Scientists Discover An “Off Switch” For Cholesterol—And It Could Save Millions Of Lives
In a discovery that sounds like something straight out of a science fiction film, researchers have identified a sneaky little enzyme in the human body that could be quietly sabotaging our health—and making us more vulnerable to some of the most dangerous diseases of modern times. The real twist? Shutting down this enzyme might help shield us from conditions like heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and even dementia.
So, what’s the name of this microscopic troublemaker? It’s an enzyme called IDO1, and scientists believe that figuring out how to “switch it off” could fundamentally change how our immune system handles cholesterol—potentially saving millions of lives in the long run.
The Cholesterol Story You Haven’t Heard
We’ve all heard it countless times: “Watch your cholesterol!” But what many people don’t realize is that cholesterol itself isn’t inherently bad. In fact, it plays a vital role in the body, helping to build cell membranes, produce hormones, and support brain function.
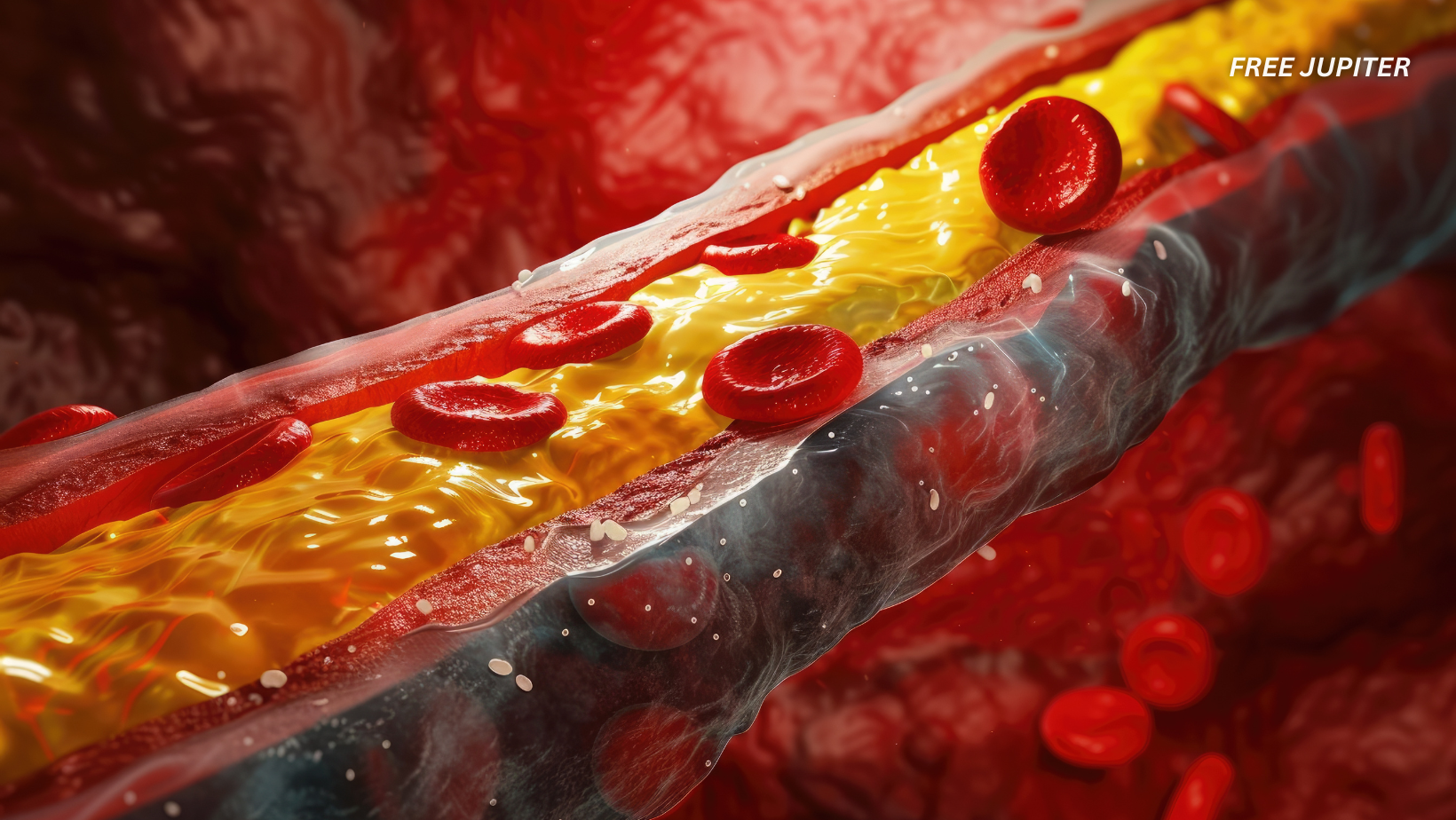
The real problem begins when cholesterol becomes unregulated—when too much of it builds up in places it doesn’t belong, like the walls of your arteries. This buildup can lead to atherosclerosis, narrowing of arteries, and eventually serious cardiovascular events.
That’s where your immune system steps in—especially a class of cells known as macrophages. Think of them as your body’s cellular cleanup crew. They roam through your tissues, ingesting harmful invaders, dead cells, and yes—excess cholesterol.
But here’s the issue: under chronic stress or persistent inflammation, these macrophages start to lose their effectiveness. They slow down, become dysfunctional, and eventually fail to keep cholesterol under control. When that happens, cholesterol accumulates, arteries clog, and the risk of disease skyrockets.
The Culprit: IDO1 and the Sabotage of Your Cholesterol Cleanup Crew
Enter IDO1—short for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1. It might sound like a mouthful, but this little enzyme could be one of the most important biological targets in medicine today.
In a study led by Dr. Subhrangsu S. Mandal and his team at the University of Texas at Arlington, researchers discovered that IDO1 becomes highly active during inflammation. When it turns on, it doesn’t just go about its normal cellular duties—it starts interfering with the cholesterol-clearing function of macrophages.
How does it do this? By triggering a biochemical chain reaction that creates a compound called kynurenine. This molecule confuses macrophages, causing them to ignore cholesterol and focus on other tasks. Imagine giving a janitor a strange new checklist that says, “Forget cleaning the mess, just rearrange the furniture.” The result? A buildup of cellular junk—including cholesterol.
But here's the exciting part: when scientists blocked IDO1 in lab models, macrophages regained their cholesterol-clearing powers. This seemingly small tweak restored immune function and pointed toward a potential new therapeutic strategy.
Inflammation: From Lifesaver to Silent Killer
To understand why this matters so much, it's important to grasp how inflammation works. In small, short-lived doses, inflammation is essential—it helps us fight infections, heal injuries, and recover from trauma.
But when inflammation becomes chronic, it turns into a stealthy saboteur. Rather than protecting the body, it disrupts its systems—causing harm over time. Chronic inflammation is now widely linked to diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, autoimmune disorders, and even some forms of cancer.
