
The Sun’s Power: Earth Lives on Just 0.000002%
When you flip on a light switch or feel the warmth of sunlight streaming through your window, you’re experiencing a tiny fraction of the most powerful energy source in our solar system. Remarkably, Earth intercepts and utilizes only 0.000002% of the Sun’s total energy output, yet this minuscule portion drives virtually every process that sustains life on our planet. Understanding this incredible energy relationship reveals the profound efficiency of Earth’s systems and highlights the immense potential of solar energy for our future.
Table of Contents
The Sun’s Incredible Energy Output
The Sun generates approximately 3.8 × 10²⁶ watts of power continuously through nuclear fusion in its core. To put this in perspective, this amount of energy equals burning 100 billion tons of dynamite every second. The fusion process converts roughly 4 million tons of hydrogen into helium each second, with the “missing” mass converted directly into energy according to Einstein’s famous equation E=mc².
This energy radiates outward in all directions as electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, infrared heat, ultraviolet rays, and other wavelengths across the spectrum. The Sun’s surface temperature reaches about 5,778 Kelvin (5,505°C or 9,941°F), while its core burns at an incredible 15 million°C.
Earth’s Solar Energy Reception
Despite the Sun’s enormous output, Earth receives only a tiny fraction due to its distance and size relative to the Sun’s radiating sphere. Located approximately 93 million miles away, our planet intercepts roughly 1.7 × 10¹⁷ watts of solar energy—that seemingly insignificant 0.000002% of the Sun’s total output.
This intercepted energy amounts to about 174 petawatts, which still represents an almost incomprehensibly large amount of power. To understand the scale, consider that global human energy consumption in 2023 was approximately 580 exajoules, or roughly 18 terawatts of continuous power—less than 0.01% of what Earth receives from the Sun.
Solar Energy Distribution on Earth
The solar energy reaching Earth gets distributed through several pathways:
Atmospheric Absorption and Reflection: Approximately 30% of incoming solar radiation gets reflected back to space by clouds, atmospheric particles, and Earth’s surface. Another 20% gets absorbed by the atmosphere, including ozone absorption of harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Surface Heating: About 50% of solar energy reaches Earth’s surface, where it drives weather patterns, ocean currents, and the water cycle. This surface heating creates temperature differences that generate wind patterns and storm systems.
Photosynthesis: Plants capture less than 1% of available solar energy through photosynthesis, yet this small fraction supports virtually all life on Earth by converting carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds.
How This Tiny Percentage Powers Everything
The 0.000002% of solar energy Earth receives drives numerous interconnected systems that make our planet habitable and dynamic.
Weather and Climate Systems
Solar heating creates temperature gradients between different regions, driving atmospheric circulation patterns. Warm air rises at the equator and flows toward the poles, while cool air moves toward the equator, creating trade winds and weather systems. Ocean currents follow similar patterns, distributing heat around the globe and moderating regional climates.
The water cycle depends entirely on solar energy for evaporation from oceans, lakes, and rivers. This evaporated water forms clouds and eventually falls as precipitation, replenishing freshwater sources and supporting terrestrial ecosystems.

