
An Underwater Volcano the Size of a City is Ready to Erupt
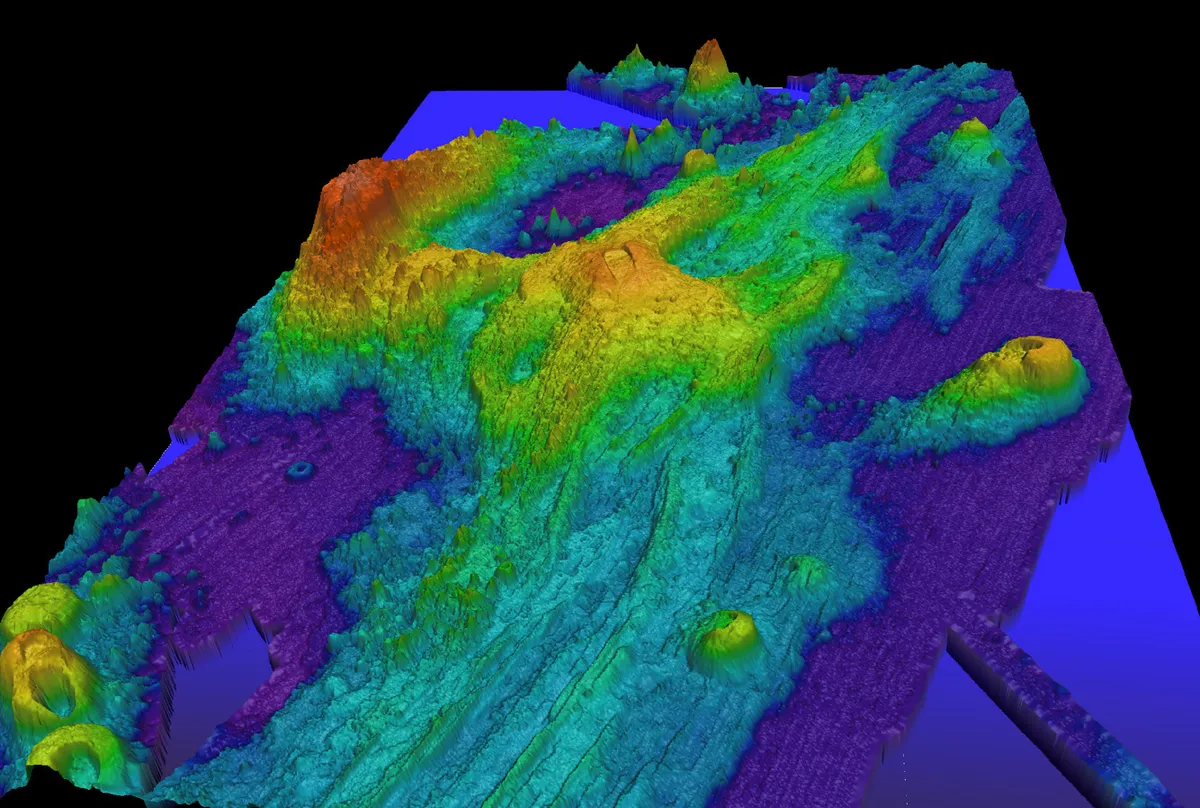
The Quiet Giant Beneath the Pacific
Far beneath the rolling blue expanse of the Pacific Ocean—so deep that sunlight can never reach it—a colossal force is quietly gathering strength. It might sound like the setup for a science fiction epic, but it’s entirely real. Nearly a mile below the surface and covering an area about the size of a major city, Axial Seamount, one of the most closely studied submarine volcanoes on Earth, is swelling once again. Scientists believe its next eruption could be imminent.
But don’t expect fiery skies, towering ash clouds, or sudden alerts interrupting your evening news. You won’t feel the ground tremble beneath your feet, and there will be no frantic evacuations. In fact, when it happens, most of the world won’t notice a thing. And yet, some of the planet’s top geologists, oceanographers, and planetary scientists are watching Axial’s every movement with intense focus.
Why? Because Axial is no ordinary volcano. It is a living, breathing engine of the seafloor—an ever-active geological system that not only shapes the planet but sustains entire ecosystems in perpetual darkness. And thanks to a sophisticated web of sensors stretching across the ocean floor, humanity now has a front-row seat to one of Earth’s most mysterious and mesmerizing natural processes.
What’s building beneath the waves is more than molten rock—it’s knowledge: insight into how our planet forms, how life thrives in extreme environments, and how even the quietest forces can reshape the world.
A Volcano Hidden in Plain Sight
About 300 miles off the Oregon coast, under nearly a mile of ocean water, Axial Seamount rises from the depths—out of sight and often out of mind. For those not in the know, it’s just a dot on a nautical chart. But to scientists tracking the pulse of the Earth, it’s one of the most important natural laboratories in existence.
Unlike Mount St. Helens or Italy’s Vesuvius, Axial does not explode with destructive fury. It doesn’t blot out the sky with ash or rain lava down on towns. Instead, it works in secret, its eruptions invisible to anyone at the surface. “If you were out there on a ship right over the seamount, you would never know anything was happening,” explains Dr. Bill Chadwick, a volcanologist at Oregon State University.
Yet, for all its silence, Axial is among the most volcanically active sites in the Pacific, erupting three times in the past quarter-century—1998, 2011, and 2015. The next event could be just months away. Even more intriguing is its remarkably predictable cycle. Most volcanoes sleep for centuries before violently reawakening. Axial, however, behaves like a slowly inflating balloon—swelling steadily until it reaches a familiar breaking point, then releasing pressure and beginning the process anew.
This regularity has turned Axial into a scientific goldmine. Each eruption reshapes the seafloor, fuels complex ecosystems, and produces streams of high-resolution data that could help forecast more dangerous volcanic events elsewhere.
Why Axial Is So Special

