
Breakthrough Discovery: PARP1 Enzyme Could Revolutionize the Fight Against Aging
In a groundbreaking scientific breakthrough, researchers have identified a powerful enzyme that holds the potential to revolutionize the fight against aging. This enzyme, known as poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1, or PARP1, functions as a "DNA glue," capable of repairing cellular damage at the molecular level and possibly reversing some of the effects of aging.
PARP1 plays a pivotal role in preserving the integrity of our DNA, which is constantly exposed to a variety of harmful factors. Every day, our cells are subjected to toxins, stress, radiation, and other environmental challenges that cause DNA to break or become disordered. If these DNA breaks remain unrepaired, they can accelerate the aging process, trigger inflammation, and contribute to the development of serious diseases, including cancer, dementia, and organ failure.
PARP1 serves as the cell's repair mechanism, detecting DNA damage and swiftly sealing the breaks to restore the genetic blueprint before any mutations can take root. Researchers have likened this enzyme to molecular glue, as it binds the broken DNA strands together with remarkable precision and speed.
However, as we age, the activity of PARP1 naturally decreases, leading to an accumulation of DNA damage. New research, however, suggests that by boosting the activity of this enzyme—whether through targeted compounds, gene therapies, or even lifestyle changes—we could delay the aging process, enhance cell regeneration, and ultimately extend our healthspan.
Promising results have already emerged from laboratory studies in animals, where boosting PARP1 activity led to improvements in brain function, stronger immunity, and a reduction in age-related cell deterioration. As a result, researchers are now focused on developing methods to safely enhance PARP1 activity in humans.
This discovery represents a significant shift in how scientists approach aging. Unlike treatments that only address the symptoms of aging, boosting PARP1 activity targets the underlying cause by helping cells repair themselves from the inside out. If successful, this could mark a turning point in the quest to slow, halt, or even reverse biological aging, offering the possibility of healthier, longer lives.
Sources:
-
National Institutes of Health (NIH), "PARP1 and its Role in DNA Repair," 2024.
-
Nature Aging, “The Promise of Enzyme-Based Anti-Aging Therapies,” 2024.
News in the same category


How Carmel, Indiana Transformed Its Streets with Roundabouts, Boosting Safety, Reducing Costs, and Cutting Emissions

China Discovers the First Plant Capable of Forming Rare-Earth Minerals Inside Its Tissues

