Health 23/12/2025 08:14
Everything You Need to Know About Eczema on the Ears
News in the same category

Health 23/12/2025 08:56
Tips for Dealing With Nail Psoriasis
Health 23/12/2025 08:03

Two Family Habits That Increase the Risk of Cancer for Everyone – Avoid Them Now to Prevent Regret
Health 23/12/2025 07:59
Your legs are screaming ‘HELP!:’ 5 warning signs from your liver
Health 23/12/2025 07:08

Nighttime Olfactory Enrichment and Cognitive Enhancement in Older Adults
Health 23/12/2025 00:20
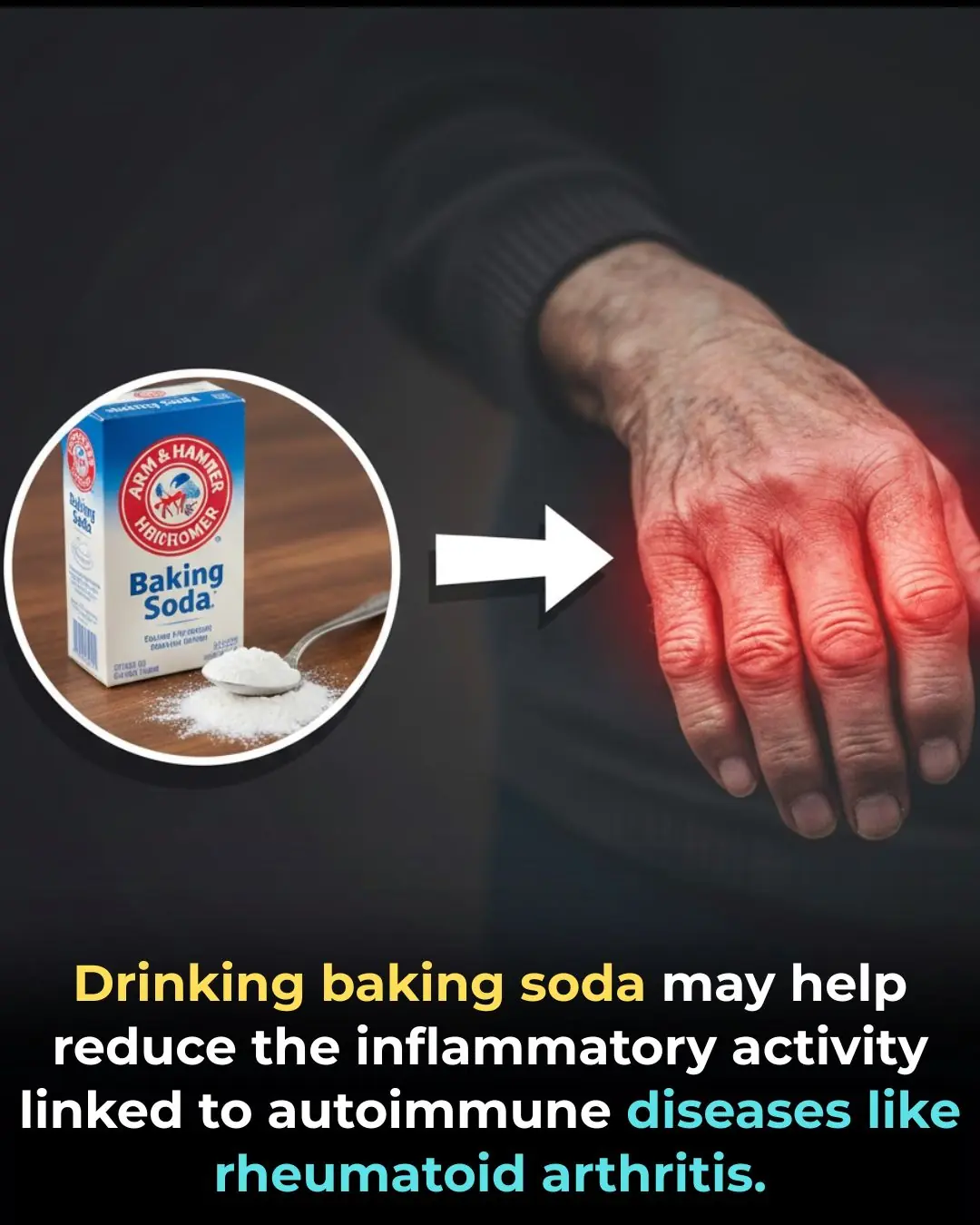
Sodium Bicarbonate and Immune Regulation: Evidence for an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism
Health 23/12/2025 00:18
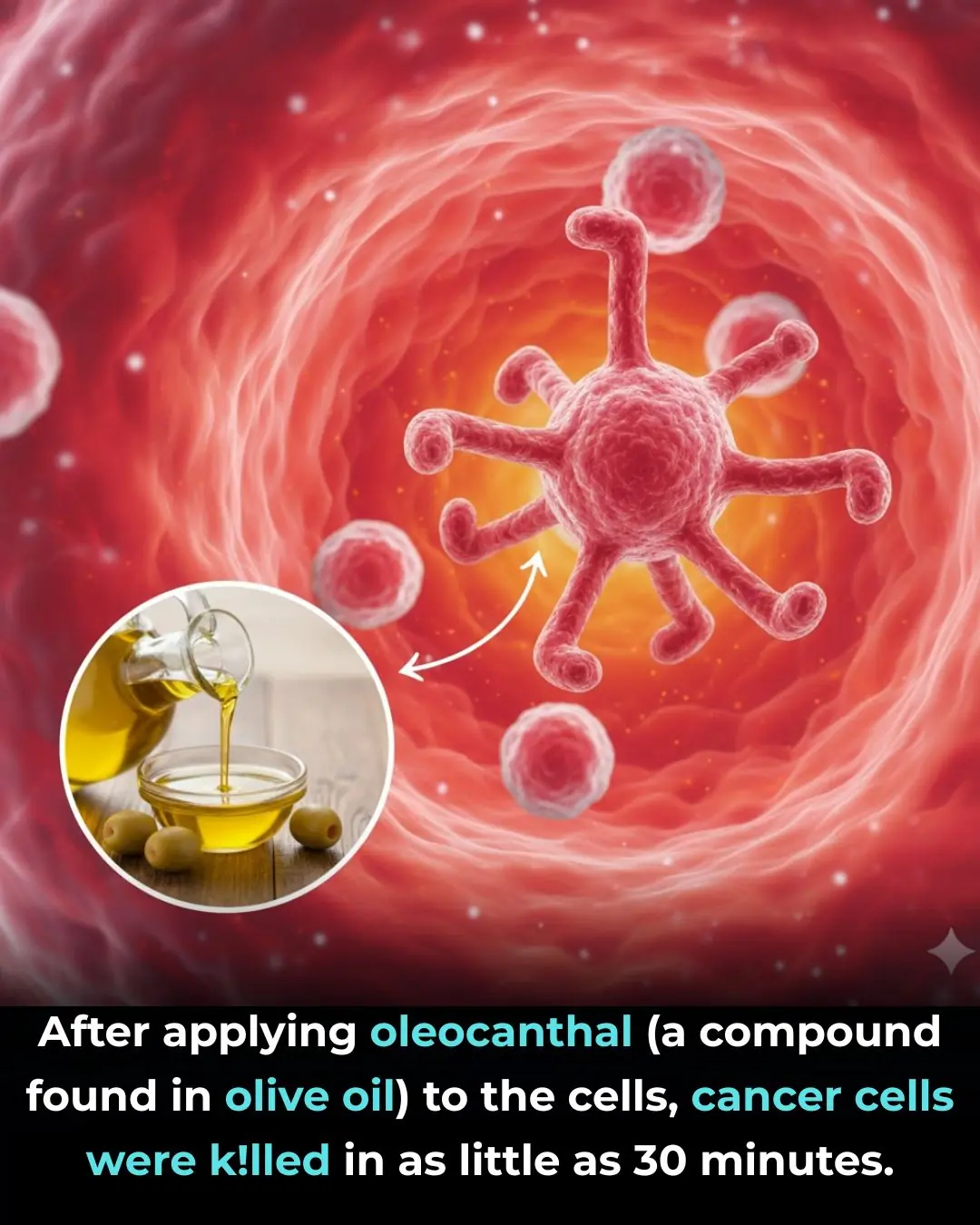
Oleocanthal from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil: A Multi-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Compound
Health 23/12/2025 00:17

