
Nature's Anticoagulants: Exploring Foods, Supplements, and Vitamins for Healthier Blood
Nature's Anticoagulants: Exploring Foods, Supplements, and Vitamins for Healthier Blood
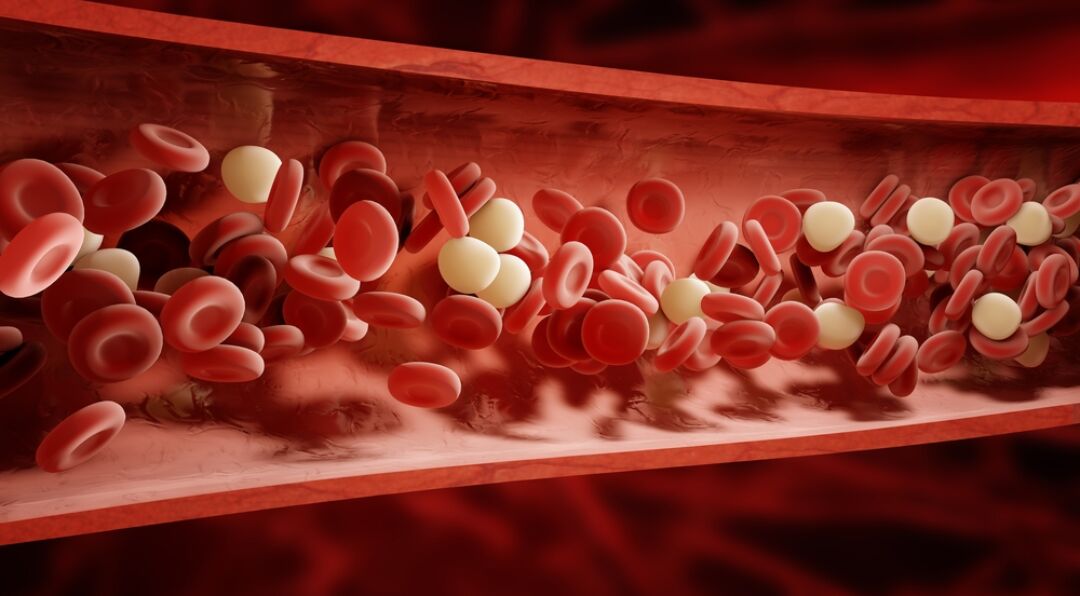
Ever wondered if what you eat can naturally help your blood flow more smoothly? Certain foods, supplements, and vitamins act as natural blood thinners, helping to prevent blood from becoming too thick and reducing the risk of clot formation. Ingredients like turmeric, garlic, and omega-3s are just a few examples with scientifically backed benefits for your circulation and heart health.
While blood clotting is essential for healing injuries, excessive clotting can lead to dangerous blockages in arteries, potentially impacting your heart, lungs, or brain. Incorporating these natural anti-clotting agents into your diet can be a proactive step towards better cardiovascular well-being.
Important disclaimer: Natural blood thinners are not a substitute for prescribed medication. If you're on blood thinners like warfarin (Coumadin) or Xarelto, or if you have concerns about your blood health, always consult your doctor before making any dietary or supplement changes.
This article will delve into the science behind these natural anticoagulants, highlighting proven foods, supplements, and vitamins that support healthier blood, along with important precautions to keep in mind.
What Exactly Are Natural Blood Thinners?
The term "blood thinner" is commonly used, but it's more accurate to think of these natural substances as anti-clotting agents. They work in two main ways: by acting as anticoagulants, which slow down the overall blood clotting process, or as antiplatelets, which prevent blood platelets from clumping together to form clots. (1)
These compounds influence the fibrinolytic system, a crucial part of your blood's natural ability to prevent and dissolve clots. (34) For example, coumarin, a natural anticoagulant found in some types of cinnamon, is also the basis for synthetic anticoagulants like warfarin. (1)
Who Can Benefit from Blood Thinning Strategies?
You might be prescribed blood-thinning medication if you're at risk for serious conditions like a heart attack, stroke, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). These medications prevent blood vessels from becoming blocked, which can otherwise cut off blood flow to vital organs. (2) Other risk factors include being overweight, recovering from surgery, or having existing blood vessel disease. (3)
While numerous natural substances possess anticoagulant activity, they should not be seen as direct replacements for prescription medication. If your doctor has identified a risk for blood clots, prescribed anticoagulants are usually essential. We'll discuss important precautions regarding their combined use later in the article.

