Scientists Identify Bacteria That May Trigger Multiple Sclerosis (MS): A Breakthrough in Neurological Research
Scientists Identify Bacteria That May Trigger Multiple Sclerosis (MS): A Breakthrough in Neurological Research
A groundbreaking discovery in neurological science has revealed that certain types of bacteria may play a key role in triggering multiple sclerosis (MS) — a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects nearly 2.8 million people worldwide, according to the Multiple Sclerosis International Federation (MSIF). This finding represents a major advancement in understanding the root causes of MS, a disease that has puzzled experts for decades due to its complex interaction between genetics, immunity, and environmental factors.'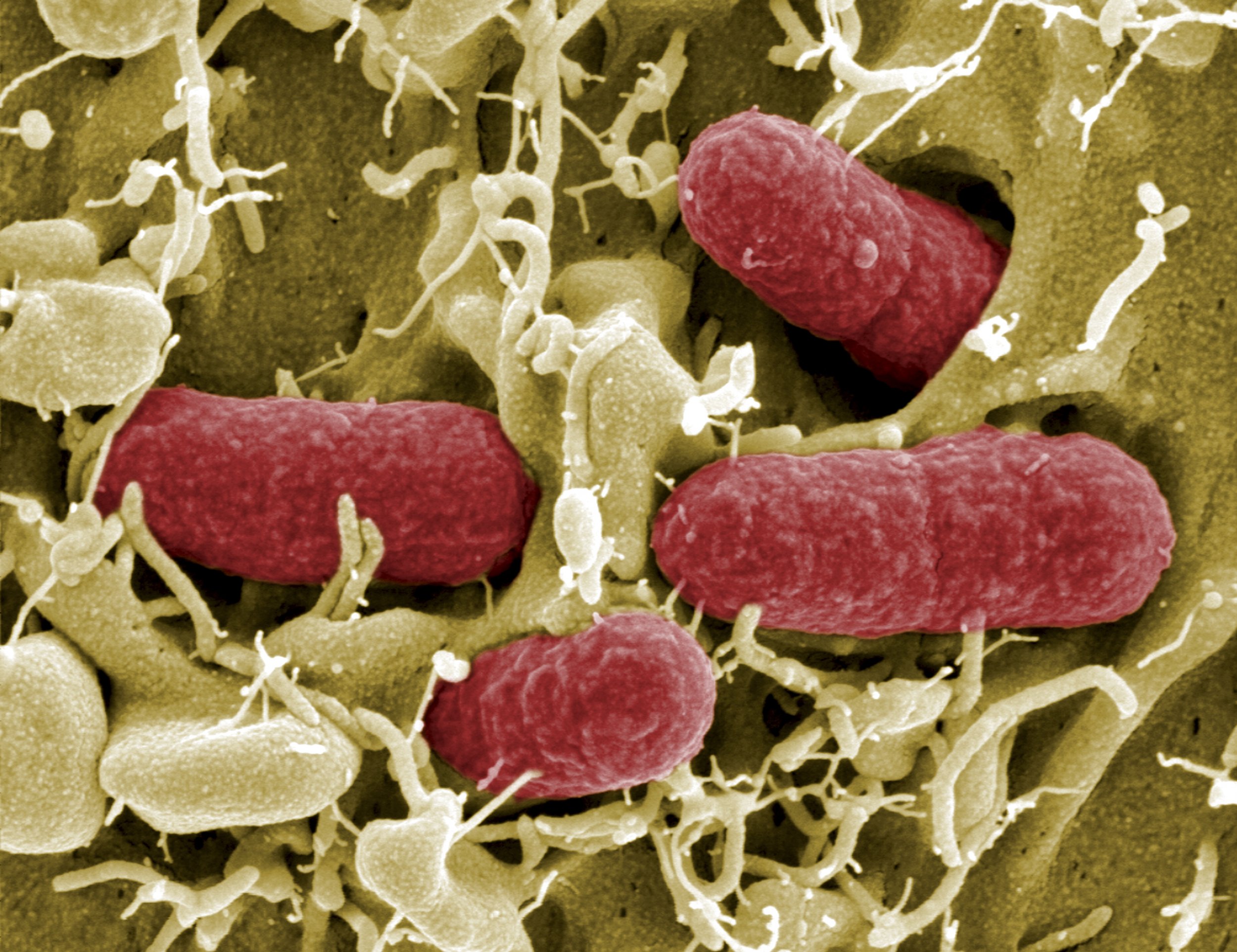
How Bacteria May Influence MS Development
Recent studies suggest that specific bacteria in the gut can interact with the immune system in ways that may cause it to malfunction. According to researchers, these bacteria appear to activate immune responses that mistakenly target the body's own nerve fibers. This attack leads to nerve inflammation, myelin damage, and neurological symptoms commonly associated with MS — such as fatigue, numbness, muscle weakness, and coordination problems.
The discovery supports a growing body of research highlighting the connection between the gut microbiome and brain health, often referred to as the gut–brain axis. Institutions such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Cleveland Clinic have long emphasized the influence of gut microbes on immune regulation, making this new MS-related finding a significant step forward.
Why This Discovery Matters
Understanding how bacteria are linked to MS could open the door to a wide range of medical breakthroughs, including:
1. Earlier and More Accurate Detection
