
Redefining Diabetes Treatment
-
Traditional approach: For decades, diabetes care has centered on symptom management—primarily through insulin therapy, glucose monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments.
-
New paradigm: Researchers are now exploring treatments that aim to restore the body’s natural ability to regulate blood sugar, offering hope for long-term remission rather than indefinite disease control.
Key Breakthroughs
1. Immunotherapy for Type 1 Diabetes
-
Goal: Protect pancreatic beta cells from autoimmune destruction.
-
Progress: Clinical trials in Europe and the U.S. show that immune-modulating therapies can delay or reduce the progression of Type 1 diabetes.
-
Evidence: A 2024 review in Journal of Translational Medicine highlights advances in cell-based therapies, including islet and stem cell transplantation, which may preserve pancreatic function and reduce dependence on insulin.
2. Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes
-
Impact: Bariatric and metabolic surgeries have demonstrated long-term remission in many patients with Type 2 diabetes.
-
Mechanism: These procedures alter gut hormones and metabolism, improving insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation.
-
Evidence: The American Diabetes Association reports remission rates of up to 40–60% in certain patient groups following surgery.
3. Innovative Medications
-
New drug classes: GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors not only lower blood sugar but also improve cardiovascular and kidney outcomes.
-
Recent developments: Research in 2024 emphasized combination therapies that enhance durability of remission and reduce complications.
Global Research Landscape
-
Germany: Leading immunotherapy trials targeting autoimmune pathways in Type 1 diabetes.
-
United States & Asia: Expanding use of metabolic surgery and novel drug regimens.
-
International collaboration: Shared data across continents accelerates progress toward a universal cure.
Challenges and Limitations
-
No universal cure yet: While remission is possible, it is not guaranteed for all patients.
-
Accessibility: Advanced therapies like cell transplantation and surgery remain costly and limited to specialized centers.
-
Long-term monitoring: Even after remission, patients require ongoing follow-up to prevent relapse.
Bottom Line
For the first time, advances in immunotherapy, metabolic surgery, and innovative medications are enabling remission in certain diabetes patients. While a universal cure remains elusive, these breakthroughs highlight the potential reversibility of chronic conditions and offer hope for millions worldwide.
Sources
-
Journal of Translational Medicine (Springer Nature, 2024)
-
Diabetes in 2024: Advances in Research and New Therapies (Diabetes Guide, 2025)
-
American Diabetes Association Standards of Care, 2024
-
World Health Organization – Global Diabetes Report, 2023
Disclaimer: This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be considered medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment.
News in the same category


What a Strong Hug From a Man Can Truly Mean
Man loses pulse for 45 minutes, wakes up, and shares this spine-chilling vision of afterlife

Nostradamus predicted that those who have a cat at home will...

What Does “Durex” Actually Stand For

The reason might surprise you... Read more
What the First Animal You See Reveals About Your Hidden Flaw

Dreaming of a deceased person: here's what it means

The Common Bra Mistake
What Your Sleeping Position as a Couple Might Reveal

Envy Rarely Looks Like Hate

Why Slugs Keep Showing Up in Your Home

Almost Everyone Experiences This After Turning 70, Like It or Not

Did you know that if a white and yellow cat approaches you, it's because…

A baby is born in the United States from an embryo frozen more than 30 years ago.

12 nasty habits in old age that everyone notices, but no one dares to tell you

Why do couples sleep separately after age 50?
Scientists create a universal kidney: it is compatible with all blood types

When a person keeps coming back to your mind: possible emotional and psychological reasons
A promising retinal implant could restore sight to blind patients
News Post

The Viral Video That Exposed a Monster, Freed a Hero, and Rewrote a Town’s Fate

A Little Girl Whispered, “My Dad Had That Same Ink

The Billionaire Who Believed He Had Erased

The Fifteen Seconds That Changed Everything

Hospice chef reveals the one comfort food most people ask for before they die

More people are dying from heart failure, doctors warn: give up these 4 habits now

