
7 Household Appliances That Consume More Electricity Than Air Conditioners — I Sadly Realized My Home Has Them All
Air conditioners are not the only culprits behind skyrocketing electricity bills.
Many people instinctively blame air conditioners as the biggest energy guzzlers in the home. However, in reality, there are many other electrical appliances that, when used improperly or frequently, consume even more electricity than air conditioners.
These devices may seem small or insignificant but can substantially increase your monthly electricity costs.
1. Refrigerator

The refrigerator is the only appliance that must operate continuously, day and night, without any real downtime. Although its power ranges from about 100 to 400 watts depending on the model, its non-stop operation means the total energy consumption over days and months is quite high.
Older refrigerators without modern inverter technology or those that are not cleaned regularly can consume twice as much electricity compared to energy-efficient models.
Bad habits like leaving the fridge door open too long, overpacking it, or placing hot food inside increase energy consumption even more.
So, even though it’s quieter than an air conditioner, your fridge silently "nibbles away" at your monthly electricity bill.
2. Induction Cooker
Induction cookers are increasingly popular for their fast, safe, and clean cooking capabilities. To achieve this super-fast heating, they operate at very high power levels — usually between 1,800W and 3,500W per use.
If you cook daily with dishes that require long cooking times like stewing or boiling a lot of water, the monthly electricity consumption can be significant. Double-burner or multi-zone induction cookers can consume twice as much power as single burners.
Improper usage — such as turning on the cooker without a pot, using the wrong pot size, or running it at full power constantly — can lead to even higher electricity consumption than air conditioners.
3. Clothes Dryer
For families living in humid regions or during prolonged rainy seasons, clothes dryers become indispensable for drying clothes quickly and keeping them fresh. However, they are among the most power-hungry appliances, with power ratings from 2,000W to 5,000W.
Each drying cycle can last from 40 minutes to over an hour. Using dryers daily or multiple times per week results in massive electricity consumption.
Especially if clothes aren’t well spun before drying or if multiple batches are dried consecutively, energy consumption can spike. Modern dryers may feature energy-saving modes, but overall, they still consume a large amount of electricity compared to air conditioners over time.
4. Washing Machine
The washing machine is a familiar appliance in every household and is also a significant electricity consumer. When washing with cold water, energy usage is moderate, but using hot water cycles — especially on high-end machines — can push power consumption up to 2,000W.
Frequent washing, combined with drying or high-speed spinning functions, increases energy consumption further. Overloading the machine or selecting unnecessarily long wash cycles can also inflate your electricity bill.
Using your washing machine efficiently by sorting laundry and choosing appropriate cycles can help save considerable electricity.
5. Microwave Oven
Microwaves are often underestimated in terms of electricity consumption due to their short usage times. However, their average power ranges from 800W to 1,500W, and using them multiple times daily for heating, cooking, or defrosting adds up significantly.
Microwave ovens with additional grill or convection functions consume power comparable to dedicated ovens.
If you frequently reheat food or cook meals entirely in the microwave, this device might be consuming more electricity than you realize. Controlled and mindful usage can avoid unnecessary energy waste.
6. Oven

Ovens are beloved for baking and roasting, especially for cakes and grilled meats. However, the high temperatures and long cooking times required lead to very high power consumption, usually between 1,500W and 2,500W, with cooking times ranging from 30 minutes to over an hour depending on the dish.
Frequent oven use several times a week can easily result in electricity bills that exceed those of air conditioners in the summer.
Additionally, habits such as opening the oven door frequently during cooking let heat escape and prolong cooking time, increasing power usage.
7. Air Fryer
Air fryers are popular for their convenience and ability to prepare healthier, low-oil meals. However, they have high power ratings, typically between 1,500W and 2,200W.
Though cooking times are generally shorter than ovens, frequent use throughout the day for multiple dishes raises total electricity consumption significantly.
Larger-capacity air fryers (over 5 liters) or models with dual cooking and drying functions consume even more electricity. This illustrates how even small appliances can significantly impact electricity costs if used excessively or improperly.
Beyond Air Conditioners: Understanding and Managing Household Energy Use
Sometimes, air conditioners are not the biggest energy drain in your home. Many other seemingly “harmless” devices, either due to their compact size or quiet operation, can consume vast amounts of electricity if not used wisely.
To save electricity, consumers should understand the power ratings and usage patterns of their appliances. Opting for products with energy efficiency labels and inverter technology can substantially reduce consumption.
Regular maintenance, good habits like not overusing devices, and thoughtful appliance choices contribute not only to lowering electricity bills but also to environmental protection.
Additional Tips for Energy Savings
-
Regularly clean and maintain appliances to ensure efficient operation.
-
Avoid leaving devices on standby for extended periods.
-
Use appliances during off-peak hours when possible.
-
Invest in smart plugs or energy monitors to track consumption.
-
Combine drying clothes with natural sun-drying when weather permits.
A little attention to how you use electricity every day can bring significant savings and reduce your household’s carbon footprint.
News in the same category


Be careful — one single action at the airport could ruin your en:tire life.

