12 Subtle Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms That Most People Ignore
12 Subtle Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms That Most People Ignore
Vitamin D deficiency is a widespread problem, often referred to as a "pandemic." It is crucial for a healthy immune system and the proper function of muscles, the heart, lungs, and brain. The body can produce its own vitamin D from sunlight, but many people have low levels, especially during winter months. A small amount can also be obtained from foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified products.

Common Causes of Low Vitamin D Levels
Several factors can contribute to a vitamin D deficiency:
-
Limited Sunlight Exposure: People living at northern latitudes, wearing long clothing, or spending most of their time indoors are at risk. Sunscreen also inhibits vitamin D production.
-
Dark Skin: Higher melanin levels in darker skin reduce the skin's ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight.
-
Kidney and Liver Issues: These organs are vital for converting vitamin D to its active form. Diseases affecting them can hinder this process.
-
Strict Vegetarian Diet: Many food sources of vitamin D are animal-based, making it difficult for those on a strict vegetarian diet to get enough.
-
Digestive Problems: Conditions like Crohn's or celiac disease can impair the absorption of vitamin D from food.
-
Obesity: Research suggests that vitamin D may become "trapped" in fat tissue, reducing its availability in the bloodstream.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Related Diseases
A lack of vitamin D has been linked to a number of chronic health issues:
-
Osteoporosis: Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, which is critical for bone density and strength. A deficiency can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
-
Asthma: Low vitamin D levels are associated with reduced lung function and poor asthma control, particularly in children. It may contribute to inflammation in the lungs.
-
Heart Health: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to a higher risk of high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease.
-
Inflammation: A deficiency is associated with a negative immune response and has been linked to inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease.
-
Cholesterol: Without adequate sun exposure, vitamin D precursors can be converted into cholesterol instead of vitamin D.
-
Allergies: Children with low vitamin D levels are more likely to have multiple food allergies.
-
Influenza: Studies show a link between low vitamin D levels and a higher incidence of common respiratory infections like colds and the flu. Some research suggests vitamin D supplementation is more effective than a flu vaccine in preventing these illnesses.
-
Depression: Vitamin D receptors are found in many areas of the brain, suggesting a role in mood regulation. Deficiency is linked to an increased risk of depression.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: Low vitamin D levels have been correlated with the development of type 2 diabetes, as the vitamin may influence insulin secretion and sensitivity.
-
Oral Health: Deficiency is associated with poor periodontal health and a higher rate of tooth loss in elderly patients.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Low vitamin D levels may play a role in the development and severity of rheumatoid arthritis, particularly in women.
-
Cancer: Some studies have found a link between low vitamin D levels and an increased risk of various cancers, with the lowest levels being associated with more advanced cancers. More research is needed to fully understand this connection.
-
Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: A significant study found that adults with moderate vitamin D deficiency had a 53% increased risk of developing dementia, and those with a severe deficiency had a 125% increased risk. Similar risks were found for Alzheimer’s disease.
What to Do if You Have a Vitamin D Deficiency
If you are concerned about your vitamin D levels, a simple blood test can determine if you have a deficiency. Your doctor can then advise on whether you should take a supplement, as there is no single recommendation for everyone. While sun exposure is a natural way to produce vitamin D, it's important to do so safely and be mindful of other factors like skin type and time of day.
News in the same category


Clear Throat Mucus Fast With These Tried-and-Tested Remedies They Don’t Want You to Know
9 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency You Shouldn't Ignore

Poor Postcancer Surgery Outcomes Tied to 3 Factors

Teamwork Boosts Primary Care Doc Job Satisfaction, Cuts Stress
HIV Was Successfully Eliminated from Human Immune Cells Using CRISPR Gene Editing in Landmark Study
Scientists Discover An “Off Switch” For Cholesterol—And It Could Save Millions Of Lives

How to Treat Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Naturally According to Science
4 Common Causes of Body Pain on the Right Side