James Webb Telescope Captures Stunning Einstein Ring, Unlocking Secrets of the Early Universe
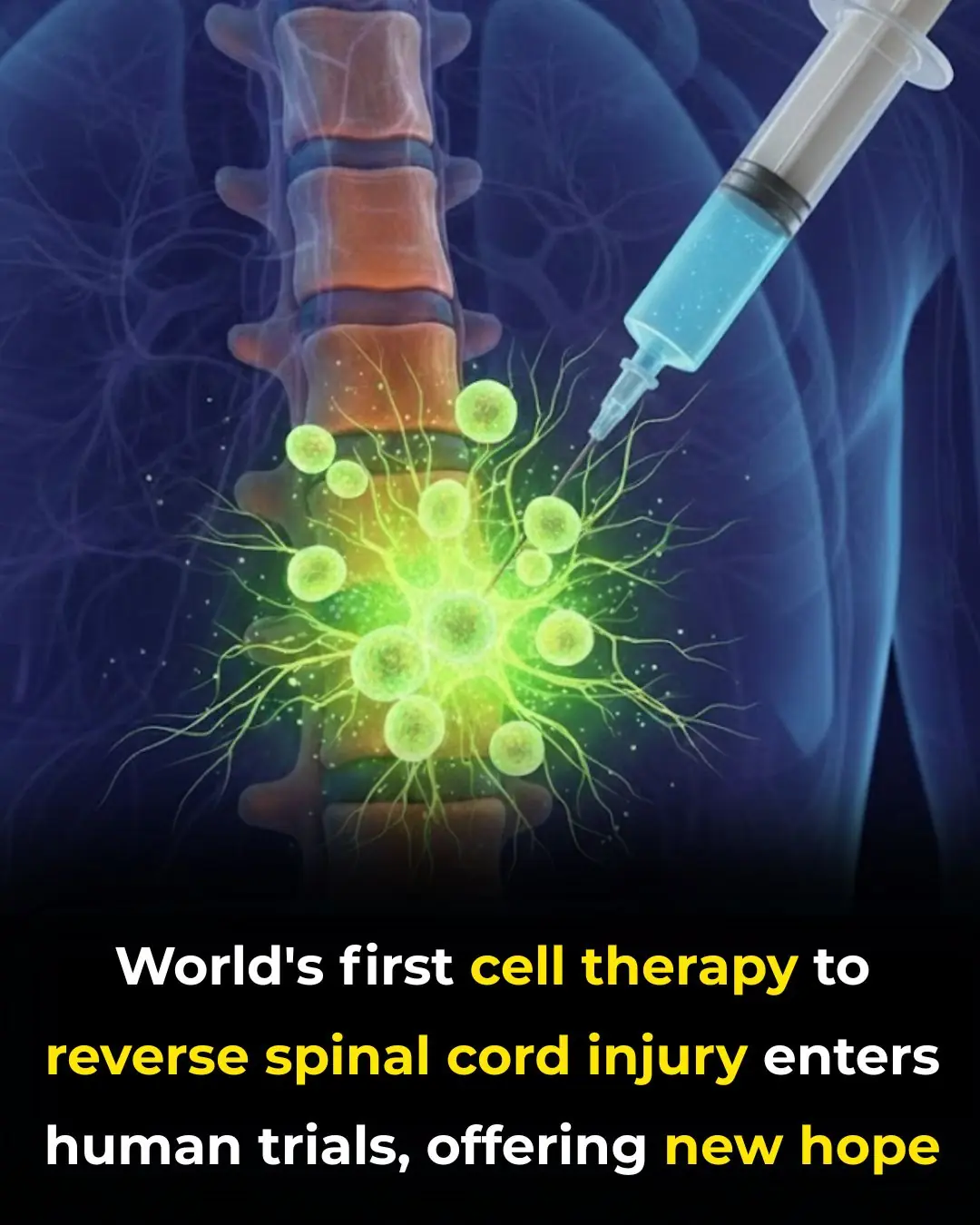
Groundbreaking Cell Therapy Offers New Hope for Spinal Cord Injury Recovery

A Soldier’s Heartfelt Moment: A Birth Across Distance and Strangers’ Applause

Japan's Groundbreaking Tsunami Wall Combines Engineering and Environmental Resilience