If specific bacterial strains are proven to be associated with MS onset, doctors may eventually be able to detect high-risk individuals before symptoms appear. Early identification is known to improve treatment outcomes, according to the National MS Society.
2. Targeted New Therapies
Rather than relying solely on medications that broadly suppress the immune system, scientists may develop microbiome-focused treatments—such as probiotics, antibiotics, or dietary interventions—to reduce inflammation or prevent immune misfiring.
3. Potential for MS Prevention
Should further research confirm a causal link, modifying the gut microbiome could become a viable strategy to lower MS risk, a concept supported by modern immunology and microbiome studies published in journals such as Nature and Cell.
More Research Still Needed
Although the discovery is promising, scientists stress that additional studies are required to determine exactly how these bacteria influence MS progression. Autoimmune conditions are highly complex, and MS is known to involve a combination of factors, including:
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Environmental exposures
-
Viral infections such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
-
Lifestyle and overall immune health
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and NIH emphasize that no single cause has yet been confirmed for MS. Therefore, while these bacterial findings represent a key piece of the puzzle, they are not the final answer.
A New Direction for MS Research
This breakthrough underscores the increasing importance of studying microbial health and its impact on the immune and nervous systems. As scientists continue exploring the relationship between gut bacteria and MS, this line of research could reshape how the disease is diagnosed, managed, and potentially prevented in the future.
The discovery marks an exciting advancement in unraveling one of medicine’s most challenging neurological disorders — offering new hope to millions of people affected by MS worldwide.
News in the same category