Fenbendazole and Unexpected Cancer Remission: Insights from a 2024 Case Report
Health 23/12/2025 00:16
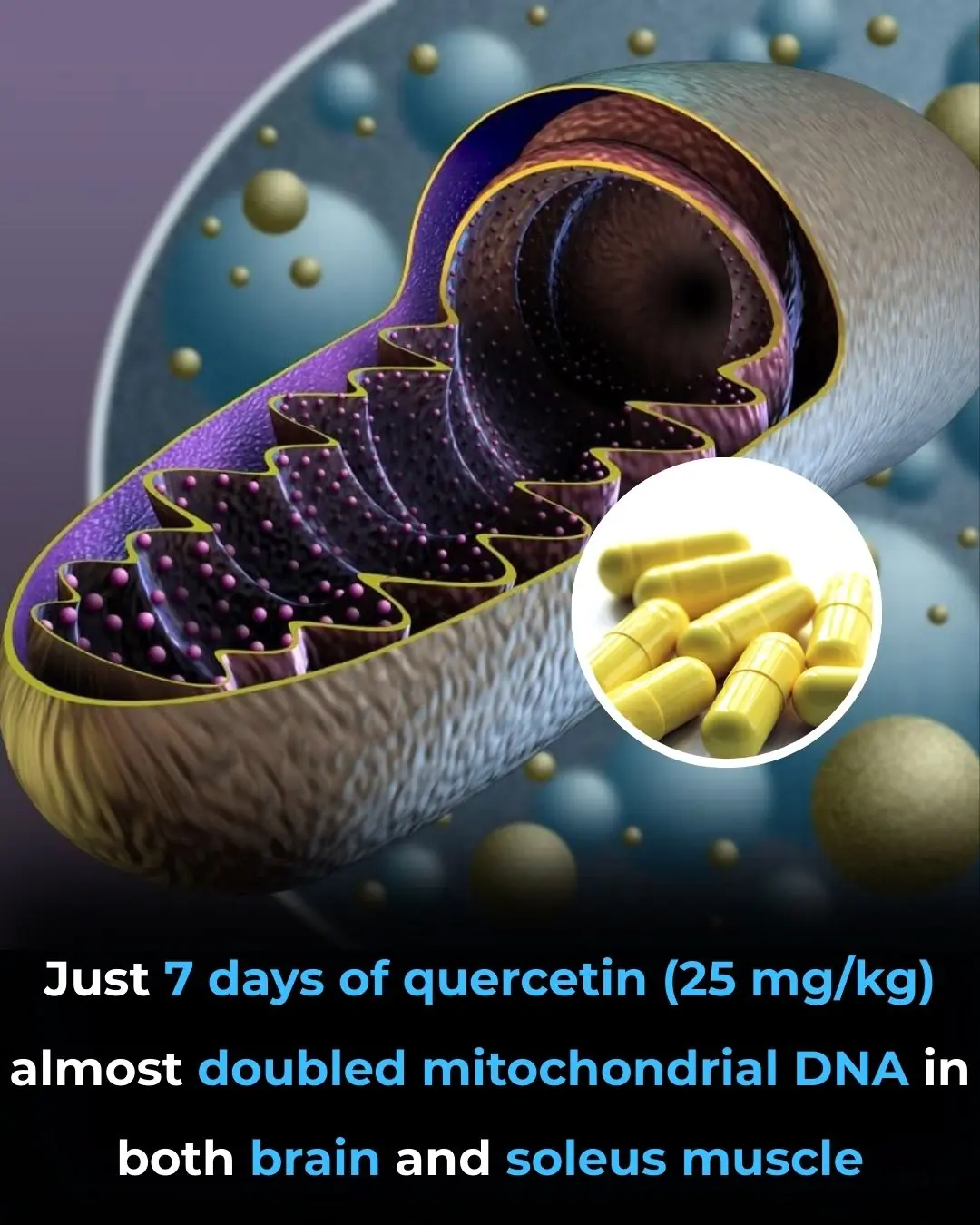
Quercetin as an Exercise Mimetic: Enhancing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Physical Performance
Health 23/12/2025 00:15
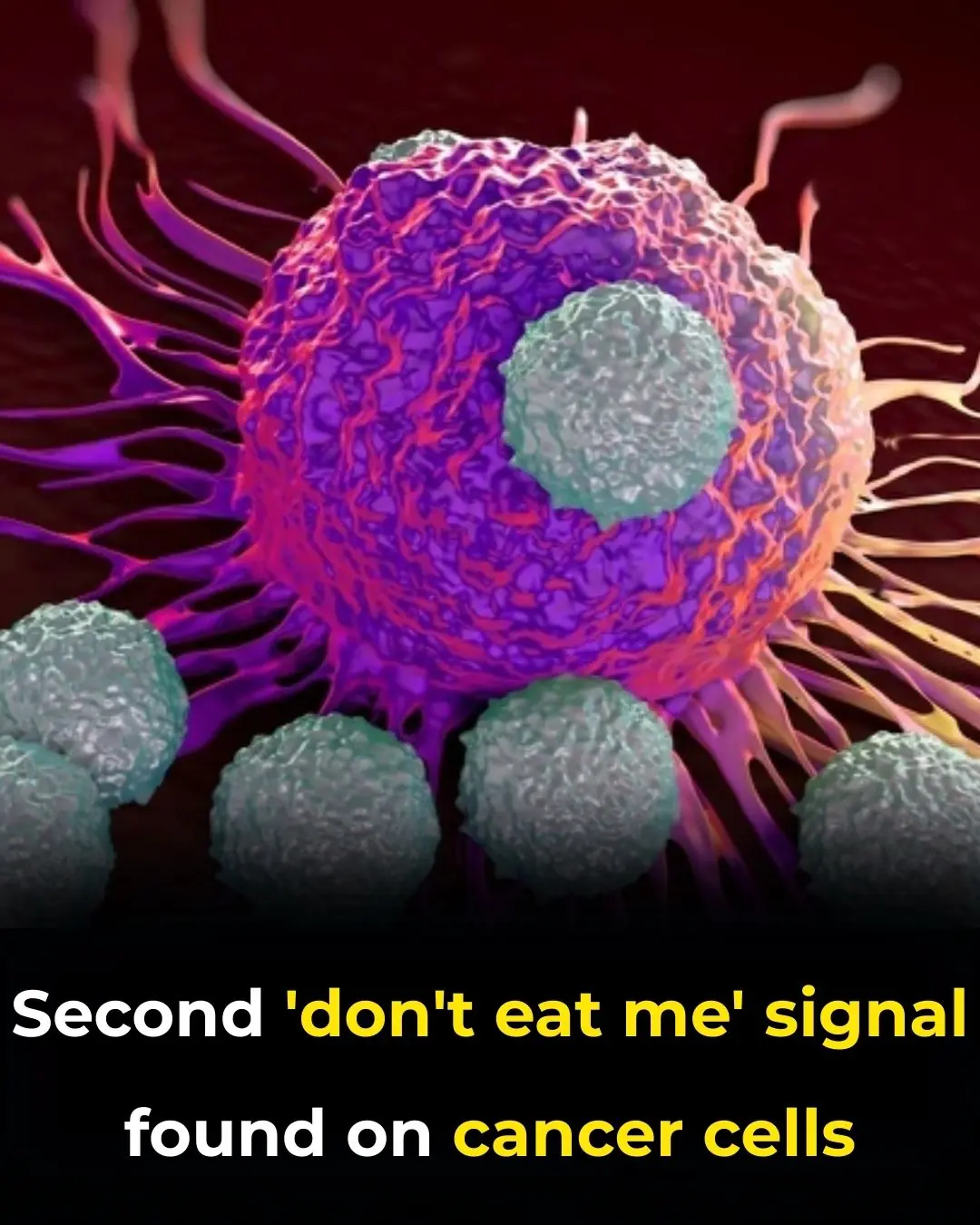
Dual “Don’t-Eat-Me” Signals: A New Paradigm in Cancer Immune Evasion
Health 23/12/2025 00:14

