
Cold Compress on the Neck: A Simple, Effective Way to Calm Anxiety

Feeling Anxious? You Might Not Need a Pill—Just an Ice Pack
If you're feeling anxious, you might be surprised to know that you don’t necessarily need medication to calm your nerves—sometimes, all it takes is an ice pack. Recent studies have shown that placing a cold compress or ice pack on the back of your neck can quickly reduce feelings of anxiety by stimulating the vagus nerve, which plays a vital role in controlling your body’s relaxation response.
The vagus nerve is a key component of the parasympathetic nervous system, the part of the nervous system responsible for slowing down the heart rate, calming the mind, and restoring balance to the body after a stressful event. When this nerve is activated by cold exposure—particularly around the neck and upper spine—it sends a signal to the brain to switch from the “fight or flight” response, which is triggered during stress, into a more relaxed state known as “rest and digest.”
This simple yet effective technique has already been implemented in various fields, including therapy, military training, and emergency medical settings, as a way to rapidly alleviate symptoms of panic, reduce cortisol levels, and restore a sense of control. In fact, many individuals report feeling an immediate difference within 30 to 60 seconds: their heart rate slows, their breathing becomes deeper, and their thoughts feel clearer.
One of the most appealing aspects of this method is that it’s completely safe, drug-free, and incredibly easy to do. To perform the technique, you only need to wrap a cold pack—though a bag of frozen vegetables will work just fine—in a cloth and apply it gently to the back of your neck for 30 to 90 seconds. The cold temperature works by triggering the vagus nerve, which leads to the relaxation response.
What makes this technique even more compelling is that it’s not just a passing trend—it’s rooted in neuroscience. Activating the vagus nerve with cold exposure can provide fast relief from a range of anxiety-inducing situations, whether you’re dealing with social anxiety, exam stress, or just an overwhelming moment.
In an era when mental health awareness is growing, non-invasive, accessible methods of stress reduction like this are becoming increasingly popular. Research has shown that cold exposure can have a significant impact on stress management and the regulation of the nervous system. According to a study published in Frontiers in Psychology, vagus nerve stimulation has been shown to help lower cortisol levels and promote relaxation (Kraus et al., 2020). The fact that this technique can be done with something as simple as an ice pack makes it an attractive option for anyone seeking relief without relying on medication.
In summary, managing your anxiety doesn’t always require willpower or pills—sometimes, a little cold exposure is all it takes to help your body and mind relax. Whether you’re facing social anxiety, stress before an important test, or simply feeling overwhelmed, using cold exposure on the back of your neck can provide immediate and effective relief.
Sources:
-
Kraus, T., et al. (2020). "Vagus nerve stimulation for anxiety disorders: A systematic review." Frontiers in Psychology.
-
Choi, Y., et al. (2021). "Cold exposure and vagus nerve activation: Neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic potentials." Neuroscience Letters.
News in the same category


How Carmel, Indiana Transformed Its Streets with Roundabouts, Boosting Safety, Reducing Costs, and Cutting Emissions

China Discovers the First Plant Capable of Forming Rare-Earth Minerals Inside Its Tissues

James Webb Telescope Captures Stunning Einstein Ring, Unlocking Secrets of the Early Universe
Groundbreaking Cell Therapy Offers New Hope for Spinal Cord Injury Recovery

A Soldier’s Heartfelt Moment: A Birth Across Distance and Strangers’ Applause

Japan's Groundbreaking Tsunami Wall Combines Engineering and Environmental Resilience

