Meet Borealopelta markmitchelli: The Best-Preserved Dinosaur Fossil Ever Discovered
Meet Borealopelta markmitchelli: The Best-Preserved Dinosaur Fossil Ever Discovered
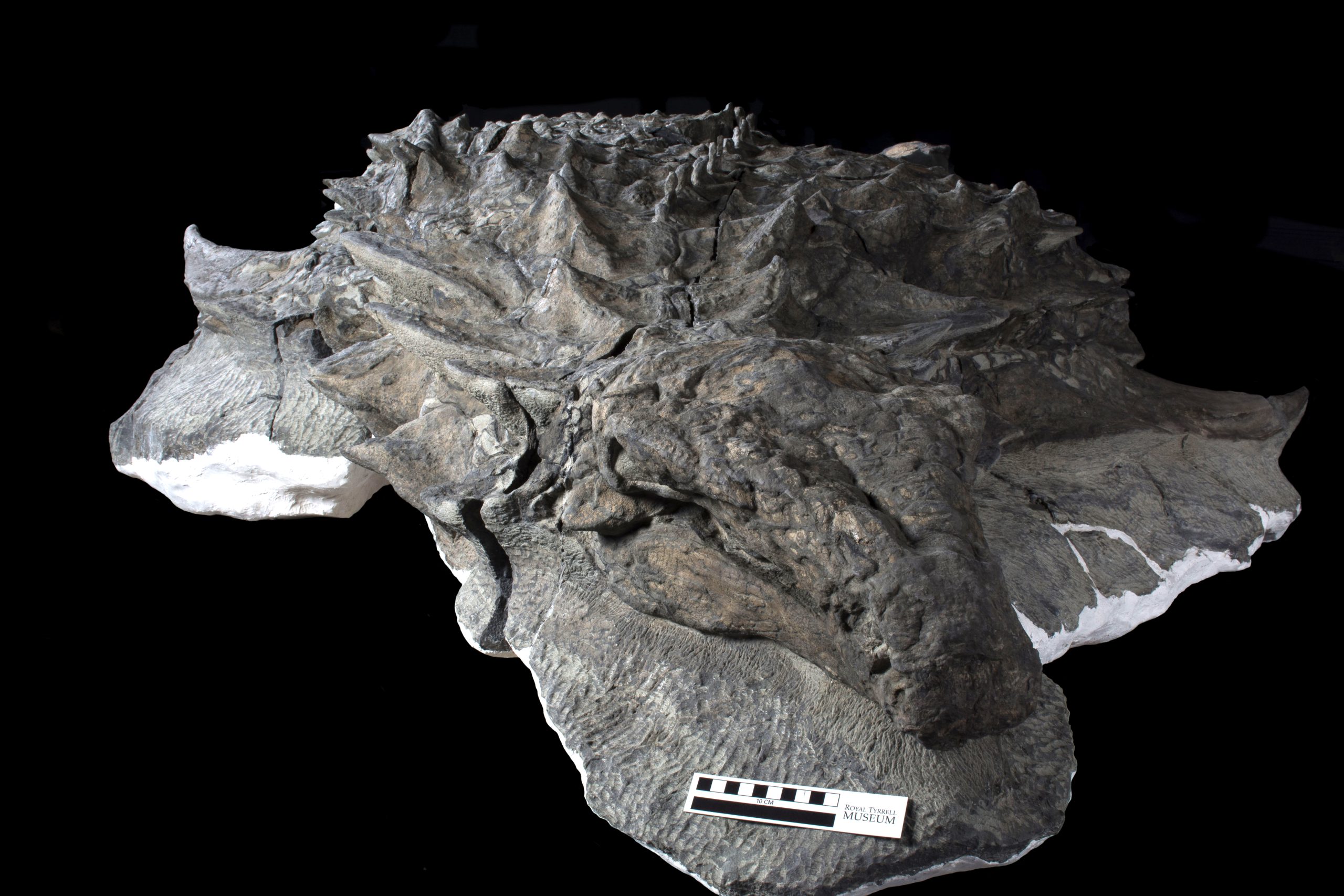