IDO1 plays a pivotal role in this transformation. Activated by inflammation, it adds fuel to the fire by disabling macrophages and letting cholesterol accumulate. It creates a vicious cycle: more inflammation leads to more IDO1 activity, which leads to worse cholesterol regulation, and so on.
But Wait—There’s Another Accomplice
Just when you thought IDO1 was bad enough, there’s more. The research also uncovered a second enzyme contributing to the damage: nitric oxide synthase (NOS).
On its own, NOS helps produce nitric oxide, a molecule vital for relaxing blood vessels and maintaining proper circulation. But in this case, NOS teams up with IDO1 in a double-trouble partnership. When both enzymes are active, the body’s cholesterol-clearing and inflammation-regulating mechanisms fall even further out of balance.
This discovery has prompted researchers to consider a dual-enzyme inhibition strategy—designing medications that target both IDO1 and NOS simultaneously. Think of it as cutting power to two misfiring circuit breakers rather than just one.
What This Means for You—and the Future of Medicine
According to Dr. Mandal, these findings could radically shift how we treat diseases tied to cholesterol and inflammation. Rather than focusing only on lowering cholesterol with medications like statins, doctors might eventually be able to prevent cholesterol buildup from happening in the first place—by targeting the inflammation that leads to it.
This could mean a new class of drugs that help reduce heart attacks, manage diabetes more effectively, slow the progression of Alzheimer’s, and possibly even lower the risk of certain cancers. It also opens the door to personalized medicine—treatments tailored to how a person’s immune system and enzymes behave under stress or inflammation.
And because IDO1 is active in multiple systems—including the brain—this discovery could help explain links between inflammation and mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and dementia, offering fresh insight into how these diseases start and progress.
What’s Next? The Road Ahead
Of course, we’re still at the early stages. More research is needed to fully understand how IDO1 and NOS interact with the rest of the body’s complex systems. Scientists are now investigating whether other enzymes or signaling molecules play supporting roles in this cholesterol-inflammation tug-of-war.
The ultimate goal is to develop safe, targeted medications that block these harmful pathways without disrupting the good ones. Ideally, these new drugs would work alongside existing treatments—like statins, insulin, or immunotherapy—or even offer alternatives for people who don’t respond well to current medications.
Imagine a future where chronic diseases are prevented, not just treated—by addressing the biological “misfires” before they spiral out of control.
Final Thoughts: Big Impact from Tiny Discoveries
It’s easy to overlook something as small as an enzyme. After all, they’re microscopic and invisible to the naked eye. But as this research shows, these tiny molecular actors can play outsized roles in human health.
A single switch—flipped at the right moment—can mean the difference between balance and disease, between breakdown and healing.
Thanks to the dedication of researchers in Texas—including not only seasoned scientists but also graduate students and early-career scientists—we might be closer than ever to flipping that switch in the right direction.
And if that happens, this discovery may go down not just as an interesting lab finding, but as a medical turning point for millions around the world.
News in the same category