Photosynthesis and the Food Chain
Plants use solar energy to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen through photosynthesis. This process not only produces the oxygen we breathe but also creates the foundation of virtually every food chain on Earth. Even fossil fuels represent ancient solar energy, stored by prehistoric plants and organisms millions of years ago.
Primary productivity from photosynthesis supports an estimated 550 gigatons of carbon fixation annually, providing energy for everything from microscopic bacteria to massive whales.
Ocean Dynamics
Solar heating drives ocean currents that regulate global climate patterns. The Gulf Stream, for example, transports warm water northward, keeping Western Europe significantly warmer than it would be otherwise. These current systems also distribute nutrients throughout marine ecosystems and influence weather patterns worldwide.
The Efficiency Question
Earth’s ability to sustain complex life with just 0.000002% of the Sun’s energy demonstrates remarkable efficiency in natural systems. This efficiency comes from several factors:
Energy Recycling: Natural systems excel at recycling and reusing energy through multiple pathways. The carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle all represent efficient energy and material recycling systems.
Cascade Effects: Small amounts of solar energy create cascade effects through atmospheric and oceanic systems, amplifying their impact far beyond the initial energy input.
Storage Systems: Oceans store vast amounts of thermal energy, moderating temperature changes. Similarly, the atmosphere stores energy that gets released during weather events.
Implications for Solar Energy Technology
Understanding Earth’s relationship with solar energy highlights the enormous potential for solar power technology. Current photovoltaic solar panels typically convert 15-22% of received sunlight into electricity, while concentrating solar power systems can achieve higher efficiencies.
Even capturing a tiny fraction of available solar energy could meet all human energy needs. For example, covering just 1% of the Sahara Desert with solar panels could theoretically generate enough electricity to power the entire world.
Solar Technology Advancement
Modern solar technology continues improving efficiency while reducing costs. Perovskite solar cells show promise for exceeding 40% efficiency, while concentrated solar power systems can store energy for use after sunset.
Distributed solar installations allow individual buildings to generate their own power, reducing transmission losses and grid dependence. Community solar projects enable shared renewable energy access even for those who cannot install panels on their property.
Future Energy Perspectives
As we face climate change challenges and growing energy demands, understanding our planet’s solar energy relationship becomes increasingly important. The Sun provides more than 10,000 times the energy humanity currently consumes, suggesting abundant potential for sustainable energy development.
Space-based solar power represents one frontier for capturing more solar energy by avoiding atmospheric losses. Orbital solar installations could potentially capture and beam energy to Earth using microwave transmission.
Advanced materials research focuses on creating more efficient photovoltaic cells and energy storage systems. Quantum dot solar cells, organic photovoltaics, and other emerging technologies may dramatically improve solar energy conversion efficiency.
Conclusion
Earth’s existence on just 0.000002% of the Sun’s energy output reveals both the incredible power of our nearest star and the remarkable efficiency of natural systems. This tiny fraction drives weather patterns, ocean currents, photosynthesis, and every aspect of life on our planet. As we develop renewable energy technologies, this relationship reminds us that abundant clean energy surrounds us—we simply need better tools to capture and utilize it effectively.
The Sun’s power offers hope for sustainable energy solutions that could meet human needs while preserving Earth’s natural systems. By learning from nature’s efficiency and developing advanced solar technologies, we can harness more of this abundant resource to create a cleaner, more sustainable future.
News in the same category

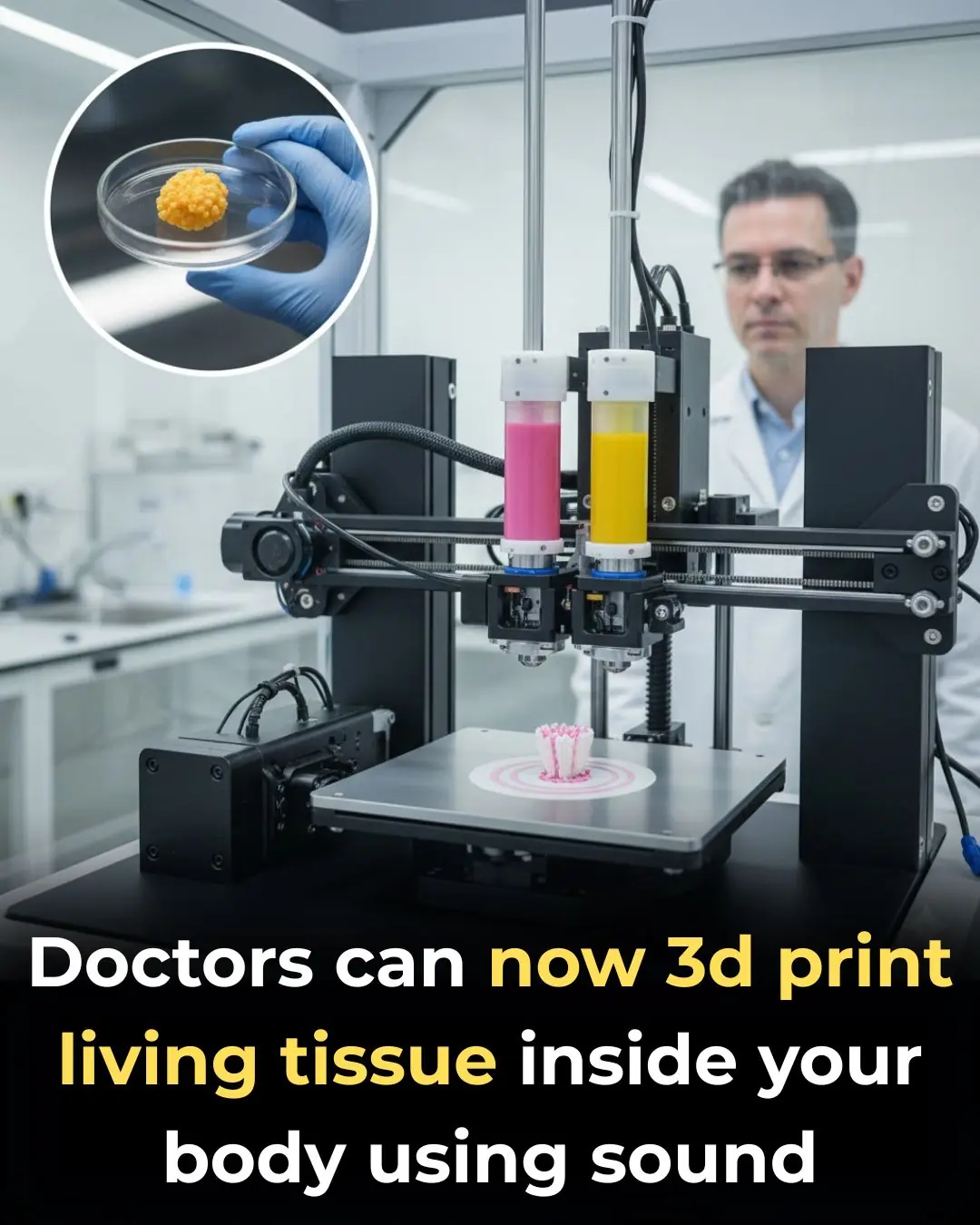
Medicine Breaks New Ground as Ultrasound Builds Tissue Without Surgery