Imagine a dinosaur fossil so detailed that its face, skin, and armor appear untouched by time. Meet Borealopelta markmitchelli — an incredibly well-preserved armored dinosaur that has stunned scientists and fossil enthusiasts worldwide. This rare find offers a one-of-a-kind glimpse into prehistoric life during the Early Cretaceous period.
A One-in-a-Billion Fossil Discovery
Unearthed in Alberta, Canada, this nodosaur fossil stands out as one of the most complete and best-preserved dinosaur fossils ever found. Encased in an ancient seabed, Borealopelta still retains its skin, body armor, facial features, and even the individual scales — something virtually unheard of in the fossil record.
A Land Dinosaur Preserved in the Ocean
Although Borealopelta lived on land, it was discovered in marine sedimentary rock. Scientists believe it was swept out to sea during a major flood event. After floating belly-up due to internal gases, the dinosaur eventually sank into deep, cold ocean waters — an environment that protected it from decay and scavengers, preserving it in near-pristine condition.
Discovered by Chance in an Oil Sands Mine
This extraordinary fossil was found not in a traditional dig site, but in an oil sands mine in northern Alberta. Heavy machinery exposed the specimen, and shovel operator Shawn Funk — a fossil enthusiast — immediately recognized its potential. Just weeks before, Funk had visited a museum, further fueling his interest in paleontology. Remarkably, had the fossil been just 10 meters away, it may have never been found.
What Scientists Have Learned from Borealopelta
Thanks to this fossil’s exceptional preservation, researchers have gained unprecedented insight into nodosaur biology:
-
Diet: Fossilized stomach contents reveal what this dinosaur ate.
-
Defense Mechanisms: The structure and placement of its armor spikes suggest sophisticated predator deterrence.
-
Skin Pigmentation: Melanin remnants hint at the dinosaur’s original coloration — possibly a form of camouflage.
-
Ecological Role: This find helps paleontologists better understand the ecosystems of the Early Cretaceous.
Why Borealopelta markmitchelli Is a Paleontological Treasure
Borealopelta markmitchelli is more than just a fossil — it’s a window into a lost world. Its incredible condition bridges the gap between modern science and ancient Earth, helping scientists decode the lives of dinosaurs with an unprecedented level of detail.
News in the same category


Why Slugs Keep Showing Up in Your Home

Almost Everyone Experiences This After Turning 70, Like It or Not

Did you know that if a white and yellow cat approaches you, it's because…

A baby is born in the United States from an embryo frozen more than 30 years ago.

12 nasty habits in old age that everyone notices, but no one dares to tell you

Why do couples sleep separately after age 50?
Scientists create a universal kidney: it is compatible with all blood types

When a person keeps coming back to your mind: possible emotional and psychological reasons
A promising retinal implant could restore sight to blind patients

Scientists develop nanorobots that rebuild teeth without the need for dentists

Grip Strength and Brain Health: More Than Muscle
Bioprinted Windpipe: A Milestone in Regenerative Medicine

Bagworms Inside Your Home
Scientists discover that stem cells from wisdom teeth could help in regenerative medicine

What the Research Shows

Rethinking Flu Transmission: New Evidence Challenges Long-Held Assumptions

Nanobot Technology: A New Frontier in Cardiovascular Disease Treatment

Redefining Diabetes Treatment

If your partner says goodbye with a kiss on the forehead, be very careful: this is what it really means
News Post

Rich Kids Blackmailed Scholarship Student—His Mom Was Their Maid

The Thing Waiting in the Forest

Influencer Mocks Gym Cleaner… Then Learns Who She Really Is
Woman reveals five colon cancer symptoms that should not be ignored

