
A study shows that oxytocin, the ‘love hormone,’ can help regenerate the heart after injury.

Oxytocin, widely known as the “love hormone,” has revealed an unexpected and promising role in heart repair. Recent scientific research suggests that this hormone can stimulate cardiac stem cells, opening new avenues for treating heart damage caused by heart attacks and paving the way for more effective regenerative therapies in the future.
Oxytocin and Cardiac Progenitor Cells

A study conducted by Michigan State University found that oxytocin activates epicardium-derived progenitor cells (EpiPCs). These cells are crucial because they have the ability to differentiate into cardiomyocytes—the muscle cells responsible for the heart’s rhythmic contractions.
When a cardiac injury occurs, such as during a heart attack, the damaged tissue loses much of its natural regenerative capacity. This often leads to permanent scarring and reduced heart function. However, oxytocin appears to reverse part of this process by stimulating EpiPCs, enabling them to rebuild damaged cardiac tissue and support structural recovery.
In experiments using cultured human cells, oxytocin outperformed other molecules previously tested for similar regenerative purposes. This indicates that the hormone not only activates cardiac progenitor cells but does so more efficiently and consistently than alternative compounds.
One of the most significant aspects of this discovery is that oxytocin is already widely used in medicine, particularly to induce labor and control postpartum hemorrhage. Its established safety profile and availability make it an attractive candidate for repurposing in cardiac therapies, potentially reducing both research timelines and regulatory barriers.
Researchers believe this breakthrough could transform the treatment of patients who have suffered heart attacks, offering a more natural and biologically compatible approach to heart tissue repair. Oxytocin, long associated with emotional bonding and social behavior, is now emerging as a powerful tool in regenerative medicine.
Scientific Evidence and Experimental Validation
The study included experiments conducted on zebrafish as well as on human cells grown in laboratory conditions. Zebrafish are well known for their remarkable ability to regenerate organs, including the heart. What makes this research particularly compelling is the confirmation that oxytocin produces a similar regenerative effect in human cells.
After a cardiac injury, zebrafish significantly increase their production of oxytocin. This surge activates EpiPCs, which then migrate to the damaged area and contribute to tissue regeneration. Under laboratory conditions, oxytocin successfully replicated this mechanism in human cardiac cells, suggesting that the hormone could have real therapeutic potential in human patients.
Furthermore, researchers compared oxytocin with other molecules previously tested for cardiac regeneration. The results consistently showed that oxytocin delivered superior performance, strengthening the case for its clinical relevance.
This level of experimental validation is critical, as it demonstrates that oxytocin’s effects are not limited to animal models but also directly influence human cardiac cells. Such findings provide a strong foundation for moving toward clinical applications.
The successful laboratory results have encouraged scientists to consider future clinical trials aimed at evaluating oxytocin’s effectiveness in patients recovering from heart attacks. If proven successful, this therapy could benefit millions of people worldwide who suffer from cardiovascular disease.
Medical Implications and Future Directions
Oxytocin’s current use in hospitals for various medical purposes significantly simplifies its potential transition into cardiac treatment protocols. Its known safety, affordability, and widespread availability offer clear advantages over experimental drugs that require lengthy approval processes.
The next critical step involves conducting controlled clinical trials in humans to determine whether oxytocin can truly regenerate damaged heart tissue after a heart attack. These studies will focus on identifying optimal dosages, treatment timing, long-term effectiveness, and any potential side effects.
In parallel, researchers are developing long-acting formulations of oxytocin designed to sustain its regenerative effects over extended periods. Such formulations could enhance treatment outcomes, especially for patients requiring prolonged recovery and rehabilitation.
If these efforts succeed, oxytocin could become a revolutionary tool in modern cardiology—reducing mortality rates, improving cardiac function, and significantly enhancing quality of life for heart disease patients.
Beyond cardiology, this discovery also opens new research pathways in regenerative medicine. Scientists are now exploring whether oxytocin could play a similar reparative role in other organs and tissues, broadening its therapeutic potential.
Ultimately, the hormone once celebrated solely as a symbol of affection and emotional connection may evolve into a symbol of medical hope. Oxytocin’s ability to activate cardiac stem cells represents a major step forward in regenerative science, with the potential to reshape the future of heart disease treatment and save countless lives.
News in the same category


What a Strong Hug From a Man Can Truly Mean
Man loses pulse for 45 minutes, wakes up, and shares this spine-chilling vision of afterlife

Nostradamus predicted that those who have a cat at home will...

