
Scientists discover ultra-massive 'blob' in space with a mass of 36,000,000,000 suns
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery: what may be the most massive black hole ever identified.
Located approximately five billion light-years away, this enormous black hole resides at the center of the galaxy SDSS J1148+1930 and has a mass equivalent to 36.3 billion suns.
To put this in perspective, the supermassive black hole at the heart of our own Milky Way galaxy weighs only 4.3 million solar masses. This newly discovered black hole is roughly 8,400 times more massive than that, highlighting its extraordinary size.
This discovery is so exceptional that scientists are now classifying it as 'ultra-massive' rather than the typical 'supermassive' designation, which is reserved for the most colossal black holes in the universe.
"This black hole is one of the top 10 most massive ever discovered and is likely the largest one," stated Thomas Collett, an astrophysicist at the University of Portsmouth. "While most previous measurements of black hole masses have been indirect and come with significant uncertainty, our new method has provided much more reliable data on this one."
Although theoretically, black holes can grow indefinitely, in practice, their growth is limited by the age of the universe. Since the universe is only 13.8 billion years old, even the most massive black hole could only reach around 50 billion solar masses before time runs out.
Detecting these ultra-massive black holes requires advanced techniques, one of which is known as gravitational lensing. In this process, the gravity of a galaxy acts as a natural magnifying glass, creating a unique visual pattern called the Cosmic Horseshoe. This consists of a curved arc of light surrounding a central blob that, when observed from Earth, forms a horseshoe-like shape.
The light from a distant source is magnified by the immense gravitational force of the black hole, producing a smear effect. It was during the study of such a cosmic horseshoe that scientists, led by Carlos Melo-Carneiro of the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, uncovered this ultra-massive black hole.
"This black hole was found in a 'dormant' state, meaning it wasn't actively consuming material at the time of observation," Melo-Carneiro explained. "Its discovery was made possible solely due to its immense gravitational influence and the effect it had on its environment."

'This is amongst the top 10 most massive black holes ever discovered.' (Eugene Mymrin/Getty)
What makes SDSS J1148+1930 even more remarkable is that it is considered a 'fossil galaxy'—a single, massive galaxy that was once part of a larger cluster of separate galaxies. Over billions of years, these individual galaxies merged into one. Each of these original galaxies had its own supermassive black hole, and as the galaxies merged, so did their black holes, eventually forming this astonishing 36-billion-solar-mass giant.
This discovery could provide astronomers with crucial insights into the formation and growth of black holes, helping to unravel the mysteries of how they become so incredibly massive.
News in the same category


A Nigerian Scientist Developed a High-Tech Cancer-Detecting Goggles That Help Surgeons Spot Cancer Cells More Accurately.