What Are Eye Floaters? Here What To Do If you Start Seeing Them, According to an Eye Doctor

5 warning signs of cancer developing in the body

5 Concerning Red Flags That May Signal Colon Cancer
Essential vitamins for strong and cramp-free legs

Influencer Demands “Fat” Woman Be Removed From First Class—Plot Twist
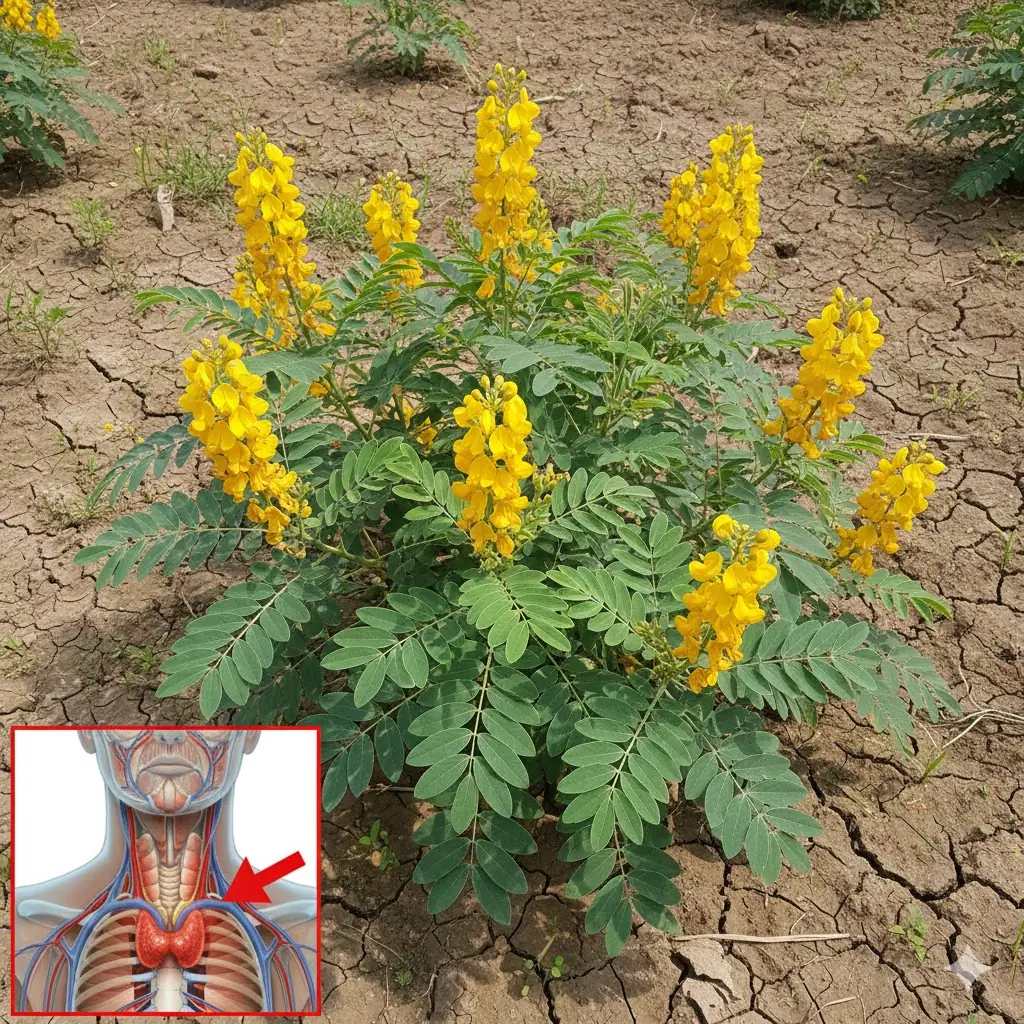