Top Natural Blood Thinners: What the Science Says
Let's explore some of the most effective natural anticoagulants that can help improve your circulation and maintain healthy blood.
Turmeric: The Spice with Anticoagulant Power
Turmeric contains compounds with significant anticoagulant properties, primarily due to curcumin. This well-known anti-inflammatory substance also helps thin the blood. Studies show curcumin inhibits clotting enzymes, exhibiting anti-thrombotic properties that can support blood health. (4, 5)
Ginger: A Herbal Antiplatelet
Ginger helps "thin the blood" by preventing platelets from sticking together. While some studies show its effectiveness in reducing platelet aggregation, others are less conclusive. (6) It's important to note that ginger, especially in supplement form, may increase bleeding risk after surgery and should not be combined with prescribed blood thinners like warfarin without medical supervision. (7)
Garlic: Nature's Anti-Clotting Food
Garlic helps prevent clotting by reducing clotting enzymes in the blood. Research indicates fresh garlic has an anti-thrombotic effect, improving blood health. Aged garlic supplements are also shown to prevent clot formation and boost blood vessel health. (7, 8) Garlic is also known for its benefits in lowering blood pressure and supporting cardiovascular health. (9)
Vitamin E: Supporting Circulation and Preventing Clots
Vitamin E supplements can enhance blood circulation and help prevent clotting. A large study found that 600 IU of vitamin E every other day might help prevent venous thromboembolism. (10) It can also help prevent heart attacks and strokes in at-risk individuals. (11) However, some research suggests that while beneficial for blood health, excessive vitamin E might be detrimental to cardiovascular health. (12)
Cayenne Pepper: The Spicy Anticoagulant
Cayenne pepper, thanks to its active compound capsaicin, possesses blood-thinning properties, acting as both an anticoagulant and an antiplatelet. (13) It also contains salicylates, similar to aspirin, which contributes to its anti-clotting effects. (14, 15) Caution is advised when combining capsaicin supplements with antiplatelet or anticoagulant drugs. (17)
Cinnamon: A Natural Coumarin Source
Certain types of cinnamon contain coumarin, a powerful anticoagulant similar to warfarin. Cassia cinnamon is particularly rich in coumarin, but high doses may negatively impact liver health. (18) For this reason, Ceylon cinnamon is generally preferred, although it may not contain enough coumarin to effectively thin the blood. (19)
Ginkgo Biloba: Herbal Aid for Blood Flow
Ginkgo biloba may help resolve blood clots due to its anticoagulation properties. (20) However, because it reduces clotting, it might not be suitable for use with anticoagulant medication and could increase bleeding risk, especially in older individuals. (21)
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential for Blood Health
Omega-3 supplements, found in oily fish like salmon and mackerel, can boost cardiovascular health and prevent blood from becoming too thick. Animal studies show omega-3 fish oil prevents rapid blood coagulation. (22) Omega-3s can interact with warfarin, so patients taking both should be regularly monitored. (23)
Green Tea: A Healthy Blood-Thinning Beverage
Regularly consuming green tea can help manage thick blood. Its compound, epigallocatechin (EGC), has antiplatelet and anticoagulation effects. (24, 25) While highly beneficial, green tea is a source of vitamin K, which can affect the efficacy of warfarin, requiring caution if you're on this medication. (26)
Red Wine: Moderate Consumption for Blood Thinning
When consumed in moderation, alcohol, particularly red wine, can thin the blood and benefit your coagulation system. Moderate amounts of wine and beer have anticoagulant, anti-inflammatory, and hypotensive properties. (27) Red wine, in particular, helps prevent platelet aggregation and balances blood coagulation. (28) However, excessive alcohol consumption significantly increases risks for conditions like venous thromboembolism and stroke. (29)
Other Natural Blood Thinners:
- Grape Seed Extract: Its anticoagulant properties mean caution is needed if taking warfarin or aspirin. (30)
- Feverfew: This medicinal plant inhibits platelet activity and should be avoided with blood thinners. (31)
- Dong Quai: Traditionally used in Chinese medicine, it helps prevent platelet clumping. (32)
- Bromelain: An enzyme found in pineapples, bromelain has antithrombotic activities and can help reduce clotting. (33)