10 Bizarre Home Remedies
Recognizing a Stroke Fast
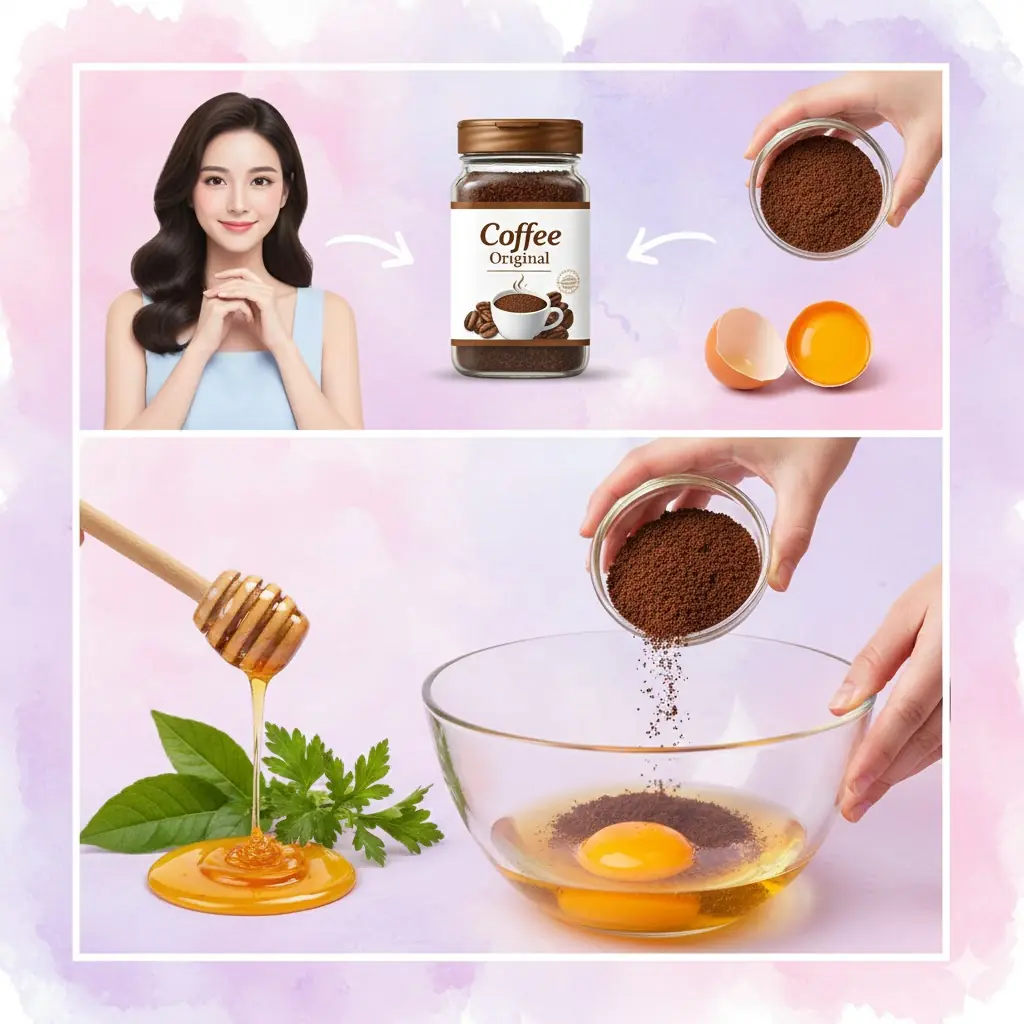

Egg, Honey & Coffee Mix – The 3-Ingredient “Bedroom Rocket Fuel” Men Over 40 Are Using for Morning Wood, Stamina & Confidence
THE SHADOW IN BOOTH SEVEN: She Poured His Coffee for a Thousand Mornings

