Doctors warn: 4 types of inflammation can easily turn into cancer in just one year if treatment is delayed
Many people often take common inflammatory diseases lightly, not realizing that they can be the hidden roots leading to cancer. Doctors warn that if the following four types of inflammation are left untreated or treatment is delayed, the risk of dangerous complications will increase, potentially even resulting in cancer.
First: Chronic hepatitis B
Chronic hepatitis B occurs when a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus for more than six months, causing liver damage at varying degrees such as inflammation, necrosis, or cirrhosis.
What is particularly concerning is that many patients are often complacent, believing they are merely “virus carriers” and therefore neglect regular monitoring. This indifference allows the disease to progress silently, leading to cirrhosis and even liver cancer. Therefore, people with hepatitis B need to maintain the habit of regular health check-ups to detect abnormalities early.
Second: Chronic atrophic gastritis
During gastroscopy, doctors commonly identify two prevalent forms of gastritis: chronic superficial gastritis and chronic atrophic gastritis. Among them, chronic atrophic gastritis is considered the most dangerous. This condition is characterized by the gradual atrophy of the gastric mucosa and glands, severely impairing digestive function. If it persists for a long time, it may progress to gastric cancer.
Third: Chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatitis has two forms: acute and chronic. While acute pancreatitis often responds well to treatment, chronic pancreatitis progresses silently, lasts long, and is difficult to cure completely.
Long-term chronic inflammation stimulates pancreatic cells to undergo malignant transformation, increasing the risk of pancreatic cancer—one of the most aggressive cancers, known for early metastasis and a very low survival rate after diagnosis.
Fourth: Chronic ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic intestinal disease characterized by prolonged inflammation of the colonic mucosa. Patients often experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stools, fever, and weight loss, which significantly reduce quality of life.
Treatment usually relies on medications, including hormones, to control inflammation. However, long-term use of hormonal drugs carries many unwanted side effects.
What is especially alarming is that if ulcerative colitis is not well controlled, the risk of progression to colorectal cancer is very high. Statistics show that patients with ulcerative colitis have a significantly increased likelihood of developing colorectal cancer.
News in the same category

Diagnosed with terminal cancer that had metastasized to the brain, the woman went for a check-up and burst into tears upon learning that her husband and son were the culprits
Triple Therapy Linked to Lower Lung Clearance Index in Children With Cystic Fibrosis

Drink Water First: Hydration on Waking May Sharpen the Brain More Than Your Morning Coffee

Nobel-Winning Discovery Reveals How to Stop the Immune System From Attacking the Body