Senna Alexandrina: Benefits, Uses, and How to Take This Powerful Natural Laxative
🌿 Kyllinga Brevifolia: The Hidden Healing Herb for Everyday Wellness
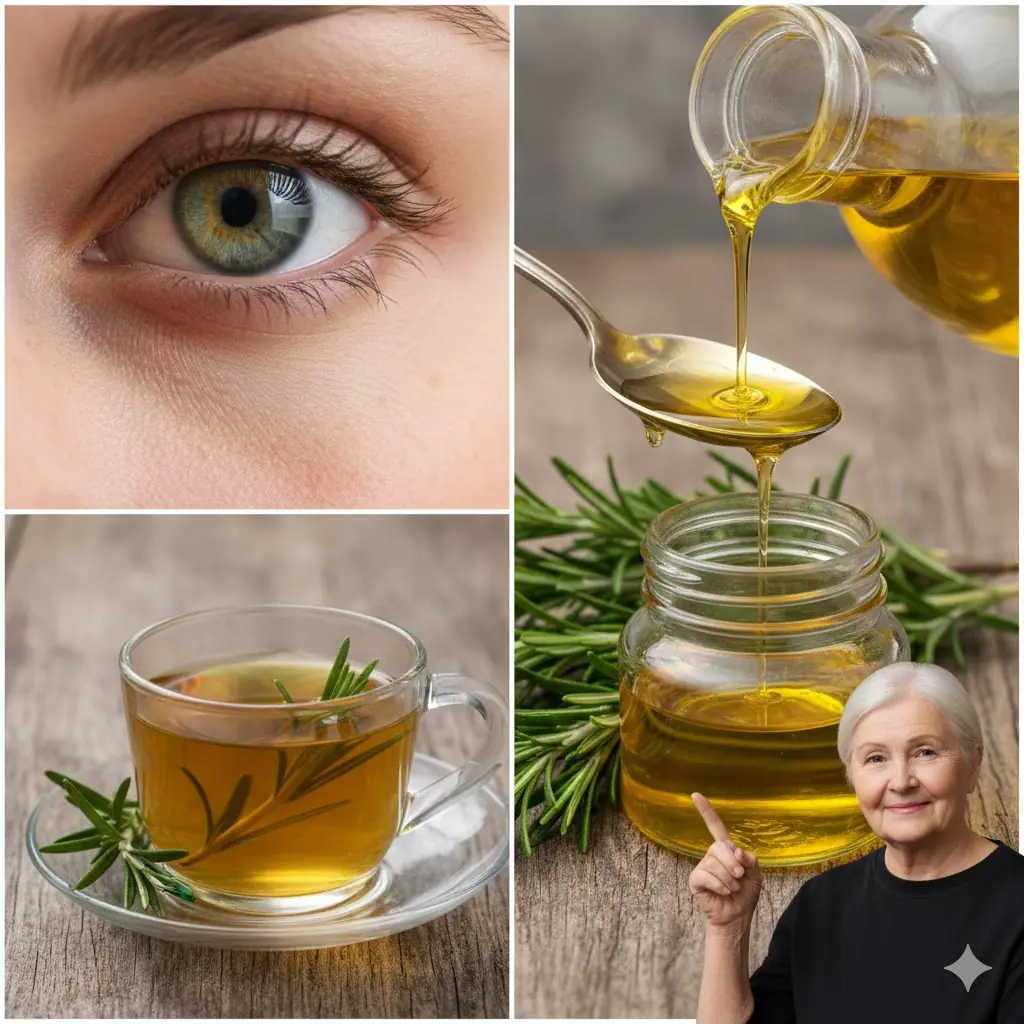