Don't Throw Away That Old Non-Stick Pan! Try This Simple Trick to Make It Like New

Pouring Salt Down the Drain: A Surprising Trick More People Are Trying

3 Simple Ways to Keep Your Home Completely Rodent-Free

Four Plants in Your Garden That Attract Snakes Like Crazy — Remove Them Immediately for Family Safety

Tips for pickling white eggplants that are crispy, do not turn black, and do not form scum when left for a long time

How to grow papaya in pots, the fruit is heavy, big and sweet

4 habits that may be silently accelerating your body’s aging process

Eating ginger without peeling it – a lifelong health risk? The surprising truth that shocks everyone.

Boiling perilla leaves with a few stalks of lemongrass gives your body these 7 amazing benefits.

Even the Most Expensive Electric Kettle Can Turn Into a "Time B0 m b" If Your Household Has These 4 Habits

If a Non-Stick Pan Shows These 3 Signs, It’s Best to Throw It Away Immediately to Avoid Health Risks

Fish Sellers Reveal: 2 Types of Fish So Cheap You Should Never Buy, Yet Many People Still Unknowingly Purchase Them

95% of People Don’t Know the Meaning of the Numbers at the Bottom of Plastic Bottles and Containers

The hidden electricity-draining device at home that few people notice: It consumes more power than a refrigerator or washing machine

Seafood seller warns: Avoid these 4 types of shrimp or risk your health!

Place a bowl of salt in the fridge: A simple yet powerful trick I wish I had known 30 years ago
News Post

5 Delicious Eating Habits That Put the Whole Family at Risk of C:ancer – Extremely Dangerous and Should Be Avoided Immediately

Be careful — one single action at the airport could ruin your en:tire life.

Condolences to those who are using these 4 types of electric kettles: Throw them away while you still can, thousands of people have already developed c:ancer.

How Magnesium Keeps Your Heart Rhythm Healthy

Why Do I Cough When Taking a Deep Breath?

Taking the Stairs Could Help You Live Longer
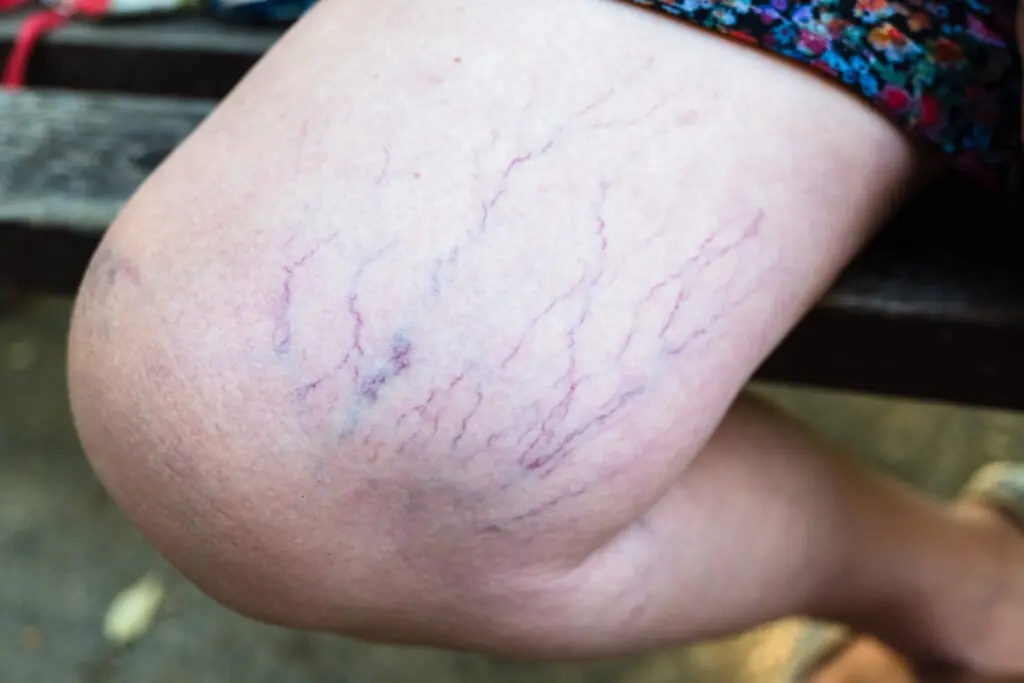
Purple Veins on Your Legs: When to Worry

Man develops 'pork worms' in his brain after years of doing this specific cooking habit

Signs Your Cortisol Is Dangerously High
Woman who d::ied for 24 minutes before being brought back to life details exactly how it felt

The Sleep Saboteur: The One Thing You Should Never Do When You Wake Up at Night
Nightly Habits That Could Increase Your Risk of Stroke
🚨 ALERT! 7 Strange Signs Your Kidneys Are Crying for Help
Vitamin E Oil uses for Skin – Glowing Skin, Dark Circles & Wrinkles

DIY Aloevera ice cubes to Remove Dark Spots & Clear Skin | Aloevera Benefits for Skin

Tips for pickling white eggplants that are crispy, do not turn black, and do not form scum when left for a long time

11 Secret Baking Soda Tricks for Women That Will Change Your Life!

Mattresses used for a long time are dirty and smelly, sprinkle this on the surface, no need to wash with water, it will be clean as new

‘Healthy Man’ Diagnosed With Cancer After Noticing Dog’s Bizarre Behavior Around Him