Clear Throat Mucus Fast With These Tried-and-Tested Remedies They Don’t Want You to Know
9 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency You Shouldn't Ignore

Poor Postcancer Surgery Outcomes Tied to 3 Factors

Teamwork Boosts Primary Care Doc Job Satisfaction, Cuts Stress
HIV Was Successfully Eliminated from Human Immune Cells Using CRISPR Gene Editing in Landmark Study

How to Treat Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Naturally According to Science
4 Common Causes of Body Pain on the Right Side

12 Subtle Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms That Most People Ignore

What Your Heart Experiences When You Drink Energy Drinks

How to Eat Right for Your Blood Type
When to Worry About Veins That Appear Out of Nowhere
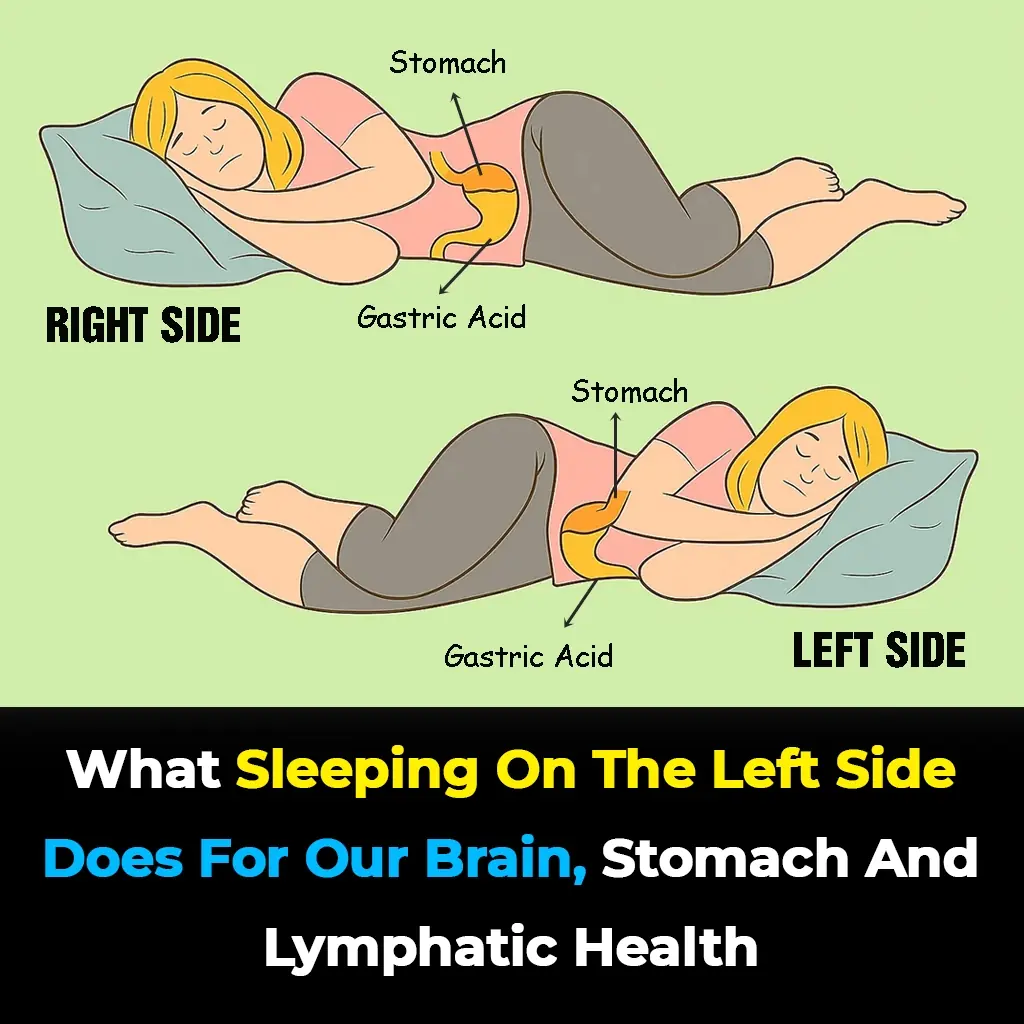
This is what sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach & glymphatic health
Sleeping position might be the last thing you think about before bed, but it can have a powerful impact on your health. Experts say that lying on your left side could improve digestion, support brain detox, ease back pain, and even enhance circulation.
Mother Rushes To Emergency Room To Deliver Triplets: Then Nurses Look Closer At Their Faces And Freeze

The First Ever Albino Twins Born In Argentina Will Leave You In Awe
Doctor Reveals: MRI Scan Of The Face Of A 33-Year-Old Woman Reveals Where All Of Her Filler Went

Man Loses Pulse For 45 Minutes, Wakes Up, And Reveals This Spine-Chilling Vision Of Afterlife

Your Heart May Be Older Than You Are

6 Types of Pain You Shouldn’t Ignore
News Post

Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments (Evidence Based)

