How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs
Nerve pain in the feet, toes, and legs can be frustrating, persistent, and disruptive to daily life. Often caused by peripheral neuropathy, this condition affects millions worldwide, making walking, standing, and even resting uncomfortable. Fortunately, there are multiple ways to manage symptoms and address the underlying causes. In this guide, we’ll cover the causes, treatments, and practical strategies to help relieve nerve pain.
Key Takeaways
-
Identify the Causes: Peripheral neuropathy can result from diabetes, alcohol use, injuries, vitamin deficiencies, and other medical conditions.
-
Get a Proper Diagnosis: Consulting a healthcare professional ensures the right treatment for your specific condition.
-
Consider Multiple Treatments: Medications, lifestyle changes, home remedies, and alternative therapies can all contribute to relief.
-
Adopt Preventive Measures: Foot care, proper nutrition, and supportive footwear can prevent symptoms from worsening.
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy occurs when the peripheral nerves are damaged, leading to symptoms such as pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness, particularly in the feet and hands. Common causes include:
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar can gradually damage nerves, often affecting the longest nerves first, which explains why the feet and legs are usually impacted.
-
Alcohol Use: Chronic alcohol consumption can harm nerve fibers and deplete essential nutrients, resulting in burning pain, numbness, and weakness.
-
Injuries: Trauma to the spine, legs, or feet can compress or sever nerves. Herniated discs, fractures, or severe sprains can cause radiating pain down the legs (sciatica).
-
Vitamin Deficiencies: B vitamins (B1, B6, B9, B12) and vitamin E are crucial for nerve health. Deficiencies can damage the protective nerve sheath, leading to pain and tingling.
-
Other Medical Conditions: Thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), kidney disease, infections (like shingles or Lyme disease), and certain medications can contribute to nerve damage.
Why Accurate Diagnosis Matters
Proper diagnosis is essential, as nerve pain may mimic other conditions. Accurate identification allows for targeted treatment. Recommended steps include:
-
Podiatrist Consultation: Foot specialists can differentiate neuropathy from other foot conditions such as plantar fasciitis and recommend orthotics or supportive shoes.
-
Neurologist Evaluation: Neurologists perform exams, nerve conduction studies (NCS), and electromyography (EMG) to locate nerve damage.
-
Imaging Tests: X-rays or MRIs can detect structural problems like herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
-
Blood Tests: These can identify diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, autoimmune markers, or infections contributing to nerve pain.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, treatment often involves a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, home remedies, and alternative therapies.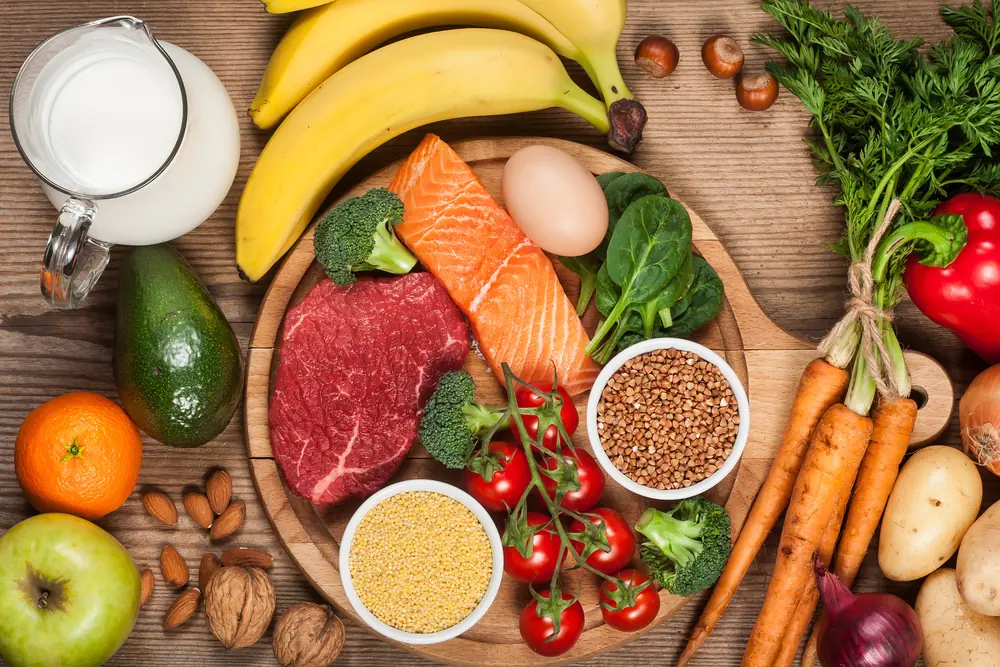
Medications
-
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help mild pain. Severe cases may require prescription options such as tramadol.
-
Antidepressants: Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline) or SNRIs (duloxetine) can reduce nerve pain by affecting brain pain pathways.
-
Anti-seizure Medications: Gabapentin and pregabalin calm overactive nerve signals, helping alleviate neuropathic pain.
-
Topical Treatments: Capsaicin or lidocaine creams provide localized relief by desensitizing nerve endings.
Lifestyle Changes
-
Balanced Diet: Emphasize B vitamins, antioxidants, and foods that control blood sugar for diabetic neuropathy.
-
Regular Exercise: Walking, swimming, yoga, and cycling improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and strengthen muscles.
-
Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Both can worsen nerve damage; reducing or eliminating them can slow symptom progression.
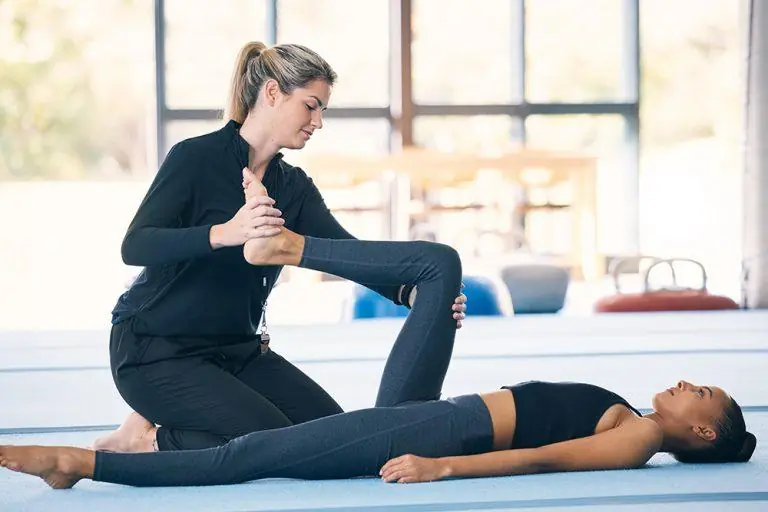
Home Remedies

