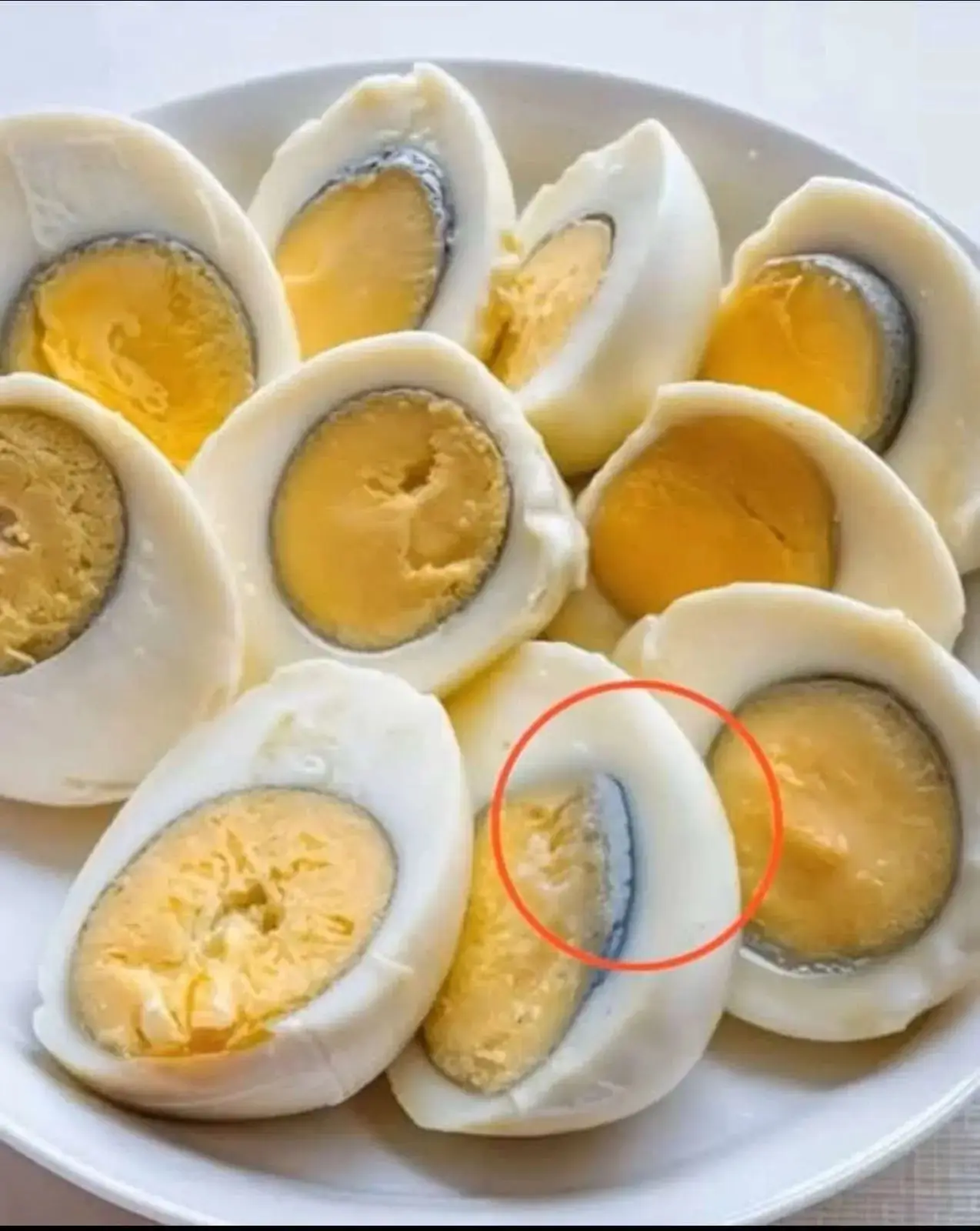

Is the Green Ring on Your Egg Dangerous? Experts Reveal the Truth
If you are one of those people who prefer their eggs hard-boiled, you have certainly noticed that green color ring around the yolk.
Anxiety disorders affect over 300 million people worldwide, making them among the most common mental health challenges across all age groups. Typically managed using medications such as SSRIs or benzodiazepines, these treatments can produce unwanted or even dangerous side effects - ranging from sedation and emotional numbness to dependence. Now, groundbreaking scientific research offers a potential alternative: a direct way to turn off anxiety at its neurological source, with no observed side effects so far. This discovery may transform anxiety treatment completely, offering a precision-based approach that silences anxious reactions while preserving overall brain function.

Mapping Anxiety: Discovering the Neural “Circuit Breaker”
For decades, scientists have studied the roles of the amygdala, prefrontal cortex, and hippocampus in anxiety. Yet only recently have researchers at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) pinpointed a specific brain circuit essential to the anxiety response. Their focus centers on the periaqueductal gray (PAG) - a brainstem region known for orchestrating defensive behaviors and panic-like reactions. Within this region, UCSF researchers identified a tiny cluster of neurons that act as an emotional “toggle switch.” When these neurons are inhibited, lab animals exhibit marked reductions in anxiety-related behavior - without impairing decision‑making, attention, or motor skills.