Cinnamon and Neuroprotection: Evidence for Anti-Alzheimer’s Mechanisms
Health 23/12/2025 00:13

High-Dose Thiamine and Cancer Cell Metabolism: Evidence from Experimental Cell-Line Studies
Health 23/12/2025 00:11
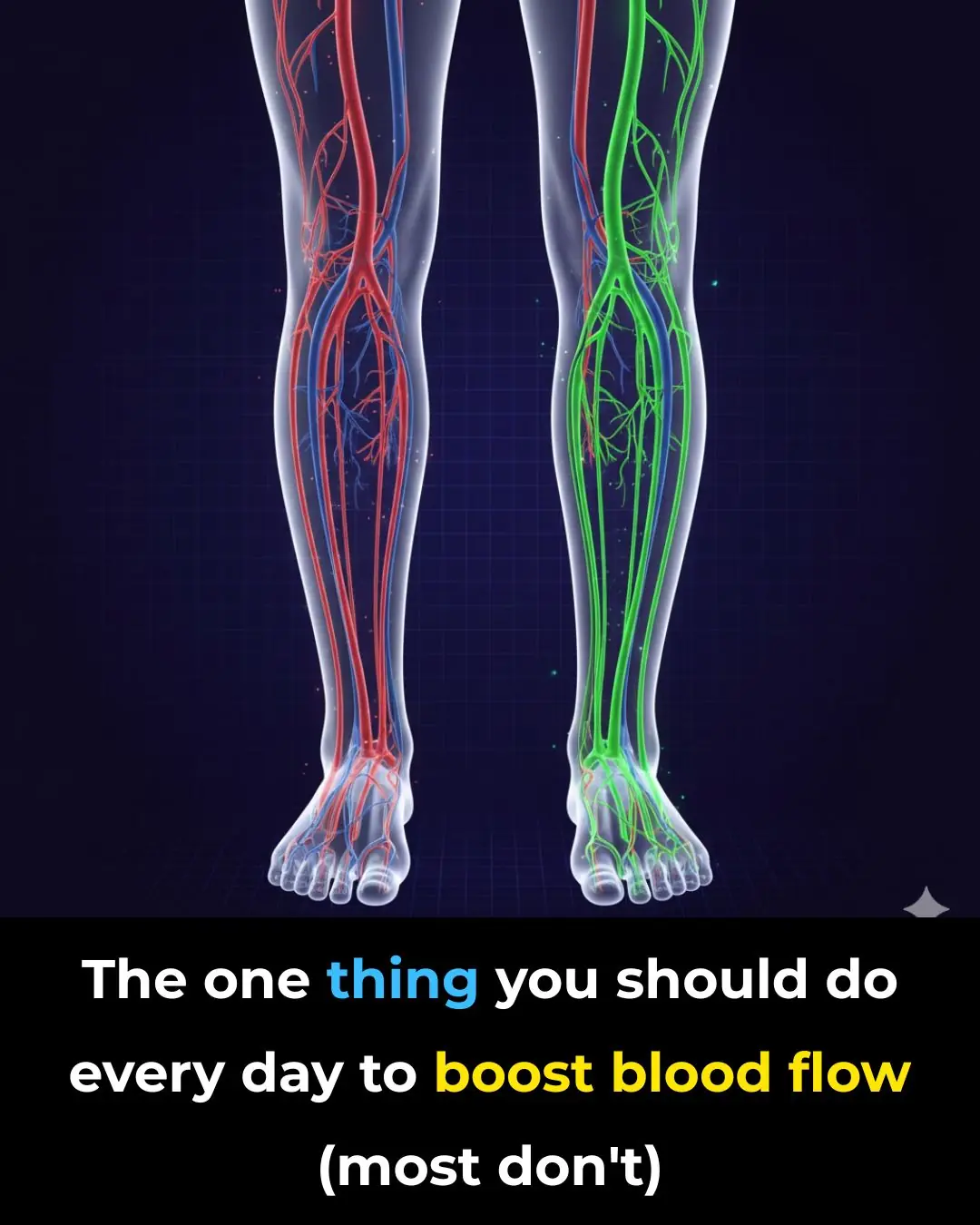
How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)
Health 22/12/2025 22:54