A Heartbreaking Survival Trick: How a Stray Cat Learned to Hide His Pain

Bears Turn Honey Theft Into a Surprising Taste Test in Turkey

Scientists Say Your Butt Shape May Say More About Your Health Than You Think
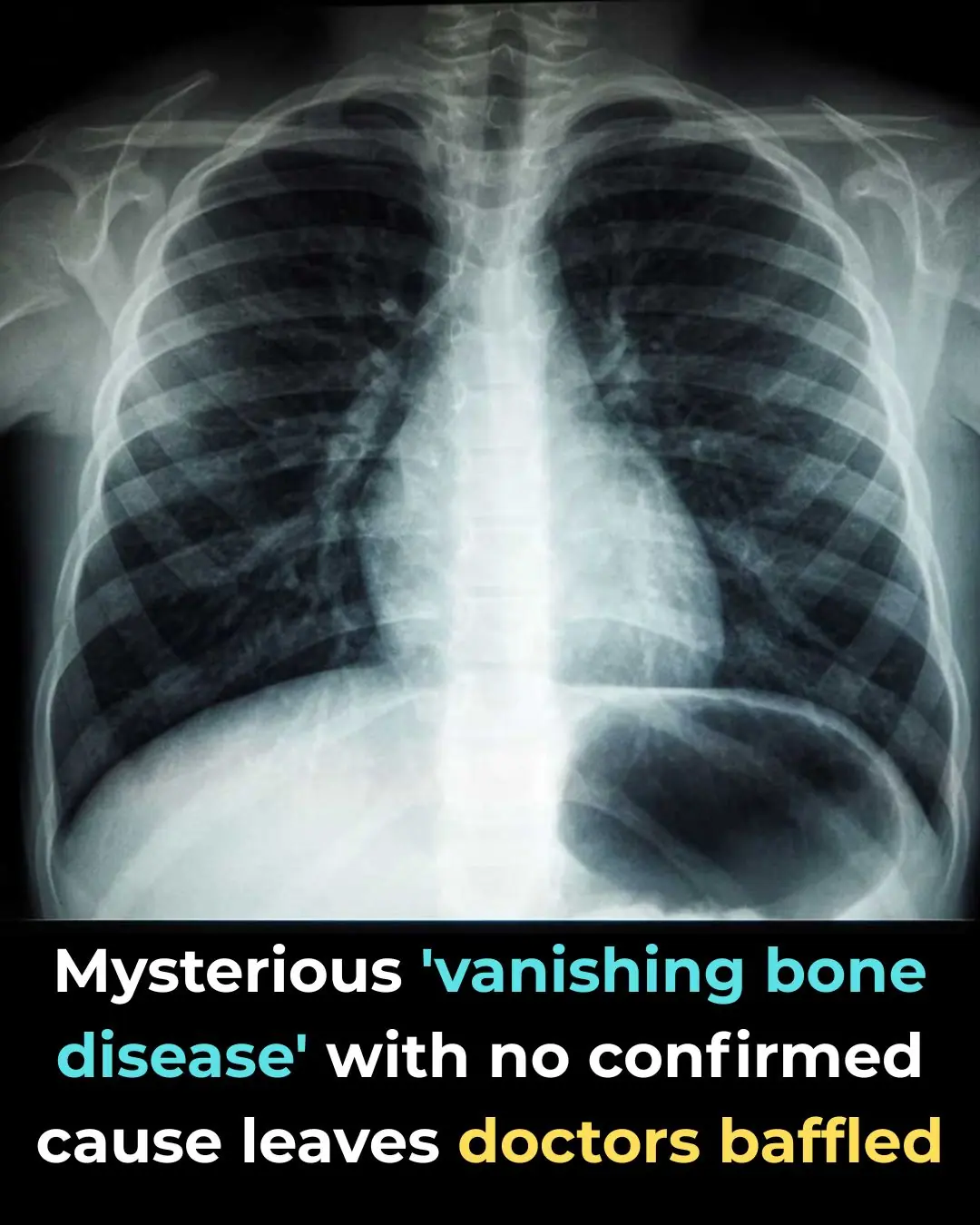
The Rare Condition That Makes Human Bones Slowly Vanish

