
Doctors Reveal What Eating Broccoli Really Causes in the Body

Broccoli has long been regarded as one of the world’s healthiest vegetables—but what actually happens in your body when you eat it regularly?
According to doctors and nutritionists, broccoli is not harmful. When consumed as part of a balanced diet, it sets off a chain reaction of scientifically proven benefits that promote overall health.
Here’s what eating broccoli actually does to your body.
1. Eating Broccoli Activates the Body’s Natural Defense Systems
One of broccoli’s most studied compounds is sulforaphane, a naturally occurring phytochemical.
Medical experts explain that sulforaphane:
- Activates antioxidant enzymes in the body
- Supports cellular detoxification pathways
- Helps protect cells from oxidative stress
This mechanism is associated with reduced cellular damage over time, which plays a role in healthy aging and chronic disease prevention.

2. Broccoli Consumption Supports Cardiovascular Health
Doctors frequently recommend broccoli as part of a heart-healthy diet.
Regular intake has been associated with:
- Improved cholesterol balance
- Reduced inflammation in blood vessels
- Support for normal blood pressure due to potassium and fiber content
The combination of fiber, antioxidants, and plant compounds makes broccoli a valuable vegetable for long-term cardiovascular support.
3. Eating Broccoli Improves Digestive Function
Broccoli contains both soluble and insoluble fiber, which supports digestive health in several ways.
Doctors note that this leads to:
- Improved bowel regularity
- Nourishment of beneficial gut bacteria
- Better overall gut function
Additionally, certain compounds in broccoli help maintain the integrity of the digestive lining, supporting comfort and nutrient absorption.

4. Broccoli Intake Strengthens Immune Health
From a clinical nutrition perspective, broccoli contributes key immune-supporting nutrients, including:
- Vitamin C
- Beta-carotene (a precursor to vitamin A)
- Antioxidants and trace minerals
These nutrients help support immune cell production and function, making broccoli a valuable addition to diets focused on immune resilience.
5. Eating Broccoli Supports Healthy Blood Sugar Regulation
Doctors often recommend non-starchy vegetables like broccoli for individuals focused on metabolic health.
Broccoli:
- Has a low glycemic load
- Slows glucose absorption due to fiber
- May support insulin sensitivity
Research suggests that sulforaphane may play a role in glucose metabolism, making broccoli particularly useful for people managing insulin resistance or prediabetes.

6. Broccoli Contributes to Bone Health
Broccoli provides nutrients essential for skeletal health, including:
- Vitamin K, which supports proper calcium utilization
- Calcium and magnesium in plant-based form
Medical professionals emphasize that vitamin K plays a critical role in bone mineralization, helping maintain bone strength over time.
7. Mild Digestive Discomfort Can Occur in Some Individuals
Doctors are also clear about one honest side effect: Broccoli contains fermentable fibers that can cause gas or bloating in sensitive individuals
This is not harmful and often improves when broccoli is:
- Cooked instead of eaten raw
- Introduced gradually into the diet
This reaction is a sign that gut bacteria are actively breaking down healthy fibers.

Best Ways to Eat Broccoli for Nutritional Value
Nutrition experts recommend:
- Light steaming instead of boiling to preserve nutrients
- Pairing broccoli with healthy fats to improve absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
- Including broccoli sprouts occasionally, which contain higher concentrations of sulforaphane
Avoid excessive cooking times, which can significantly reduce nutrient density.
Final Thoughts
Doctors agree that eating broccoli does not cause harm when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Instead, it causes measurable, beneficial effects such as:
- Improved cardiovascular support
- Enhanced digestive and immune function
- Better blood sugar regulation
- Support for bone and cellular health
News in the same category

Why Neck Skin Sags as We Age

Doctors Reveal: Eating Cabbage Can Trigger Hidden Health Problems If You’re Not Careful