How the “Off Switch” Works at the Cellular Level
The critical cells in question are GABAergic neurons, which produce the neurotransmitter GABA - the brain’s primary inhibitory messenger. When these neurons within the PAG are activated, anxiety and fear reactions are suppressed nearly immediately. Using advanced optogenetics, which enables researchers to control neural activity with light, scientists selectively stimulated these GABA-producing neurons in mice. The result? A calm and composed response in situations that previously triggered anxiety - like elevated platforms or open spaces. Once stimulation stopped, the anxious behavior returned, confirming that the neurons directly regulate anxiety without dulling sensory awareness or coordination.

Why This Could Outperform Traditional Medications
Current medications, such as benzodiazepines and SSRIs, influence large areas of the brain and usually take weeks to achieve full effect. Moreover, they may lead to unwanted outcomes such as sedation, emotional blunting, or risk of addiction. In contrast, this new neural-targeting technique activates a very specific group of neurons and works in seconds. In the animal studies, anxiety was effectively turned off with nearly no side effects - no drowsiness, no cognitive impairment, and no addiction or tolerance observed. This level of targeted precision marks a transformative moment in psychiatric research and paves the way for customized, rapid treatments that respect the complexity of brain function.
Optogenetics: The Tool That Mapped the Anxiety Switch
Optogenetics is a cutting-edge technique combining genetic engineering and photonic control to modulate specific groups of neurons. By introducing light-sensitive proteins into targeted brain cells, researchers can selectively activate or silence those cells using fiber optic cables. This precision allowed the UCSF team to identify the anxiety-regulating neurons without disturbing neighboring cells. Beyond mapping one neural pathway, optogenetics suggests multiple anxiety circuits may exist - for example, social anxiety might involve different circuits than trauma-related anxiety.
A Landmark with Zero Observed Side Effects
The possibility of an anxiety-suppressing circuit with no side effects is rare in neuroscience. Traditional drugs interact broadly with multiple receptor systems, often producing complex and unpredictable outcomes. In the mouse studies, researchers observed no tolerance buildup, no social behavior deficits, no weight gain, and, crucially, no addiction or withdrawal signs. These findings elevate this approach above current pharmacological methods and raise the exciting possibility that similar neural circuits exist for other conditions - such as depression, chronic pain, or substance dependency.
Evolution, Fear, and the Brain’s Survival Mechanism
Anxiety evolved as an essential survival tool - an early warning system rooted in some of the oldest parts of the brain. The periaqueductal gray region operates across many species, suggesting this anxiety switch is an evolutionarily conserved feature. By targeting this deeply embedded circuit, scientists hope to reduce unnecessary anxiety while maintaining the ability to respond to real threats. In effect, this treatment could fine-tune survival instincts, making people more emotionally balanced without erasing caution altogether.
Future Technologies: From Lab to Life
Although optogenetics remains too invasive for routine human use, its principles inspire new technologies. For instance:
Imagine a future where managing anxiety is as simple, effective, and risk-free as controlling blood sugar in diabetes - delivering relief without compromise.
Critical Cautions and Open Questions
Despite the excitement, experts urge restraint. The brain is extraordinarily complex, and altering one part could affect others in unpredictable ways. Some researchers question whether disabling anxiety might also reduce useful instincts like self-protection or risk assessment. Others note that human anxiety is influenced by a combination of genetic, experiential, and environmental factors, meaning a singular neural switch may not account for all cases. And the gap between rodent models and humans remains significant - clinical trials will be essential before any human application can be considered safe or effective.
How This Fits Into a Broader Mental Health Revolution
This discovery aligns with a larger shift in mental health research toward precision brain therapies. Advances in brain imaging, neuromodulation, and AI-based diagnostics are enabling scientists to target specific brain circuits rather than administering broad-spectrum drugs. The discovery of an identifiable neural “off switch” for anxiety provides a clear biological target for future interventions. When combined with emerging treatments - like psychedelic-assisted therapy, personalized mental health apps, and digital therapeutics - the outlook for anxiety treatment is entering a new era of hope.
A Turning Point in Emotional Medicine
Discovering a precise, side‑effect‑free neural switch for anxiety is a major scientific breakthrough. It builds on decades of neuroscience research, reinforcing the idea that emotions like fear and stress can be finely regulated within the brain. While more study is needed before translating these findings to people, the foundation is set for a new class of mental health treatments - ones that are specific, fast-acting, and gentle on the brain.
If researchers can continue to uncover the brain’s hidden circuitry, the day may come when anxiety can be turned off as easily as a light switch - unlocking a future where emotional well-being is both empowered and enduring.

If you are one of those people who prefer their eggs hard-boiled, you have certainly noticed that green color ring around the yolk.




Unlike traditional sodas loaded with added sugar and artificial ingredients, Milaf Cola delivers a refreshingly sweet experience using only the natural sugars found in dates.


It reminds us that the story of Jesus wasn’t just passed down through scripture - it also traveled through languages, translations, and centuries of human culture.