What Does “Durex” Actually Stand For

The reason might surprise you... Read more
What the First Animal You See Reveals About Your Hidden Flaw

Dreaming of a deceased person: here's what it means

The Common Bra Mistake
What Your Sleeping Position as a Couple Might Reveal

Envy Rarely Looks Like Hate

Why Slugs Keep Showing Up in Your Home

Almost Everyone Experiences This After Turning 70, Like It or Not

Did you know that if a white and yellow cat approaches you, it's because…

A baby is born in the United States from an embryo frozen more than 30 years ago.

12 nasty habits in old age that everyone notices, but no one dares to tell you

Why do couples sleep separately after age 50?
Scientists create a universal kidney: it is compatible with all blood types

When a person keeps coming back to your mind: possible emotional and psychological reasons
A promising retinal implant could restore sight to blind patients
News Post

A Little Girl Whispered, “My Dad Had That Same Ink

The Billionaire Who Believed He Had Erased

The Fifteen Seconds That Changed Everything

Hospice chef reveals the one comfort food most people ask for before they die

More people are dying from heart failure, doctors warn: give up these 4 habits now

10 Bizarre Home Remedies
Recognizing a Stroke Fast
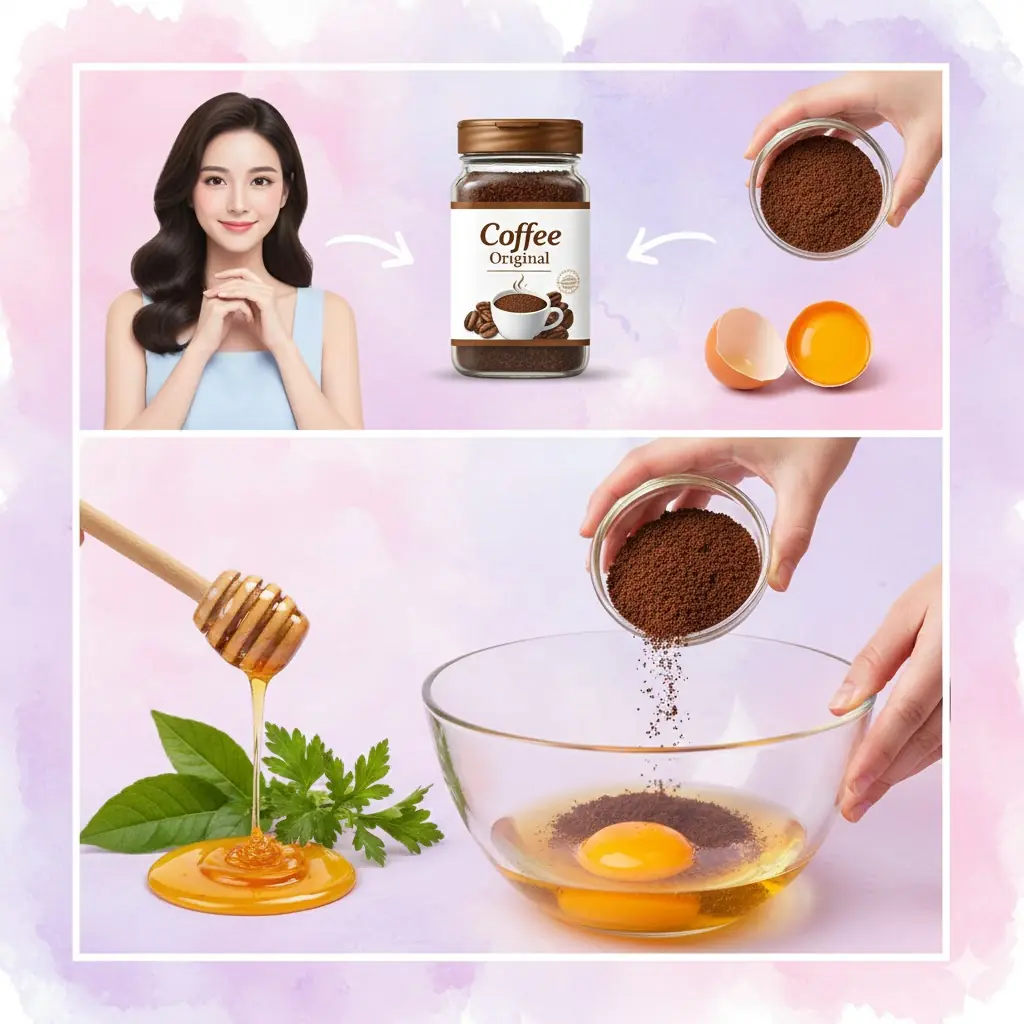

Egg, Honey & Coffee Mix – The 3-Ingredient “Bedroom Rocket Fuel” Men Over 40 Are Using for Morning Wood, Stamina & Confidence
THE SHADOW IN BOOTH SEVEN: She Poured His Coffee for a Thousand Mornings