The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears
Health 22/12/2025 22:51
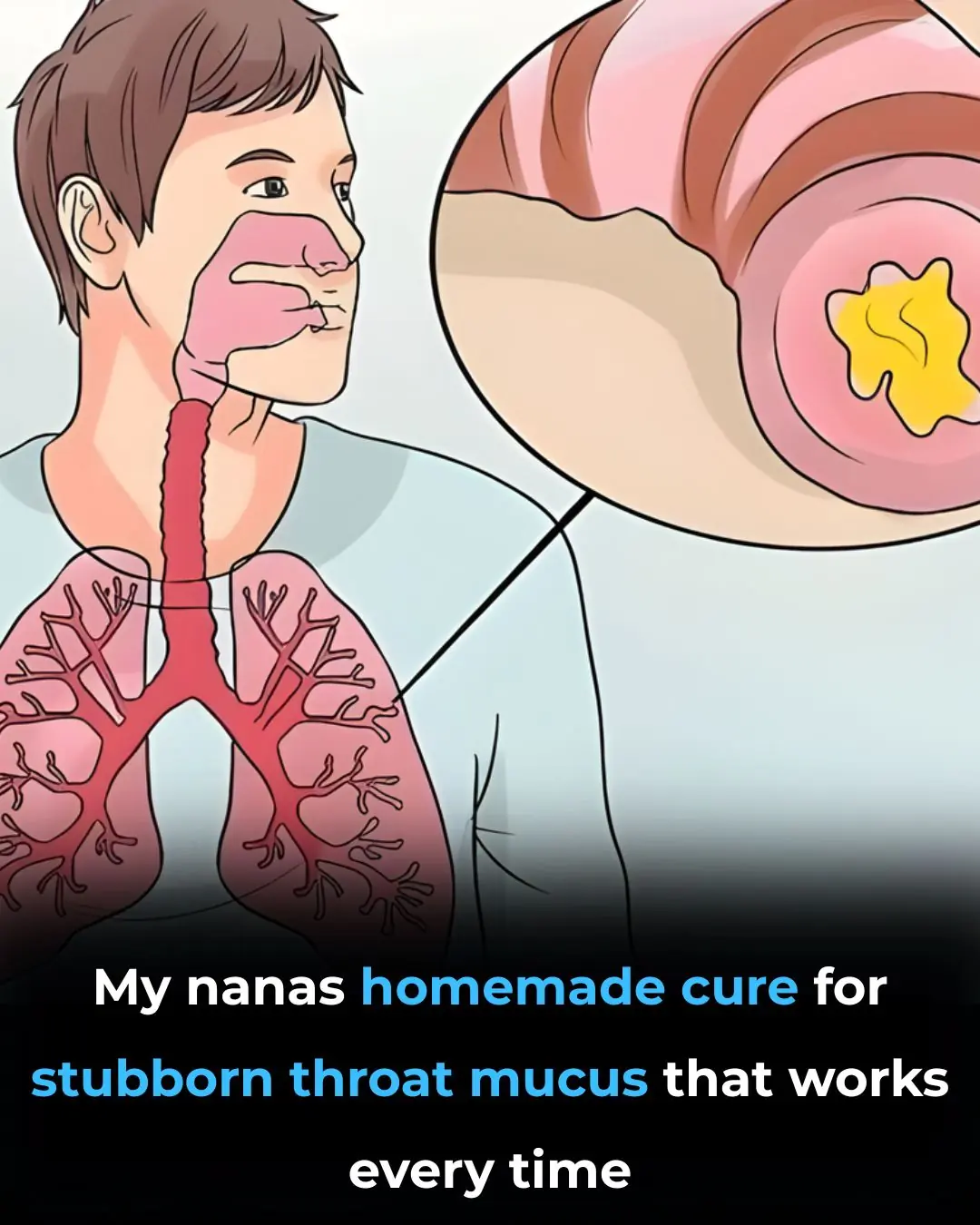
Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments (Evidence Based)
Health 22/12/2025 22:49