A Hidden Consequence of Tick Bites You Should Know About

Smoking, Obesity, and Hypertension: The Leading Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer

When Blue Wings Return: A Second Chance for the Spix’s Macaw

Three Friends, One Hive, and a Very Bad Idea

Measles Cases Hit 30-Year High in the US, Raising Urgent Public Health Concerns

Why Skipping Housework on New Year’s Day Might Bring You Good Luck

Millie Bobby Brown’s Reaction to Eleven’s Ending Goes Viral After Stranger Things Finale

Baby Name Expert Predicts the Most Popular Naming Trends for 2026

No Fines, No Enforcement: How Trust Worked During Japan’s Toll System Failure

This “Easy” Puzzle for Kids Is Completely Stumping Adults

Beavers Build a Dam in the Czech Republic, Solving a Years-Long Environmental Problem

Social Media Users Agree on the Most Painful Physical Experience — and It’s Not What You’d Expec

James Webb Space Telescope Reveals Hidden Mid-Infrared Flares from the Milky Way’s Central Black Hole

New Vision Correction Technique Reshapes the Cornea Without Surgery
News Post

Stranger Things fans have bizarre theory over final episode and everyone's saying the same thing

In Yakutsk, Winter Is So Cold People Never Turn Off Their Cars

Florida Officially Recognizes Gold and Silver as Legal Currency Starting July 2026

JFK's grandson Jack Schlossberg shares emotional tribute to sister Tatiana after her death from cancer aged 35

Someone asked ChatGPT what it would do if it became human for a day and it gave a shocking response

Love and Generosity: How a Turkish Couple Shared Their Wedding with Refugees

Love and Perseverance Beneath the Waves: The 14-Year Search for Yuko

Rare Amoeba Infection Highlights the Importance of Safe Nasal Rinsing

A Legacy of Service: Bretagne’s Role in 9/11 and Disaster Response

Say Goodbye to Varicose Veins Naturally: A Simple Garlic, Onion, and Olive Oil Remedy That May Offer Relief

Why Seniors Are Turning to Honey and Cloves for Everyday Comfort After 60

Can Garlic and Lemon Really Support Better Vision? Kitchen Staples Your Eyes Might Appreciate

Banana Flower: The Underrated Superfood Taking Over in 2025

Fears of a Texas Serial Killer Intensify After Three More Bodies Are Recovered from Houston Bayous