Revolutionary Contact Lenses with Night Vision Unveiled by Japanese Researchers
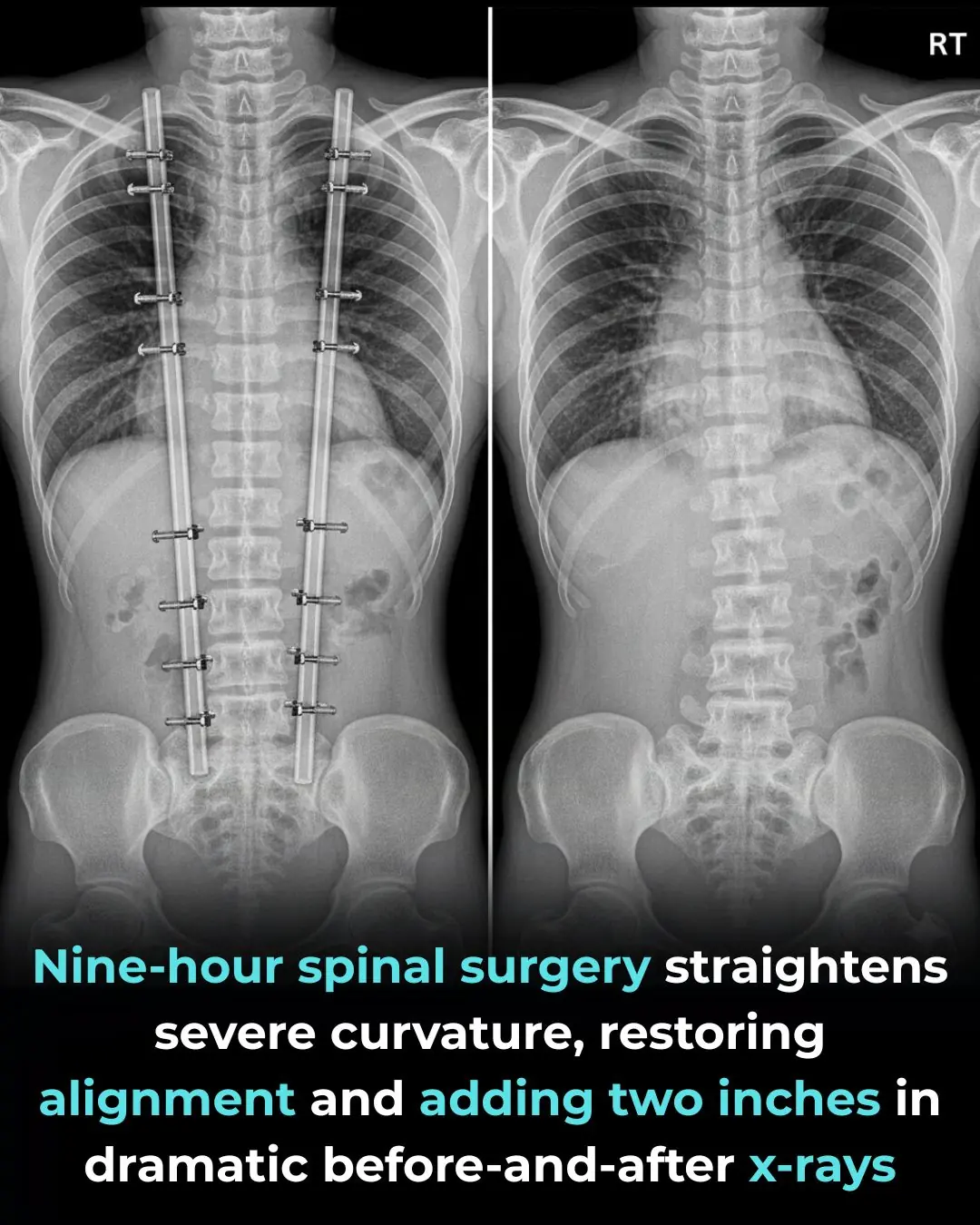
A Life-Changing Spinal Surgery Restores Health and Confidence

The Lost Human Species: A Glimpse Into Our Shared Past

The Swedish Oak Forest: A Symbol of Foresight and the Unpredictability of Progress

Promising New mRNA Vaccine Shows Potential to Combat Pancreatic Cancer

Plant in the Bible Said to Heal All Ailments

Why Successful People Often Wear Rings on Their Right Hand

Which Raw Food Would You Eat

88-Year-Old U.S. Army Veteran Receives Generous Retirement Gift After Viral Video Inspires Global Donations

Blood Falls: Antarctica's Mysterious Red Waterfall That Never Freezes

Brazilian Skydiver Drops 100 Million Tree Seeds to Help Restore the Amazon Rainforest

Japan Unveils Its First Hydrogen-Powered Train, Paving the Way for Clean and Sustainable Transportation

China's AI-Powered, Driverless Tractors Revolutionize Farming with 5G Connectivity and Precision Agriculture
News Post

8 Warning Signs of Ovarian Cancer Women Should Never Ignore

The Hidden Causes of Bloating — And the Fastest Way to Fix It Naturally

No Man Should Die From Prostate Cancer: The Natural Remedy Every Man Should Know

Jessica Cox: The World’s First Licensed Armless Pilot and Her Journey to Inspire the Impossible

How Carmel, Indiana Transformed Its Streets with Roundabouts, Boosting Safety, Reducing Costs, and Cutting Emissions

China Discovers the First Plant Capable of Forming Rare-Earth Minerals Inside Its Tissues

James Webb Telescope Captures Stunning Einstein Ring, Unlocking Secrets of the Early Universe