Why Bees Land on Your Fresh Laundry

A Doctor Explains What “Lightning Bum” Really Is

Why Scallions Deserve More Credit as a Health Food

Why Nose Picking Isn’t as Harmless as You Think
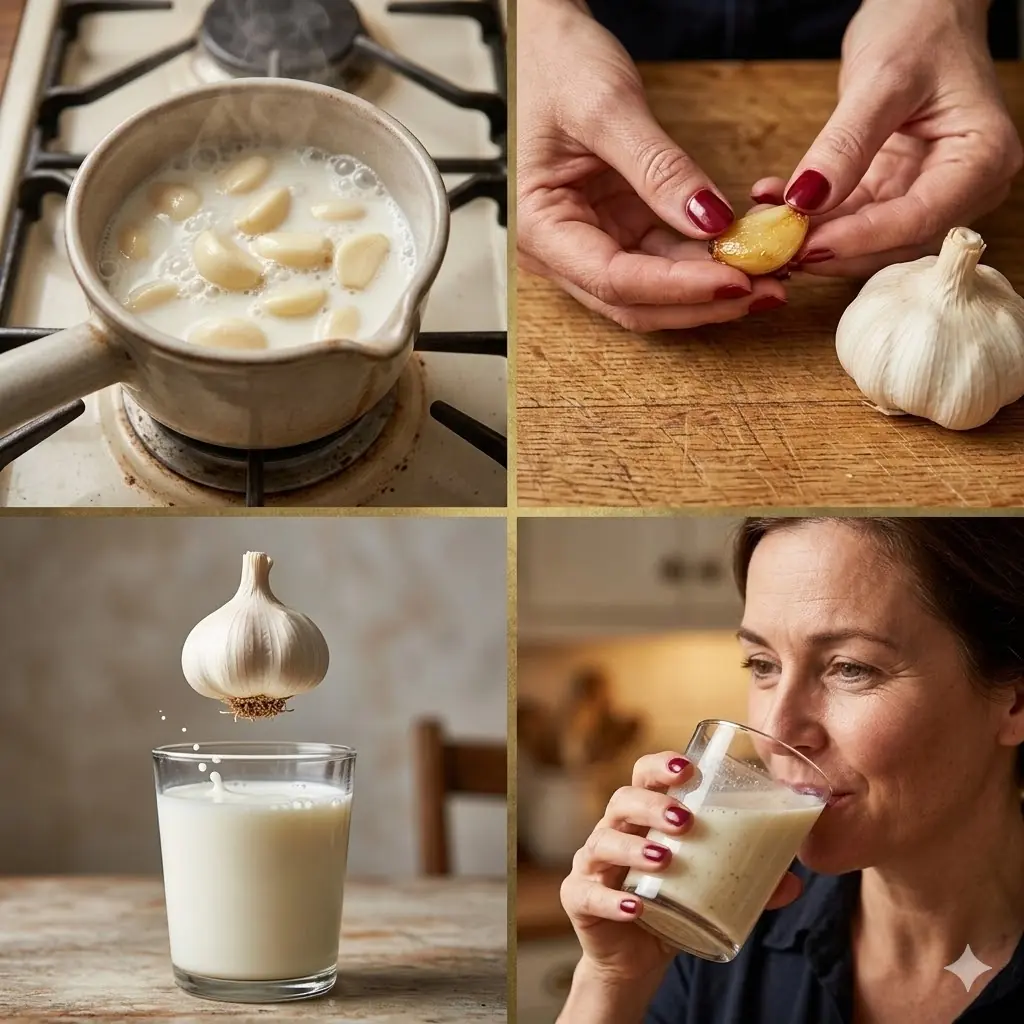

Natural Remedies to Relieve Muscle and Joint Pain (Proven Home Solutions)
7 Things That Happen To Your Body When You Don’t Have Sex For A While

A Simple Daily Drink Men Over 40 Can Make at Home to Naturally Support Prostate Wellness

7 Everyday Foods That Help Maintain Muscle Strength and Activity After 50

Papaya Leaf for Hair Growth: A Gentle, Natural Ritual for Stronger, Healthier Hair
