Why Do You Get Thick Toenails?
Thick toenails are a common condition that can develop gradually over time. While they are often associated with aging, they may also result from fungal infections, repeated trauma, or underlying medical conditions. Thickened nails can become uncomfortable, difficult to trim, and sometimes painful—especially when wearing shoes.
Understanding the different causes and treatment options can help prevent complications and restore nail health.
Common Types of Thick Toenails
1. Onychomycosis (Fungal Nail Infection)
Onychomycosis is the most common cause of thick toenails. It is a fungal infection that affects the nail bed and sometimes the nail matrix (the crescent-shaped area where nail growth begins). As the body attempts to fight the infection, the nail may thicken, discolor, and become brittle.
Symptoms often include:
-
Yellow, brown, or green discoloration
-
Crumbling edges
-
Thickened, distorted shape
-
Debris buildup under the nail
-
A noticeable odor
Fungal infections thrive in warm, moist environments such as locker rooms and public showers.
2. Onychauxis (Nail Overgrowth)
Onychauxis, sometimes referred to as onychogryphosis in more advanced cases, involves abnormal thickening and excessive nail growth. It may result from aging, repeated trauma, diabetes, psoriasis, or poor circulation.
In severe cases, the nail may:
-
Turn yellow or brown
-
Curl and resemble a ram’s horn or oyster shell
-
Separate from the nail bed
-
Become extremely hard and difficult to trim
This condition is more common in older adults due to slower nail cell turnover.
3. Onycholysis (Nail Separation)
Onycholysis occurs when the nail plate separates from the nail bed. It is usually painless at first but can lead to infection if debris becomes trapped underneath.
Causes include:
-
Nail injuries
-
Allergic reactions
-
Psoriasis
-
Fungal infections
The affected nail may appear white, yellow, or opaque where it has lifted.
What Thick Toenails Look and Feel Like
Healthy toenails typically measure about 1.4 mm thick in females and 1.65 mm in males. When thickened, noticeable changes occur:
Changes in Appearance
-
Yellow, green, brown, or white discoloration
-
Curled or distorted nail shape
-
White buildup under or on the nail
-
Ram-horn-like curvature (in severe cases)
-
In rare conditions such as yellow nail syndrome, nails grow slowly and appear thick and yellow
Changes in Texture
-
Rough, brittle surface
-
Flaking or crumbling when trimmed
-
Uneven regrowth
Changes in Odor
A cheese-like smell may develop, particularly with fungal infections.
Other Symptoms
-
Pain when wearing tight shoes
-
Pressure while walking
-
Increased risk of ingrown nails
-
Possible discharge (pus) if bacterial infection develops
What Causes Thick Toenails?
Thick toenails develop when keratin—the protein that makes up nails—accumulates excessively. Normally, the nail matrix sheds old keratin cells efficiently. With age or certain medical conditions, this process slows, allowing layers to build up.
Common underlying causes include:
-
Autoimmune disorders (e.g., psoriasis, lichen planus)
-
Fungal infections
-
Poor blood circulation
-
Paronychia (infection around the nail)
-
Repeated trauma or tight footwear
Risk Factors
You may be more likely to develop thick toenails if you:
-
Are over 65
-
Smoke
-
Swim frequently
-
Have athlete’s foot
-
Get frequent pedicures in unsanitary conditions
-
Have diabetes or immune system disorders
-
Undergo chemotherapy or radiation
-
Wear ill-fitting shoes
-
Use public pools or locker rooms regularly
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider may refer you to a podiatrist (a foot specialist). Diagnosis may involve:
-
Visual examination
-
Nail clipping biopsy
-
Swab testing for fungal organisms
Identifying the exact cause is important because treatments differ significantly depending on whether the condition is fungal, autoimmune, or injury-related.
Treatment Options
Thick toenails can take months—or even over a year—to return to normal due to slow nail growth.
Topical Treatments (For Mild Cases)
Over-the-counter antifungal creams may contain ingredients such as:
-
Clotrimazole
-
Miconazole
-
Tolnaftate
-
Undecylenic acid
-
Povidone-iodine
These work best when applied consistently and early in infection.
Prescription Antifungal Medications
More severe fungal infections may require:
-
Ciclopirox
-
Terbinafine
-
Efinaconazole
-
Tavaborole
-
Itraconazole
Oral medications are often more effective but require medical supervision due to potential side effects.
Psoriasis Treatments
If psoriasis is the cause, treatment may include:
-
Biologic medications
-
Corticosteroids
-
Methotrexate
-
Cyclosporine
-
Retinoids
-
Topical vitamin D
Debridement
This involves trimming or removing thickened portions of the nail to reduce discomfort and allow healthier regrowth. In severe cases, partial or full nail removal (avulsion) may be necessary.
Laser Therapy
Laser treatment targets fungal organisms using heat. While promising, results vary and multiple sessions may be needed.
Complementary Remedies
Some individuals try:
-
Tea tree oil
-
Urea cream (to soften thick nails)
-
Menthol-based ointments such as Vick’s VapoRub
While some people report improvement, these approaches are generally supportive rather than curative.
Prevention Tips
To reduce your risk of developing thick toenails:
-
Keep feet clean and dry
-
Change socks daily
-
Disinfect nail clippers
-
Avoid sharing grooming tools
-
Wear properly fitting shoes
-
Trim nails straight across
-
Protect feet in public showers and pools
-
Treat athlete’s foot promptly
Thick toenails may seem like a minor cosmetic issue, but they can signal underlying health problems. Early treatment and consistent foot care are key to preventing discomfort and long-term complications. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking professional medical advice is the safest course of action.
News in the same category


The Real Purpose of the Aluminum Ring on Sausage Bars

Over 60? Struggling to Sleep Through the Night? Try This Simple Bedtime Drink for Deeper Rest

Discover a Simple Daily Habit: How to Incorporate Lemon and Nopal into Your Wellness Routine

How to Keep Salad Greens Fresh Longer

Hospice chef reveals the one comfort food most people ask for before they die

The secret to making homemade tomato sauce: affordable, delicious, and free from additives.

Why should you put a clove of garlic in the toilet at night? Knowing its uses, every family wants to follow suit

To make pickled garlic, you need to add this one step; the garlic will be white and crispy, won't turn green, and won't spoil easily

Place an empty plastic bottle in the washing machine, I have to admit, the person who came up with this hack has an "exceptional" IQ.

Discover: A Glass of Water, Vinegar, and Salt Can Cleanse Your Home
A 25-Year-Old Liver Cancer Survivor Shares: “5 Foods You Must Avoid — No Matter How Much You Crave Them”

Soaking Lemon Peels in Vinegar: A Simple Homemade Solution with Powerful Benefits

7 Foods To Help You Live a Longer, Healthier Life

Clogged Sink? Don’t Use Hot Water
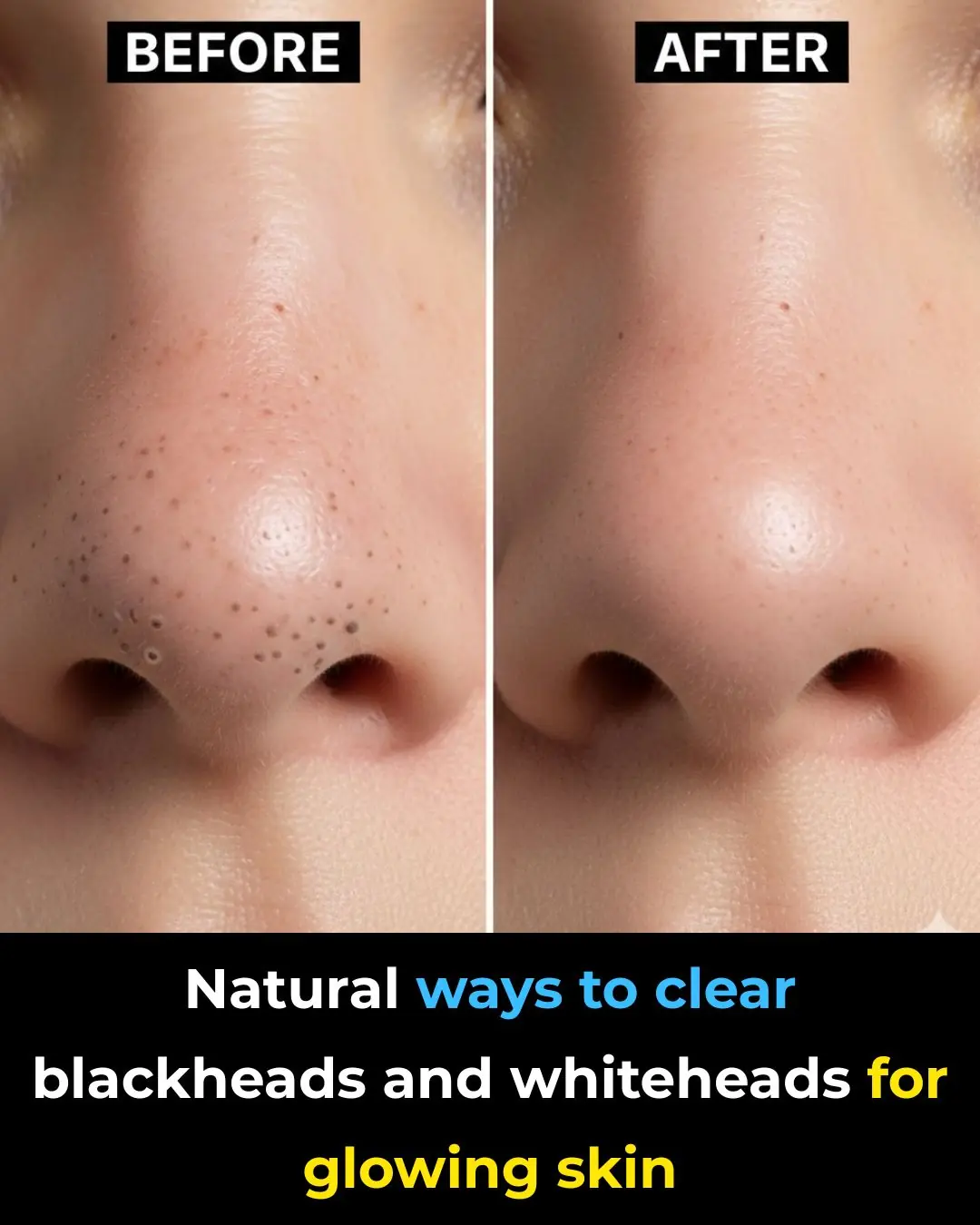

Natural Ways to Clear Blackheads and Whiteheads

4 Things Oncologists Do Regularly to Lower Their Cancer Risk

5 Foods to Avoid When Taking Blood Pressure Medication

Can You Spot the Hidden Mistake in This Hospital Picture
News Post

The military sleep method that can help you fall asleep in just two minutes
5 warning signs of stroke in young adults

20 Early Signs Your Body is Fighting Cancer

9-year-old dies after dental procedure
The HEALTHIEST FRUIT on Earth: what happens to your body if you eat just 3 a day

Billionaire’s Son Abuses Janitor – She’s His Dead Mother’s Best Friend

Garlic & Cloves: The Timeless Duo for Stronger Veins and Better Circulation

Taro: The Tropical Treasure Your Kitchen — and Your Body — Will Love
Benefits and How to Use This Powerful Herb

Boy Slaps Girl at Starbucks – Her Dad’s Response Went Viral

Woman Attacks Homeless Man — Loses City 5,000 Jobs

Some of the Benefits of Castor Leaves and the Seed

Goldenberries (Physalis peruviana): A Nutrient-Packed Powerhouse for Health and Vision

Wild Lettuce Extract – Natural Pain Medicine

🌿 Miracle Leaf for Wellness: Why Bryophyllum Calycinum (Kalanchoe Pinnata) Is Gaining Attention

🌿 Mint: The Cooling Herb with Surprising Health Benefits & Everyday Uses 🍃

🌿 Dandelion Tea: The Gentle Herbal Secret for Daily Wellness

Emma Attacks Teen Worker—His Uncle Owns 200 Stores