The Winged Bean Secret: A Simple Vegetable With Big Benefits for Eyes, Immunity, and Heart Health
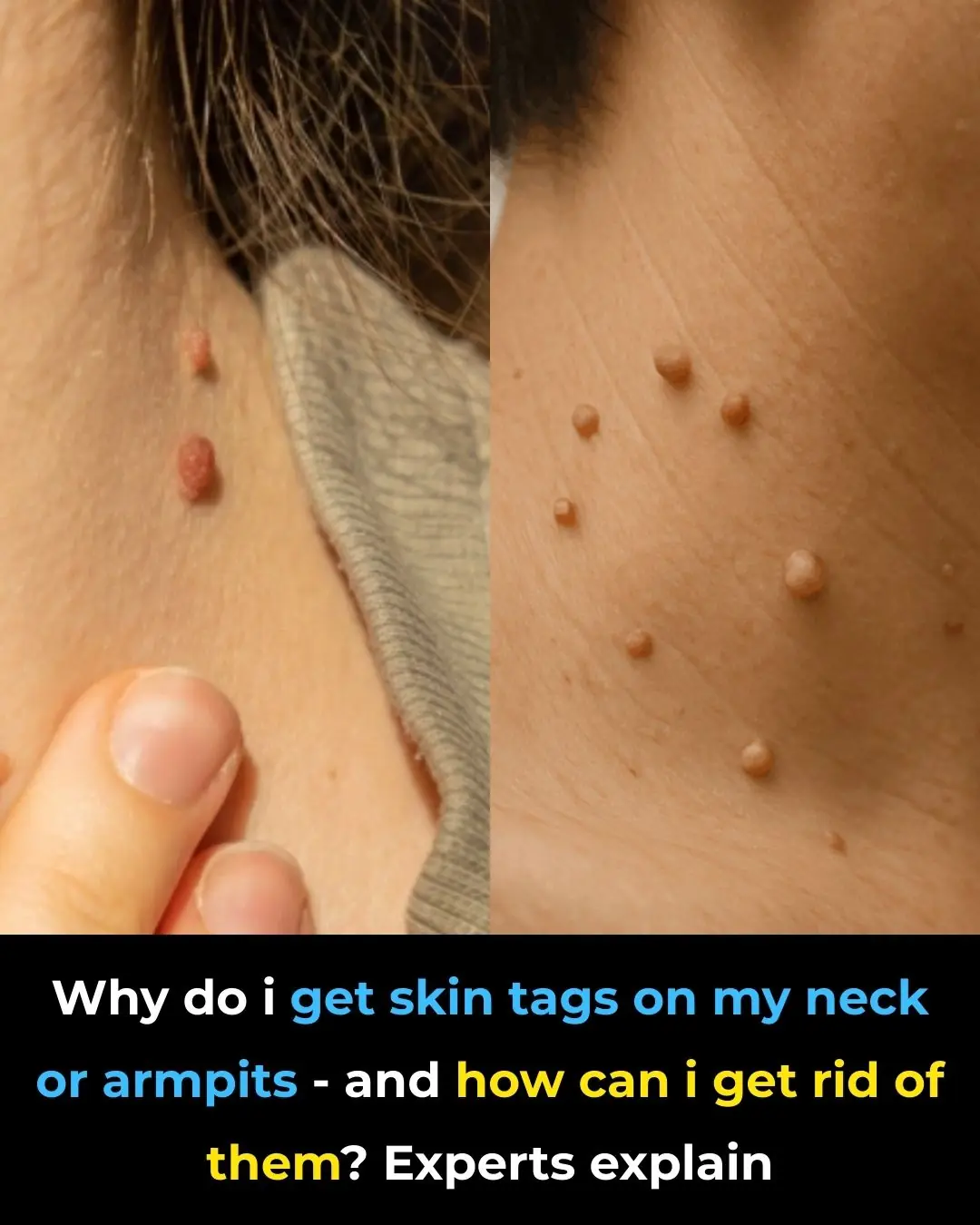
Why Do I Get Skin Tags on My Neck or Armpits—and How Can I Get Rid of Them? Experts Explain

What Weak or Brittle Nails May Be Telling You About Your Health
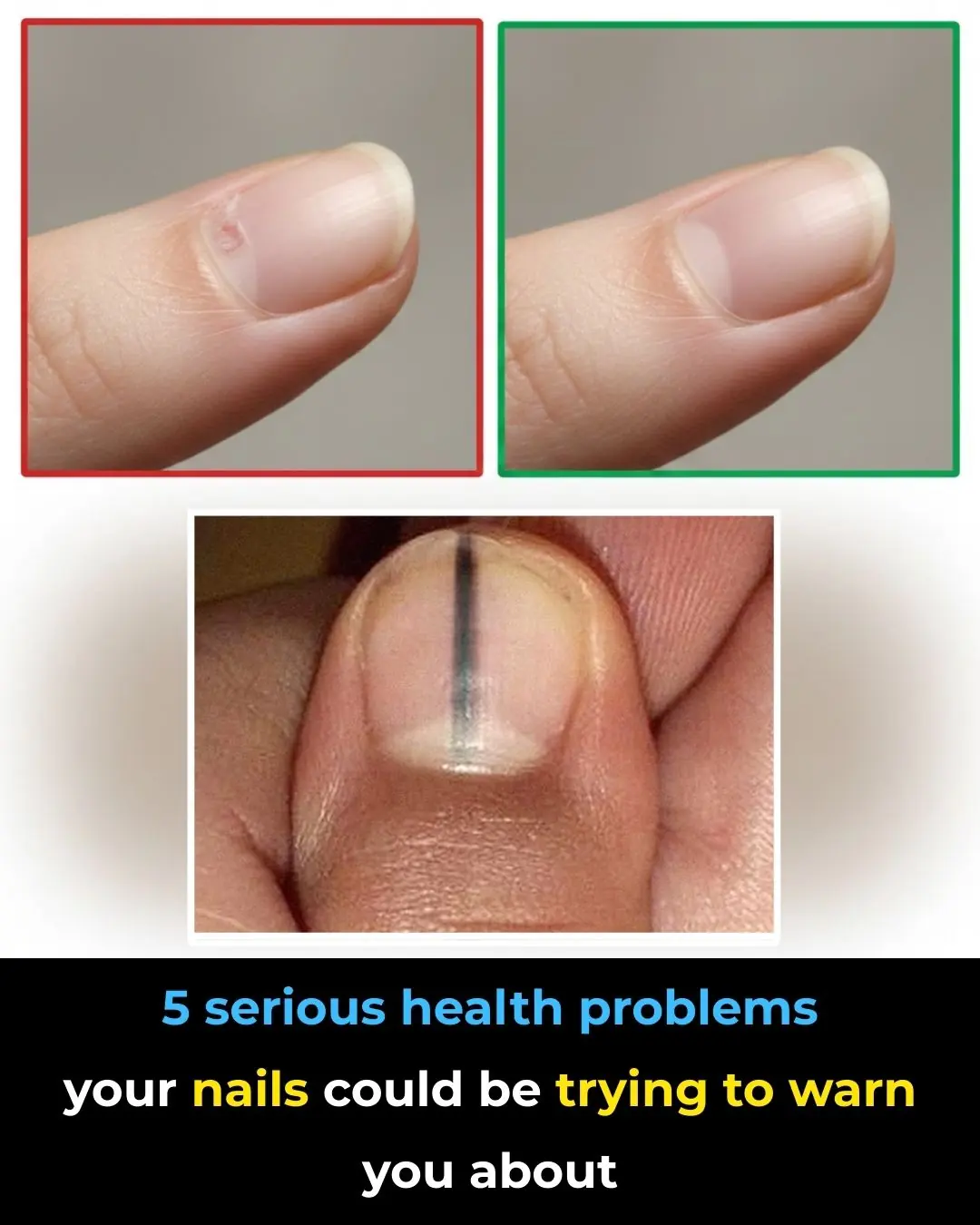
Nail Clues: 5 Health Problems You Shouldn’t Ignore
New Protein Breakthrough Unmasks Cancer Cells, Boosting the Power of Immunotherapy

Sugary Soft Drinks, Gut Bacteria, and Depression: How What You Drink May Shape Mental Health

Are You Using New Tools to Support Patients With DD-CKD Anemia?

Drug Shortages in the United States Are Forcing Major Changes in Primary Care Practice

Five Reasons to Eat One Banana a Day: A Simple Habit for Better Health and Longevity

Three Simple Ways to Use White Radish to Reduce Phlegm, Relieve Cough, and Support Lung Health

A Couple Diagnosed With Liver Cancer at the Same Time: Doctors Urgently Warn After Opening Their Refrigerator
🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape
Diagnosed with terminal cancer that had metastasized to the brain, the woman went for a check-up and burst into tears upon learning that her husband and son were the culprits
Doctors warn: 4 types of inflammation can easily turn into cancer in just one year if treatment is delayed
Triple Therapy Linked to Lower Lung Clearance Index in Children With Cystic Fibrosis

Drink Water First: Hydration on Waking May Sharpen the Brain More Than Your Morning Coffee
News Post

What It Really Means When Your Partner Starts Kissing You With Their Tongue More Often

Easy Tips to Keep Your Bathroom Smelling Fresh All Day

Why Neck Skin Sags as We Age

Doctors Reveal: Eating Cabbage Can Trigger Hidden Health Problems If You’re Not Careful

The Winged Bean Secret: A Simple Vegetable With Big Benefits for Eyes, Immunity, and Heart Health

Why Do I Get Skin Tags on My Neck or Armpits—and How Can I Get Rid of Them? Experts Explain

What Weak or Brittle Nails May Be Telling You About Your Health

Nail Clues: 5 Health Problems You Shouldn’t Ignore

Why Eggplant Is an Affordable Superfood for Heart Health and Weight Management
Why Bamboo Shoots Are a Fiber-Rich Vegetable Worth Cooking the Right Way

Can Herbal Hair Washes Really Reduce Hair Loss and Promote Hair Growth?

Why You Should Avoid Hanging Clothes in These Places During Winter

New Protein Breakthrough Unmasks Cancer Cells, Boosting the Power of Immunotherapy

Sugary Soft Drinks, Gut Bacteria, and Depression: How What You Drink May Shape Mental Health

Exploring the Traditional Uses and Potential Wellness Benefits of Prickly Lettuce Leaves (Lactuca serriola)

Pumpkin Seeds for Health: Natural Remedies, Recipes, and Benefits
11 Benefits of Dandelion Roots

7 Essential Leaves to Naturally Improve Your Eye Health