Why Sugar Matters More Than Cholesterol in Heart Disease Risk
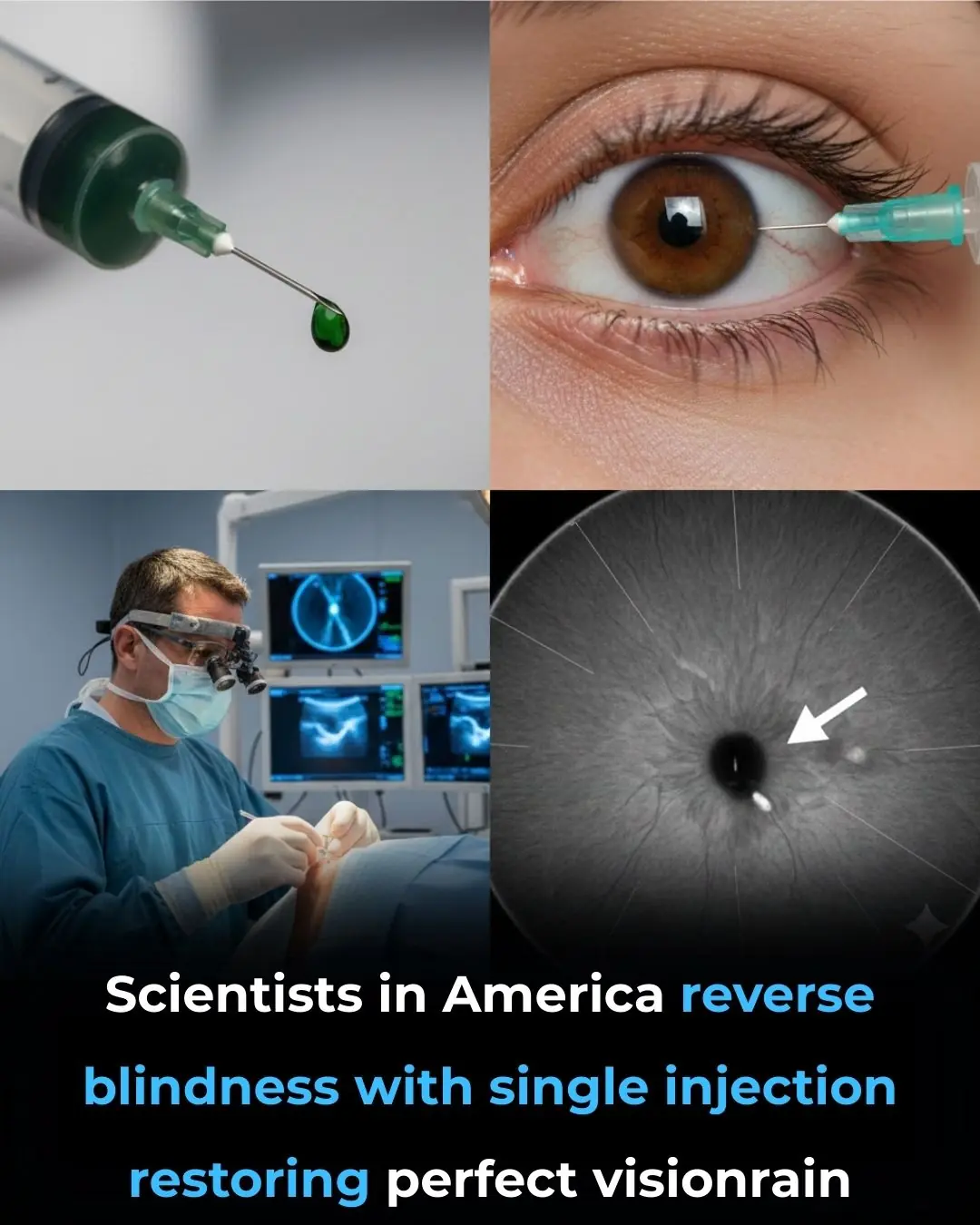
Single-Injection Gene Therapy Restores Vision in Patients With Inherited Blindness