Important Precautions When Using Natural Blood Thinners
While many foods, supplements, and vitamins can contribute to blood thinning, it's vital to remember that naturally dissolving existing blood clots is challenging, and natural remedies may not match the effectiveness of prescription medication.
If you are taking prescribed blood-thinning medication (e.g., for stroke prevention or thick blood), be aware that natural substances can interact with these drugs. Consuming medicinal amounts of natural remedies like turmeric, garlic, or ginger alongside prescription blood thinners can thin the blood excessively, significantly increasing your risk of bleeding.
For instance, research shows that too much garlic can affect platelet function and increase bleeding risk, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of prescription anticoagulants. (35) Similarly, many herbal remedies can negatively impact warfarin. (36)
Generally, using foods like garlic, turmeric, or cinnamon as culinary flavorings won't significantly affect prescription blood thinners. However, it is absolutely essential to consult your doctor before taking any herbal supplements if you are currently on blood-thinning medication.
News in the same category

Groundbreaking Research: Reversing Memory Loss In Alzheimer’s Disease Without Removing Plaques

Rfk Jr. Raises Health Concerns Over 5G, Says It May Affect Brain Function And Cancer Risk

Eat Just 3 of These Daily and Watch What Happens to Your Body
. Their ability to benefit nearly every major system in the body - from the heart and liver to the brain and bones - makes them a powerful ally in maintaining health and vitality.

Blood Type O Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid

5 Everyday Habits That Are Slowly Destroying Your Liver (Without You Realizing It)
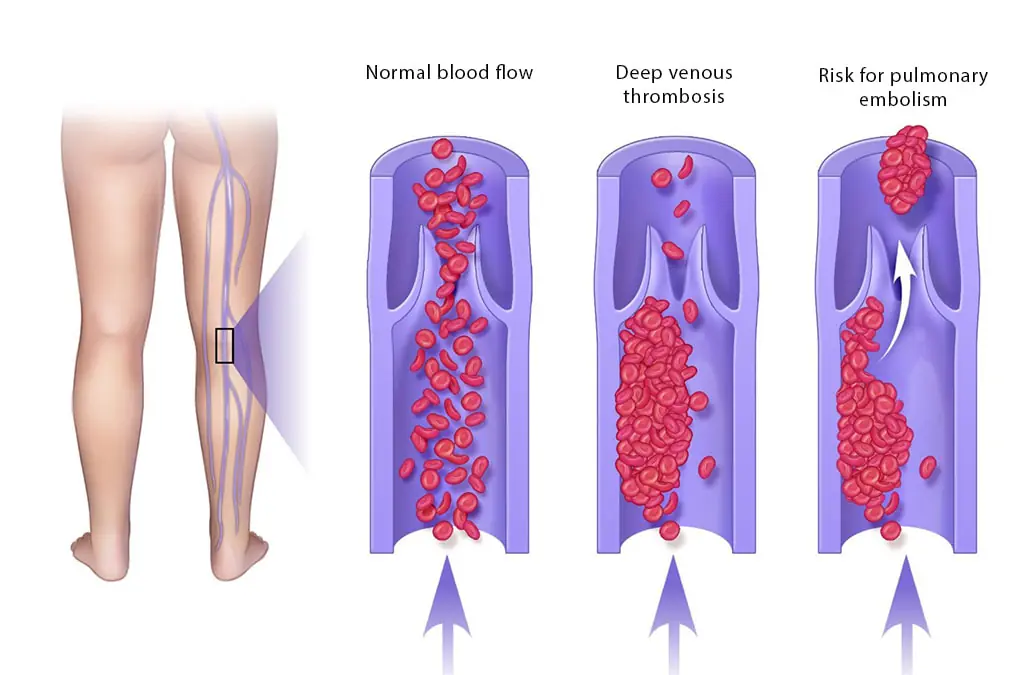
Blood Clot in Leg: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