Why Bees Land on Your Fresh Laundry

A Doctor Explains What “Lightning Bum” Really Is

Why Scallions Deserve More Credit as a Health Food

Why Nose Picking Isn’t as Harmless as You Think
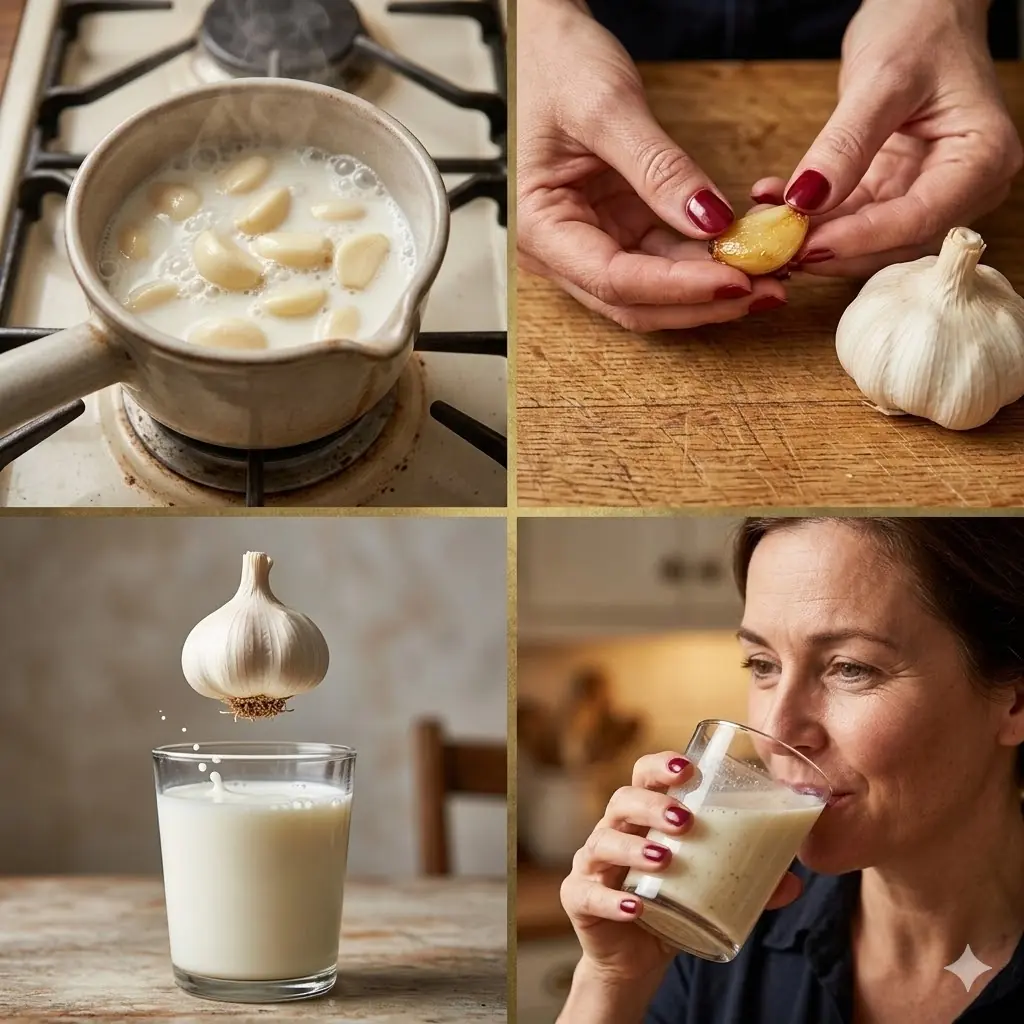

Natural Remedies to Relieve Muscle and Joint Pain (Proven Home Solutions)
7 Things That Happen To Your Body When You Don’t Have Sex For A While

A Simple Daily Drink Men Over 40 Can Make at Home to Naturally Support Prostate Wellness

7 Everyday Foods That Help Maintain Muscle Strength and Activity After 50

Papaya Leaf for Hair Growth: A Gentle, Natural Ritual for Stronger, Healthier Hair

10 Ways To Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally
