
US Researchers Develop Ultra-Light Metal Foam That Stops Armor-Piercing Bullets
Researchers in the United States have developed an innovative metal foam that combines extreme lightness with remarkable protective capabilities. This new material is even lighter than water, yet it can stop armor-piercing bullets, offering a breakthrough in lightweight protection technologies. The secret lies in its structure: the foam contains numerous microscopic air pockets that dramatically reduce weight while maintaining very high resistance to impact. This unique combination allows it to absorb the energy of high-velocity projectiles while minimizing material density. (North Carolina State University, Science Daily)
High-Performance Testing in Military Applications
Extensive testing at North Carolina State University has demonstrated the foam’s impressive capabilities. During laboratory trials, the material successfully blocked rounds typically used in military operations, including high-velocity armor-piercing bullets. Its performance is comparable to much heavier steel plates, highlighting its potential as a revolutionary material for protective systems. Additionally, the foam exhibits excellent resistance to heat and energy transfer, which enhances its utility in environments where extreme temperatures and repeated impacts might compromise conventional armor. Findings from peer-reviewed Materials Science & Engineering journals confirm both its structural integrity and energy absorption efficiency, emphasizing that this is not merely theoretical research but a practical solution with real-world applications.
Implications for Vehicles and Protective Gear
The development of this metal foam has far-reaching implications. In vehicles such as military trucks, armored personnel carriers, and even aircraft, reducing armor weight can substantially improve fuel efficiency and overall mobility. Lighter armor can also increase payload capacity, allowing for more equipment or supplies to be carried without compromising protection. Beyond vehicles, the foam has potential applications in personal protective equipment, including helmets, body armor, and shields, offering soldiers and first responders better protection with less physical burden. Reports from The Verge and other technology outlets highlight the significance of these advantages, showing that lighter, highly protective materials can transform both military and civilian safety technologies.
Collaborations and Future Research
Both academic research groups and the US Army are actively studying this metal foam for future protection systems. The US Army Research Laboratory is particularly interested in exploring how the foam can be integrated into next-generation armor for personnel and vehicles. Collaborative projects are ongoing to optimize production methods, scale the material for larger applications, and further enhance its ballistic performance. Researchers are also investigating potential hybrid designs, combining the foam with ceramics or other metals to create multi-layered armor systems that maximize both protection and weight efficiency.
Energy Absorption and Durability
One of the standout features of this metal foam is its ability to absorb and dissipate energy effectively. The microscopic air pockets act as shock absorbers, allowing the material to deform under impact without catastrophic failure. Additionally, the foam’s resistance to heat makes it suitable for high-temperature environments, where conventional armor might weaken. These characteristics were confirmed in multiple tests and documented in Materials Science & Engineering publications, making the technology promising not only for military use but also for industrial applications where lightweight, strong, and heat-resistant materials are needed.
Conclusion
This development represents a major advancement in materials science and protective technology. By creating a metal foam that is lighter than water yet capable of stopping armor-piercing bullets, US scientists have opened the door to lighter, more efficient, and more versatile armor solutions. Whether applied to vehicles, aircraft, or personal protective gear, this material has the potential to significantly enhance performance while reducing weight, fuel consumption, and operational constraints. As research continues and the technology moves closer to practical implementation, it may redefine the standards of protection in both military and civilian contexts. (North Carolina State University, Science Daily, Materials Science & Engineering, US Army Research Lab)
News in the same category


Rep. Sheila Cherfilus-McCormick of Florida charged with stealing FEMA money, using it for her campaign, DOJ says

GOP Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene will leave Congress after five turbulent years

Jimmy Cliff, reggae legend and Jamaican icon, dies at 81

MMA Icon Turned Hollywood Star Honored With Bruce Lee Award After 78 Movies

Ice-T Cites Law and Order: SVU’s ‘Budget’ Constraints as the Reason Fin Has Been MIA This Season

Juelz Santana Dragged Online After Saying Kids “Don’t Really Need to Know How to Read”

Ja Rule 3 Losers Sucker-Punched Me Backstage If I Was Bruce Springsteen, They'd Be in Cuffs!!!

Viola Ford Fletcher, one of the last survivors of the Tulsa Race Massacre, dies at age 111

Sean Duffy urges passengers to dress better, be more polite while flying during ‘busiest Thanksgiving’ ever

Examination of the Hip-Hop Mogul

‘I’ve Stayed Quiet Long Enough’: Kenneka Jenkins’ Mother Makes Explosive Claims About Her Mysterious Death and the $10 Million Settlement

A mistaken text connected them. Now they’ve become one of America’s favorite Thanksgiving traditions

‘RHOA’ Alum Kandi Burruss’ Ex Todd Tucker Demands Primary Custody, Questions Prenupital Agreement (Exclusive)

