anesthesiologists never leave the room and are constantly monitoring patients, adjusting drug levels and watching for even minor physiological changes.
What It’s Like to Wake Up
Emerging from anesthesia is a process — not an instant switch. According to Medel, your brain’s networks “reboot gradually,” leading to that familiar groggy, confused state many patients describe.
This disoriented phase is also when people often say humorous or unfiltered things, as parts of the brain that manage social behavior and memory come back online at different rates. It’s harmless — and often entertaining for your loved ones!
Is Anesthesia Safe?
For healthy patients, modern anesthesia is remarkably safe. In fact, anesthesia-related complications have plummeted over the past few decades due to improved medications, better equipment, and enhanced training.
However, there are heightened risks for patients with:
-
Heart or lung conditions
-
Neurological disorders
-
Advanced age, which can increase the chance of post-operative confusion or memory issues
That said, all patients undergo pre-operative screenings to tailor anesthesia plans to their specific health needs.
Facing the Fear: Trust and Perspective
Dr. Medel offers a powerful closing thought:
“It’s one of the few times in life where we literally hand over our existence to another person, trusting they’ll return us safely. And the fact that they almost always do — I think that’s pretty amazing.”
He’s right. Anesthesia requires an immense level of trust — not only in medical science, but in the skilled professionals who dedicate their lives to ensuring your safety while you're unconscious.
Takeaway: Understanding Eases Fear
Fear of anesthesia is natural — but understanding it helps transform fear into trust and confidence.
Whether you’re preparing for a minor procedure or a major surgery, know that you’re being cared for by experts trained to guide your body through one of medicine’s most precise and choreographed processes.
And while anesthesia may feel mysterious, it's also one of the most elegant tools in modern medicine — allowing us to undergo complex procedures without trauma, pain, or memory.
So the next time you hear “count back from ten,” you can do it with the reassuring knowledge that science — and your care team — has your back.
News in the same category


My feet feel hot and burning when I lie down at night, even though they’re cold to touch. What’s going on?

🥚 Doctors Reveal What Happens When You Eat Eggs in the Morning—Science-Backed Benefits (and How to Maximize Them)

Chew Just 2 Cloves a Day — See How Your Body After 50 Starts Feeling Younger Again

People Swear by This Drink for Pain Relief
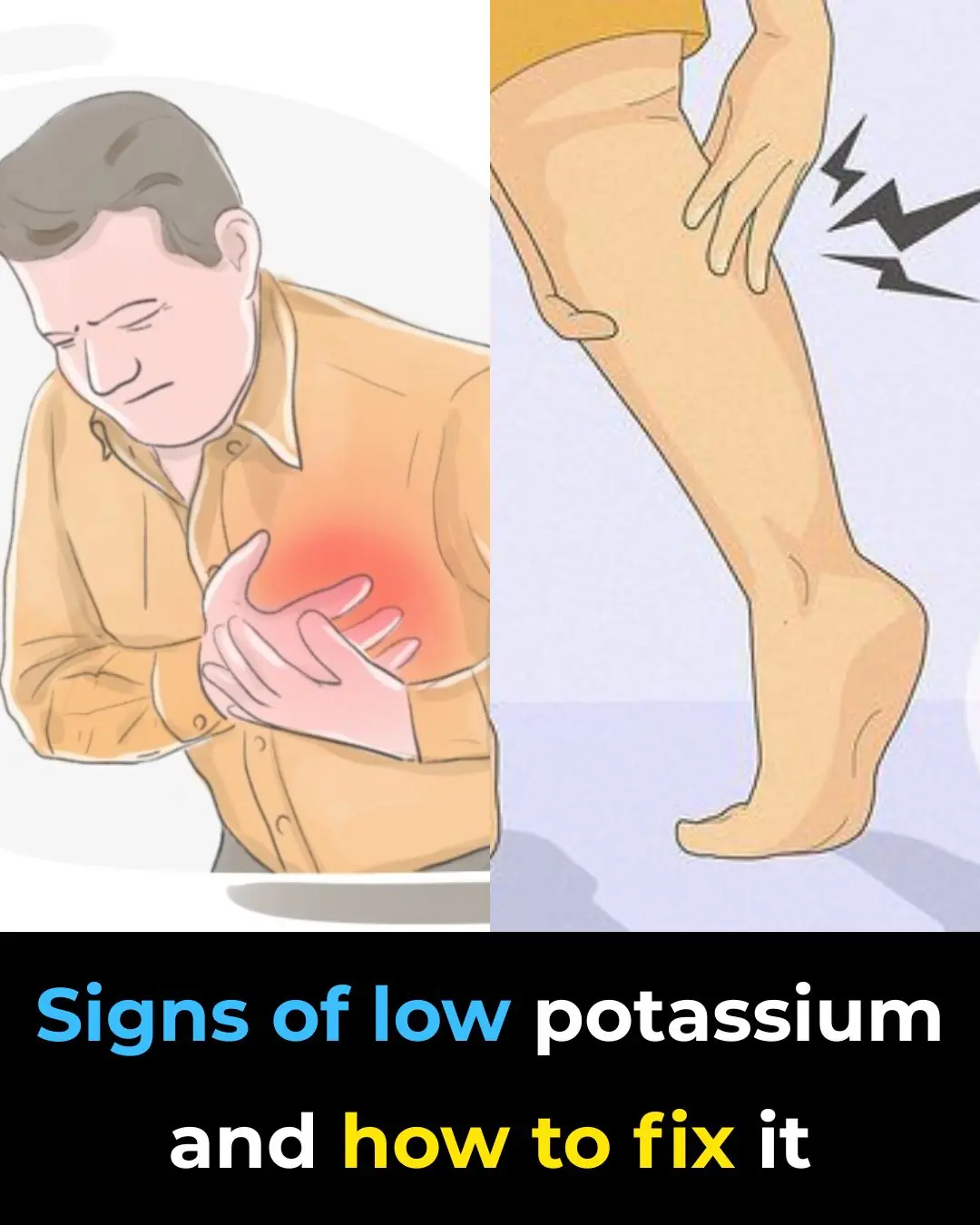
How To Recognize a Potassium Deficiency