Clear Throat Mucus Fast With These Tried-and-Tested Remedies They Don’t Want You to Know

9 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency You Shouldn't Ignore

Poor Postcancer Surgery Outcomes Tied to 3 Factors

Teamwork Boosts Primary Care Doc Job Satisfaction, Cuts Stress

HIV Was Successfully Eliminated from Human Immune Cells Using CRISPR Gene Editing in Landmark Study

How to Treat Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Naturally According to Science

4 Common Causes of Body Pain on the Right Side

The Truth About Eating the Black Vein in Shrimp Tails

12 Subtle Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms That Most People Ignore

What Your Heart Experiences When You Drink Energy Drinks

How to Eat Right for Your Blood Type

Eyes Full of Hope, Heart Full of Trust.

When to Worry About Veins That Appear Out of Nowhere

This is what sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach & glymphatic health
Sleeping position might be the last thing you think about before bed, but it can have a powerful impact on your health. Experts say that lying on your left side could improve digestion, support brain detox, ease back pain, and even enhance circulation.

I Haven’t Seen My Daughter in 13 Years — Then a Letter Arrived from a Grandson I Never Knew

This is why you should keep the bathroom light on when sleeping in a hotel
Leaving your hotel bathroom light on at night might seem unnecessary, but it could be a small habit that makes a big difference for your comfort and safety. From preventing nighttime accidents to deterring intruders, experts say this simple tip can protec

Wife Left Husband to Raise Their Baby Alone — 20 Years Later, She Reached Out to Their Daughter