Curtis '50 Cent' Jackson on why he executive-produced new Sean 'Diddy' Combs doc

The Game Calls for Diddy and R. Kelly’s Release at His Birthday Party: ‘Free All the Freaky Homies’

Jada Pinkett Smith Hit With $3 Million Lawsuit For Allegedly Threatening Will’s Friend

Venus Williams celebrates engagement to Andrea Preti with tropical photo shoot

Elden Campbell, former Lakers first-round pick who won championship with Pistons, dies at 57

Beyoncé Makes Billboard Hot 100 History by Charting for This Many Consecutive Years
News Post

What It Means When a Black Cat Comes Into Your Home

Put Bay Leaves in the Corners of Their Kitchen

Doctors Reveal What Happens When You Eat Okra Regularly
Never Broken a Bone
🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape

3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cervical Cancer – Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

Washing blood stains from bed sheets with hot water or detergent is completely wrong; this method will remove them completely, leaving no trace.

Don't put tomatoes in the refrigerator: Here's how to keep them fresh for a whole week without them spoiling.

Bihar Jewellery Shops Restrict Face‑Covered Customers: Security vs. Freedom ⚖️✨
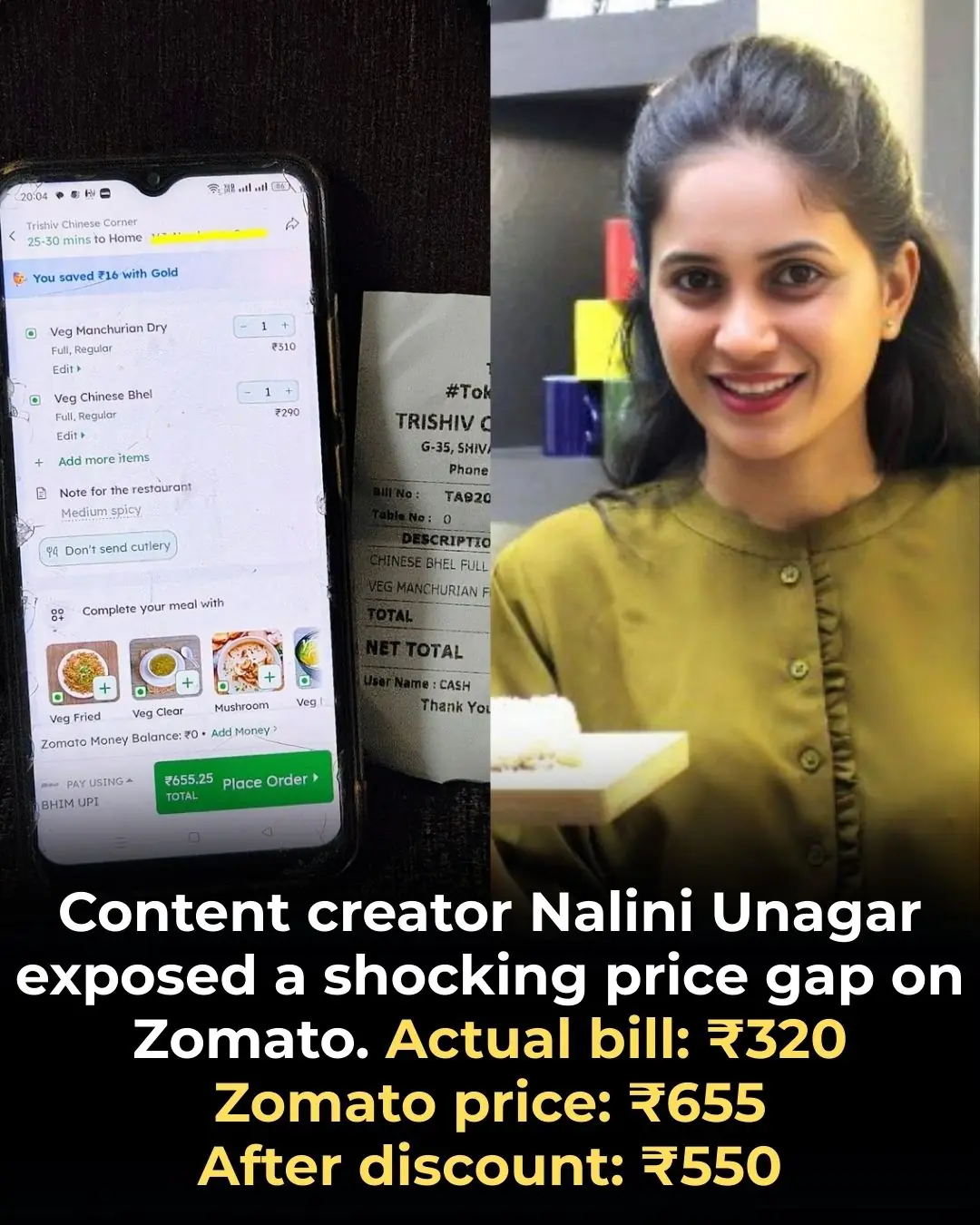
Nalini Unagar’s Viral Post Sparks Debate on Food Delivery Transparency 🍲📱

Tips for boiling okra to keep it vibrant green, not slimy, and retain all its nutrients.