Some believe your finger length can reveal key aspects of your personality through a theory called the digit ratio. Though not scientifically proven, it links finger proportions to traits like confidence, empathy, and risk-taking.

While flight attendants are being polite, there is another reason why they say 'hello' as you board

According to the Arizona State University researchers, in Alzheimer’s disease, this natural cycle of stress granule formation and dissolution goes off track.

If you see a flight attendant seated with their hands tucked underneath them during landing, remember—it’s not just a quirky habit.









If you are one of those people who prefer their eggs hard-boiled, you have certainly noticed that green color ring around the yolk.









Unlike traditional sodas loaded with added sugar and artificial ingredients, Milaf Cola delivers a refreshingly sweet experience using only the natural sugars found in dates.
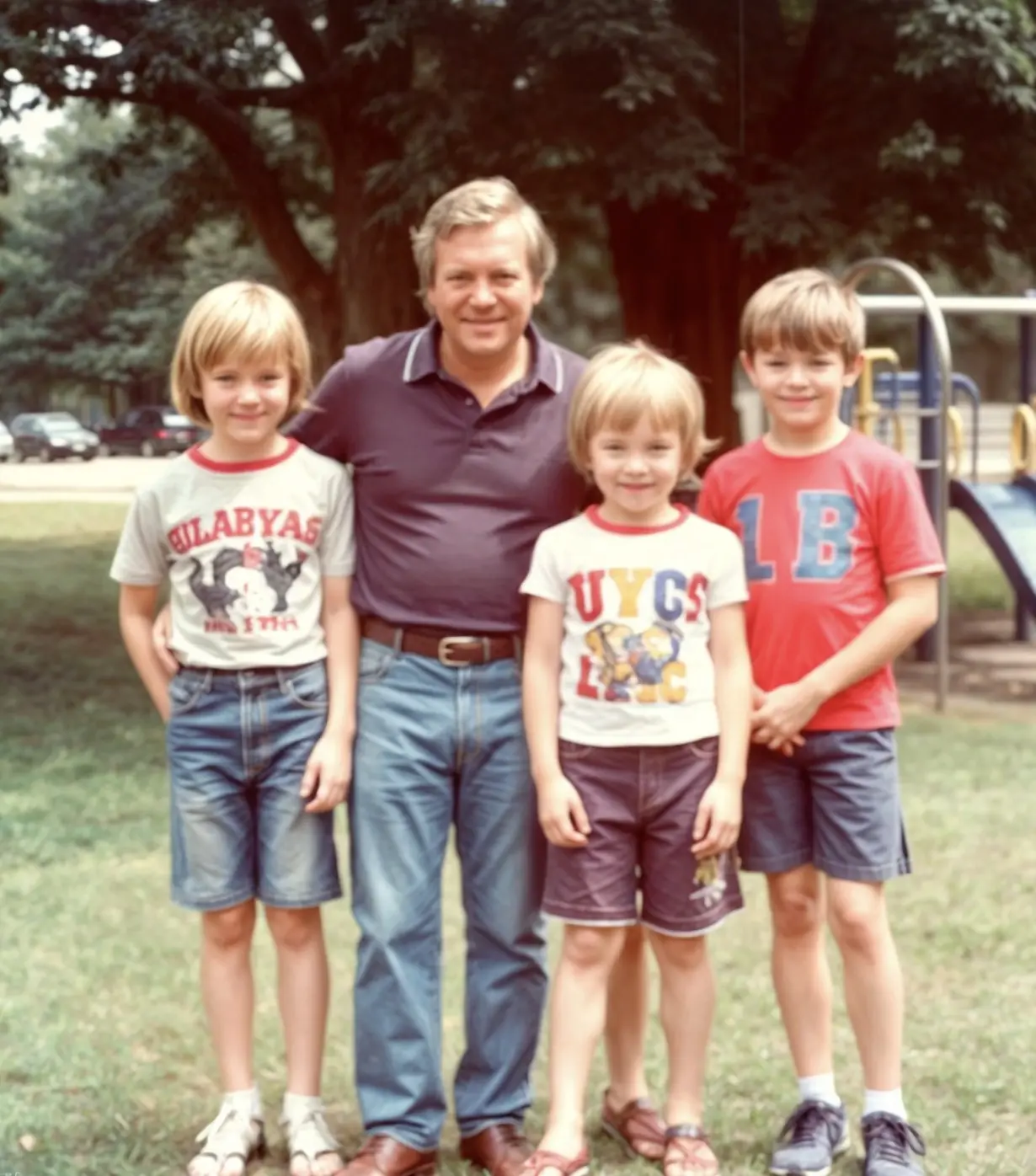

The embryo the Pierces adopted was originally created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) back in 1994, making it older than many of today’s prospective parents themselves, according to MIT Technology Review.





Passing gas up to 25 times a day can be considered normal - but when you notice a sudden increase, especially if it's paired with discomfort or other symptoms, it's time to tune in.

It reminds us that the story of Jesus wasn’t just passed down through scripture - it also traveled through languages, translations, and centuries of human culture.