The Most Likely Symptoms of a Gallbladder Problem (Don’t Ignore Them)
Health 22/12/2025 22:45
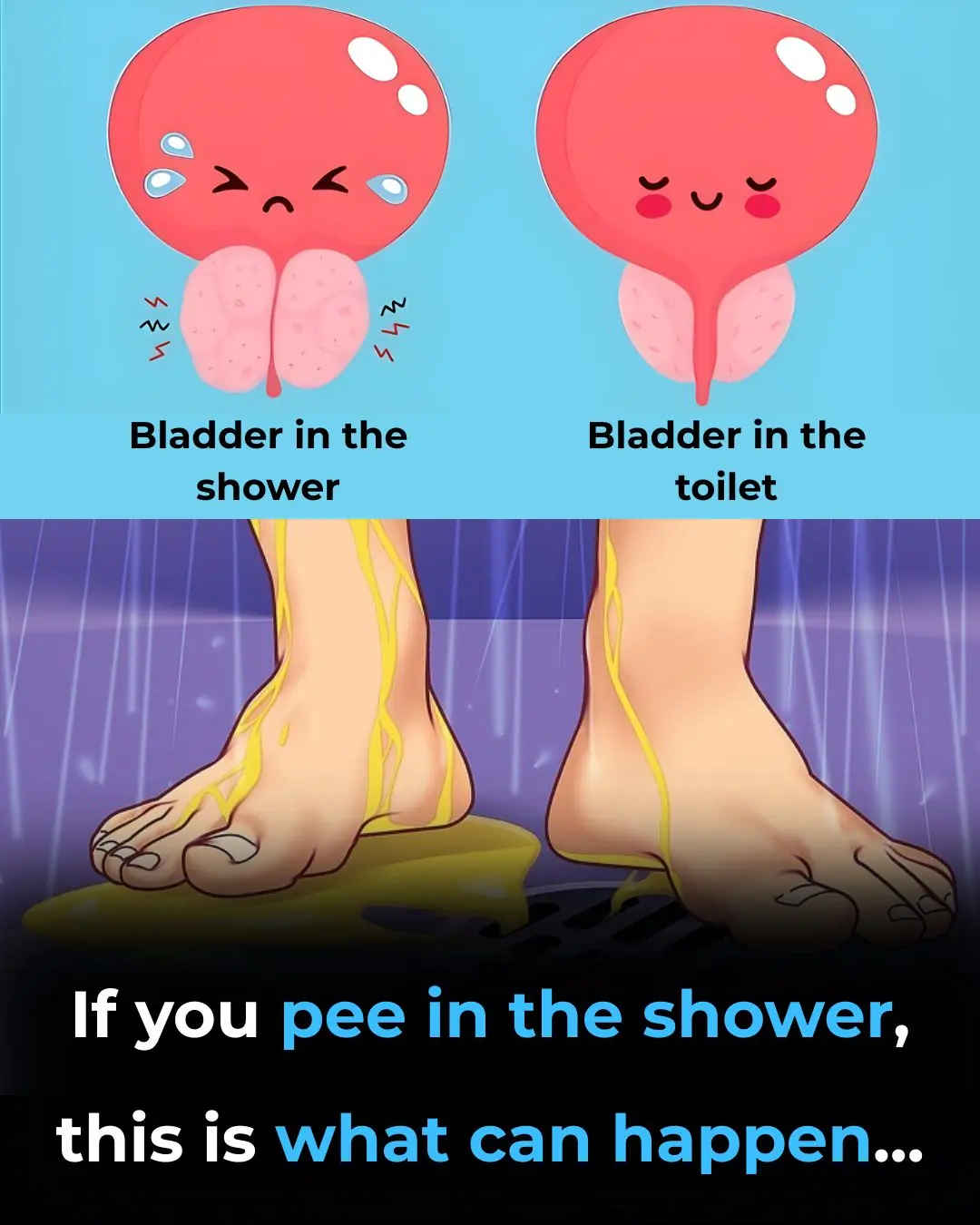
Why Hearing Running Water Makes You Suddenly Need to Pee
Health 22/12/2025 20:35

The strange phenomenon of sleep paralysis: When the body stops listening
Health 22/12/2025 19:26

Surprising Health Benefits of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea)
Health 22/12/2025 17:11
News Post

A 65-Year-Old Man Collapses at Midnight: Doctors Warn Against Four Drinks Not to Consume Before Sleeping
Health 23/12/2025 08:56

Tips for Dealing With Nail Psoriasis
Health 23/12/2025 08:03

Two Family Habits That Increase the Risk of Cancer for Everyone – Avoid Them Now to Prevent Regret
Health 23/12/2025 07:59

Your legs are screaming ‘HELP!:’ 5 warning signs from your liver
Health 23/12/2025 07:08

Nighttime Olfactory Enrichment and Cognitive Enhancement in Older Adults
Health 23/12/2025 00:20

Sodium Bicarbonate and Immune Regulation: Evidence for an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism
Health 23/12/2025 00:18

Oleocanthal from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil: A Multi-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Compound
Health 23/12/2025 00:17

Fenbendazole and Unexpected Cancer Remission: Insights from a 2024 Case Report
Health 23/12/2025 00:16

Quercetin as an Exercise Mimetic: Enhancing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Physical Performance
Health 23/12/2025 00:15

Dual “Don’t-Eat-Me” Signals: A New Paradigm in Cancer Immune Evasion
Health 23/12/2025 00:14

Cinnamon and Neuroprotection: Evidence for Anti-Alzheimer’s Mechanisms
Health 23/12/2025 00:13