How Just 75 Minutes of Running Per Week Can Make Your Body Up to 12 Years Younger

Why Many Middle-Aged Women Are Choosing Divorce

Remove This from Your Home to Live Longer

Hygiene Mistakes That Many People Make

Why the Kindest People Are Often the Most Overlooked

The untold dangers of falling in love after 60: What nobody tells you

The Real Reason Behind the Bed Runner

Why Finland Leads the World in Education With Only 5 Hours of School a Day

Germany Unveils the First Ultra-Detailed 3D Map of All 2.75 Billion Buildings on Earth

18,000 Dinosaur Tracks Discovered in Bolivia Reveal Extraordinary Behavioral Evidence
Eliminating Quiescent Tumor Cells: A New Frontier in Breast Cancer Survivorship Care

Sweden’s Circular Economy: The Advanced System Turning Trash into Energy
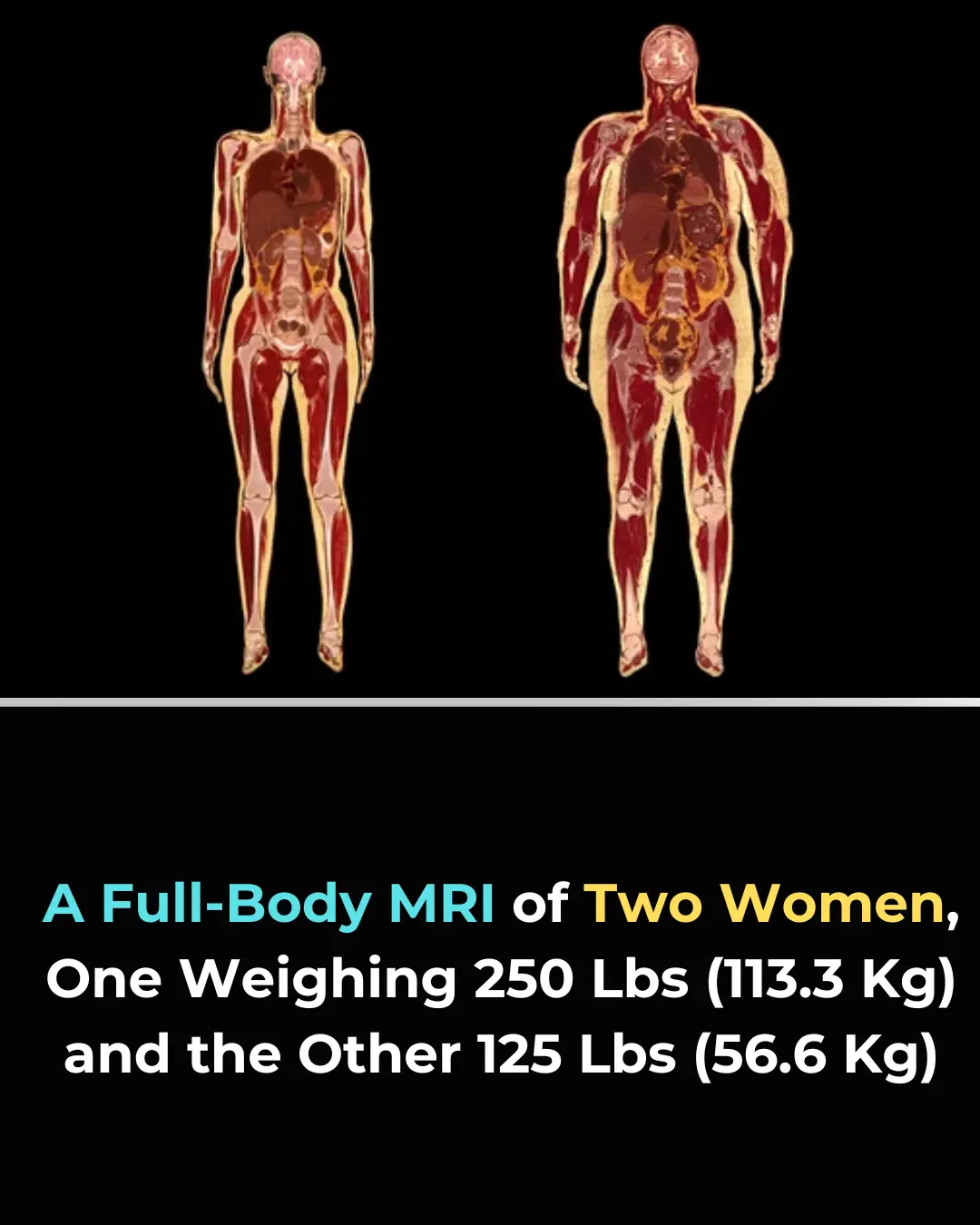
Inside the Human Body: How MRI Images Show the True Impact of Fat Composition