Axial sits at the Juan de Fuca Ridge, a tectonic boundary where two plates are slowly drifting apart. This rifting lets magma rise from deep in the mantle to form new oceanic crust—a process that has been quietly building the seafloor for millions of years. Adding to its uniqueness, Axial is also fueled by a mantle hotspot, a vertical plume of superheated rock that feeds the volcano year-round.
The meeting of a ridge and a hotspot is rare, creating a well-supplied volcano that doesn’t wait centuries between eruptions. Instead, it erupts roughly every decade or two. And unlike explosive volcanoes, Axial is a shield volcano—broad, with gentle slopes and low-viscosity lava that oozes rather than blasts, cooling into rounded “pillow” formations as it hits cold seawater.
Its greatest scientific advantage is its constant monitoring. The Regional Cabled Array, a network of more than 140 seafloor instruments connected by 660 miles of fiber-optic cable, streams real-time data on ground movement, seismic activity, and hydrothermal vent chemistry. High-definition video cameras even livestream life in and around the caldera.
This monitoring has revealed a strikingly consistent pattern: before each eruption, the volcano inflates to nearly the same level. When the threshold is reached, magma escapes, the seafloor drops slightly, and the inflation cycle begins again—like the planet itself exhaling.
Signs of the Next Eruption
The first and clearest warning sign is inflation. As magma gathers, it pushes upward, lifting the crust by measurable amounts—sometimes just millimeters at a time. Before each of its last three eruptions, Axial inflated to almost the exact same height. It is now about 95% of the way to that level, says Dr. Chadwick.
The second signal is seismic swarms. When magma forces its way upward, it cracks surrounding rock, triggering thousands of tiny earthquakes. In 2015, researchers recorded around 10,000 microquakes in a single day just before the eruption. Current activity ranges from 200 to 1,000 per day—still far above background levels.
Adding a twist, Axial’s behavior is influenced by the moon. During low tide, when the weight of water pressing on the crust is slightly reduced, earthquake rates can spike—sometimes enough to trigger an eruption if the system is already primed. As marine geophysicist Dr. Maya Tolstoy notes, “Axial is under critical stress now. Even tiny decreases in pressure could be enough to tip it over.”
In 2014, Chadwick and geophysicist Scott Nooner predicted an eruption within seven months—and nailed it when Axial erupted in April 2015. It was one of the first successful volcano forecasts in history, proving that careful monitoring can yield predictive power, even for forces hidden miles beneath the sea.
Life in the Dark