Why You Should Put Deodorant In Your Hair

5 ways to deal with people who disrespect you

11 Reasons Why You Should Eat a Few Pistachios Before Bed

🌿 Discover Nature’s Hidden Calming Secret: The Soothing Power of Wild Lettuce Sap

Experts Reveal How Many Times a Day You Should Be Peeing

Ginger, Garlic, Onion, and Lemon Mix: Cleanse Your Body and Lungs Naturally

Seniors: Discover How to Use Baking Soda This Simple Way for Everyday Comfort in Later Years

Managing Elevated Creatinine Levels: Which Fruits Are Generally Safer Choices and Which to Enjoy in Moderation

Discovering the Morning Habit of Baking Soda and Lemon Water: What You Need to Know

Discover How Incorporating Fresh Parsley into Your Daily Routine Can Support Knee Joint Comfort and Mobility Naturally

Discover How to Add Chayote to Your Daily Routine to Support Natural Health and Wellness

Scientifically Proven Health Benefits of Papaya (Fruit) + Uses for the Seeds
20 Impressive Health Benefits Of Okra!

Discover the Hidden Power of Inga Laurina: 9 Incredible Health Benefits You Shouldn’t Miss
News Post

My husband cooked dinner, and right after my son and I ate, we collapsed

I Returned From War To Find A Teacher Scrolling Facebook While A Bully Dragged My Daughter By Her Hair—He Thought I Was Just A Helpless Parent, Until He Saw The Uniform