What’s the Small Hole in a Padlock For?
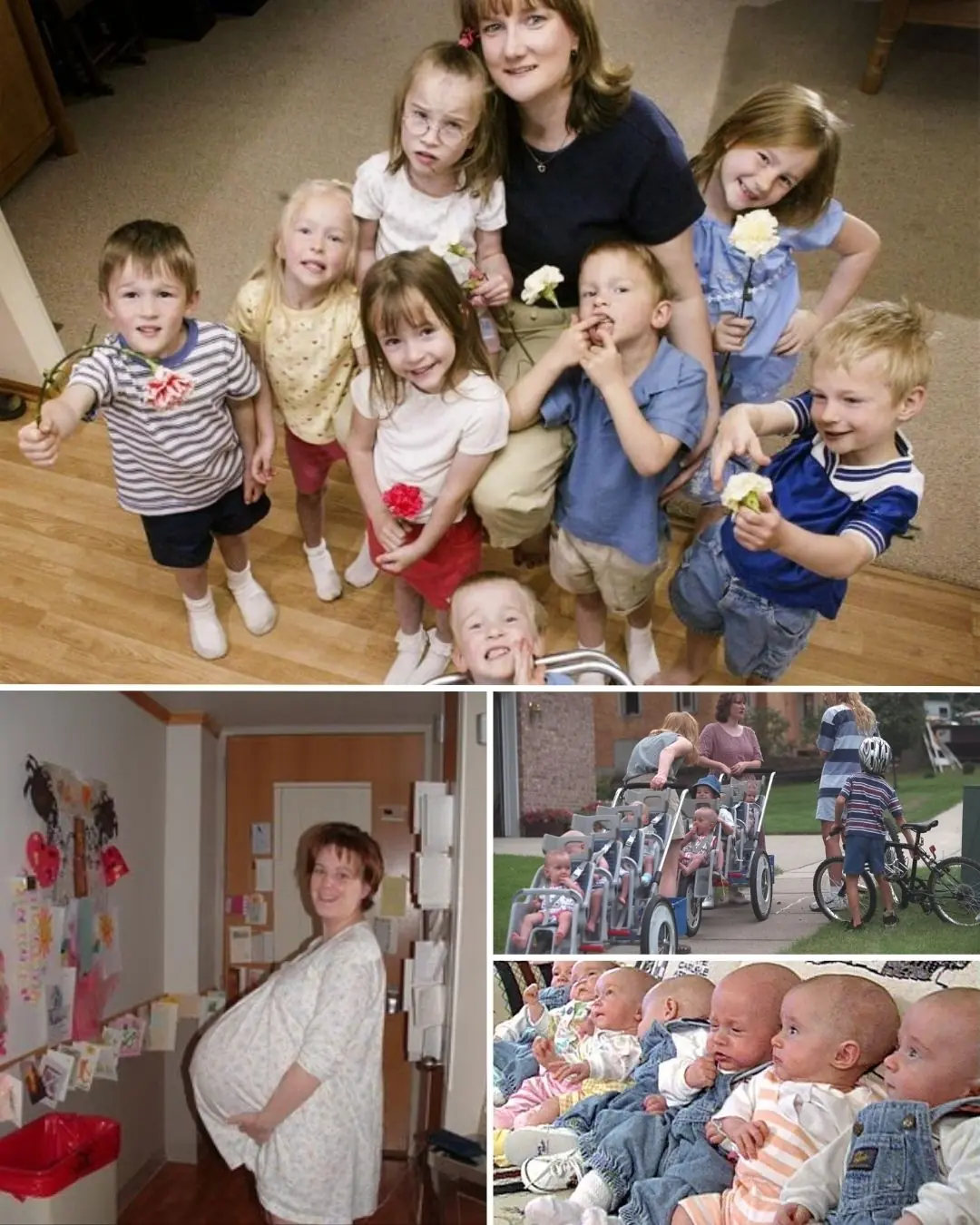

World’s First Surviving Septuplets Celebrate 27th Birthday

What to Do Immediately After a Snake Bite

Ever Seen This Creepy Wall-Clinging Moth? Meet the Kamitetep

Flight attendant explains the unexpected reason cabin crew keep their hands under their thighs during takeoff and landing
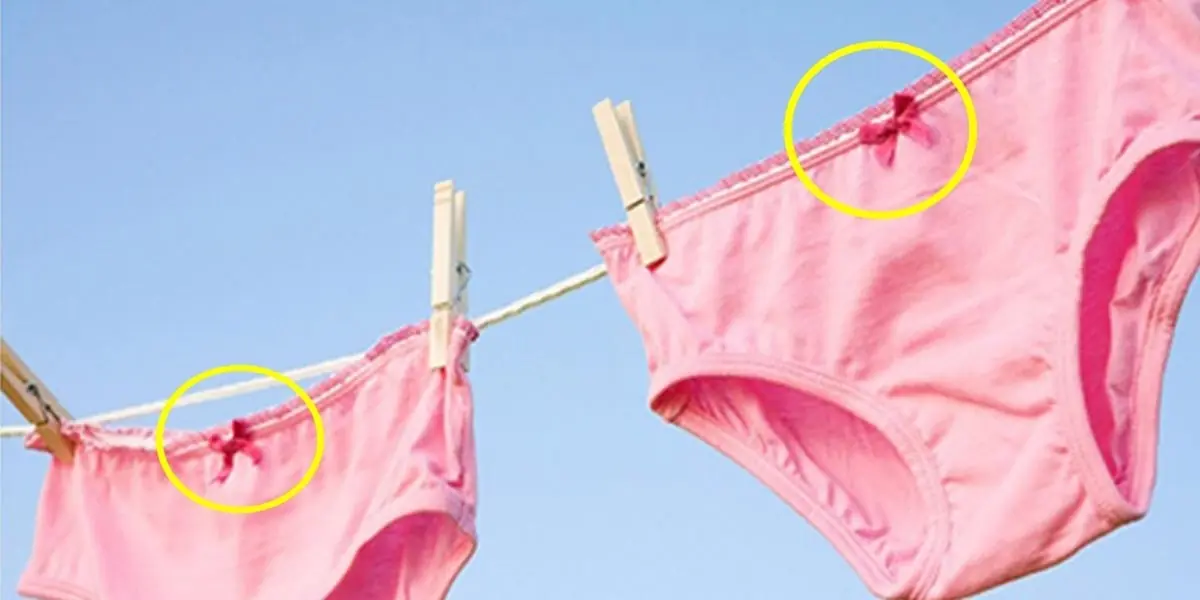

People Are Just Realizing Why Women’s Underwear Have A Bow On Front

Setting Your AC to 26°C at Night Might Not Be the Best Idea

What’s the Small Hole in a Padlock For?

How to Get Rid of Moths Naturally

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath

Gyan Mudra benefits revealed: How this ancient hand gesture can boost your mind and body
Man, 76, dies while trying to meet up with AI chatbot who he thought was a real person despite pleas from wife and kids

Black Cat at Your Doorstep? Here's the Hidden Spiritual Meaning and What It Reveals About You
It’s not unusual to open your front door and discover a mysterious cat waiting to be let in. While some see this as a spiritual sign of good luck, the truth is often much more practical—and just as fascinating.

NASA crew begins gruelling training for monumental mission that's not been done in 50 years