Revolutionary Contact Lenses with Night Vision Unveiled by Japanese Researchers
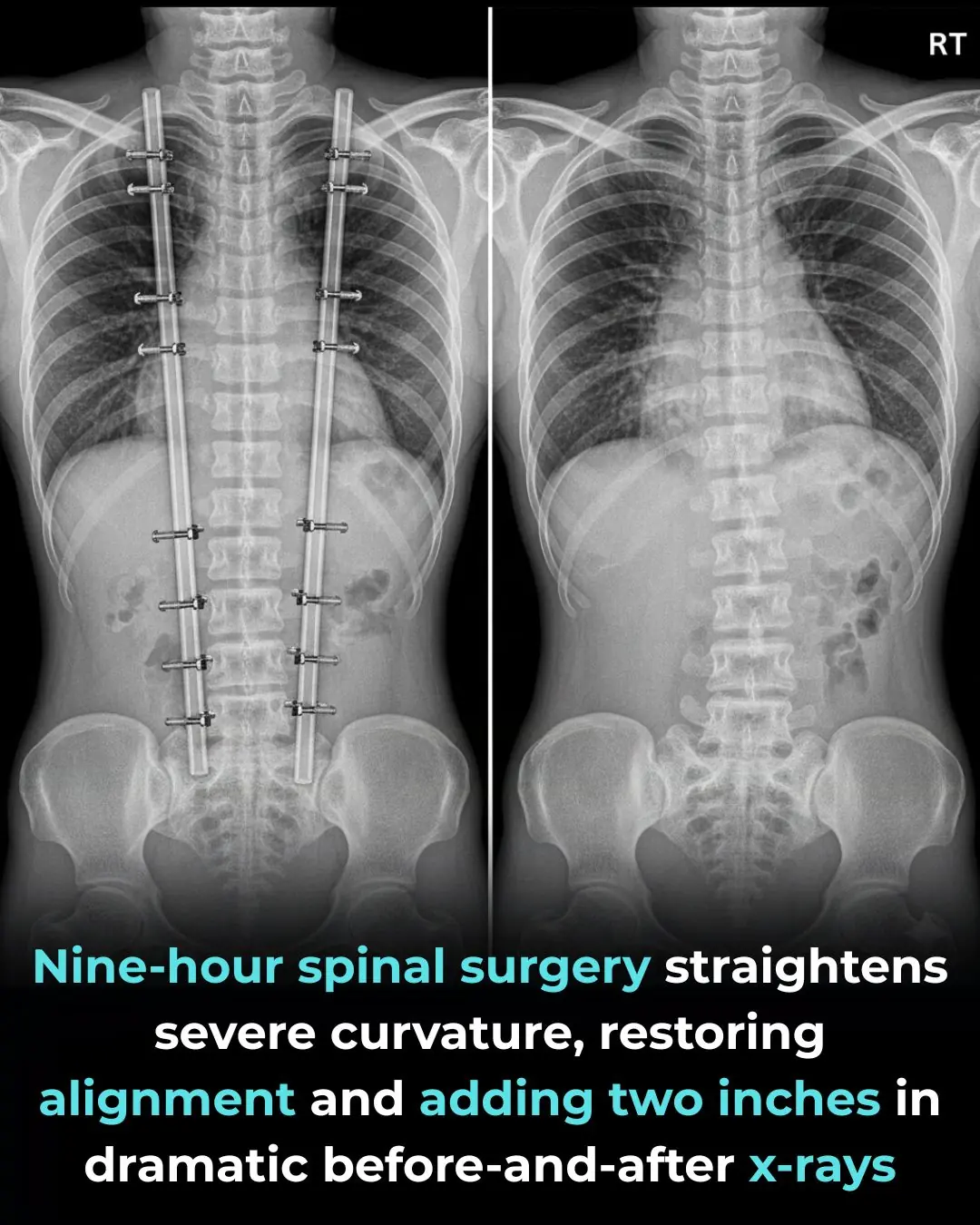
A Life-Changing Spinal Surgery Restores Health and Confidence

The Lost Human Species: A Glimpse Into Our Shared Past

The Swedish Oak Forest: A Symbol of Foresight and the Unpredictability of Progress

Promising New mRNA Vaccine Shows Potential to Combat Pancreatic Cancer

Plant in the Bible Said to Heal All Ailments

Why Successful People Often Wear Rings on Their Right Hand

Which Raw Food Would You Eat

88-Year-Old U.S. Army Veteran Receives Generous Retirement Gift After Viral Video Inspires Global Donations

Blood Falls: Antarctica's Mysterious Red Waterfall That Never Freezes

Brazilian Skydiver Drops 100 Million Tree Seeds to Help Restore the Amazon Rainforest

Japan Unveils Its First Hydrogen-Powered Train, Paving the Way for Clean and Sustainable Transportation

China's AI-Powered, Driverless Tractors Revolutionize Farming with 5G Connectivity and Precision Agriculture
News Post