High-Dose Thiamine and Cancer Cell Metabolism: Evidence from Experimental Cell-Line Studies
Health 23/12/2025 00:11
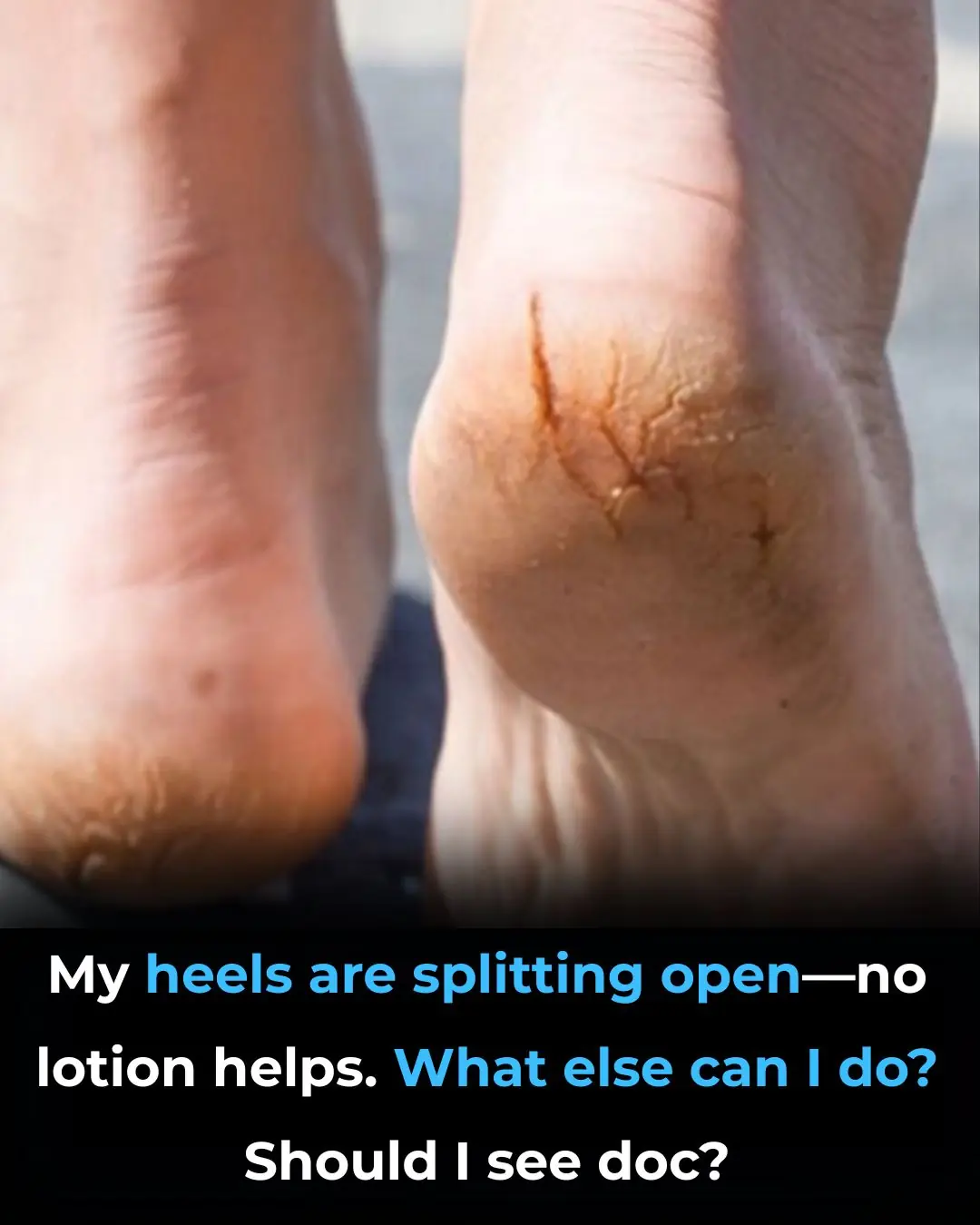
My heels are splitting open—no lotion helps. What else can I do? Should I see doc?
Tips 22/12/2025 23:03
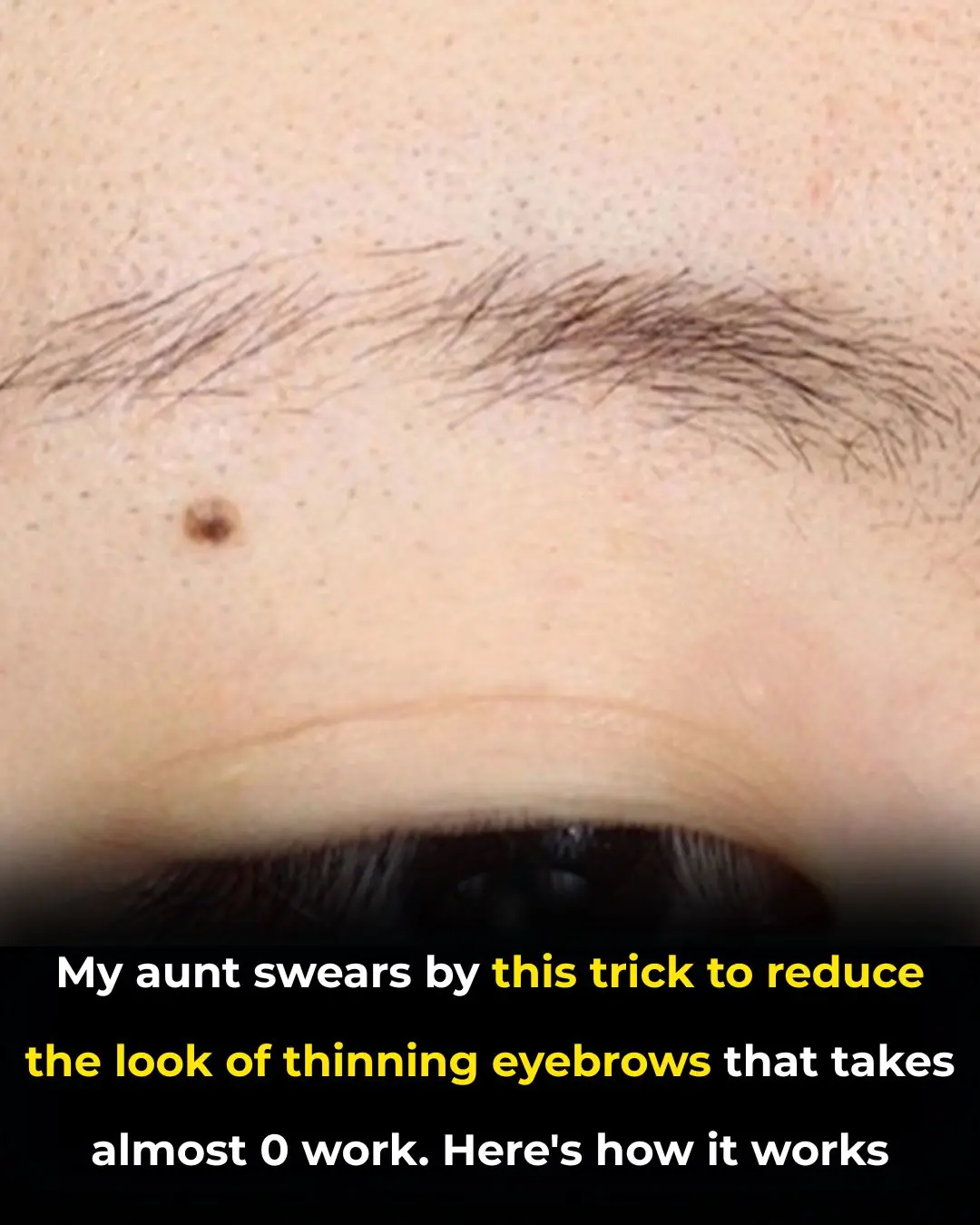
My aunt swears by this trick to reduce the look of thinning eyebrows that takes almost 0 work. Here's how it works
Tips 22/12/2025 23:01
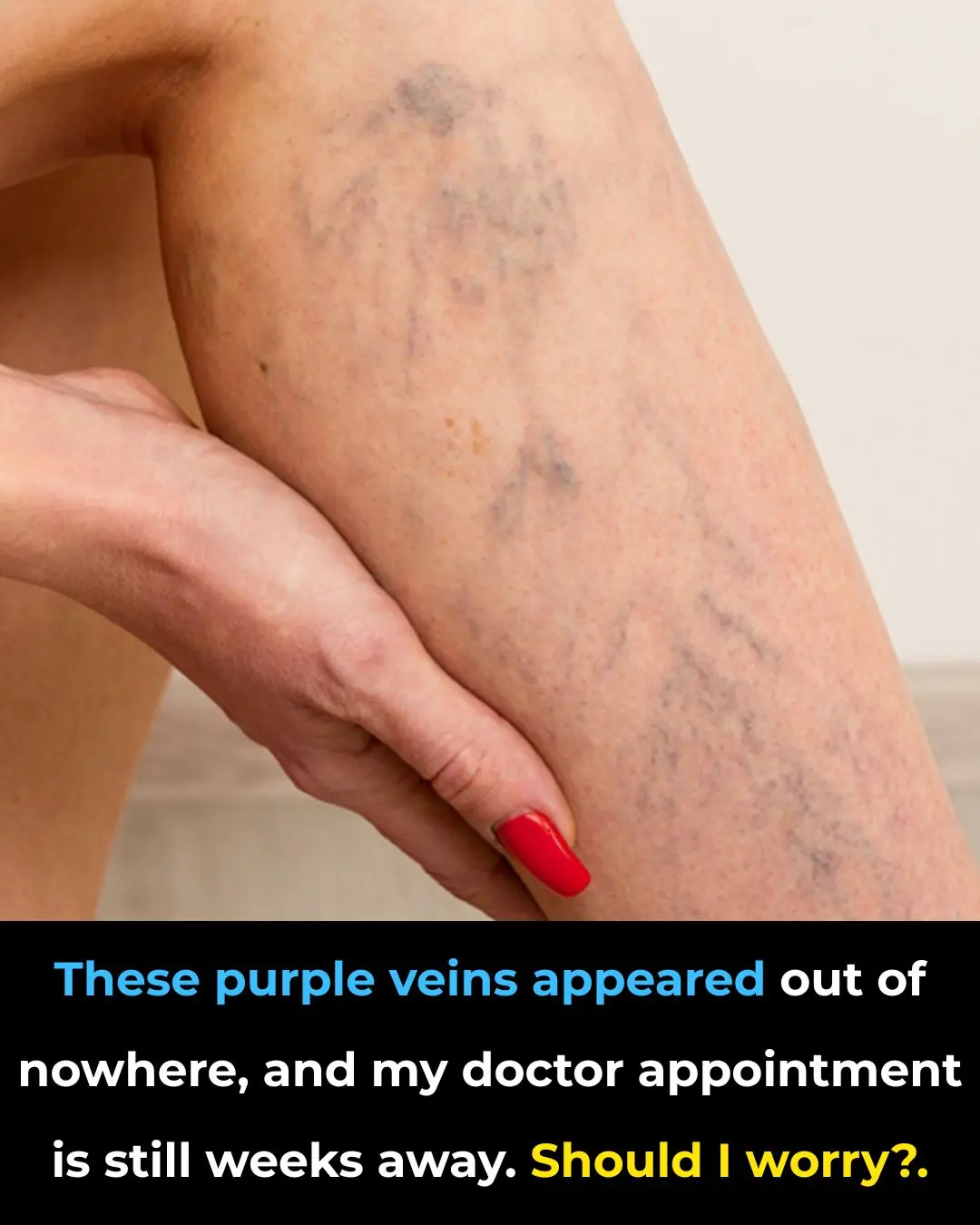
These purple veins appeared out of nowhere, and my doctor appointment is still weeks away. Should I worry?
Tips 22/12/2025 22:58

Brown flat spots keep showing up on the back of my hands. Doctor appt is forever away. What should I do?
Tips 22/12/2025 22:57

How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)
Health 22/12/2025 22:54

The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears
Health 22/12/2025 22:51

Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments (Evidence Based)
Health 22/12/2025 22:49