Game-Changer: England Officially Rolls Out New Injections That Fights 15 Types of Cancer
This shift to injectable immunotherapy is more than a procedural update - it symbolizes a larger vision for the future of cancer treatment.
If Your Nails Show These 6 Signs, See a Doctor Immediately
While some alterations may be harmless, others could be early warnings of serious health conditions.
‘Healthy’ 38-year-old shares the only bowel cancer symptom he noticed — And it wasn’t blood in the loo

Young Dad Misses Key Cancer Symptom That Left Him Terrified

5 Things Doctors Say You Should Never Give Your Kids to Help Prevent Cancer
Indiana Boy, 8, Dies Hours After Contracting Rare Brain Infection At School
World-First Gene Therapy Restores Sight to Boy Born Blind

A Warning About The ‘Worst Thing’ That People Should Never Do When Awakening in the Night

Horrifying simulation shows life-threatening impact of drinking too much water and how it can lead to death
These simulations, tragic stories, and medical data remind us that moderation matters.
Cancer Breakthrough: Scientists Discover Protein That Puts Tumors to Sleep!
With promising results in preclinical trials and a growing understanding of the tumor microenvironment, type III collagen may become a key player in the fight against cancer - not by eradicating it, but by keeping it permanently asleep.

The Amazing Health Benefits and Uses of Castor Oil

Evidence-Based Health Benefits of Raw, Pure, Natural Honey + Turmeric Golden Honey Recipe
Home Remedies for Blocked and Stuffy Nose
News Post

She held on, certain they would come back. Yet as days turned into weeks, her strength waned—until a fresh kind of love unexpectedly entered her life.

The Hidden Light In Your Hands That Shouldn’t Be Dimmed

Mosquitoes Rain From The Sky Over Hawaii—Scientists Explain Why

Doctor Shares 30-Second Hand Test That Could Reveal Hidden Brain Tumor

Nasa Tracks Plane-Sized Asteroid Speeding Toward Earth At 47,000 Mph

Groundbreaking Research: Reversing Memory Loss In Alzheimer’s Disease Without Removing Plaques

Rfk Jr. Raises Health Concerns Over 5G, Says It May Affect Brain Function And Cancer Risk

Two-Year-Old Boy Bites Cobra To Death After Snake Coils Around His Hands In India

Four Famous Psychics Warn World War III Could Begin By End Of 2025

Abandoned puppy was found in terrible shape — see his incredible transformation one year later in the comments 🥹

Eat Just 3 of These Daily and Watch What Happens to Your Body
. Their ability to benefit nearly every major system in the body - from the heart and liver to the brain and bones - makes them a powerful ally in maintaining health and vitality.

Psychic who suffered near-death experience reveals shocking truth about the afterlife
A psychic has detailed about afterlife after claiming to have experienced the feeling "dea@th" four times.

Blood Type O Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid

5 Everyday Habits That Are Slowly Destroying Your Liver (Without You Realizing It)

Blood Clot in Leg: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

Real story behind Amelia Earhart and the Bermuda Triangle as scientists 'solve mystery' after 88 years

Airlines forced to cancel flights after 'Japanese Baba Vanga' predicts catastrophic disaster

8.7 magnitude earthquake off Russia: Japan experiences first tsunami, many countries issue warnings

After Seeing Her Husband's Photo with a Pregnant Stranger, Nadya Chose Silence – But What Happened Next Was Sh0cking
It was unthinkable! How could this be happening? Nadezhda thought, staring at a photograph of a young pregnant woman sitting on her husband’s lap, smiling, and clinging to him. Twenty-five years of marriage... and now this? Her heart tightened painfully

I Went Undercover as a Homeless Person to Test My Granddaughter's Fiancé – What I Found Was Beyond Sh0cking
I dressed in old, ragged clothes, hid my face beneath a weathered hat, and stood on the street like a beggar—just to see what kind of man my granddaughter was marrying. I thought I was prepared for anything, but what happened next left me speechless and