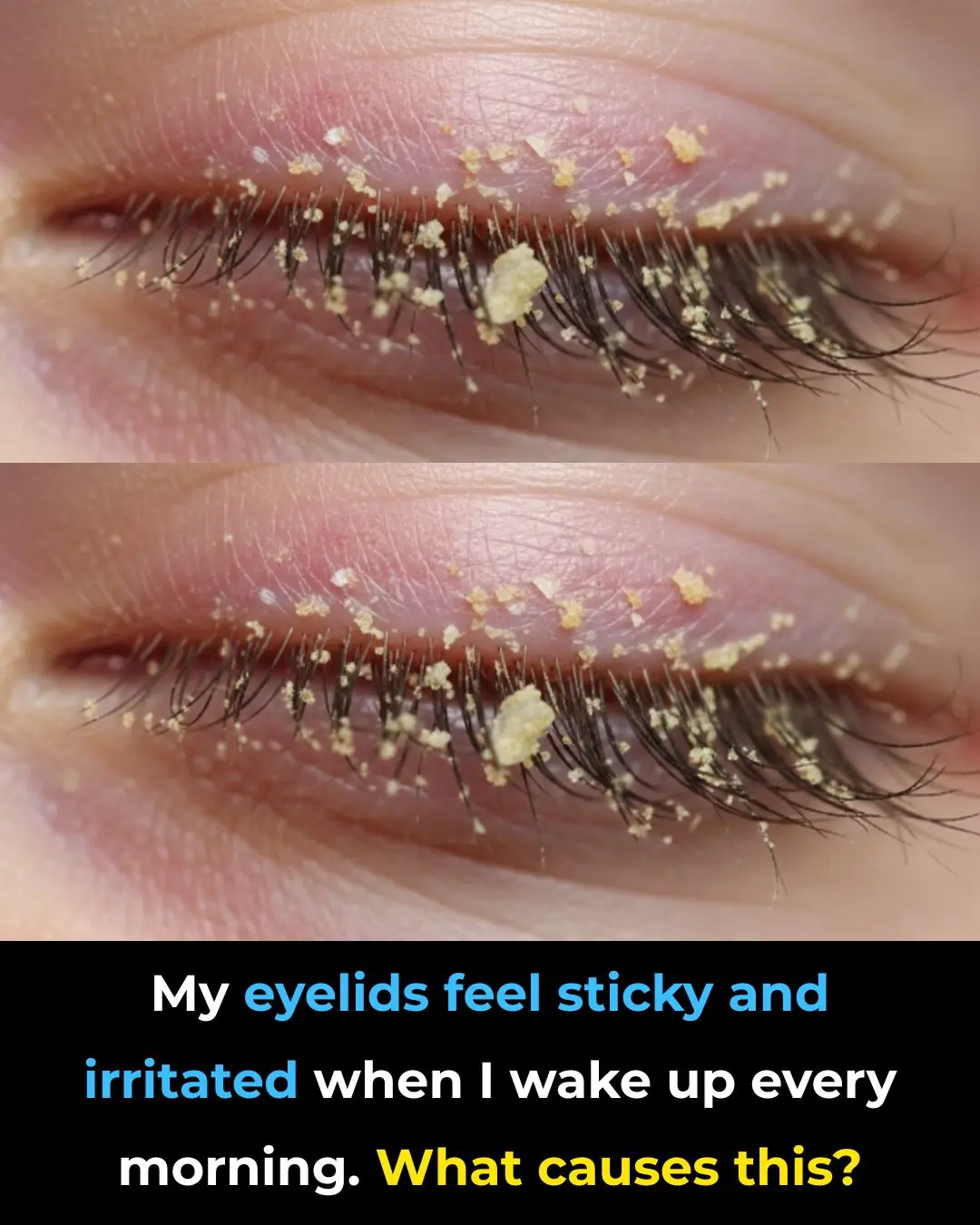
My eyelids feel sticky and irritated when I wake up every morning. What causes this?

My feet feel hot and burning when I lie down at night, even though they’re cold to touch. What’s going on?

🥚 Doctors Reveal What Happens When You Eat Eggs in the Morning—Science-Backed Benefits (and How to Maximize Them)

Chew Just 2 Cloves a Day — See How Your Body After 50 Starts Feeling Younger Again

People Swear by This Drink for Pain Relief

How To Recognize a Potassium Deficiency

Why You Should Put Deodorant In Your Hair

5 ways to deal with people who disrespect you

11 Reasons Why You Should Eat a Few Pistachios Before Bed

🌿 Discover Nature’s Hidden Calming Secret: The Soothing Power of Wild Lettuce Sap

Experts Reveal How Many Times a Day You Should Be Peeing

Ginger, Garlic, Onion, and Lemon Mix: Cleanse Your Body and Lungs Naturally

Seniors: Discover How to Use Baking Soda This Simple Way for Everyday Comfort in Later Years

Managing Elevated Creatinine Levels: Which Fruits Are Generally Safer Choices and Which to Enjoy in Moderation

Discovering the Morning Habit of Baking Soda and Lemon Water: What You Need to Know

Discover How Incorporating Fresh Parsley into Your Daily Routine Can Support Knee Joint Comfort and Mobility Naturally

Discover How to Add Chayote to Your Daily Routine to Support Natural Health and Wellness