Groundbreaking Cell Therapy Offers New Hope for Spinal Cord Injury Recovery

A Soldier’s Heartfelt Moment: A Birth Across Distance and Strangers’ Applause

Japan's Groundbreaking Tsunami Wall Combines Engineering and Environmental Resilience

Revolutionary Contact Lenses with Night Vision Unveiled by Japanese Researchers

A Life-Changing Spinal Surgery Restores Health and Confidence

The Lost Human Species: A Glimpse Into Our Shared Past

The Swedish Oak Forest: A Symbol of Foresight and the Unpredictability of Progress

Promising New mRNA Vaccine Shows Potential to Combat Pancreatic Cancer

⚠️ Toxic If Improperly Prepared: The Hidden Risk of Cassava

How to Get Rid of Milia
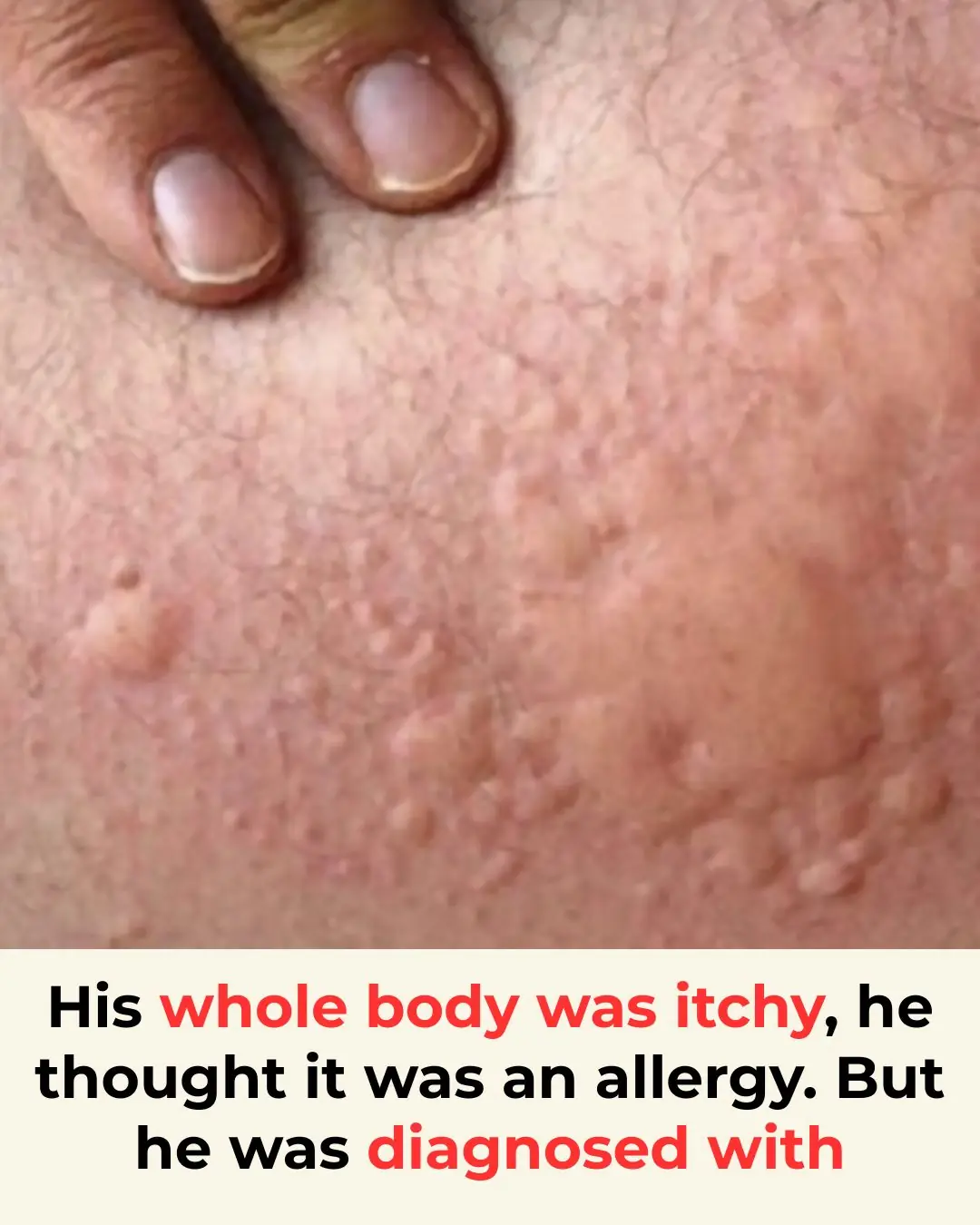
His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy but then he was diagnosed

Plant in the Bible Said to Heal All Ailments