Do you know its value? let's see

Two Buttons, Big Impact: The Hidden Water-Saving Power of Dual-Flush Toilets
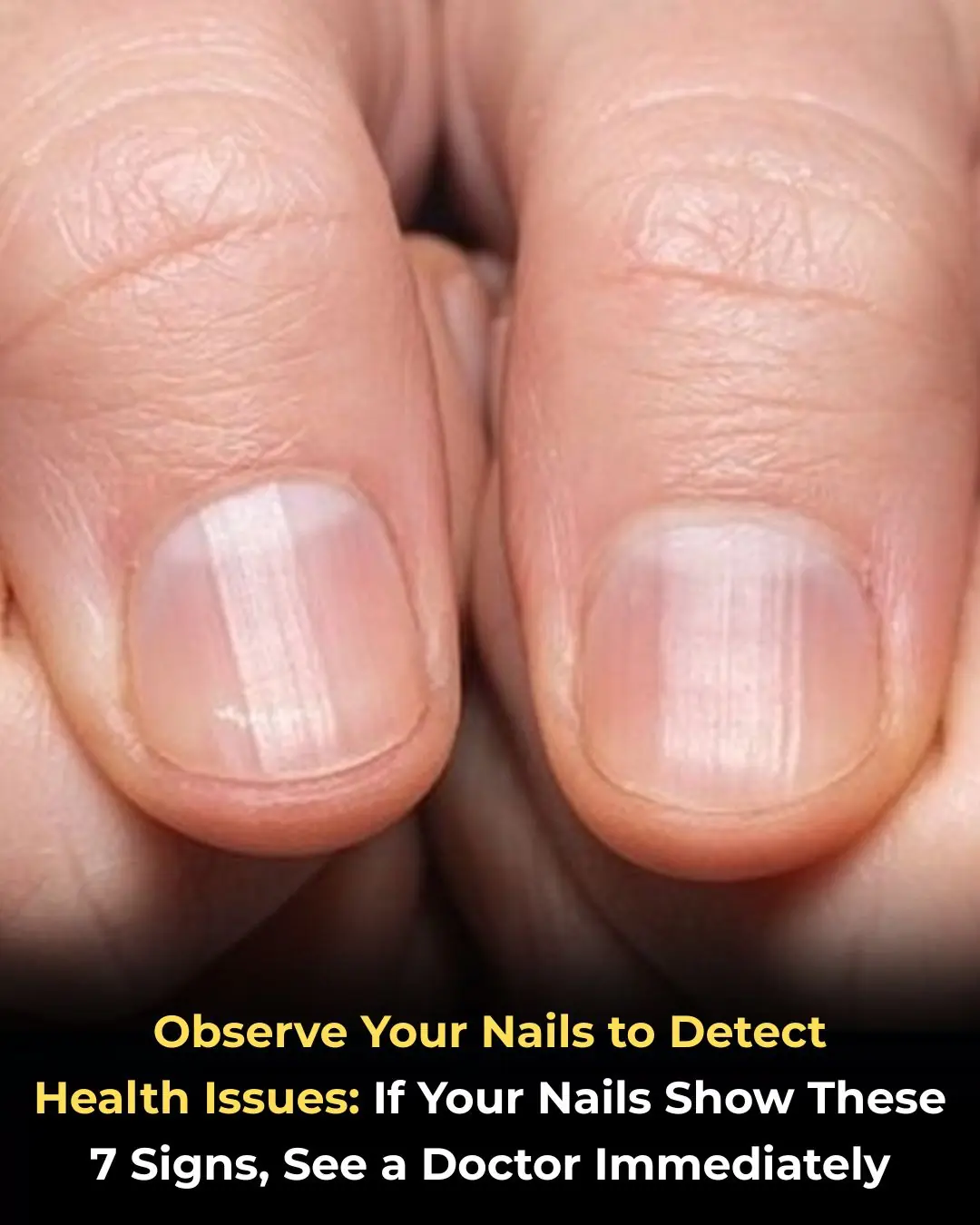
Nails: What Do They Reveal About Your Health

Why wood—not diamonds—is the universe’s rarest treasure

A Nearby Earth-Sized World Raising New Hopes for Habitability
News Post

Nobody Told You This Vitamin Deficiency Might Be Behind Your Migraines

The Hidden Symptoms of Low Magnesium That Are Silently Draining Your Health

Lemon in Coffee? The Simple Morning Twist People Are Loving

So this is what it does, here is the answer

How To Detox Each Organ To Reset Your System

Why Cars Have Metal Rods in Headrests — The Safety Feature Most Drivers Overlook

What Happens When You Drink Baking Soda Water Before Bed? A Gentle 2-Week Wellness Practice

The Surprising Health Benefits of Humming: How 10 Seconds Can Boost Your Brain and Body

How Just 75 Minutes of Running Per Week Can Make Your Body Up to 12 Years Younger