🌿 Rosemary: The Gentle Herb Supporting Brighter, Healthier Eyes
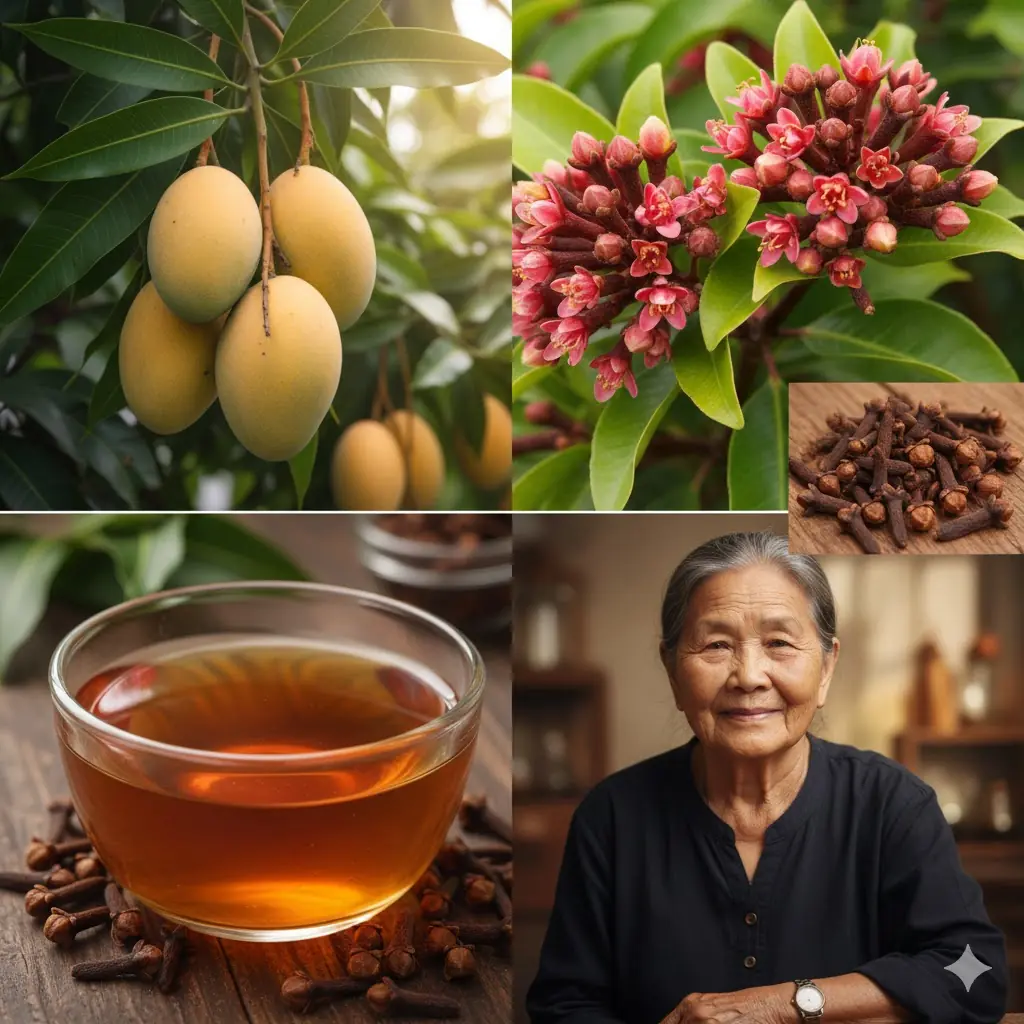

🌿 A Simple Tea for Senior Wellness: Mango Leaves & Cloves 🍵

Herbal Leaves for Everyday Wellness: A Traditional Infusion That Supports Blood Sugar, Circulation, and Heart Health Naturally 🌿

Hoja de la Vida (Kalanchoe pinnata): A Practical Guide to Traditional Uses and Everyday Wellness Habits

Master Tonic: A Powerful Natural Drink for Immune Strength and Vitality 🌿🍋

11 Little-Known Secrets About Eating Grilled Corn — Even If You Love It, Remember These

12 Powerful Reasons to Drink Milk with Garlic Every Day

Discover the Power of the Red Onion: How to Regulate Blood Sugar with This Simple Recipe