8 Warning Signs of Ovarian Cancer Women Should Never Ignore

The Hidden Causes of Bloating — And the Fastest Way to Fix It Naturally
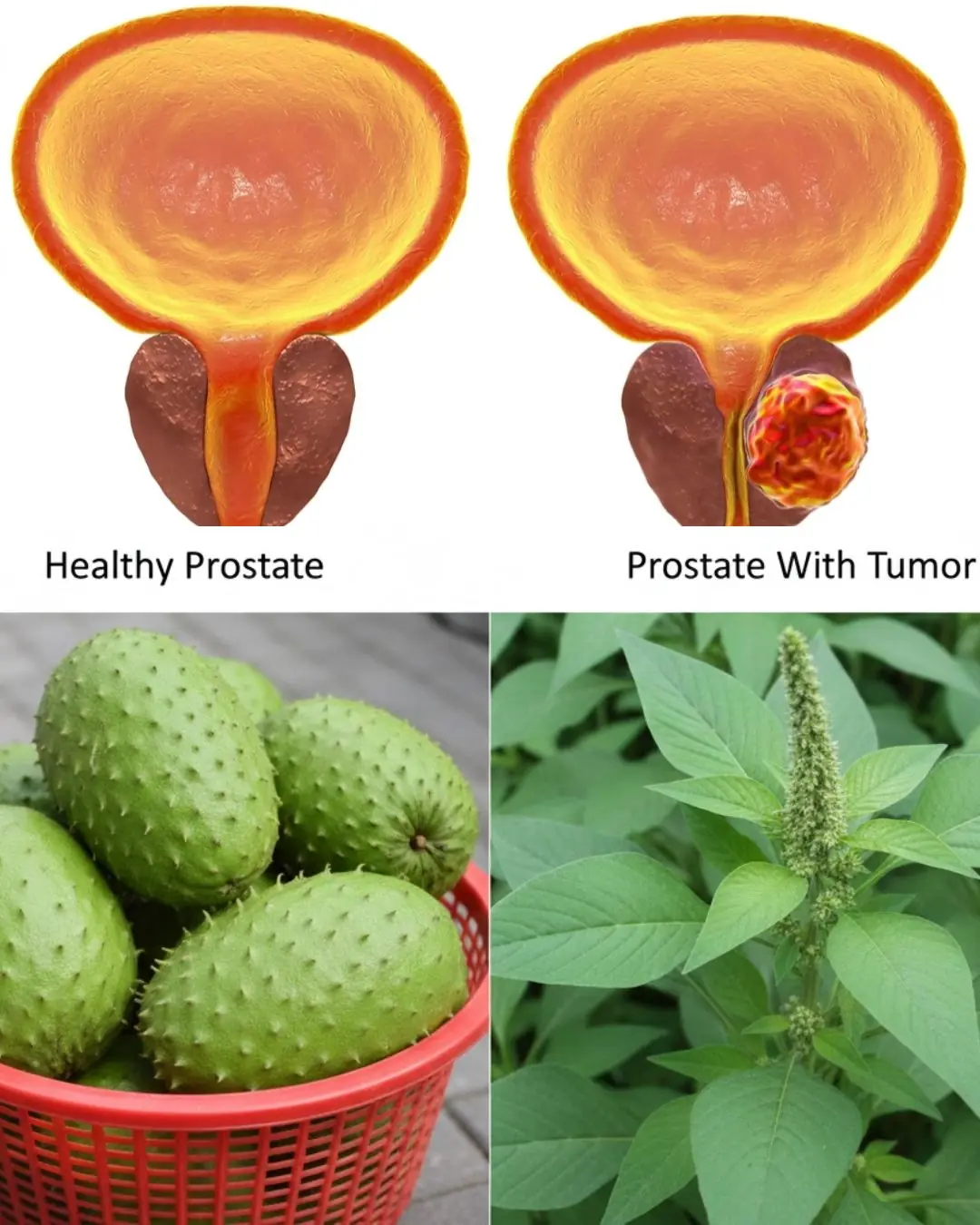

No Man Should Die From Prostate Cancer: The Natural Remedy Every Man Should Know

Jessica Cox: The World’s First Licensed Armless Pilot and Her Journey to Inspire the Impossible

How Carmel, Indiana Transformed Its Streets with Roundabouts, Boosting Safety, Reducing Costs, and Cutting Emissions

China Discovers the First Plant Capable of Forming Rare-Earth Minerals Inside Its Tissues

James Webb Telescope Captures Stunning Einstein Ring, Unlocking Secrets of the Early Universe

Groundbreaking Cell Therapy Offers New Hope for Spinal Cord Injury Recovery

A Soldier’s Heartfelt Moment: A Birth Across Distance and Strangers’ Applause

Japan's Groundbreaking Tsunami Wall Combines Engineering and Environmental Resilience

Revolutionary Contact Lenses with Night Vision Unveiled by Japanese Researchers

A Life-Changing Spinal Surgery Restores Health and Confidence

The Lost Human Species: A Glimpse Into Our Shared Past

The Swedish Oak Forest: A Symbol of Foresight and the Unpredictability of Progress

