
Harvard Doctor Reveals Foods You Should Avoid to Prevent Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural and essential response that helps the body heal from injury and fight infection. In the short term, it protects us. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can quietly damage tissues and increase the risk of serious health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and digestive problems. According to a Harvard-affiliated gut health specialist, what we eat on a daily basis plays a powerful role in either fueling or calming inflammation.
The Gut–Inflammation Connection
The gut is one of the body’s most important regulators of inflammation. A healthy gut microbiome helps maintain immune balance and prevents excessive inflammatory responses. When gut health is compromised—often due to poor diet, stress, or processed foods—the body’s inflammatory pathways can become overactive.
The Harvard doctor explains that diets high in inflammatory foods can damage the gut lining and disrupt beneficial bacteria. This imbalance makes it harder for the body to regulate inflammation, potentially leading to chronic symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, digestive discomfort, and long-term disease.
Below are some of the most common inflammation-triggering foods identified by the Harvard expert, along with healthier alternatives.
1. Highly Processed Coconut and Palm Oil
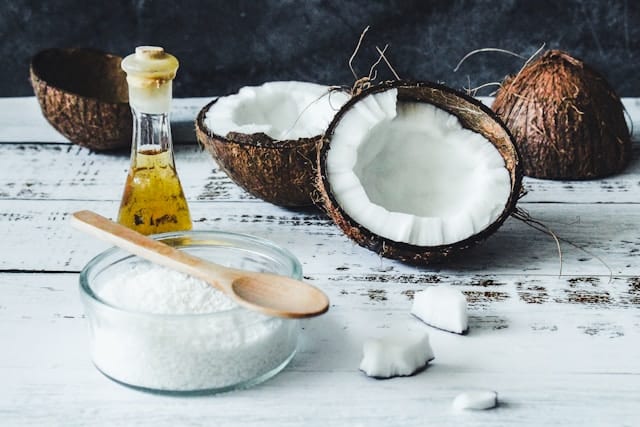

Coconut and palm oils are widely used in packaged foods and some cooking methods. While they are plant-based, they are very high in saturated fats. Excessive consumption of saturated fats has been linked to increased inflammation and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease.
Dr. Wolf recommends limiting these oils, especially in their highly processed forms, and choosing healthier fats that support heart and gut health.
Healthy alternatives:
-
Extra-virgin olive oil
-
Flaxseed oil
These oils are rich in monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids, as well as antioxidants that actively help reduce inflammation.
2. Fatty and Processed Meats
Fatty cuts of red meat, such as beef and pork, along with processed meats like sausages and bacon, contain high levels of saturated fats and inflammatory compounds. Regular consumption has been associated with heart disease, metabolic disorders, and chronic inflammation.
While enjoying these foods occasionally is unlikely to cause harm, Dr. Wolf advises limiting their presence in everyday meals.
Healthy alternatives:
-
Skinless poultry
-
Fatty fish like salmon and sardines
-
Plant-based proteins such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas
These options provide protein without triggering inflammatory pathways.
3. Highly Processed Foods
Ultra-processed foods are among the biggest contributors to chronic inflammation. They often contain artificial additives, preservatives, refined carbohydrates, and trans fats, all of which can disrupt gut bacteria and provoke inflammatory responses.
Dr. Wolf strongly encourages a diet centered on whole, minimally processed foods. These foods naturally provide fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients that help calm inflammation and nourish gut bacteria.
Healthy alternatives:
-
Fresh fruits and vegetables
-
Whole grains like oats and brown rice
-
Nuts and seeds
As a general rule, choose foods with short, recognizable ingredient lists.
4. Sugary Drinks
Sugary beverages—including sodas, energy drinks, sports drinks, and sweetened juices—are packed with added sugars and provide little to no nutritional value. Excess sugar intake promotes inflammation, contributes to insulin resistance, and increases the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Dr. Wolf recommends replacing sugary drinks with options that hydrate and support metabolic health.
Healthy alternatives:
-
Herbal teas
-
Infused water with lemon, berries, or mint
-
Plain water with fresh fruit or herbs
Building an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
To protect long-term health, the Harvard doctor recommends shifting toward a balanced anti-inflammatory diet. This includes eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats such as olive oil. Fatty fish like salmon, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, are particularly effective at reducing inflammation.
These foods are loaded with antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients that support gut health and help the body regulate its inflammatory response more effectively.
Lifestyle Habits Also Matter
Diet alone is not the only factor influencing inflammation. Dr. Wolf emphasizes that healthy lifestyle habits are equally important. Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and effective stress management all help keep inflammation under control. Chronic stress and poor sleep can worsen gut health and amplify inflammatory processes.
Final Takeaway
Chronic inflammation often develops quietly, but its effects can be profound. By making thoughtful dietary choices and adopting healthy daily habits, it is possible to reduce inflammation, protect gut health, and support overall well-being.
Small, consistent changes—such as choosing whole foods, reducing added sugars, and prioritizing healthy fats—can make a meaningful difference over time.
News in the same category


Doctor Warns of Mesotherapy’s Risky Side, Causing Reptile-Like Skin

If you buy corn and don't finish it, boil it first before freezing it or put it straight into the freezer – this is the professional way.

Tips for preserving banh chung (Vietnamese sticky rice cake) so it stays soft and delicious even after Tet.

Place a bottle of medicated oil by your bedside and receive 3 special benefits.

5 tips to keep your bathroom smelling fresh and clean using natural ingredients.

Most do this wrong. Here's how often to refresh everything

Just Two Ice Cubes: A Simple Trick for Softer, More Fragrant Rice

What It Means When a Black Cat Comes Into Your Home

Put Bay Leaves in the Corners of Their Kitchen

Washing blood stains from bed sheets with hot water or detergent is completely wrong; this method will remove them completely, leaving no trace.