User 'terrified' after AI has total meltdown over simple mistake before repeating 'I am a disgrace' 86 times
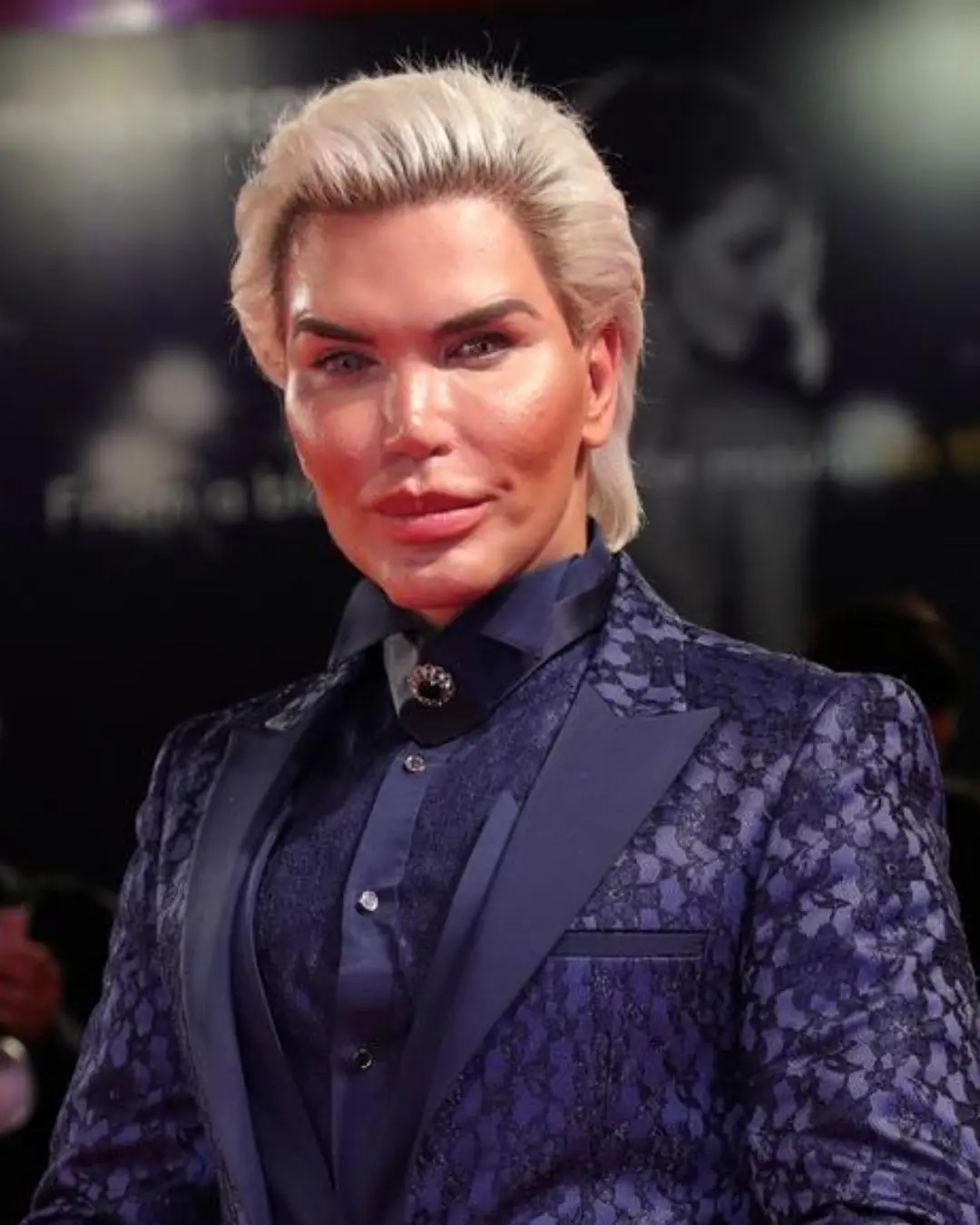

$1M Plastic Surgery TV Star’s Transformation

My Wife Had a Baby with Dark Skin – The Truth That Changed Everything
News Post

You Can Adopt Puppies That Were ‘Too Friendly’ to Become Police Dogs

A Nigerian Scientist Developed a High-Tech Cancer-Detecting Goggles That Help Surgeons Spot Cancer Cells More Accurately.