Smelly but Smart? Weird Study Claims Your Own Gas Could Benefit Brain Health
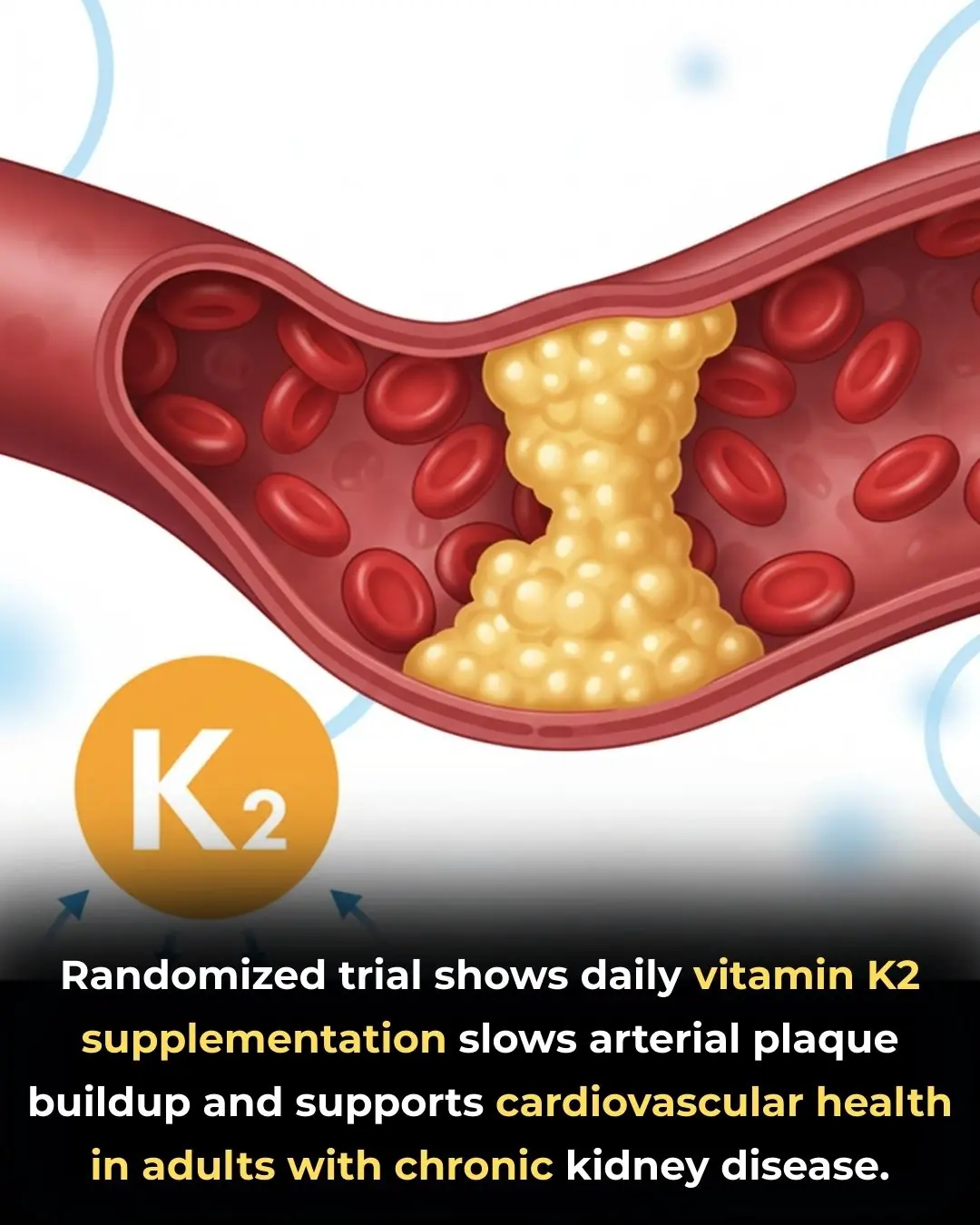
Vitamin K2 Supplementation Slows Arterial Plaque Progression in Chronic Kidney Disease

Everyone Fears Diabetes, but Diabetes “Fears” These 5 Foods

A Hard-Earned Lesson for Middle-Aged Parents: Let Go of These Habits, and Your Children Will Naturally Grow Closer
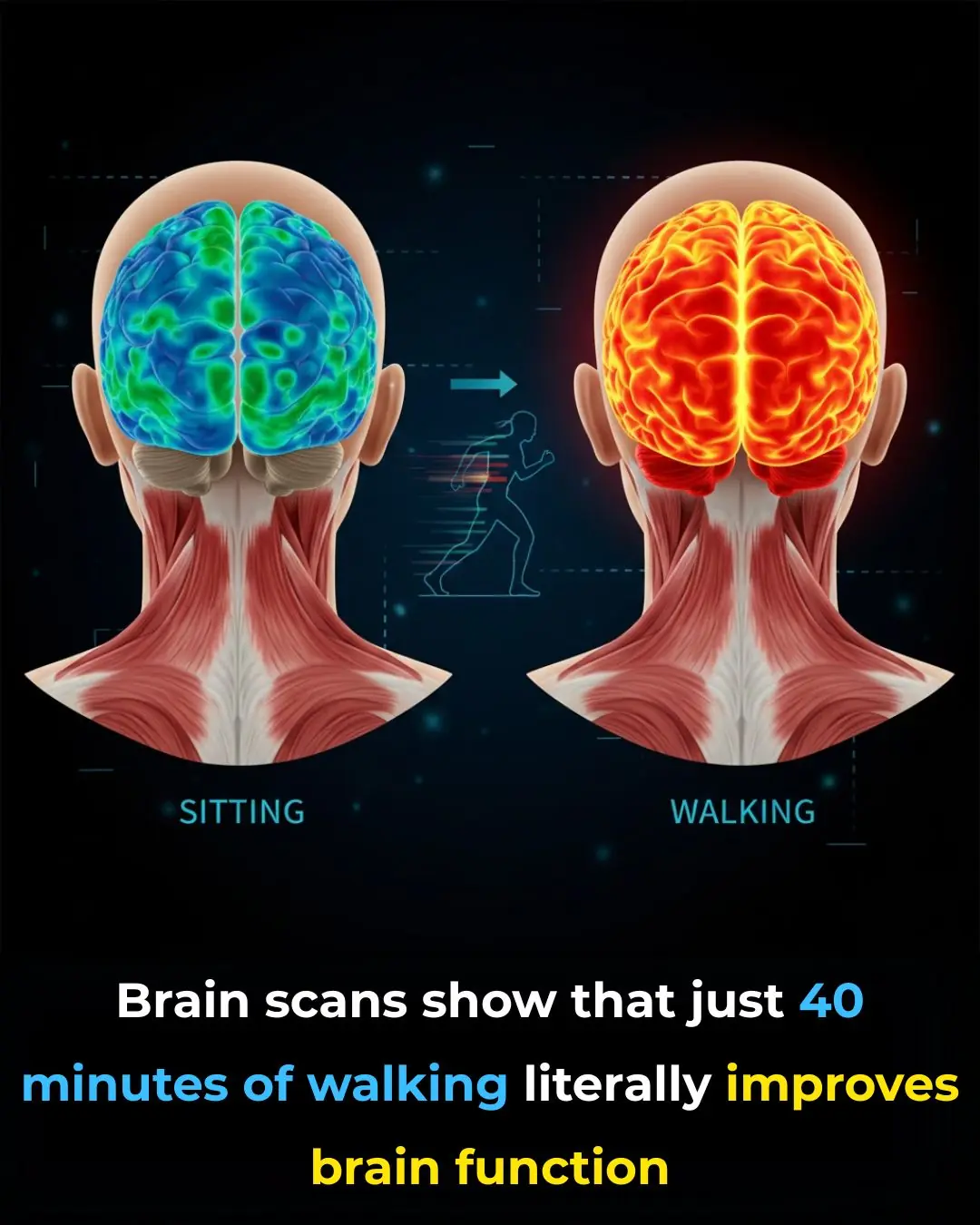
How Walking Activates the Brain: The Hidden Link Between Movement, Focus, and Mental Clarity