Beneath the waves, Axial’s hydrothermal vents gush mineral-rich water heated to over 700°F (370°C) by underlying magma. In total darkness, life thrives not through photosynthesis, but chemosynthesis—microbes convert volcanic chemicals like hydrogen sulfide into energy. These microbes form the base of a food chain that includes giant tubeworms, clams, crabs, and octopuses.
“Most of the seafloor is barren,” says Deborah Kelley, director of the Regional Cabled Array. “But when you get to the vent fields, it’s like stumbling upon an oasis.”
The cycle of destruction and renewal is rapid by geological standards. After Axial’s 2011 eruption buried entire vent communities, scientists returned months later to find microbial mats spreading again and animals recolonizing the area. Studying these systems offers a window into how life might exist on icy moons like Europa or Enceladus, and how Earth’s earliest life may have emerged in similar vent environments billions of years ago.
The Risk Factor
For all its activity, Axial poses no danger to people on land. Its depth, distance, and type of eruption mean there are no tsunamis, ash clouds, or explosive blasts to fear. Even marine life beyond the immediate vent area is largely unaffected.
The real risk lies in not paying attention. By studying Axial’s cycles, scientists refine their ability to predict eruptions elsewhere—potentially saving lives in regions with hazardous volcanoes.

A Teacher, Not a Threat
Axial Seamount may never make front-page headlines when it erupts. There will be no dramatic footage—only subtle tremors in the deep, lava flows hardening into stone, and ecosystems reshaping themselves in the dark.
This is a volcano that teaches rather than threatens. It shows that eruptions can be part of a natural rhythm of renewal, and that the planet’s most profound transformations often happen quietly, far from human eyes.
Beneath the Pacific, the Earth is breathing. And thanks to Axial, we’re finally learning to listen.
News in the same category


12 Health Hacks Doctors Rarely Share: Secrets for Optimal Health and Well-being

A Parade Moment That Became Global Joy

Nick Vujicic: Living Proof That the Human Spirit Knows No Limits

You’re Made of Stardust – Literally! 🌌🚀

Sea Levels Are Rising Faster Than At Any Time In 4,000 Years 🌍

Your Dog Might Actually Love You More Than Food
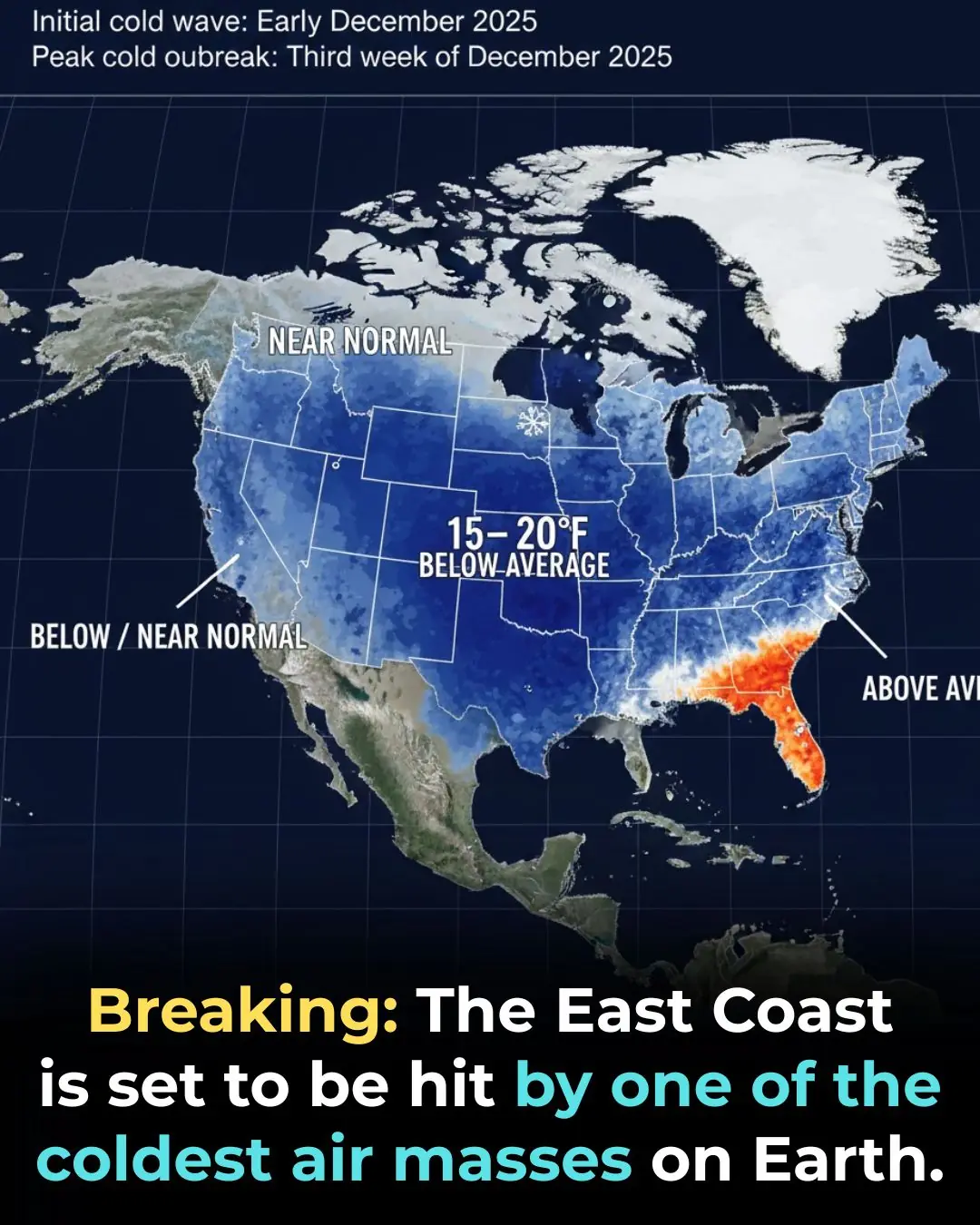
Deep Freeze Set to Slam the Eastern U.S. This December