-
Proper Footwear: Supportive shoes with cushioning and wide toe boxes reduce nerve pressure. Consider orthotics for additional support.
-
Massage & Stretching: Foot and leg massage improves circulation, while stretching reduces muscle tightness and nerve compression.
-
Warm Soaks & Epsom Salt Baths: Soaking feet in warm water relaxes muscles; adding Epsom salts provides magnesium, which may further reduce pain.
Alternative Therapies
-
Acupuncture: Thin needles stimulate nerve function and release natural pain-relieving chemicals.
-
Compression Therapy: Stockings or devices improve circulation and reduce swelling, which can ease nerve pressure.
-
TENS Therapy: Low-voltage electrical currents can block pain signals and stimulate endorphin release.
-
Physical Therapy: Tailored programs improve strength, balance, and flexibility, helping prevent falls and reduce discomfort.
When to Seek Further Help
If pain persists or worsens despite treatment, more advanced interventions may be necessary:
-
Surgical Options: Nerve decompression surgery can relieve pressure from tumors, herniated discs, or carpal tunnel syndrome.
-
Advanced Pain Management: Techniques like nerve blocks or spinal cord stimulation may be considered for chronic, intractable pain.
-
Regular Follow-ups: Continuous monitoring ensures early detection of worsening nerve damage or complications.
Additional Tips for Long-Term Relief

-
Maintain foot hygiene and inspect feet daily for injuries, especially if sensation is reduced.
-
Combine different treatment approaches—medications, lifestyle adjustments, and home therapies often work best together.
-
Stay hydrated and manage stress, as dehydration and tension can exacerbate nerve discomfort.
-
Consider support groups or counseling if chronic pain affects mental health, as stress and depression can worsen perception of pain.
Conclusion
Nerve pain in the feet, toes, and legs can be debilitating, but understanding its causes and pursuing a comprehensive treatment plan can lead to substantial relief. By combining lifestyle modifications, medications, home remedies, and alternative therapies under medical guidance, you can improve nerve function, reduce discomfort, and enhance your quality of life. Early intervention and consistent care are key to preventing long-term complications.
News in the same category


Could the bacteria in your nose be causing Alzheimer’s?

Bee venom wiped out 100% of aggressive breast cancer cells in just 6 hours

10 Ways to Lower Uric Acid Naturally

6 Foods That Can Drain Your Calcium and Weaken Bones
How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs …
Scientists identify the only two foods consistently linked to higher cancer risk
COULD THE BACTERIA IN YOUR NOSE BE CAUSING ALZHEIMER’S?

The Shocking Impact of Honey with Cloves on Your Health

Clear Your Lungs and Soothe Your Cough Naturally with Onion Remedy

Guava Leaf Tea: A Simple Habit With Powerful Health Benefits
The single move that instantly clears congestion and drains your sinuses

This common diabetes medication may undo the benefits of your workouts
Your legs have a “second heart” — and one simple move can reactivate it fast
9 cancer warning signs your body is sending you (don’t ignore these!)

Here’s the secret why everyone puts avocados on the fire!

Scientifically Proven Benefits of Pumpkin Seeds (Pepitas) and Pumpkin Seed Oil
The single move that instantly clears congestion and drains your sinuses

11 Health Warnings Your Fingernails May Be Sending
News Post
Vaseline Uses and Benefits for Skin, Lips, and Hair

10 simple ways to reduce dust at home that most people overlook

You’re Doing It All Wrong: Here’s the Right Way to Defrost Frozen Pipes

7 Powerful Fruits to Preserve Muscle Strength and Energy After 50

I Didn’t Know!

The #1 FASTEST way to reverse fatty liver naturally

Could the bacteria in your nose be causing Alzheimer’s?

The air conditioner only has wind but is not cool. Don't rush to call a repairman and waste money. If you do this, it will be cold.

The more flowers the money tree has, the more luck it attracts: Do this and the money tree flowers will grow 5 times faster.

When boiling duck, don't add ginger and cold water. Add this to remove all the bad smell from the meat and you won't get tired of eating it.

Avocado Seeds: The Overlooked Nutritional Power Inside the Fruit

Bee venom wiped out 100% of aggressive breast cancer cells in just 6 hours

A New Breakthrough: Magnetic Microrobots Designed to Navigate Blood Vessels and Stop Strokes

10 Ways to Lower Uric Acid Naturally

A Dual Climate Solution: Solar Panels Over Canals Could Save Billions of Gallons of Water
Regenerative Medicine Milestone: Stem-Cell Trial Restores Motor Function in Paralyzed Patients

From Crow to Cleaner: How Feathered Geniuses Are Fighting Litter in Spain

6 Foods That Can Drain Your Calcium and Weaken Bones