It’s Time to Protect Your Stomach: Remove These 5 Popular Vietnamese Breakfast Foods from Your Morning Menu
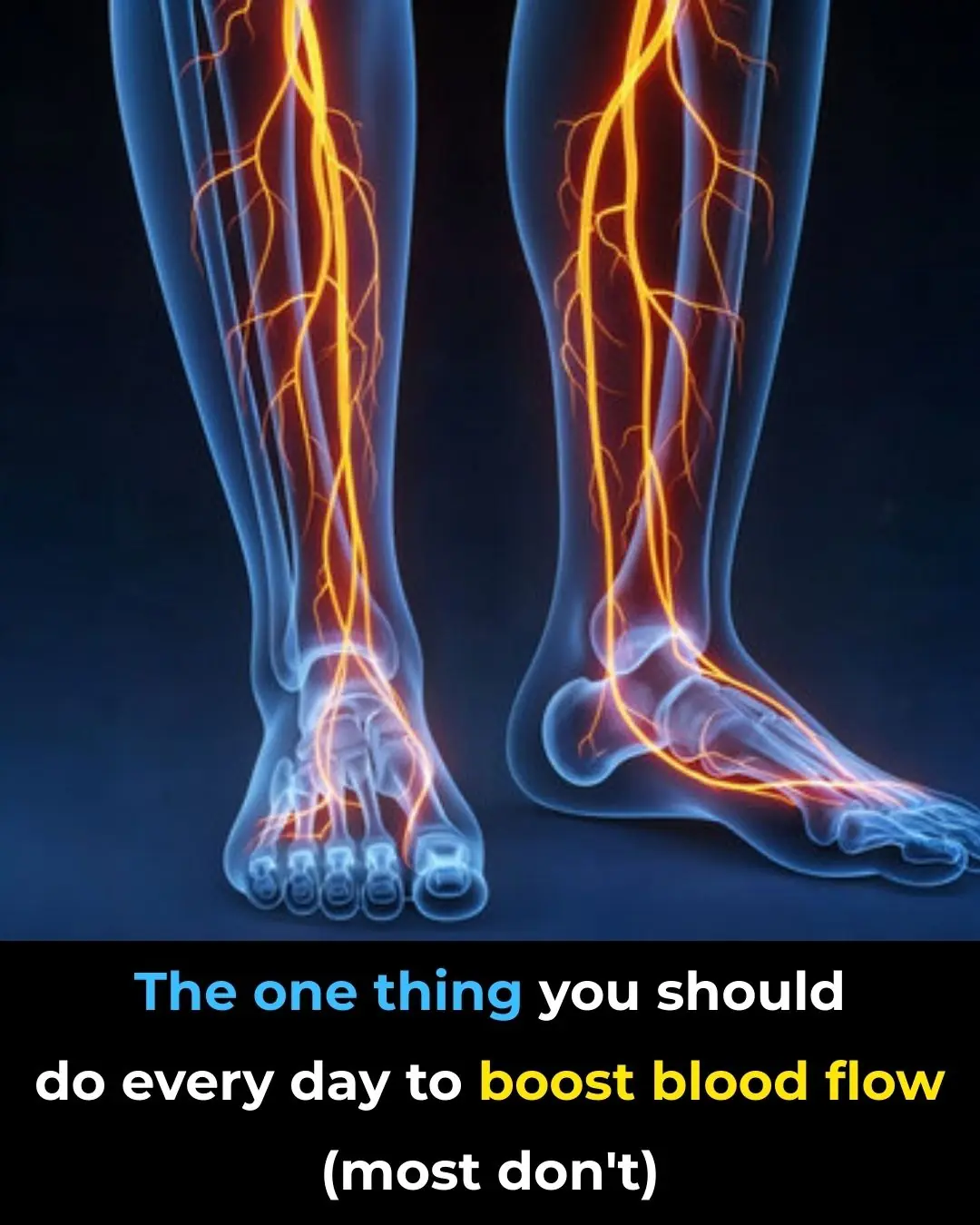
How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)
The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears
7 powerful vitamins you need for strong, healthy legs
Scientists Discover Protein That Unmasks Cancer Cells, Boosting the Immune System’s Power
4 alarming symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency you can’t ignore!
10 Scientifically Backed Reasons Why You Should Consume Ginger Everyday
News Post

11 dishes you should never cook in an air fryer; don't try it or you'll regret it.

Put Bay Leaves in the Corners of Their Kitchen

The Simple Nighttime Habit That Can Help You Fall Asleep Faster

🌙 If You Notice These 3 Signs at Night, Your Kidneys Are Likely in Great Shape

Diagnosed with terminal cancer that had metastasized to the brain, the woman went for a check-up and burst into tears upon learning that her husband and son were the culprits

Why Some People Rub Onions on Their Windows

Harbhajan Singh’s Royal Gift: A Gold‑Plated iPhone 17 Pro Max ✨📱🏏

Kumar Sangakkara: Greatness in Simplicity 🏏❤️

Smart Money Choices: Shivani Gera’s Lesson in Real Wealth 💰🌍

Mukesh Ambani’s ₹7 Lakh Crore Vision: Gujarat at the Heart of India’s Next Decade 🚀🇮🇳

Chai Guy LA: A Bihari Street Vendor’s Viral Rise in California 🌍☕

Sridhar Vembu’s Divorce Settlement: A $1.7 Billion Shockwave in Global Business ⚖️🌍

Triple Therapy Linked to Lower Lung Clearance Index in Children With Cystic Fibrosis

You're doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to set your thermostat in winter

Drink Water First: Hydration on Waking May Sharpen the Brain More Than Your Morning Coffee

Nobel-Winning Discovery Reveals How to Stop the Immune System From Attacking the Body

Why Sugar Matters More Than Cholesterol in Heart Disease Risk

Green Smoothies and Weight Management: What Cucumber and Lemon Drinks Can Realistically Do