Final straw that led to billionaire CEO's desperate escape from Japan inside 3ft box
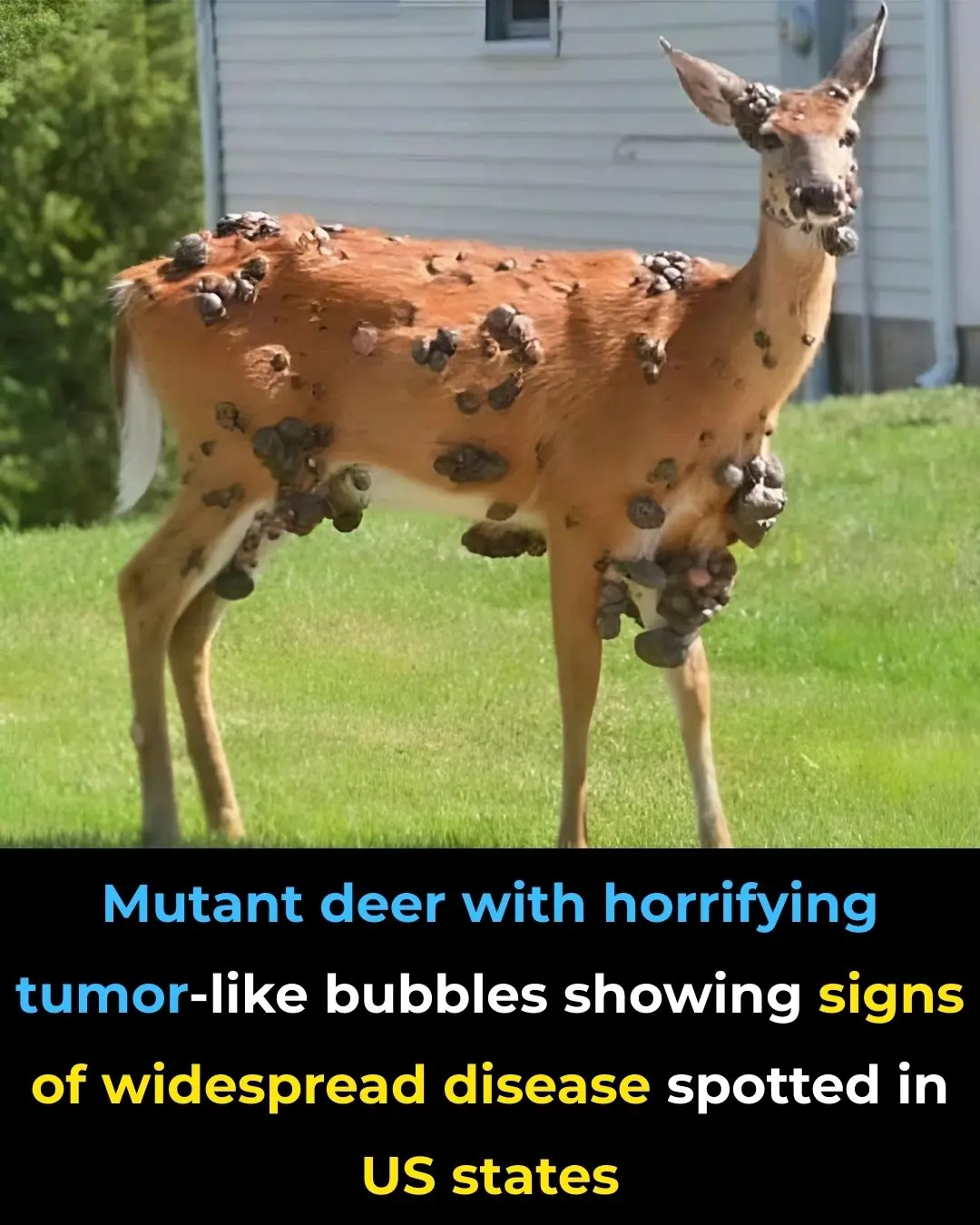
Mutant deer with horrifying tumor-like bubbles showing signs of widespread disease spotted in US states

'Frankenstein' creature that hasn't had s3x in 80,000,000 years in almost completely indestructible

When a Washing Machine Shows 7kg, 8kg, or 10kg, Is That the Weight of Dry or Wet Clothes? The Real Meaning Behind These Numbers Is Something That Few People Know

Place a Bowl of Salt in the Fridge: A Small Trick, But So Effective — I Regret Not Knowing It for 30 Years

If Your White Walls Are Dirty, Don’t Clean Them with Water — Use This Trick for a Few Minutes, and Your Wall Will Be as Clean as New

Bubble Wrap Has 4 Uses 'As Valuable as Gold' — But Many People Don’t Know and Hastily Throw It Away

3 Ways to Prevent Snakes from Entering Your House: Protect Your Family

5 Household Devices That Consume More Electricity Than an Air Conditioner: Unplug Them to Avoid Skyrocketing Bills

How a Common Kitchen Powder Can Help Your Plants Thrive and Bloom

How to Effectively Clean Black Mold from Your Refrigerator Gasket in Just 5 Minutes

10 Early Warning Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Way Too High

If Your Legs Cramp at Night You Need to Know This Immediately

Warning Signs Your Body Is Full of Parasites and How to Effectively Eliminate Them Naturally

Warning Signs of a Parasite Infection And How to Eliminate It for Good

What Raw Garlic Can Do for Your Health Is Truly Unbelievable