Promising New mRNA Vaccine Shows Potential to Combat Pancreatic Cancer

⚠️ Toxic If Improperly Prepared: The Hidden Risk of Cassava

How to Get Rid of Milia
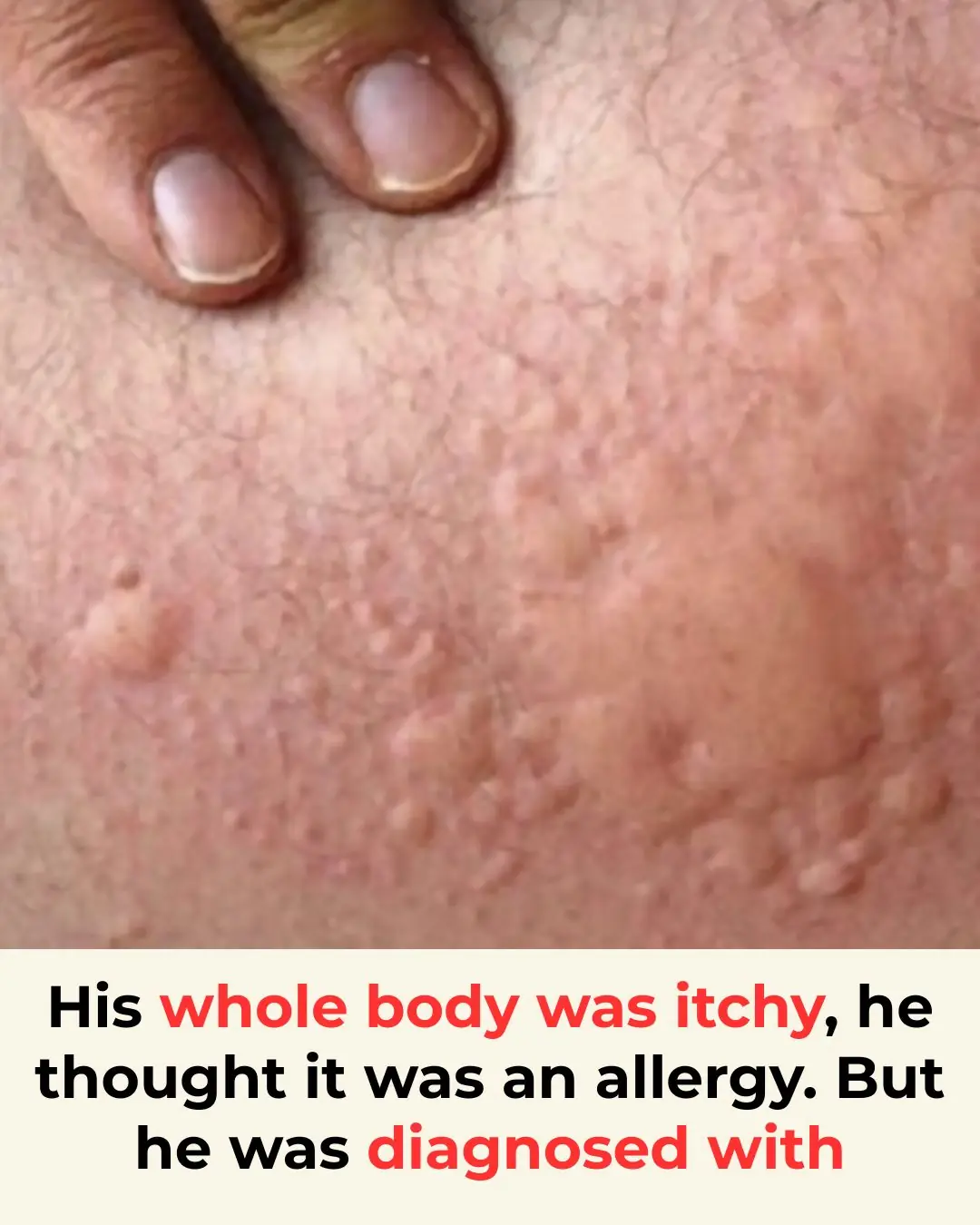
His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy but then he was diagnosed

Plant in the Bible Said to Heal All Ailments