Nike Co-Founder Phil Knight Makes Historic $2 Billion Donation to Cancer Research

Dutch Engineers Tackle the Pacific’s Plastic Crisis with 600-Meter Ocean Vacuum
How to Take a Loop of the Entire U.S. by Train

The Quiet Rise of Everyday Health-Tracking Technology
The Hidden Toll of People-Pleasing: How Emotional Suppression Can Trigger Autoimmune Disorders

The Pudu: The World’s Tiniest Deer and Its Role in South America's Forest Ecosystems

Deep Water Cycle: Scientists Discover Hidden Ocean Beneath Earth's Surface

Mexico City’s Sweeping Bullfighting Ban Marks Major Shift in Cultural and Animal-Welfare Policy

Los Angeles County Erases $180 Million in Medical Debt for 39,000 Residents

The 2025 Atlantic Hurricane Season Intensifies: A Heightened Risk for Major Storms

Europe Faces Unprecedented Heatwave: Rising Temperatures Strain People, Infrastructure, and Agriculture

Revolutionary Light-Based Cancer Treatment Offers New Hope with High Success Rate
News Post

CCF Tea to Burn Belly Fat

DIY Lip Balm with Vaseline and Beetroot: A Natural, Moisturizing Solution for Soft, Pink Lips

Coffee Gel For Eye Wrinkles

Coffee For Instant Skin Brightening

Japanese 4 Steps Glow Secret

30 minutes treatment for dark lips

How to Make a DIY Aloe Vera Night Cream for Glowing Skin

Rice Water Toner To Get Skin That Shines Like Diamond

Salon like Keratin Treatment at Home

Experts reveal the top 7 Shampoos to tackle hair loss effectively

10 Surprising Beauty Hacks You Never Thought You Could Do With Baby Powder

DIY Night Serum For Radiant Skin

Top 8 Foods to Clean and Restore Your Liver Naturally

The Ancient Secret Seed That Revolutionized Wellness: Unlocking the Power of Hibiscus and Cloves

Garlic Remedy for Removing Moles and Skin Tags Naturally: What Works and What to Know

Fibromyalgia: The Hidden Energy Crisis Behind Your Pain, Fatigue, and Sleepless Nights

The Hidden Oil That Sparks Her Desire and Rekindles Your Marriage

Unlock the Ancient Secret of Peach Tree Resin: 15 Life-Changing Benefits You’ll Wish You Knew Sooner

Aloe Vera & Cinnamon: The Traditional Duo That Naturally Supports Your Health, Vitality, and Vision