What Your Heart Experiences When You Drink Energy Drinks

How to Eat Right for Your Blood Type
When to Worry About Veins That Appear Out of Nowhere
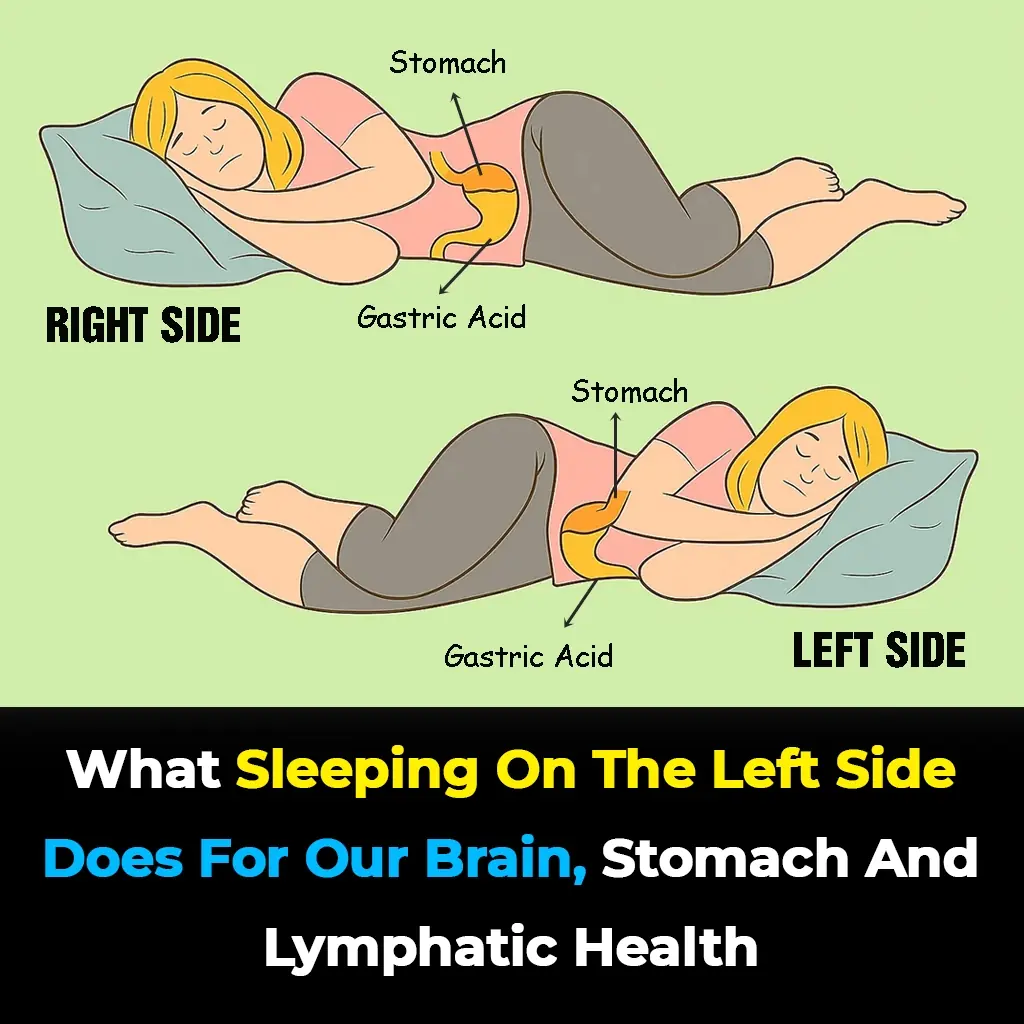
This is what sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach & glymphatic health
Sleeping position might be the last thing you think about before bed, but it can have a powerful impact on your health. Experts say that lying on your left side could improve digestion, support brain detox, ease back pain, and even enhance circulation.
Mother Rushes To Emergency Room To Deliver Triplets: Then Nurses Look Closer At Their Faces And Freeze

The First Ever Albino Twins Born In Argentina Will Leave You In Awe
Doctor Reveals: MRI Scan Of The Face Of A 33-Year-Old Woman Reveals Where All Of Her Filler Went

Man Loses Pulse For 45 Minutes, Wakes Up, And Reveals This Spine-Chilling Vision Of Afterlife

Your Heart May Be Older Than You Are

6 Types of Pain You Shouldn’t Ignore
News Post

Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments (Evidence Based)

Clear Throat Mucus Fast With These Tried-and-Tested Remedies They Don’t Want You to Know

9 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency You Shouldn't Ignore

Poor Postcancer Surgery Outcomes Tied to 3 Factors

Teamwork Boosts Primary Care Doc Job Satisfaction, Cuts Stress

HIV Was Successfully Eliminated from Human Immune Cells Using CRISPR Gene Editing in Landmark Study

Scientists Discover An “Off Switch” For Cholesterol—And It Could Save Millions Of Lives

How to Treat Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Naturally According to Science

4 Common Causes of Body Pain on the Right Side

The Truth About Eating the Black Vein in Shrimp Tails

What Your Heart Experiences When You Drink Energy Drinks

How to Eat Right for Your Blood Type

Eyes Full of Hope, Heart Full of Trust.

When to Worry About Veins That Appear Out of Nowhere

This is what sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach & glymphatic health
Sleeping position might be the last thing you think about before bed, but it can have a powerful impact on your health. Experts say that lying on your left side could improve digestion, support brain detox, ease back pain, and even enhance circulation.

I Haven’t Seen My Daughter in 13 Years — Then a Letter Arrived from a Grandson I Never Knew

This is why you should keep the bathroom light on when sleeping in a hotel
Leaving your hotel bathroom light on at night might seem unnecessary, but it could be a small habit that makes a big difference for your comfort and safety. From preventing nighttime accidents to deterring intruders, experts say this simple tip can protec

Wife Left Husband to Raise Their Baby Alone — 20 Years Later, She Reached Out to Their Daughter