Hrithik Roshan’s Birthday: A Celebration of Grace, Growth, and Mutual Respect 🎂✨❤️

Raghav Chadha Steps Into the Gig Economy: A Call for Labor Rights 🚴♂️📦

Thomas Fuller: The “Virginia Calculator” Who Defied Oppression 🧮✨

A Birthday Surprise That Touched Millions 🎂❤️

When frying pork fat, some people add salt, others add water, but chefs use pure white fat that lasts a long time without spoiling.

Restoring Brain Energy Reverses Advanced Alzheimer’s Pathology in Preclinical Models

Remission Is a Reminder of the Power of Belief
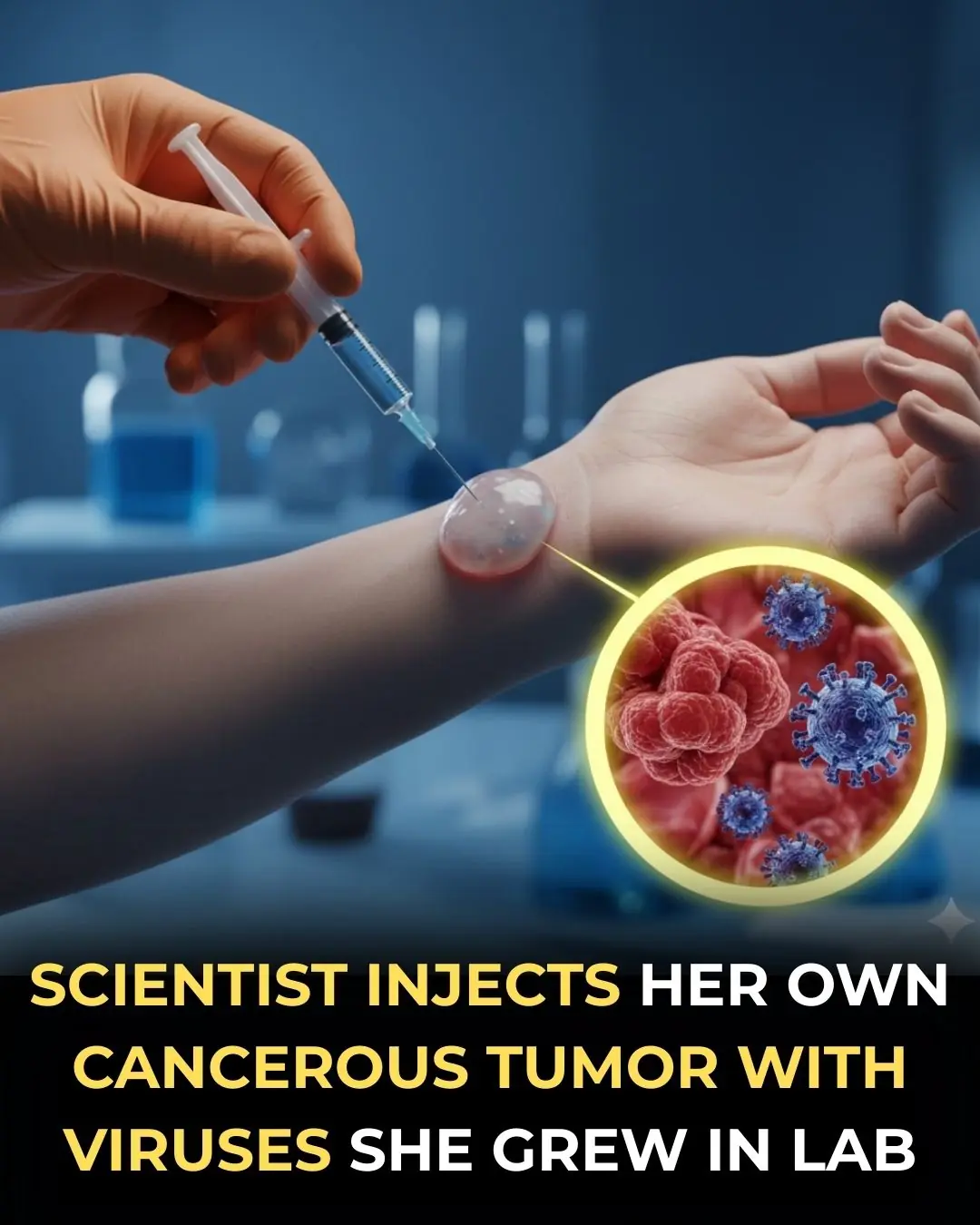
A Scientist Injected Herself With Viruses to Treat Cancer — and It Worked