From Casual Drinking to Dependence: A Recovering Alcoholic Reveals Seven Warning Signs of Addiction

Why Americans Were Shocked by the British Way of Washing Dishes

No one told me
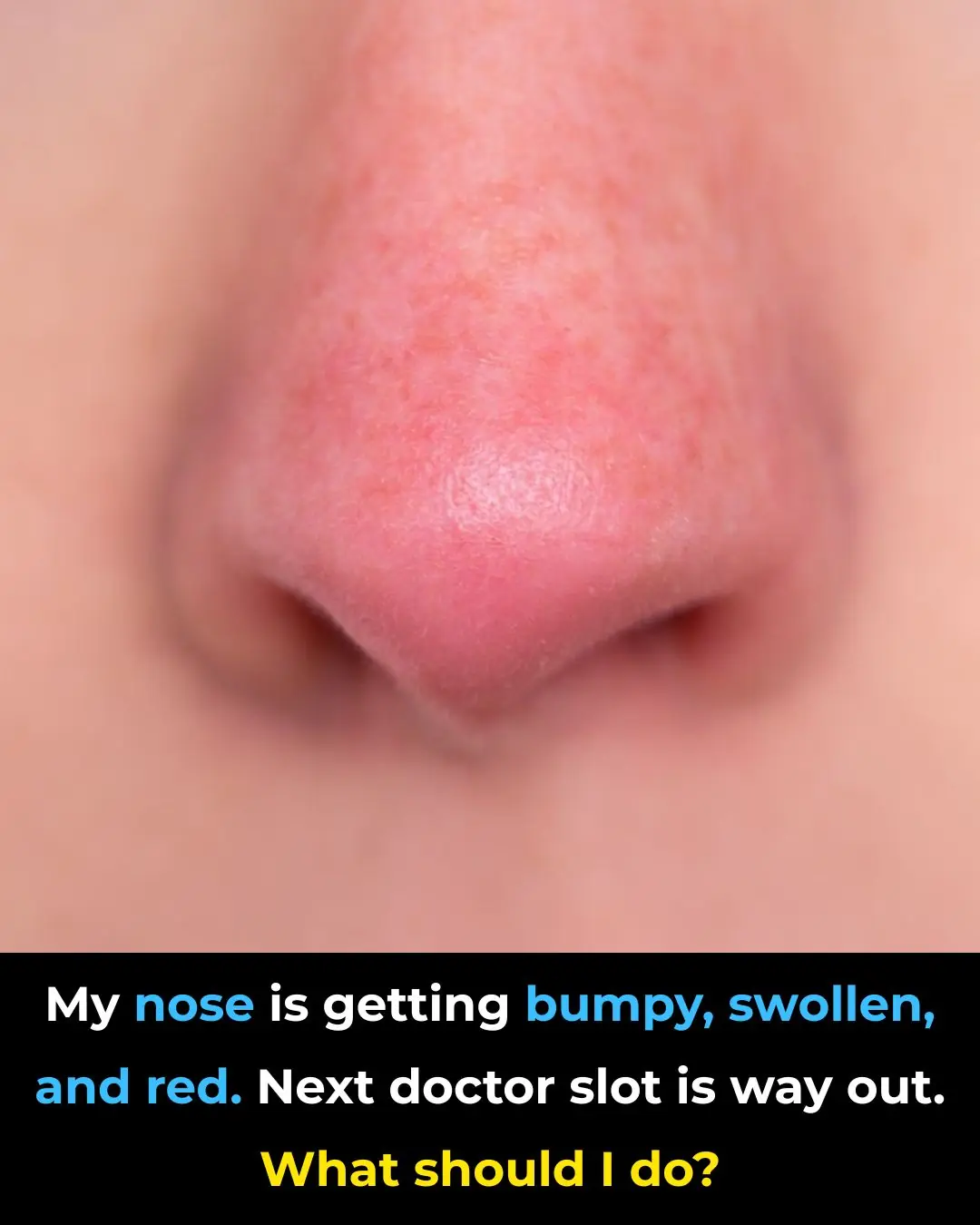
My nose is getting bumpy, swollen, and red. Next doctor slot is way out. What should I do?

Can You Spot It? The Viral “Sniper Vision” Challenge That’s Testing Human Perception