Don't put tomatoes in the refrigerator: Here's how to keep them fresh for a whole week without them spoiling.

Tips for boiling okra to keep it vibrant green, not slimy, and retain all its nutrients.

When frying pork fat, some people add salt, others add water, but chefs use pure white fat that lasts a long time without spoiling.

Easy Tips to Keep Your Bathroom Smelling Fresh All Day

Why Eggplant Is an Affordable Superfood for Heart Health and Weight Management
Why Bamboo Shoots Are a Fiber-Rich Vegetable Worth Cooking the Right Way

Can Herbal Hair Washes Really Reduce Hair Loss and Promote Hair Growth?

Why You Should Avoid Hanging Clothes in These Places During Winter
News Post
Bariatric Surgery or GLP-1 Receptor Agonists? Long-Term Effects on Fat Loss and Body Composition

How to Whiten Laundry Naturally

If You Have Fig Leaves, You Have Gold—and You Didn’t Even Know It

Doctor Warns of Mesotherapy’s Risky Side, Causing Reptile-Like Skin

It’s surprising how unclear the link between chicken color and quality still is for many people

🤧 Constant Phlegm in Throat? The Real Causes (and How to Actually Get Rid of It)

Why Daily Showers After 65 May Do More Harm Than Good
Scientists Discover Alarming Substance in Human Blood, Raising Serious Concerns
7 easy ways to quickly unclog your lymph nodes to reduce swelling and flush out toxins

What Really Happens When You Eat a Banana Before Bed

Natural Ways to Relieve Cough and Chest Congestion

People whose mouths feel dry when sleeping at night need to know these 8 reasons
Why Eating More Processed Meat Increases Your Risk for Serious Health Problems

That detail isn’t innocent… and few people know it

Doctor Reveals That Eating Guava Can Cause Powerful Changes in Your Body

Stephen A. Smith speaks out on ‘NBA Countdown’ exit

Shedeur Sanders to make first NFL start for Browns: report
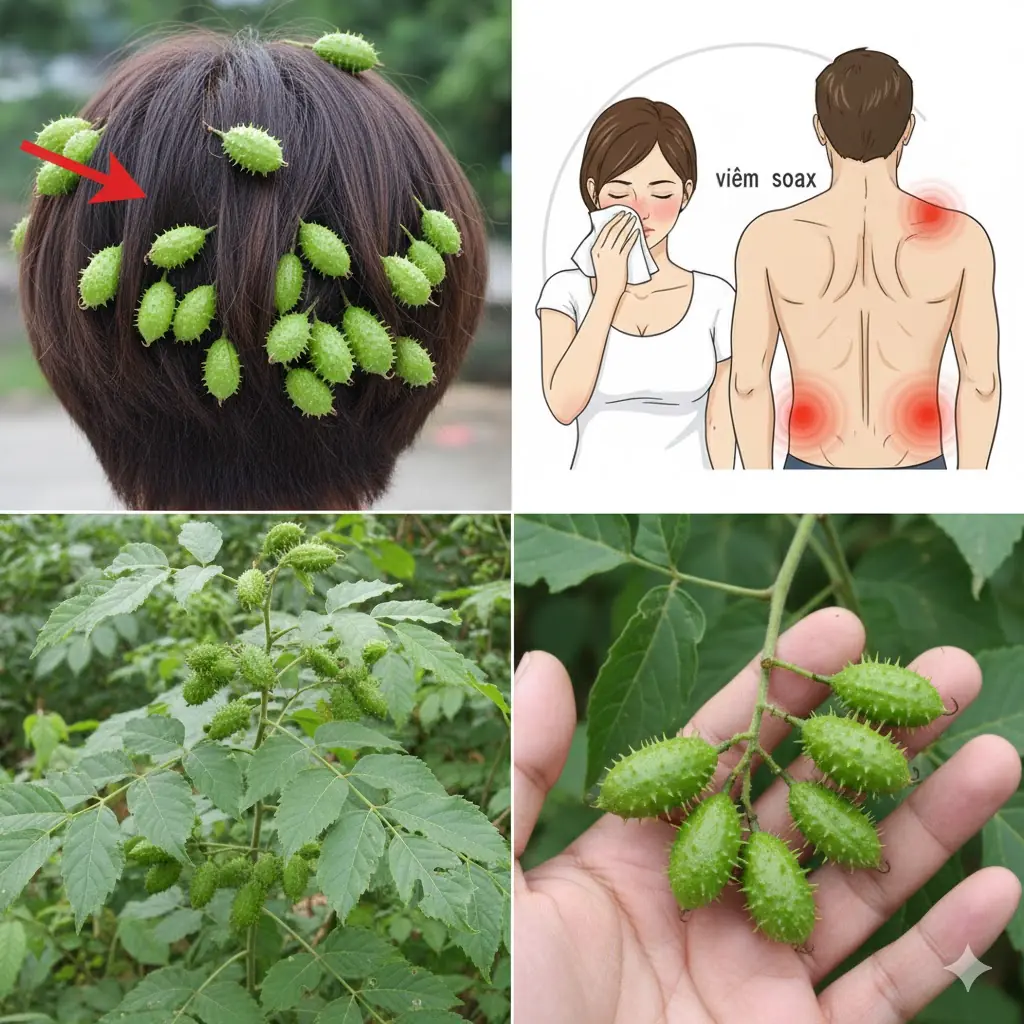

Cocklebur Uncovered: The Surprising Traditional Uses of Xanthium Strumarium