More Than Just Flavor: The Gentle Power of Onions for Wellness

Man has stroke after bathing right after meal: 3 mistakes you shouldn’t make

How To “Remove” All The Chemicals Out Of Store-Bought Chicken

Why Many Middle-Aged Women Are Choosing Divorce

Remove This from Your Home to Live Longer
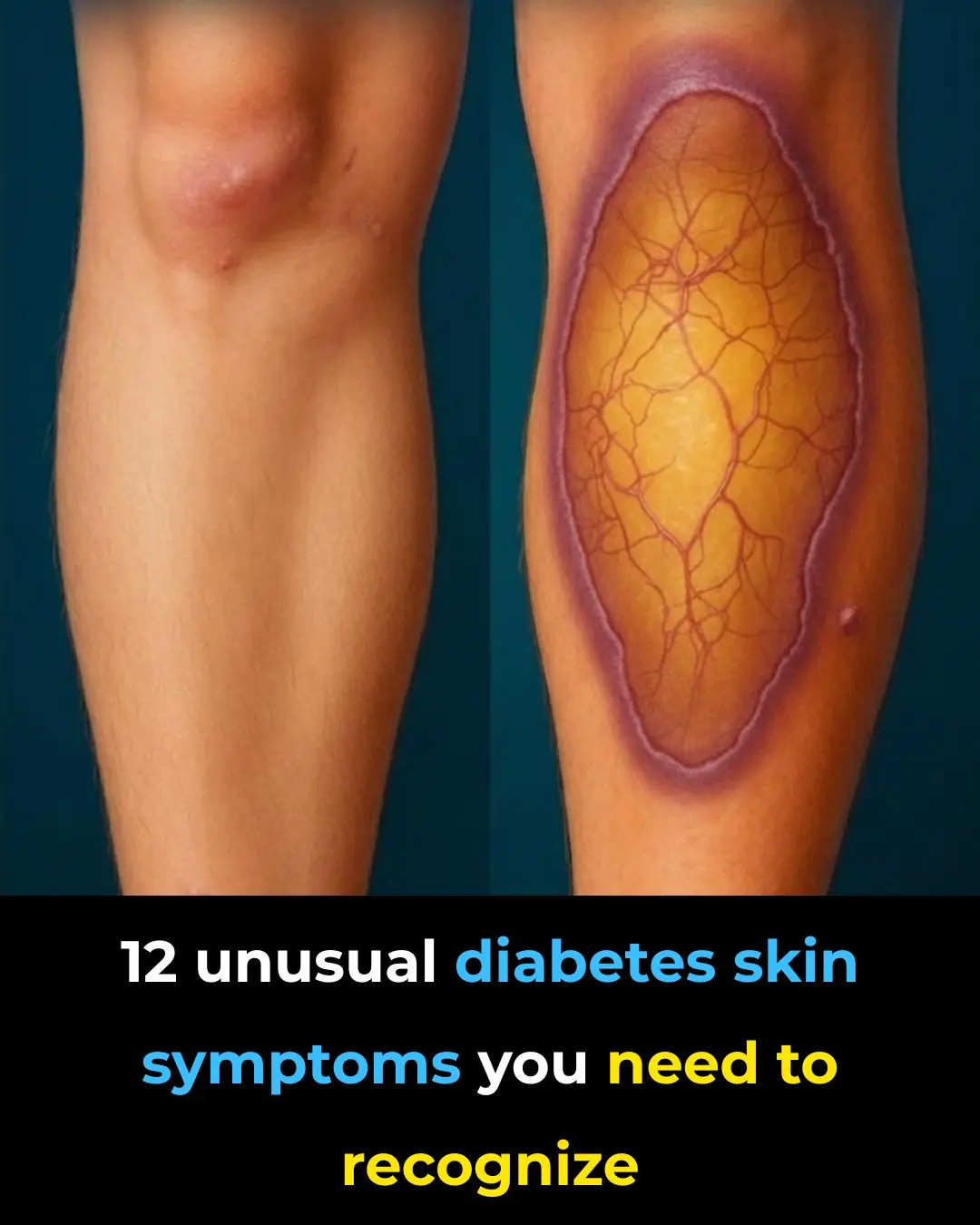
12 Weird Diabetes Skin Problems You Need To Know

Hygiene Mistakes That Many People Make

Top 5 Drinks To Improve Vision Naturally

Exact Age You Should Cease Beer Consumption